目录
安装mysql
更改账户名和密码
启动/关闭mysql
mysql的基本操作
数据库CURD
创建数据库
查看数据库
修改数据库
删除数据库
表的CURD
创建表
查看表
修改表
删除表
表数据的CURD
create数据
Retrieve数据
update数据
delete数据
DML和DDL的区别:
ddl与dml的区别
基础SQL
字符串相关函数
数学相关函数
多表查询
交叉连接(省略)
满外联接(省略)
内连接
左外连接
右外连接
对比练习
自连接
先按照oracle语法写
完善显示格式concat
显示king的老板
改用MySQL支持的SQL99语法
滤空修正nvl
表的约束
mysql中文乱码问题
安装mysql
第一步更新update
sudo apt-get update第二步更新install
sudo apt-get install第三步安装mysql服务
sudo apt-get install mysql-server第四步安装mysql服务端
sudo apt-get install mysql-client第五步切换到mysql文件夹查看初始文件密码
cd /etc/mysql
sudo cat debian.cnf
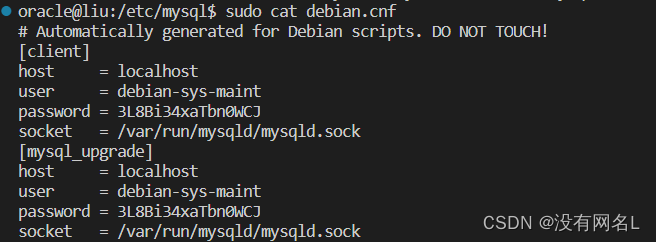
user为账户,password为密码
第六步登录
mysql -u debian-sys-maint -p输入密码即可使用mysql
更改账户名和密码
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by '123456';将用户名修改为root密码修改为123456;
刷新权限
flush privileges;退出
exit;重启mysql即可
service mysql restart;启动/关闭mysql
首先切换到根目录下
su -root启动mysql服务
service mysql start关闭mysql服务
service mysql stop查看是否启动成功
mysql的基本操作
数据库CURD
对数据库进行增(create)、删(delete)、改(update)、查(Retrieve)操作。
创建数据库
创建一个名称为mydb1的数据库。(默认为latin1)
create database mydb1;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集的mydb2数据库。
create database mydb2 character set utf8;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集,并带校对规则的mydb3数据库。会对存入的数据进行检查。
create database mydb3 character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
查看数据库
显示所有数据库
show databases;
显示创建数据库的语句信息
show create database mydb2;
“ ` ”(ESC键 下面的按键),表示反引号,默认情况下,反引号括起来的字符串,区分大小写。
show create database mydb1;
注意 :mysql默认语言集是latin1,每次在创建数据库的时候应指定字符集。Oracle是在安装时,即指定了字符集。
库名和表名是区分大小写的。
修改数据库
修改mydb1的字符集为utf8(不能修改数据库名)
alter database mydb1 character set utf8;
删除数据库
删除数据库mydb3
drop database mydb3;
表的CURD
对表本身进行操作:创建,查看,修改,删除
创建表
create table t1 (id int, name varchar(20))
但此时会报错误:ERROR 1046 (3D000): No database selected。注意,在mysql中对表操作前,必须先选择所使用的数据库。
use mydb2;
查看当前使用的是哪个库:
status 或者 select database() from dual;
查看当前选择的数据库中的表:
show tables;
查看表结构:
desc tablename;
在Mysql中显示多行数据应该在查询语句结尾处添加 \G来替换结束标记“;”
查看创建表的语法:
show create table t1; ENGINE=InnoDB 默认指定的存储引擎 innoDB。
mysql中的数据类型:
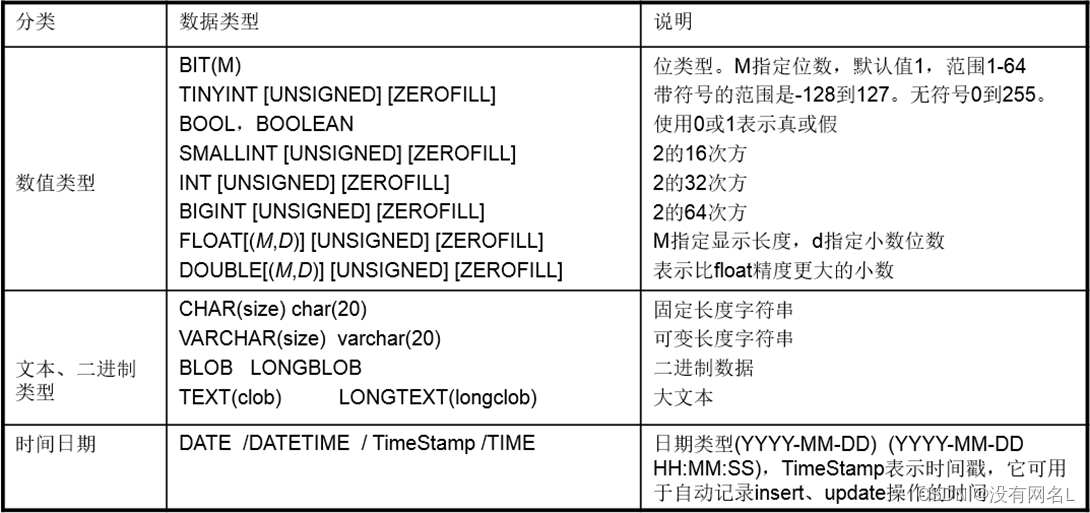
bit 1位 可以指定位数,如:bit(3)
int 2字节 可以指定最大位数,如:int<4> 最大为4位的整数
float 2个字节 可以指定最大的位数和最大的小数位数,如:float<5,2> 最大为一个5位的数,小数位最多2位
double 4个字节 可以指定最大的位数和最大的小数位数,如:float<6,4> 最大为一个6位的数,小数位最多4位
char 必须指定字符数,如char(5) 为不可变字符 即使存储的内容为'ab',也是用5个字符的空间存储这个数据
varchar 必须指定字符数,如varchar(5) 为可变字符 如果存储的内容为'ab',占用2个字符的空间;如果为'abc',则占用3个字符的空间
text: 大文本(大字符串)
blob:二进制大数据 如图片,音频文件,视频文件
date: 日期 如:'1921-01-02'
datetime: 日期+时间 如:'1921-01-02 12:23:43'
timeStamp: 时间戳,自动赋值为当前日期时间
创建一个员工表:
create table employee(empno int, ename varchar(20), sal int);
查看表
查看所有的表:
show tables;
查看指定表的创建语句
show create table employee;
注意,mysql表名称区分大小写, 对列名不区分大小写
显示指定表的结构:
desc employee;
修改表
更改表名: rename table employee to worker;
增加一个字段:alter table employee add column height double; (column关键字在Oracle中,添加则语法错误)
修改一个字段:alter table employee modify column height float;
删除一个字段:alter table employee drop column height;
修改表的字符集:alter table employee character set gbk;
删除表
删除employee表
drop table employee; (MySQL中不能使用purge,添加会出现语法错误)
表数据的CURD
create数据
创建一个员工表,新建employee表并向表中添加一些记录:
create table employee(
id int,
name varchar(20),
sex int,
birthday date,
salary double,
entry_date date,
resume text
);
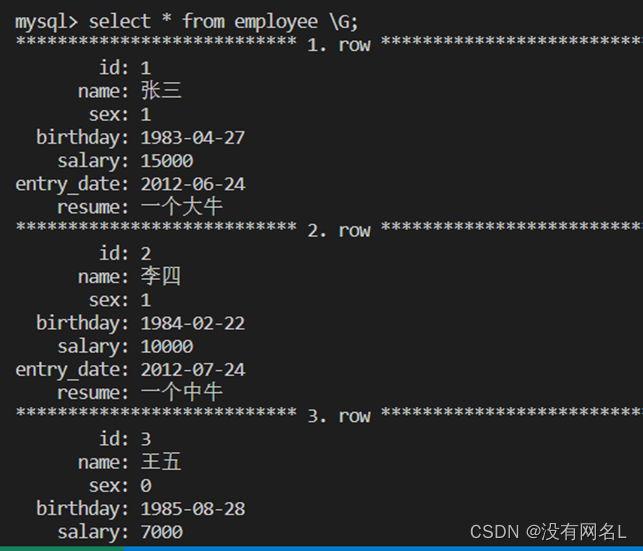
insert into employee values(1,'张三',1,'1983-04-27',15000,'2012-06-24','一个大牛');
insert into employee(id,name,sex,birthday,salary,entry_date,resume) values(2,'李四',1,'1984-02-22',10000,'2012-07-24','一个中牛');
insert into employee(id,name,sex,birthday,salary,entry_date,resume) values(3,'王五',0,'1985-08-28',7000,'2012-08-24','一个小虾');
注意: 若在插入的时候报错, 可以查看当前用户字符集是否是latin1.
Retrieve数据
select id, name as "名字", salary "月薪", salary*12 年薪 from employee where id >=2;
如果表项太长可以使用select * from employee \G;会将表信息按键值对显示出来
update数据
将所有员工薪水都增加500元。
update employee set salary=salary+500;
将王五的员工薪水修改为10000元,resume改为也是一个中牛
update employee set salary=10000, resume='也是一个中牛' where name='王五';
delete数据
删除表中姓名为王五的记录。
delete from employee where name='王五'; 【注意from不能省略】
删除表中所有记录。
delete from employee;
使用truncate删除表中记录。
truncate employee;--无条件 效率高
delete是可以恢复数据的,truncate是直接删除表数据,无法恢复,truncate比delete快一些。
DML和DDL的区别:
为了形成数据库语言,DDL和DML都是必需的。DDL和DML之间的主要区别在于:DDL是对数据库中的对象进行管理,主要是用在定义或改变表的结构;DML是对数据库中的数据进行操作。
为了形成数据库语言,DDL 和 DML 都是必需的。DDL 和 DML 之间的主要区别在于:DDL 有助于更改数据库的结构,而 DML 有助于管理数据库中的数据。DDL 比 DML 要多,主要的命令有 CREATE、ALTER、DROP 等,DDL 主要是用在定义或改变表(TABLE)的结构,数据类型,表之间的连接和约束等初始化工作上,他们大多在建立表时使用。用户通过 DML 可以实现对数据库的基本操作,但必须由计算机软件进行编译,转换为便于计算机存储、查询和操纵的格式,完成这个转换工作的程序称为模式编译器。而数据库模式定义语言DDL,是用于描述数据库中要存储的现实世界实体的语言,主要是对表中数据的插入、删除和修改。
ddl与dml的区别
本质区别 :DDL 代表数据定义语言,是一种有助于创建数据库模式的 SQL 命令。而,DML 代表数据操作语言,是一种有助于检索和管理关系数据库中数据的 SQL 命令。
命令上的区别:DDL 中常用的命令有:create,drop,alter,truncate 和 rename 等等。而,DML 中常用的命令有:insert,update,delete 和 select 等等。
影响上的区别:DDL 命令会影响整个数据库或表,但 DML 命令会影响表中的一个或多个记录。
回滚上的区别:带有 DDL 命令的 SQL 语句无法回滚;带有 DML 命令的 SQL 语句可以回滚。
DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据操纵语言
适用范围:对数据库中的数据进行一些简单操作,如 insert,delete,update,select 等.
DDL(Data Definition Language)数据定义语言
适用范围:对数据库中的某些对象(例如,database,table)进行管理,如 Create,Alter 和 Drop.
基础SQL
查询表中所有学生的信息。
select * from student;
查询表中所有学生的姓名和对应的英语成绩。
select name,english from student;
过滤表中重复数据。
select english from student;
select DISTINCT english from student;
select DISTINCT english,name from student;
select english+chinese+math from student;
select english+chinese+math as 总分 from student;
select name,english+chinese+math as 总分 from student;
在所有学生英语分数上加10分特长分。
select name,english+10 from student;
统计每个学生的总分。
select english+chinese+math from student;
使用别名表示学生分数
select name,english+chinese+math as 总分 from student;
select name,english+chinese+math 总分 from student;
查询姓名为何东的学生成绩
select * from student where name='何东';
查询英语成绩大于90分的同学
select * from student where english>90;
查询总分大于250分的所有同学
select * from student where english+chinese+math>250;
查询英语分数在 85-95之间的同学。
select * from student where english>=85 and english<=95;
select * from student where english between 85 and 95;
查询数学分数为84,90,91的同学。
select * from student where math=84 or math=90 or math=91;
select * from student where math in(84,90,91);
查询所有姓何的学生成绩。
select * from student where name like '何%';
查询数学分>85,语文分>90的同学。
select * from student where math>85 and chinese>90;
对数学成绩排序后输出。
select * from student order by math;
对总分排序后输出,然后再按从高到低的顺序输出
select * from student order by math+chinese+english desc;
对姓何的学生成绩排序输出
select * from student where name like '何%' order by math+chinese+english desc;
select name, math+chinese+english from student where name like '何%' order by math+chinese+english desc;
统计一个班级共有多少学生?
select count(*) from student;
统计数学成绩大于90的学生有多少个?
select count(*) from student where math>90;
统计总分大于250的人数有多少?
select count(*) from student where math+chinese+english>250;
统计一个班级数学总成绩?
select sum(math) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学各科的总成绩
select sum(math), sum(chinese), sum(english) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学的成绩总和
select sum(math+chinese+english)from student;
select sum(math)+sum(chinese)+sum(english) from student;
求一个班级数学平均分?
select avg(math) from student;
求一个班级总分平均分
select avg(math+chinese+english)from student;
select avg(math)+avg(chinese)+avg(english) from student;
求班级最高分和最低分
select max(math+chinese+english),min(math+chinese+english) from student;
top-N问题:
按math成绩从小大的排序, 求math成绩在5-8名的
select * from student order by math limit 4, 4;
前面这个4是跳过4个,后面这个4是取4个
分组数据
为学生表,增加一个班级列,练习分组查询。
alter table student add column class_id int;
注意语法:Oracle中不能有“column”关键字,MySQL中有没有“column”都可以执行。
更新表:
update student set class_id=1 where id<=5;
update student set class_id=2 where id>5;
(update student set class_id=2 where id between 6 and 10;)
查出各个班的总分,最高分。
select class_id, sum(chinese+english+math) "总成绩", max(chinese+english+math) "最高分" from student group by class_id;
二、having子句
having子句:having子句通常是与order by子句一起使用的,因为having的作用是对使用group by进行分组统计后的结果进行进一步的筛选。
where子句和having子句的区别:
1.where不能放在group by后面
2.having是跟group by连在一起用的,放在group by 后面,此时的作用相当于where
3.where 后面的条件中不能有聚集函数,比如SUM(),AVG()等,而HAVING可以。
一、where子句
where子句:where子句仅仅用于从from子句中返回的值,from子句返回的每一行数据都会用where子句中的条件进行判断筛选,where子句中允许使用比较运算符和逻辑运算符
求各个班级 英语的平均分:
select classid, avg(english)
from student
group by class_id
如根据组函数的语法要求,将select后增加name列,而不加至group by 之后:
select name, classid, avg(english)
from student
group by classid;
会发现MySQL检查不出错误。相比Oracle数据库,MySQL分组检查不严格。
select sum(math+chinese+english),max(math+chinese+english) from student group by class_id;
查询出班级总分大于1300分的班级ID
select class_id from student group by class_id having sum(math+chinese+english)>1300;
select class_id from student where sum(math+chinese+english)>1300 group by class_id ;
对于组函数的应用与Oracle类似,可以应用于Having中,但不能用于where子句中.
-
- 日期时间函数
MySQL里面时间分为三类:时间、日期、时间戳(含有时分秒的sysdate)。
Select sysdate() from dual;获取当前时间
如执行:select now(), year(now()) 年, month(now()) 月, day(now()) 日, date(now()); 
select CURRENT_DATE() , CURRENT_TIME(), CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() from dual; 
昨天、今天、明天:
select now()-1 昨天, now() 今天, now()+1 明天 from dual;
发现与Oracle中的日期加减操作有所不同。
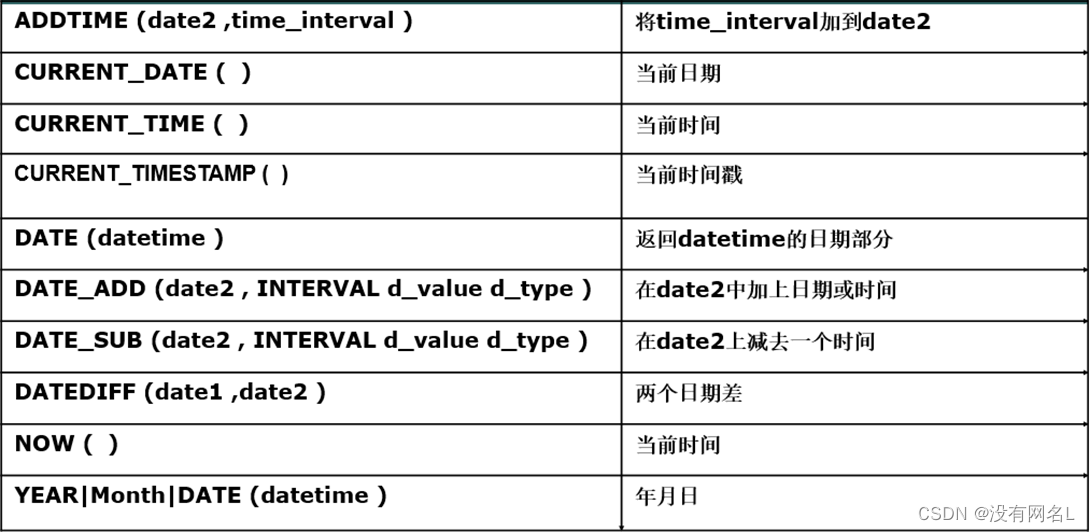
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL 2 year) from dual; //增加两年
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL -1 day) 昨天, now() 今天, date_add(now(), INTERVAL +1 day) 明天;
select date_add(now(), interval -1 day) 昨天, date, date_add(now(), interval +1 day) 明天;
注意: 上述语句中的函数名, INTERVAL不区分大小写, day, month, year也可以用大写.
设置时间的显示格式
Select date_format(now(), '%Y-%m-%d');
Select date_format(now(), '%Y-%m-%d %H-%i-%s');
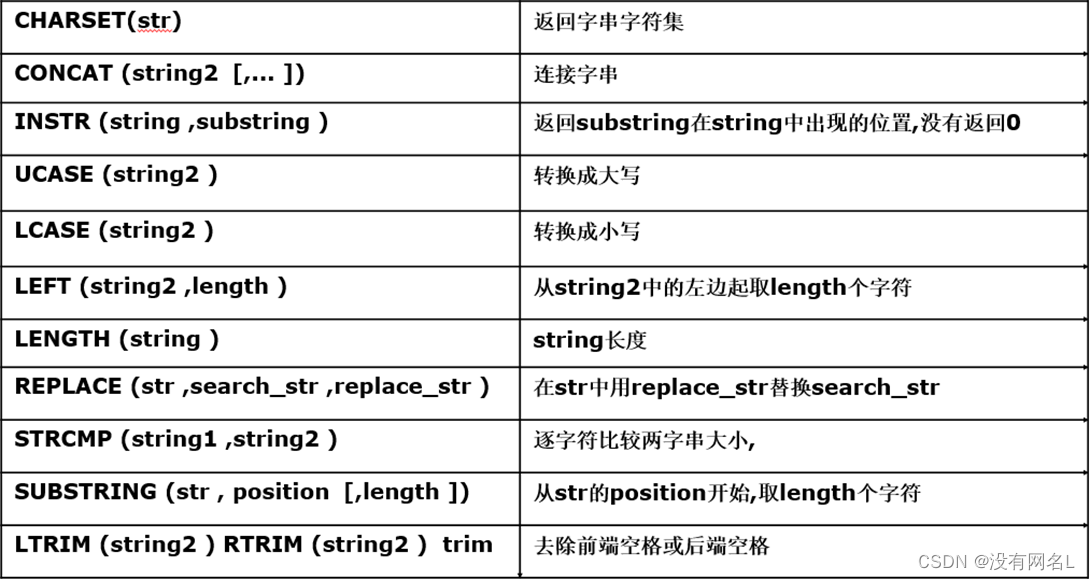
字符串相关函数
select concat('hello ', 'mysql ', 'haha ', 'hehe ') from dual;
Oracle默认只能拼两个,如需多个拼接可以使用嵌套。
select 'hello ' || 'mysql ' from dual; ‘||’ 在 MySQL不可以使用。
日期转字符串:
在MySQL中没有to_date函数,进行日期转换需使用date_format()来代替。
select date_format('2013-5-11', 'yyyy-mm-dd') from dual; 在Oracle中的‘yyyy-mm-dd’MySQL下不支持。
select date_format(now(), '%Y-%m-%d') from dual; y和Y不一样。
select date_format(now(), '%Y-%c-%d %h:%i:%s') from dual; c和m、M不一样
所以yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss格式在MySQL中对应'%Y-%c-%d %h:%i:%s'
字符串转日期:
select str_to_date('2013-6-04 05:14:15' , '%Y-%c-%d %h:%i:%s') from dual;
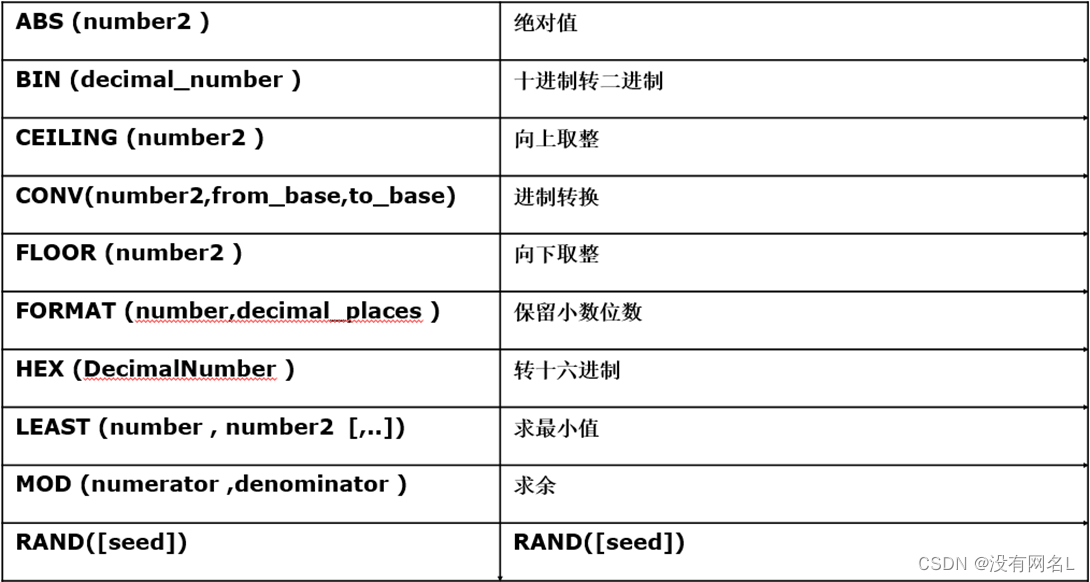
数学相关函数
多表查询
创建多表查询案例——MySQL建表_仿照oracle建表脚本.sql 【mysql> source 绝对路径/脚本名】
首先将脚本导入到linux系统中,后执行
Source
Oracle中连接方法:
等值连接
不等值连接
外连接
自连接
MySQL 使用SQL99标准的连接查询(JOIN..ON..)
交叉连接(省略)
叉集,即笛卡尔集
select e.*, d.*
from emp e cross join dept d
无连接条件
满外联接(省略)
任一边有值就会显示。
select e.*, d.*
from emp e full outer join dept d
on e.deptno=d.deptno
也可以省略outer关键字
内连接
只返回满足连接条件的数据(两边都有的才显示)。 对应等值连接
查询emp表和dept表的所有信息:
select e.*, d.*
from emp e inner join dept d
on e.deptno=d.deptno
也可以省略inner关键字。
对应Oracle写法:
select e.*, d.*
from emp e , dept d
where e.deptno=d.deptno
左连接的含义是限制表2中的数据必须满足连接条件,而不管表1中的数据是否满足连接条件,均输出表1的内容。
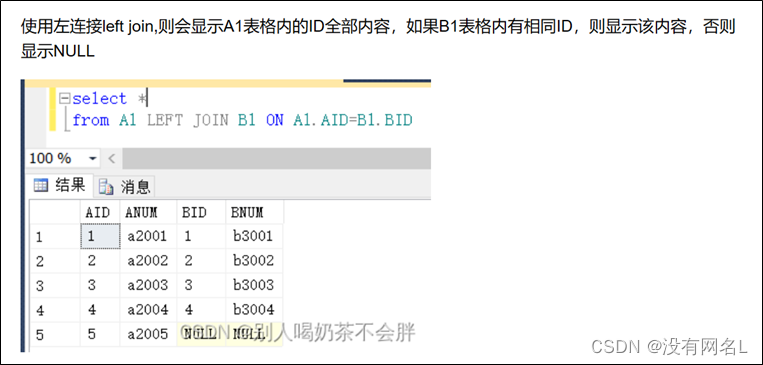
右连接的含义是限制表1中的数据必须满足连接条件,而不管表2中的数据是否满足连接条件,均输出表2的内容。
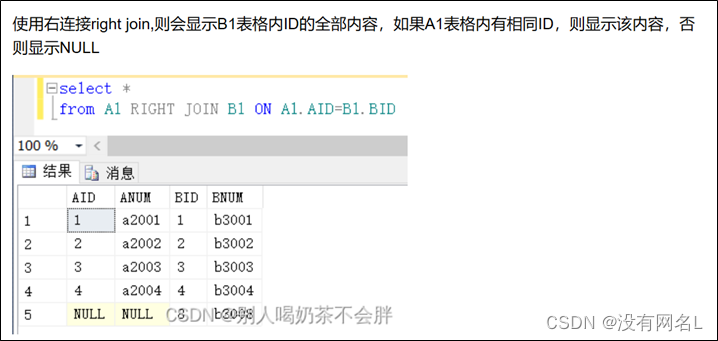
左外连接
左边有值才显示。
select e.*, d.*
from emp e left outer join dept d
on e.deptno=d.deptno
也可以省略outer关键字
右外连接
右边有值才显示。
select e.*, d.*
from emp e right outer join dept d
on e.deptno=d.deptno
也可以省略outer关键字
【注意】SQL99中,外链接取值与关系表达式=号左右位置无关。取值跟from后表的书写顺序有关。
“xxx left outer join yyy” 则为取出xxx的内容。
“xxx right outer join yyy”则为取出yyy的内容
对比练习
题目1:
查询员工信息,员工号,姓名,月薪,部门名称
select ...
from emp e, dept d
where e.deptno = d.deptno;
Oracle实现:
select e.deptno, e.ename, e.sal, d.dname
from emp e, dept d
where e.deptno = d.deptno
SQL99实现:
select e.deptno, e.ename, e.sal, d.dname
from emp e inner join dept d
on e.deptno = d.deptno
对比记忆规律:
“,” → [inner] join
where → on
对比结论:mysql能识别Oracle中使用 = 连接的书写方法。
题目2:
统计各个部门员工总人数-要求显示部门名称
分析:部门包括10/20/30 → 分组
各部门人数 → 多表
select ...
from emp e, dept d
where d.deptno = e.deptno
group by ...
(注意:group by后面出现的子集应在select下进行检索)
实现为:
select d.deptno, d.dname, count(e.empno)
from dept d, emp e
where d.deptno = e.deptno
group by d.deptno, d.dname
count(e.empno)表示统计e.empno不同的总数量,只有当empno存在才会进行统计
count(*)只要有一行存在一个值,那么就会对其进行统计,即使存在其他值为NULL的情况。
查询发现没有40号部门。此时应使用外链接保存一侧结果。
oracle实现:
select d.deptno, d.dname , count(e. empno)
from dept d, emp e
where d.deptno = e.deptno (+)
group by d.deptno, d.dname
SQL99实现:
select d.deptno, d.dname , count(e. empno)
from dept d left outer join emp e
on d.deptno = e.deptno
group by d.deptno, d.dname
对比记忆规律:
“,”→ left/right outer join (左右要看from后面表出现的顺序)
where → on
结论:oracle的语法(+) mysql不支持
自连接
查询员工、老板信息,显示: xxx的老板是xxx
分析:将一张emp表当成两张表看待:员工表、老板表(员工表的老板 是 老板表的员工)
先按照oracle语法写
select e.ename, b.ename
from emp e, emp b
where e.mgr = b.empno
完善显示格式concat
select concat( e.ename, ' 的老板是 ', b.ename )
from emp e, emp b
where e.mgr = b.empno
显示king的老板
select concat( e.ename, ' 的老板是 ', b.ename )
from emp e, emp b
where e.mgr = b.empno (+)
改用MySQL支持的SQL99语法
select concat( e.ename, ' 的老板是 ', b.ename )
from emp e left outer join emp b
on e.mgr = b.empno ;
滤空修正nvl
select concat( e.ename, ' 的老板是 ', nvl(b.ename, '他自己' ) )
from emp e left outer join emp b
on e.mgr = b.empno ;
结论 nvl 在mysql下不能使用: ERROR 1305 (42000): FUNCTION mydb61.nvl does not exist
滤空修正 ifnull
select concat( e.ename, ' 的老板是 ', ifnull(b.ename, '他自己' ) )
from emp e left outer join emp b
on e.mgr = b.empno ;
注意:
Oracle中有一个通用函数,与MYSQL中的ifnull函数名字相近:
nullif:如nullif(a, b) 当 a = b 时返回null, 不相等的时候返回a值。nullif('L9,999.99', 'L9,999.99')
mysql中nullif()函数也存在。
表的约束
*定义主键约束 primary key: 不允许为空,不允许重复
*定义主键自动增长 auto_increment
*定义唯一约束 unique
*定义非空约束 not null
*定义外键约束 constraint ordersid_FK foreign key(ordersid) references orders(id)
*删除主键:alter table tablename drop primary key ;
MySQL中约束举例:
create table myclass (
id INT(11) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique
);
create table student (
id INT(11) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique,
passwd varchar(15) not null,
classid INT(11),
constraint stu_classid_FK foreign key(classid) references myclass(id)
);
check约束在MySQL中语法保留,但没有效果。
向class表中插入两条数据:
insert into class(name) values('音乐');
insert into class(name) values('体育');
insert into class(id, name) values(5, '美术');
insert into class(name) values('文化');//此时id为6
注意: 要插入的是部分列, 一定要在class表名后面写上列名, 表示要插入哪些列
由于class表的id是主键, 可以不用显示的插入主键的值, mysql会自动插入,而且会自动增长,确保不会重复.
向student表中插入数据:
正常插入一条记录:
insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values('xiaohong', 'xxxxxx', 1);
1 测试主键的非空性
insert into student(id, name, passwd, classid) values(null, 'xiaowen', 'xxxxxx', 1);
注意: 若给主键插入一个null, mysql会自动插入一个有效的值, 所以mysql的主键肯定不会为空
2 测试主键的唯一性约束
insert into student(id, name, passwd, classid) values(1, 'xiaoliu', 'xxxxxx', 1);
----->ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'
3 测试name列的唯一性
insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values('xiaohong', 'xxxxxx', 2);
-----> ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'xiaohong' for key 'name'
insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values(null, 'xxxxxx', 2);
注意: name为unique约束, 只是不能重复, 但是可以为空
4 测试passwd的非空约束
insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values('xiaohua', null, 2);
-----> ERROR 1048 (23000): Column 'passwd' cannot be null
5 测试classid的外键约束
insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values('meizi', 'mmmm', 10);
----->OREIGN KEY (`classid`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`))
在class表中没有id为10的列的值.
mysql中文乱码问题
两层因素:
因素1: MySQL自身的设计
【实验步骤1】:
mysql> show variables like 'character%'; 查看所有应用的字符集
【实验步骤2】:
$ mysql -uroot -p123456 --default_character_set=gbk 指定字符集登录数据库
mysql> show variables like 'character%';
影响了与客户端相关联的 3处 (最外层)
在这种状态下执行use mydb2;
mysql> select * from employee;
查看输出,会出现乱码。
原来的三条数据,是以utf8的形式存储到数据库中,当使用gbk连接以后,数据库仍按照utf8的形式将数据返回,出错。
【实验步骤3】:
在该环境下插入带有中文的一行数据。
mysql> insert into employee(id,name,sex,birthday,salary,entry_date,resume) values(10,'张三疯',1,'1983-09-21',15000,'2012-06-24','一个老牛');
ERROR 1366 (HY000): Incorrect string value: '\x80\xE4\xB8\xAA\xE8\x80...' for column 'resume' at row 1
因素2:操作系统的语言集
linux操作系统 是一个 多用户的操作
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/i18n
LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8"
操作系统的菜单按照zh_CN显示, 文件存储按照utf8
linux操作系统语言环境 和 用户的配置的语言环境LANG 相互影响
[mysql01@localhost ~]$ echo $LANG
zh_CN.UTF-8
【实验步骤4】:
修改用户下的.bash_profile 中的LANG,屏蔽操作系统的LANG设置。再查数据库
mysql> select * from employee;
结论: 用户的LANG设置,影响了应用程序的语言环境,导致myql的语言环境发生了改变:
mysql> show variables like 'character%';
在此环境下,检索中文会出现乱码。
【实验步骤5】:在上述环境之下,向数据库中插入中文。
insert into employee(id,name,sex,birthday,salary,entry_date,resume) values(5,'张三疯',1,'1987-05-21',15000,'2014-06-24','一个老牛');
数据能插入到数据库中,没 有 报 任 何 错 误!但显示不正确。