简介
原型模式(Prototype Pattern)是一种创建型设计模式,使你能够复制已有对象,而无需使代码依赖它们所属的类,同时又能保证性能。
这种模式是实现了一个原型接口,该接口用于创建当前对象的克隆。当直接创建对象的代价比较大时,则采用这种模式。
如果你需要复制一些对象,同时又希望代码独立于这些对象所属的具体类,可以使用原型模式。
作用
- 利用已有的一个原型对象,快速地生成和原型对象一样的实例。
- 跳过构造函数的约束,便于提升性能。
实现步骤
- 创建原型接口,并声明克隆方法。
- 使用new运算符调用原型版本的构造函数。
- 将子类构造函数的直接调用,替换为对原型工厂方法的调用。
UML
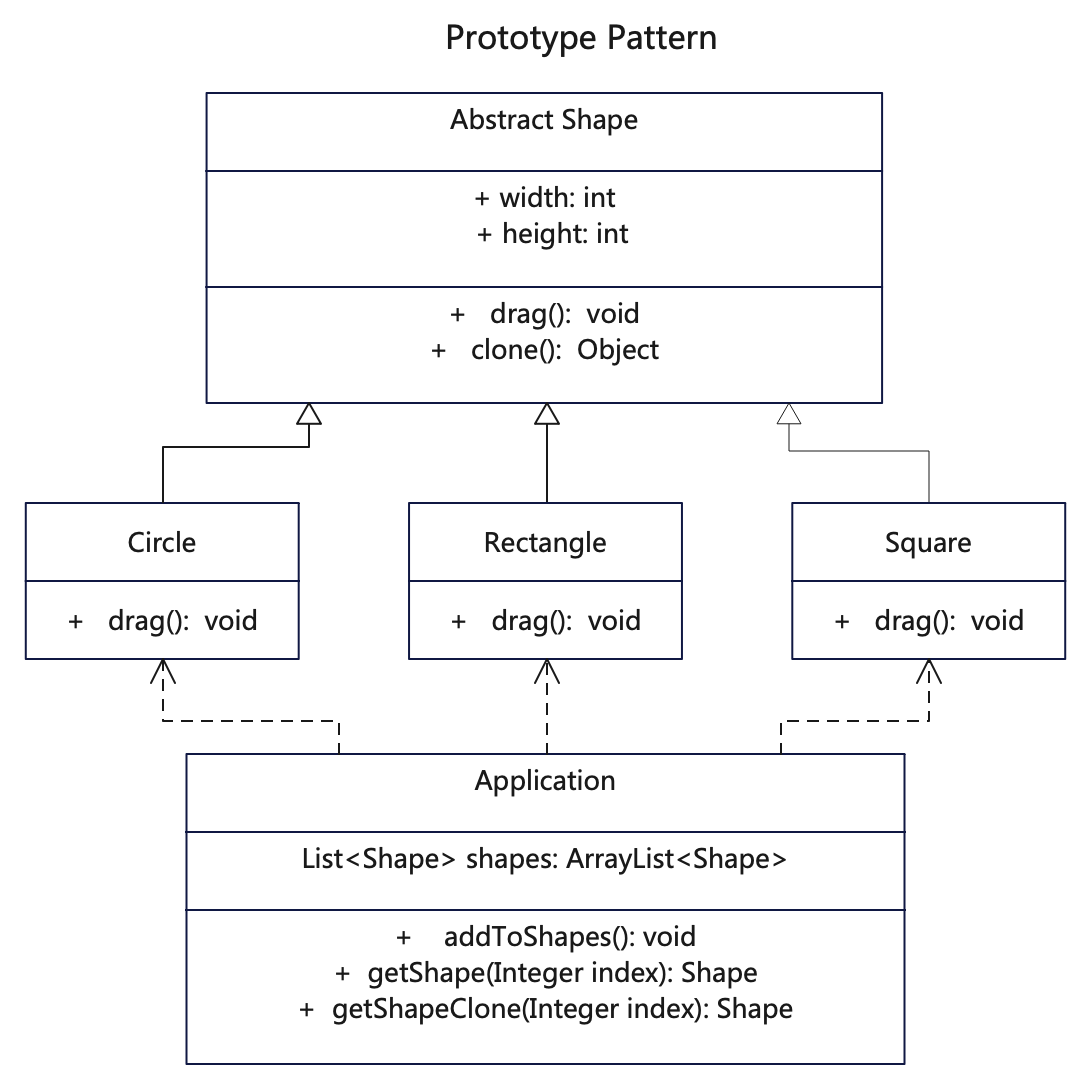
prototype-pattern.png
Java代码
基础原型抽象类
// Shape.java 基础抽象类
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private int width;
private int height;
private String color = "";
protected String type;
public Shape() {
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
// 抽象方法,子类覆盖
public abstract void draw();
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getWidth() {
return this.width;
}
public int getHeight() {
return this.height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
// 克隆方法
public Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{width = %s, height = %s, type = %s, color = %s }",
this.width, this.height, this.type, this.color);
}
}
具体原型者
// Circle.java 具体原型类,克隆方法会创建一个新对象并将其传递给构造函数。
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle() {
super();
type = "Circle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
// Rectangle.java 具体原型类,克隆方法会创建一个新对象并将其传递给构造函数。
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle() {
super();
type = "Rectangle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
// 具体原型类,克隆方法会创建一个新对象并将其传递给构造函数。
public class Square extends Shape {
public Square() {
super();
type = "Square";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Square::draw() method.");
}
}
客户使用类
// Application.java 客户调用方
public class Application {
public List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<Shape>();
public Application() {
}
public void addToShapes() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setWidth(10);
circle.setHeight(20);
circle.setColor("red");
shapes.add(circle);
// 添加clone
Circle anotherCircle = (Circle) circle.clone();
anotherCircle.setColor("pink");
shapes.add(anotherCircle);
// 变量 `anotherCircle(另一个圆)`与 `circle(圆)`对象的内容完全一样。
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setWidth(99);
rectangle.setHeight(69);
rectangle.setColor("green");
shapes.add(rectangle);
// 添加clone
shapes.add((Shape) rectangle.clone());
}
// 直接取出
public Shape getShape(Integer index) {
return this.shapes.get(index);
}
// 取出时候clone
public Shape getShapeClone(Integer index) {
Shape shape = this.shapes.get(index);
return (Shape) shape.clone();
}
public void printShapes() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.shapes.size(); i++) {
Shape shape = this.shapes.get(i);
System.out.println("shape " + i + " : " + shape.toString());
}
}
}
测试调用
/**
* 原型模式主要就是复制已有的对象,而无需实例化类,从而提升实例化对象时的性能
* 其实就是复制实例的属性到新对象上,减少了执行构造的步骤
*/
Application application = new Application();
application.addToShapes();
Shape shapeClone = application.getShapeClone(1);
// 更改clone
shapeClone.setColor("gray");
System.out.println("shapeClone : " + shapeClone.toString());
// 直接更改
application.getShape(3).setColor("yellow");
application.printShapes();
// /*********************** 分割线 ******************************************/
application.shapes.add(new Square());
for (Shape shape : application.shapes) {
shape.draw();
System.out.println(shape.toString());
}
C代码
基础原型抽象类
// func.h 基础头文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct Shape shape;
typedef struct Circle circle;
typedef struct Rectangle rectangle;
typedef struct Square square;
// 定义了Shape作为基础接口,以便各形状有统一类型
typedef struct Shape
{
char name[50];
int width;
int height;
char color[50];
char category[50];
void (*draw)(struct Shape *shape);
struct Shape *(*clone)(struct Shape *shape);
char *(*to_string)(struct Shape *shape);
void (*set_width)(struct Shape *shape, int width);
int (*get_width)(struct Shape *shape);
void (*set_height)(struct Shape *shape, int height);
int (*get_height)(struct Shape *shape);
void (*set_color)(struct Shape *shape, char *color);
char *(*get_color)(struct Shape *shape);
void (*set_category)(struct Shape *shape, char *category);
char *(*get_category)(struct Shape *shape);
} Shape;
Shape *shape_constructor(char *name);
typedef struct Circle
{
char name[50];
int width;
int height;
char color[50];
char category[50];
void (*draw)(struct Circle *shape);
struct Circle *(*clone)(struct Circle *shape);
char *(*to_string)(struct Circle *shape);
void (*set_width)(struct Circle *shape, int width);
int (*get_width)(struct Circle *shape);
void (*set_height)(struct Circle *shape, int height);
int (*get_height)(struct Circle *shape);
void (*set_color)(struct Circle *shape, char *color);
char *(*get_color)(struct Circle *shape);
void (*set_category)(struct Circle *shape, char *category);
char *(*get_category)(struct Circle *shape);
} Circle;
Circle *circle_constructor(char *name);
typedef struct Square
{
char name[50];
int width;
int height;
char color[50];
char category[50];
void (*draw)(struct Square *shape);
struct Square *(*clone)(struct Square *shape);
char *(*to_string)(struct Square *shape);
void (*set_width)(struct Square *shape, int width);
int (*get_width)(struct Square *shape);
void (*set_height)(struct Square *shape, int height);
int (*get_height)(struct Square *shape);
void (*set_color)(struct Square *shape, char *color);
char *(*get_color)(struct Square *shape);
void (*set_category)(struct Square *shape, char *category);
char *(*get_category)(struct Square *shape);
} Square;
Square *square_constructor(char *name);
typedef struct Rectangle
{
char name[50];
int width;
int height;
char color[50];
char category[50];
void (*draw)(struct Rectangle *shape);
struct Rectangle *(*clone)(struct Rectangle *shape);
char *(*string)(struct Rectangle *shape);
void (*set_width)(struct Rectangle *shape, int width);
int *(*get_width)(struct Rectangle *shape);
void (*set_height)(struct Rectangle *shape, int height);
int *(*get_height)(struct Rectangle *shape);
void (*set_color)(struct Rectangle *shape, char *color);
char *(*get_color)(struct Rectangle *shape);
void (*set_category)(struct Rectangle *shape, char *category);
char *(*get_category)(struct Rectangle *shape);
} Rectangle;
Rectangle *rectangle_constructor(char *name);
// 调用客户端
typedef struct Application
{
struct Shape **shapes;
int shapes_length;
void (*add_to_shapes)(struct Application *app);
void (*add_shape)(struct Application *app, Shape *shape);
Shape *(*get_shape)(struct Application *app, int index);
Shape **(*get_shapes)(struct Application *app);
Shape *(*get_shape_clone)(struct Application *app, int index);
void (*print_shapes)(struct Application *app);
} Application;
Application *application_constructor();
// shape.c 基础类,供各种具体形状复用
#include "func.h"
// shape基础抽象类,供子类继承覆盖
// C没有抽象和继承,此处作为公共类存在
void shape_draw(Shape *shape)
{
printf("\r\n Shape::draw()");
}
void shape_set_width(Shape *shape, int width)
{
shape->width = width;
}
int shape_get_width(Shape *shape)
{
return shape->width;
}
int shape_get_height(Shape *shape)
{
return shape->height;
}
void shape_set_height(Shape *shape, int height)
{
shape->height = height;
}
void shape_set_color(Shape *shape, char *color)
{
strncpy(shape->color, color, 50);
}
char *shape_get_color(Shape *shape)
{
return shape->color;
}
void shape_set_category(Shape *shape, char *category)
{
strncpy(shape->category, category, 50);
}
char *shape_get_category(Shape *shape)
{
return shape->category;
}
char *shape_to_string(Shape *shape)
{
static char result[1024];
sprintf(result, "[name = %s width = %d, height = %d, category = %s, color = %s]",
shape->name, shape->width, shape->height, shape->category, shape->color);
return result;
}
// 将指针指向同一内存的方式来实现clone
Shape *shape_clone(Shape *shape)
{
Shape *copy = (Shape *)malloc(sizeof(Shape));
memcpy(copy, shape, sizeof(Shape));
strcat(copy->name, "(clone)");
// printf("\r\n shape_clone: %s", copy->to_string(copy));
return copy;
}
// 定义简单结构体,复制基本属性和draw函数
Shape *shape_clone2(Shape *shape)
{
struct Shape copy = {
.width = shape->width,
.height = shape->height,
};
strcpy(copy.name, shape->name);
strcat(copy.name, "[clone]");
strcpy(copy.color, shape->color);
strcpy(copy.category, shape->category);
Shape *shape_copy = ©
shape_copy->draw = shape->draw;
// printf("\r\n shape_clone: %s", shape->to_string(shape_copy));
return shape_copy;
}
Shape *shape_constructor(char *name)
{
printf("\r\n shape_constructor() [构建Shape]");
Shape *shape = (Shape *)malloc(sizeof(Shape));
strncpy(shape->name, name, 50);
shape->draw = &shape_draw;
shape->clone = &shape_clone;
shape->to_string = &shape_to_string;
shape->set_width = &shape_set_width;
shape->get_width = &shape_get_width;
shape->set_height = &shape_set_height;
shape->get_height = &shape_get_height;
shape->set_color = &shape_set_color;
shape->get_color = &shape_get_color;
shape->set_category = &shape_set_category;
shape->get_category = &shape_get_category;
return shape;
}
具体原型者
// circle.c 具体原型类,复用父类方法,实现自己的draw函数。
#include "func.h"
// 重新定义draw函数
void circle_draw(Circle *shape)
{
printf("\r\n Circle::draw()");
}
Circle *circle_constructor(char *name)
{
printf("\r\n shape_constructor() [构建Circle]");
Shape *shape = (Shape *)shape_constructor(name);
Circle *circle = (Circle *)shape;
circle->draw = &circle_draw;
return circle;
}
// rectangle.c 具体原型类,复用父类方法,实现自己的draw函数。
#include "func.h"
// 重新定义draw函数
void rectangle_draw(Rectangle *shape)
{
printf("\r\n Rectangle::draw()");
}
Rectangle *rectangle_constructor(char *name)
{
printf("\r\n shape_constructor() [构建Rectangle]");
Shape *shape = (Shape *)shape_constructor(name);
Rectangle *rectangle = (Rectangle *)shape;
rectangle->draw = &rectangle_draw;
return rectangle;
}
// square.c 具体原型类,复用父类方法,实现自己的draw函数。
#include "func.h"
// 重新定义draw函数
void square_draw(Square *shape)
{
printf("\r\n Square::draw()");
}
Square *square_constructor(char *name)
{
printf("\r\n shape_constructor() [构建Square]");
Shape *shape = (Shape *)shape_constructor(name);
Square *square = (Square *)shape;
square->draw = &square_draw;
return square;
}
客户使用类
// application.c 客户调用方
#include "func.h"
void app_add_to_shapes(Application *app)
{
Circle *circle = circle_constructor("circle");
circle->set_category(circle, "Circle");
circle->set_width(circle, 10);
circle->set_height(circle, 20);
circle->set_color(circle, "red");
app->add_shape(app, (Shape *)circle);
// 添加Clone
Circle *another_circle = circle->clone(circle);
another_circle->set_color(another_circle, "pink");
app->add_shape(app, (Shape *)another_circle);
// 变量 `another_circle(另一个圆)`与 `circle(圆)`对象的内容完全一样。
Rectangle *rectangle = rectangle_constructor("rectangle");
rectangle->set_category(rectangle, "Rectangle");
rectangle->set_width(rectangle, 99);
rectangle->set_height(rectangle, 69);
rectangle->set_color(rectangle, "green");
app->add_shape(app, (Shape *)rectangle);
// 再添加一个clone
app->add_shape(app, (Shape *)rectangle->clone(rectangle));
}
void app_add_shape(Application *app, Shape *shape)
{
app->shapes_length += 1;
Shape **new_shapes = (Shape **)calloc(app->shapes_length, sizeof(Shape));
// 复制原有数组,并追加新内容到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < app->shapes_length - 1; i++)
{
new_shapes[i] = app->shapes[i];
}
new_shapes[app->shapes_length - 1] = shape;
free(app->shapes);
// 指向新数组
app->shapes = new_shapes;
}
Shape *app_get_shape(Application *app, int index)
{
return app->shapes[index];
}
Shape **app_get_shapes(Application *app)
{
return app->shapes;
}
Shape *app_get_shape_clone(Application *app, int index)
{
Shape *shape = app->shapes[index];
if (shape != NULL)
{
return shape->clone(shape);
}
return NULL;
}
void app_print_shapes(Application *app)
{
for (int i = 0; i < app->shapes_length; i++)
{
Shape *shape = app->shapes[i];
printf("\r\n shape%d: %s", i, shape->to_string(shape));
}
}
// 给观察者绑定主题,同时把观察者添加到主题列表
Application *application_constructor()
{
printf("\r\n application_constructor() [构建Application]");
Application *app = (Application *)malloc(sizeof(Application));
app->shapes_length = 0;
app->shapes = (Shape **)calloc(app->shapes_length, sizeof(Shape));
app->add_to_shapes = &app_add_to_shapes;
app->add_shape = &app_add_shape;
app->get_shape = &app_get_shape;
app->get_shapes = &app_get_shapes;
app->get_shape_clone = &app_get_shape_clone;
app->print_shapes = &app_print_shapes;
return app;
}
测试调用
#include "../src/func.h"
int main(void)
{
printf("test start:\r\n");
/**
* 原型模式主要就是复制已有的对象,而无需实例化类,从而提升实例化对象时的性能
* 其实就是复制实例的属性到新对象上,减少了执行构造的步骤。
*/
Application *application = application_constructor();
application->add_to_shapes(application);
Shape *shape_clone = application->get_shape_clone(application, 0);
// SetColor需要接口中定义
shape_clone->set_color(shape_clone, "gray");
printf("\r\n shape_clone : %s", shape_clone->to_string(shape_clone));
// 直接更改
// application->get_shape(application, 3)->set_color(application->get_shape(application, 3), "yellow");
application->print_shapes(application);
/*********************** 分割线 ******************************************/
// 追加一个Squre实例,相关属性为空
application->add_shape(application, (Shape *)square_constructor("square"));
// 打不打印查看结果
for (int i = 0; i < application->shapes_length; i++)
{
Shape *shape = application->shapes[i];
shape->draw(shape);
printf("\r\n shape_%d %s", i, shape->to_string(shape));
}
}
更多语言版本
不同语言实现设计模式:https://github.com/microwind/design-pattern