定义于头文件 <array>
| template< class T, | (C++11 起) |
std::array 是封装固定大小数组的容器。
此容器是一个聚合类型,其语义等同于保有一个 C 风格数组 T[N] 作为其唯一非静态数据成员的结构体。不同于 C 风格数组,它不会自动退化成 T* 。它能作为聚合类型聚合初始化,只要有至多 N 个能转换成 T 的初始化器: std::array<int, 3> a = {1,2,3}; 。
该结构体结合了 C 风格数组的性能、可访问性与容器的优点,比如可获取大小、支持赋值、随机访问迭代器等。
std::array 满足容器 (Container) 和可逆容器 (ReversibleContainer) 的要求,除了默认构造的 array 是非空的,以及进行交换的复杂度是线性,它满足连续容器 (ContiguousContainer) (C++17 起)的要求并部分满足序列容器 (SequenceContainer) 的要求。
当其长度为零时 array ( N == 0 )有特殊情况。此时, array.begin() == array.end() ,并拥有某个唯一值。在零长 array 上调用 front() 或 back() 是未定义的。
亦可将 array 当做拥有 N 个同类型元素的元组。
成员函数
| 隐式定义的成员函数 | |
| (构造函数) (隐式声明) | 遵循聚合初始化的规则初始化 array (注意默认初始化可以导致非类的 T 的不确定值)(公开成员函数) |
| (析构函数) (隐式声明) | 销毁 array 的每个元素(公开成员函数) |
| operator= (隐式声明) | 以来自另一 array 的每个元素重写 array 的对应元素(公开成员函数) |
元素访问
访问指定的元素,同时进行越界检查
std::array<T,N>::at| reference at( size_type pos ); | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr reference at( size_type pos ); | (C++17 起) | |
| const_reference at( size_type pos ) const; | (C++14 前) | |
| constexpr const_reference at( size_type pos ) const; | (C++14 起) |
返回位于指定位置 pos 的元素的引用,有边界检查。
若 pos 不在容器范围内,则抛出 std::out_of_range 类型的异常。
参数
| pos | - | 要返回的元素的位置 |
返回值
到所需元素的引用。
异常
若 !(pos < size()) 则抛出 std::out_of_range
复杂度
常数。
访问指定的元素
std::array<T,N>::operator[]| reference operator[]( size_type pos ); | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr reference operator[]( size_type pos ); | (C++17 起) | |
| const_reference operator[]( size_type pos ) const; | (C++14 前) | |
| constexpr const_reference operator[]( size_type pos ) const; | (C++14 起) |
返回位于指定位置 pos 的元素的引用。不进行边界检查。
参数
| pos | - | 要返回的元素的位置 |
返回值
到所需元素的引用。
复杂度
常数。
注意
不同于 std::map::operator[] ,此运算符决不插入新元素到容器。
访问第一个元素
std::array<T,N>::front| reference front(); | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr reference front(); | (C++17 起) | |
| const_reference front() const; | (C++14 前) | |
| constexpr const_reference front() const; | (C++14 起) |
返回到容器首元素的引用。
在空容器上对 front 的调用是未定义的。
参数
(无)
返回值
到首元素的引用
复杂度
常数
注意
对于容器 c ,表达式 c.front() 等价于 *c.begin() 。
访问最后一个元素
std::array<T,N>::back| reference back(); | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr reference back(); | (C++17 起) | |
| const_reference back() const; | (C++14 前) | |
| constexpr const_reference back() const; | (C++14 起) |
返回到容器中最后一个元素的引用。
在空容器上对 back 的调用是未定义的。
参数
(无)
返回值
到最后元素的引用。
复杂度
常数。
注意
对于容器 c ,表达式 return c.back(); 等价于 { auto tmp = c.end(); --tmp; return *tmp; }
返回指向内存中数组第一个元素的指针
std::array<T,N>::data| T* data() noexcept; | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr T* data() noexcept; | (C++17 起) | |
| const T* data() const noexcept; | (C++17 前) | |
| constexpr const T* data() const noexcept; | (C++17 起) |
返回指向作为元素存储工作的底层数组的指针。指针满足范围 [data(); data() + size()) 始终是合法范围,即使容器为空(该情况下 data() 不可解引用)。
参数
(无)
返回值
指向底层元素存储的指针。对于非空容器,返回的指针与首元素地址比较相等。
复杂度
常数。
注意
若 size() 为 0 ,则 data() 可能或可能不返回空指针。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell() = default;
Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell)
{
x *= cell.x;
y *= cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator ++()
{
x += 1;
y += 1;
return *this;
}
bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y < cell.y;
}
else
{
return x < cell.x;
}
}
bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y > cell.y;
}
else
{
return x > cell.x;
}
}
bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const
{
return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
auto generate = []()
{
int n = std::rand() % 10 + 110;
Cell cell{n, n};
return cell;
};
//遵循聚合初始化的规则初始化 array (注意默认初始化可以导致非类的 T 的不确定值)
std::array<Cell, 6> array1;
std::cout << "array1: ";
std::copy(array1.begin(), array1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::generate(array1.begin(), array1.end(), generate);
std::cout << "array1: ";
std::copy(array1.begin(), array1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
for (size_t index = 0; index < array1.size(); index++)
{
//返回位于指定位置 pos 的元素的引用,有边界检查。
//若 pos 不在容器范围内,则抛出 std::out_of_range 类型的异常。
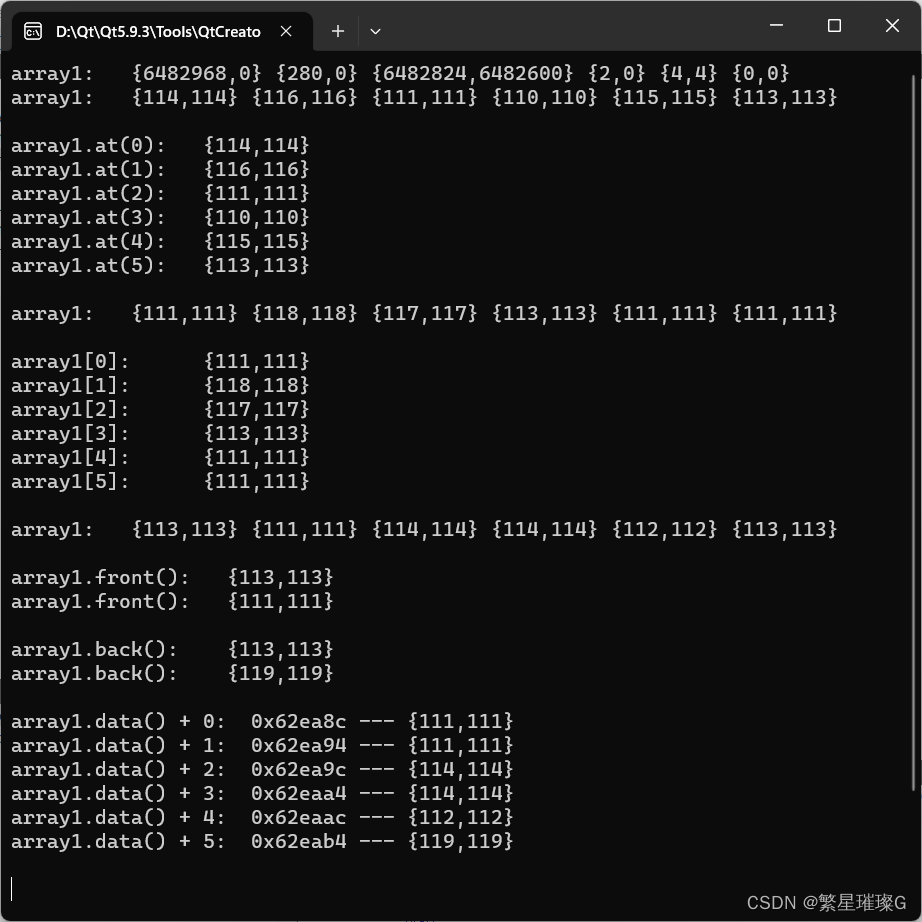
std::cout << "array1.at(" << index << "): " << array1.at(index) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
array1.at(index) = generate();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "array1: ";
std::copy(array1.begin(), array1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
for (size_t index = 0; index < array1.size(); index++)
{
//返回位于指定位置 pos 的元素的引用。不进行边界检查。
std::cout << "array1[" << index << "]: " << array1.at(index) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
array1[index] = generate();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "array1: ";
std::copy(array1.begin(), array1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//返回到容器首元素的引用。 在空容器上对 front 的调用是未定义的。
std::cout << "array1.front(): " << array1.front() << std::endl;
array1.front() = generate();
std::cout << "array1.front(): " << array1.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "array1.back(): " << array1.back() << std::endl;
array1.back() = generate();
std::cout << "array1.back(): " << array1.back() << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//返回指向作为元素存储工作的底层数组的指针。
//指针满足范围 [data(); data() + size()) 始终是合法范围,
//即使容器为空(该情况下 data() 不可解引用)。
for (size_t index = 0; index < array1.size(); index++)
{
std::cout << "array1.data() + " << index << ": " << array1.data() + index << " --- ";
std::cout << *(array1.data() + index) << std::endl;
array1[index] = generate();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出