item35:考虑虚函数的替代方案
NVI----Non-Virtual Interface
不使用虚函数接口,子类也可以实现按需求更改实现:

The Strategy Pattern via Function Pointers
也可以使用函数指针

或者使用stl::function

The “Classic” Strategy Pattern
item36:不要重新定义non-virtual函数
见https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44609676/article/details/130382495
item37:不要重新定义重写函数的默认参数
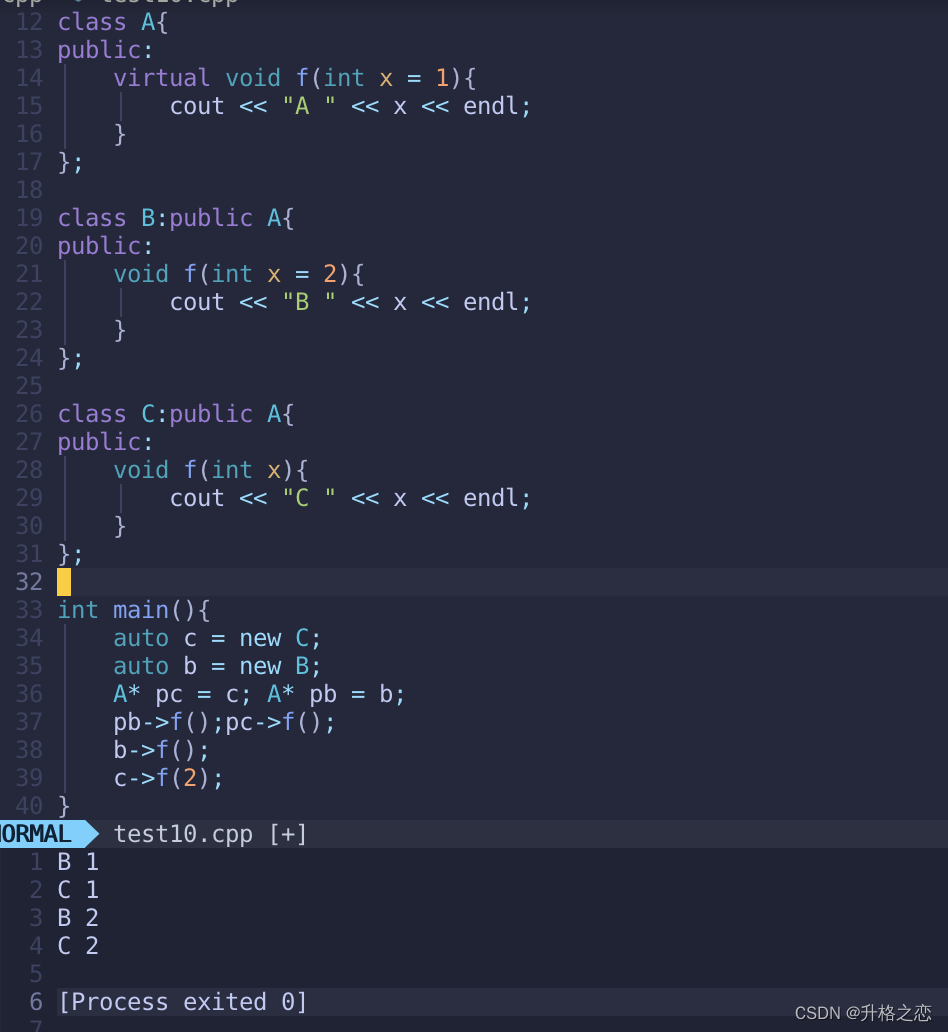
可以看到,b和pb调用的是同一个虚方法,但是输出到结果却不一样。因为f是虚函数,在运行时才动态绑定需要执行的函数,但是参数却是静态绑定的,在编译期pb的参数就已经是1了。
即使把BC的默认参数都换成1,也不推荐这样做。因为会增大维护代码的成本,如果默认参数要改,全部的相关代码都要改
可以使用第35条款的NVI来解决:
class A{
private:
virtual void f(int x) const = 0; // 子类复写f方法,调用dof方法
public:
void int dof(int x = 1) const{ // 非虚,不允许复写
cout << "A" << x <<endl;
}
}
item38:通过组合建模出has-a或实现关系
has-a关系
- has-a:For example, consider a “Car” class that has a “Engine” class as a member variable. The Car class has-a Engine, which means that the Engine object is a part of the Car object, and it cannot exist without the Car. Similarly, the Car class may have other has-a relationships with classes such as “Wheels”, “Transmission”, “Seats”, etc.
- is-a:For example, consider a “Vehicle” class and a “Car” class. The Car class is a specialized version of the Vehicle class, meaning that it inherits all of the attributes and behaviors of the Vehicle class, but it also has its own unique attributes and behaviors that make it different from other types of vehicles.
实现关系

使用list来实现set,如果用public继承,就会违反is-a的关系,因为set并不是list。就可以用包含关系来实现。
item39:EBO(空基类优化)
empty base optimization
任何对象大小至少为1(c++20:使用[[no_unique_address]])
然而,基类子对象不受此约束,而且完全可以从对象布局中优化掉

B的大小为8,因为内存对齐,在A a后面补上了3个字节。
C这种现象就叫EBO。
空类不一定是真的为空,也可以是包含了typedefs、enums、static、non-virtual函数等