目录
一、概念
二、mysql安装及设置
1.安装mysql
2.数据库服务启动停止
三、数据库基本操作
1、数据库的登录及退出
2、数据表的操作
3、mysql查询操作
一、概念
- 数据库:是存放数据的仓库,它是一个按数据结构来存储和管理数据的计算机软件系统。
- 数据库管理系统:是数据库系统的核心组成部分,主要完成对数据库的操作与管理功能,例如实现数据的存储,查询,修改,删除,及数据库用户的管理,权限管理等。
- RDBMS:关系数据库管理系统(Relational Database Management System)
- SQL :结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language),端口号1433.
- mysql 数据库是一种C/S模型(即客户端和服务端模型),在传输层,使用TCP协议通讯。客户单通过用户名,密码登录连接服务器,端口号3306。连接成功后才可以进行数据库的操作(增删改查)。如下图所示:
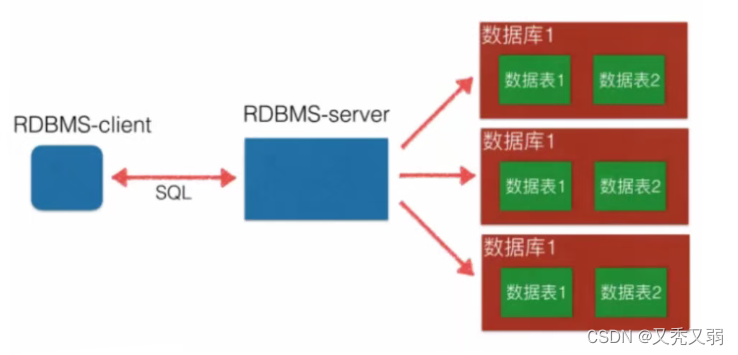
数据库分类
- 关系型数据库 :指采用了关系模型来组织数据的数据库,关系模型就是指二维表格模型,而一个关系型 数据库就是由二维表及其之间的联系所组成的一个数据组织。
- 关系型数据库核心元素:数据行(一条记录),数据列(字段), 数据表(数据行的集合),数据库(数 据表的集合)。
- 关系型数据库产品: oracle , mysql, sqlite ,DB2, Microsoft Sql Server
- 非关系型数据库(nosql) : 指非关系型的,分布式的,且一般不保证遵循ACID原则的数据存储系统。
- 非关系型数据库以键值对存储,且结构不固定。(ACID,指原子性,一致性,隔离性,持久性)
- 非关系型数据库产品: memcache , redis , mongodb, hbase
二、mysql安装及设置
1.安装mysql
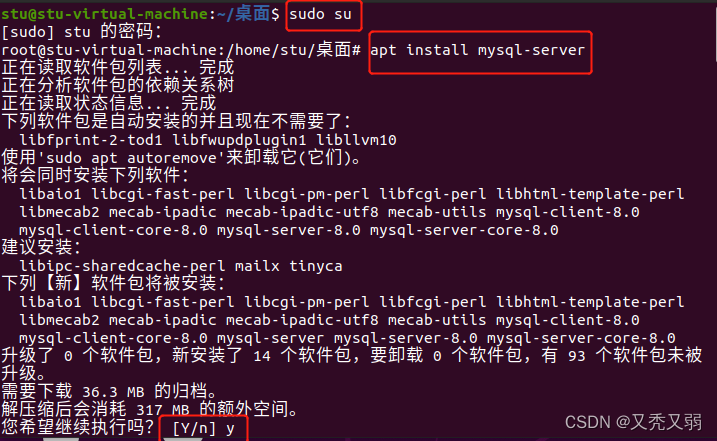
这里介绍ubuntu发行版本上使用apt命令安装的步骤。
linux上安装数据库,通过输入如下命令执行安装:
- sudo su
- apt install mysql-server
2.数据库服务启动停止
(1)检查服务器状态
命令为:
- service mysql statu
- systemctl status mysql.service
(2)重启|停止|启动 数据库
如果不是管理员需要在命令前面加上 sudo
- 重启: /etc/init.d/mysql restart
- 停止: /etc/init.d/mysql stop
- 启动: /etc/init.d/mysql start
或者执行如下命令
- root@stu-virtual-machine:/home/stu# service mysql restart
- root@stu-virtual-machine:/home/stu# service mysql stop
- root@stu-virtual-machine:/home/stu# service mysql start
(3)连接数据库
命令
- mysql -uroot -p
mysql:数据库管理系统客户端
(4)用户管理与授权
查看用户信息
- mysql> select user,host,plugin from mysql.user;
创建用户
- mysql> create user 'stu'@'localhost' identified by 'Iabc_123456';
创建用户指定加密方式
- mysql> create user 'stu1'@'localhost' identified WITH mysql_native_password by 'Iabc_123456';
更新用户密码,指定加密方式,注意密码强度大小写数字
- ALTER user 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'Iabc_123456';
创建管理员远程登陆用户
- create user 'root'@'%' identified WITH mysql_native_password by '1111111';
更新用户密码,指定加密方式,注意密码强度大小写数字
- ALTER user 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'Iabc_123456';
授权用户对那些数据库的那些表可以进行操作
- 指定user_name用户可以从任意地点登录访问所有数据库的所有表
- GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'user_name'@'%' identified by '密码' GRANT ALL ON database_name.table_name TO 'user_name'@'localhost'
删除用户
- drop user 'name'@'localhost';
三、数据库基本操作
1、数据库的登录及退出
1、连接数据库
- mysql -u用户名 -h主机地址(省略代表本机) -p密码
退出数据库,以下三种方式都可以:
- exit
- quit
- ctrl+d
2、查看所有数据库
- show databases; 要注意所有sql语句结尾都有 ‘;’分号
3、显示数据库版本
- select version();
4、显示时间
- select now();
5、创建数据库
- create database 数据库名
- create database 数据库名 charset=utf8;
6、查看创建数据库的语句
- show create database 数据库名
7、查看当前使用的数据库
- 查看当前使用的是哪个数据库 :select database();
- 为null代表没有选择使用的数据库。
8、查看当前用户
- 查看当前登录的是哪个用户:select user();
9、使用某个数据库
- 登录到mysql后,里面创建有很多数据库,选择要使用的某一个数据库: use 数据库名
10、删除数据库
- 删除数据库: drop database 数据库名
2、数据表的操作
1、查看当前数据库中所有表
- show tables;
2、创建表
创建表时,需要指定各个字段的类型,常见类型如下: 数值类型(部分)

字符串,部分类型如下:

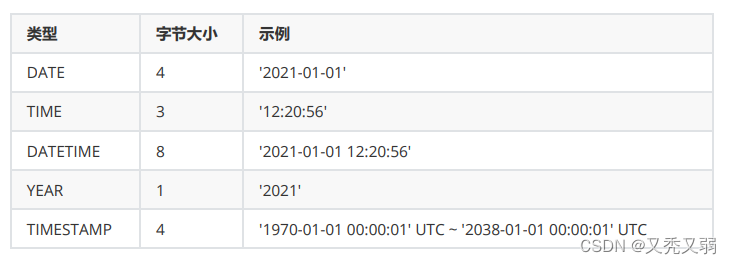
日期时间类型:
约束
- 主键 primary key : 物理上存储的顺序
- 非空 not null : 此字段不允许填写空值
- 唯一unique: 此字段的值不允许重复
- 默认default: 当不填写此值时,会使用默认值。如果填写时,以填写的值为准
- 外键foreign key : 对关系字段进行约束,当为关系字段填写值时,会到关联的表中查询此值是否存在,如果存在则写成功,如果不存在则写失败。 虽然外键约束可以保证数据的有效性,但是在进行 数据的crud(增加,修改,删除,查询)时,都会降低数据库的性能。
- auto_increment 表示自动增长
创建表的命令 :
- create table 数据库表名字 ( 字段 类型 约束 [, 字段,类型 约束] ); 中括弧中的可以省
未使用约束
- create table student1(id int, name varchar(30));
对id 字段使用约束
- create table student2(id int primary key not null auto_increment, name varchar(30));
执行以上示例,创建 student1,student2表。
- mysql> create table student1(id int, name varchar(30));
- mysql> create table student2(id int primary key not null auto_increment, name varchar(30));
创建一个students的表
- mysql> create table students(
- -> id int unsigned not null auto_increment primary key,
- -> name varchar(30),
- -> age tinyint unsigned default 0,
- -> high decimal(5,2),
- -> gender enum("男","女") default "男",
- -> cls_id int unsigned
- -> );
3、查看表结构
查看表结构也就是的各个字段的信息。
- desc 表名;
4、查看创建表的语句
查看创建表的语句
- show create table 表名
- #另一种查看方式以\G结尾,格式更好一些
- show create table 表名\G
5、向表中插入,更新,删除数据
插入数据
- 使用 insert into 表名values(字段1的值,字段2的值...);
- mysql> insert into students values(1,"小明",23,162.22,"男",1001);
更新数据
- 使用update 更新记录,示例如下:
- mysql> update student set name='小李' where id=102;
删除数据
- 使用delete删除表中的行,可以删除指定行,也可以删除所有行
- mysql> select * from student;
6、查看表中数据
使用 select * from 表名;
- mysql> select * from students;
也可以指定查询某几个字段: select id, name from students;
- mysql> select id, name from students;
mysql中注释使用
- "--"
7、修改表名字
修改表的名字,使用 alter table 原表名 rename [to] 新表名; 其中to可以省略
- mysql> show tables;
8、修改表字段信息
修改表--添加字段
- alter table 表名 add 列名 类型; 示例: alter table students add birthday datetime;
- mysql> alter table students add birthday datetime;
修改字段-- 重新命名
- alter table 表名 change 原字段名 新字段名 类型及约束;
修改字段-- 不改名字
- alter table 表名 modify 列名 类型及约束;
修改表--删除字段
- alter table 表名 drop 列名:
修改字段排列位置
- ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 属性名1 数据类型 FIRST | AFTER 属性名2;
修改表的存储引擎
- 常见引擎:MyISAM, InnoDB
- mysql> alter table student3 engine=myisam;
9 、删除表
- drop table 表名;
3、mysql查询操作
1 、基本查询
查询所有字段
- select * from 表名;
查询指定字段
- select 列1, 列2,... from 表名;
- select 表名.字段 ... from 表名;
使用as给字段起别名
- select 字段 as 名字 ... from 表名;
使用as给表起别名
- select 别名.字段 .... from 表名 as 别名;
消除重复行
- distinct 字段
- mysql> select addr from student ;
2 、条件
比较运算
- select ... from 表名 where ... 大于 > , 小于 < , 大于等于 >=, 小于等于 <=, 相等 = , 不相等 !=
- #查询年龄大于18岁的学生信息
- select * from student where age > 18;
- #查询年龄为18的所有学生,注意等号只有一个
- select * from student where age = 18;
逻辑运算: and, or , not
- #查询年龄在18到24岁之间的所有学生
- select * from student where age > 18 and age < 24;
- #查询18岁以上的所有女性
- select * from student where age > 18 and gender = "女";
- #查询年龄在18岁以上,或者 身高在180及以上的学生
- select * from student where age > 18 or height >= 180;
- #不在 18岁以上,并且是男生
- select *from student where not age > 18 and gender = "男";
- #不在 18岁以上的男生 这个范围的学生
- select * from student where not (age > 18 and gender = "男");
模糊查询
like :% 替换一个或多个
_ 替换一个
- #查询姓名中以 “小” 开始的名字
- select name from student where name like "小%";
- #查询姓名中 含有“小”字,的所有名字
- select name from student where name like "%小%";
- #查询有两个字的名字
- select name from student where name like "__";
- #查询名字至少有2个字的名字
- select name from student where name like "__%";
范围查询
in, not int,
不连续范围 between ... and ... ,
not between ... and ... 连续范围
空判断: is null
判非空: is not null
- #查询年龄为18,20,24的学生信息
- select name,age from student where age = 18 or age=20 or age = 34 ; select name,age from student where age in (18,20,24);
- #查询年龄不是18,20,24的学生信息
- select name ,age from student where age not in (18,20,24);
- #查询年龄在18到24岁之间的所有学生信息
- select name, age from student where age between 18 and 24;
- #查询年龄不在18到24岁之间的
- select * from student where age not between 18 and 24;
- #查询学生住址为空的学生
- select * from student where addr is null;
3 、排序
order by 字段 , 默认是升序 从小到大 asc, 需要降序从大到小 ,加上 desc 可以对多个字段进行判断
- #查询年龄在18岁以上的学生,年龄安从小到大
- select * from student where age > 18 order by age;
- #查询年龄在18岁以上的学生,年龄安从大到小
- select * from student where age > 18 order by age desc;
- #查询年龄在18 到24之间的学生,按照年龄从小到大,身高从高到低排序
- select * from student where (age between 18 and 34 ) order by age asc, height desc;
4 、聚合函数
count() 总数, max() 最大值, min() 最小值, sum()求和, avg() 平均值, round()四舍五入
- #查询男生有多少人
- select count(*) from student where gender='男';
- #查询最大年龄
- select max(age) from student;
- #查询年龄最小值
- select min(age) from student;
- #计算所有人的年龄总和
- select sum(age) from student;
- #计算平均年龄
- select avg(age) from student; 或 select sum(age) / count(*) from student;
- #算平均年龄,设置平均年龄的小数位数
- select round(sum(age) / count(*),2) from student;