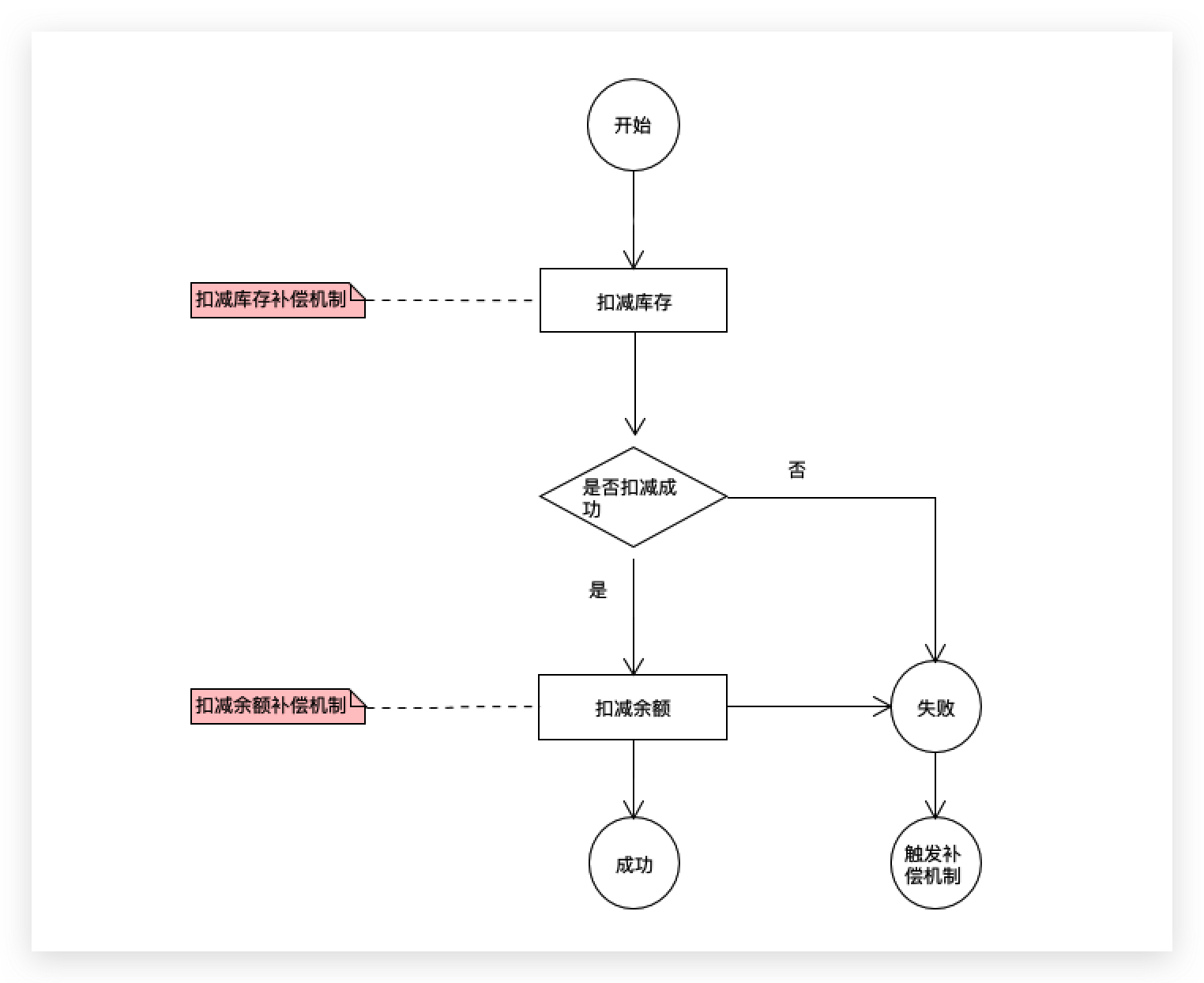
1. servicemanager 进程的启动
对于用户空间,不同进程之间彼此是不能共享的,而内核空间却是可共享的。Client进程向Server进程通信,恰恰是利用进程间可共享的内核内存空间来完成底层通信工作的,Client端与Server端进程往往采用ioctl等方法跟内核空间的驱动进行交互。
Binder通信采用C/S架构,从组件视角来说,包含Client、Server、ServiceManager以及binder驱动,其中ServiceManager用于管理系统中的各种服务。架构图如下所示:
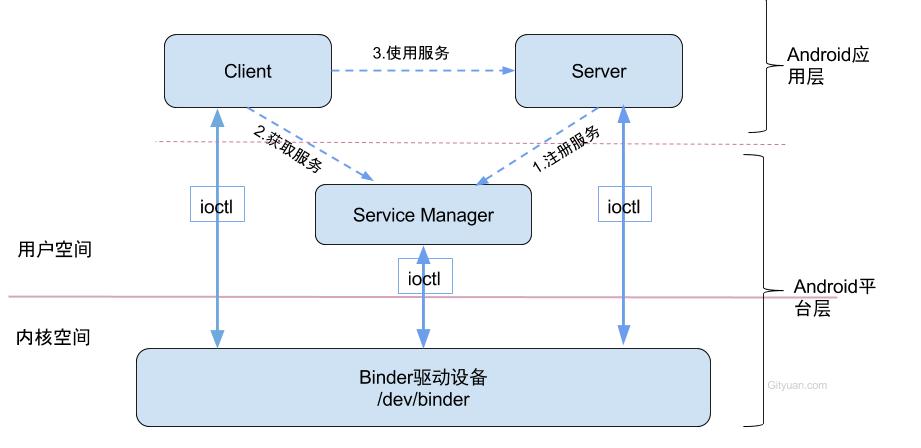
ServiceManager是整个Binder通信机制的大管家,是Android进程间通信机制Binder的守护进程
图中的Client,Server,Service Manager之间交互都是虚线表示,是由于它们彼此之间不是直接交互的,而是都通过与Binder驱动进行交互的,从而实现IPC通信方式。其中Binder驱动位于内核空间,Client,Server,Service Manager位于用户空间。Binder驱动和Service Manager可以看做是Android平台的基础架构,而Client和Server是Android的应用层,开发人员只需自定义实现client、Server端,借助Android的基本平台架构便可以直接进行IPC通信。
从 init 进程启动过程中我们知道 ServiceManager 服务管理进程是通过 init 进程 fork 出来的, 这里我们就分析一下 ServiceManager 的启动流程
/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
在 init.rc 脚本中,有去启动servicemanager 进程 ,其所对应的可执行程序/system/bin/servicemanager
on init
sysclktz 0
# Mix device-specific information into the entropy pool
copy /proc/cmdline /dev/urandom
copy /system/etc/prop.default /dev/urandom
..
# Start essential services.
start servicemanager
start hwservicemanager
start vndservicemanager/frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/
servicemanager.rc
servicemanger 的脚本:
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core animation
user system
group system readproc
critical
onrestart restart apexd
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart gatekeeperd
onrestart class_restart main
onrestart class_restart hal
onrestart class_restart early_hal
writepid /dev/cpuset/system-background/tasks
shutdown critical执行main 文件,安卓12有所变化,使用 C++
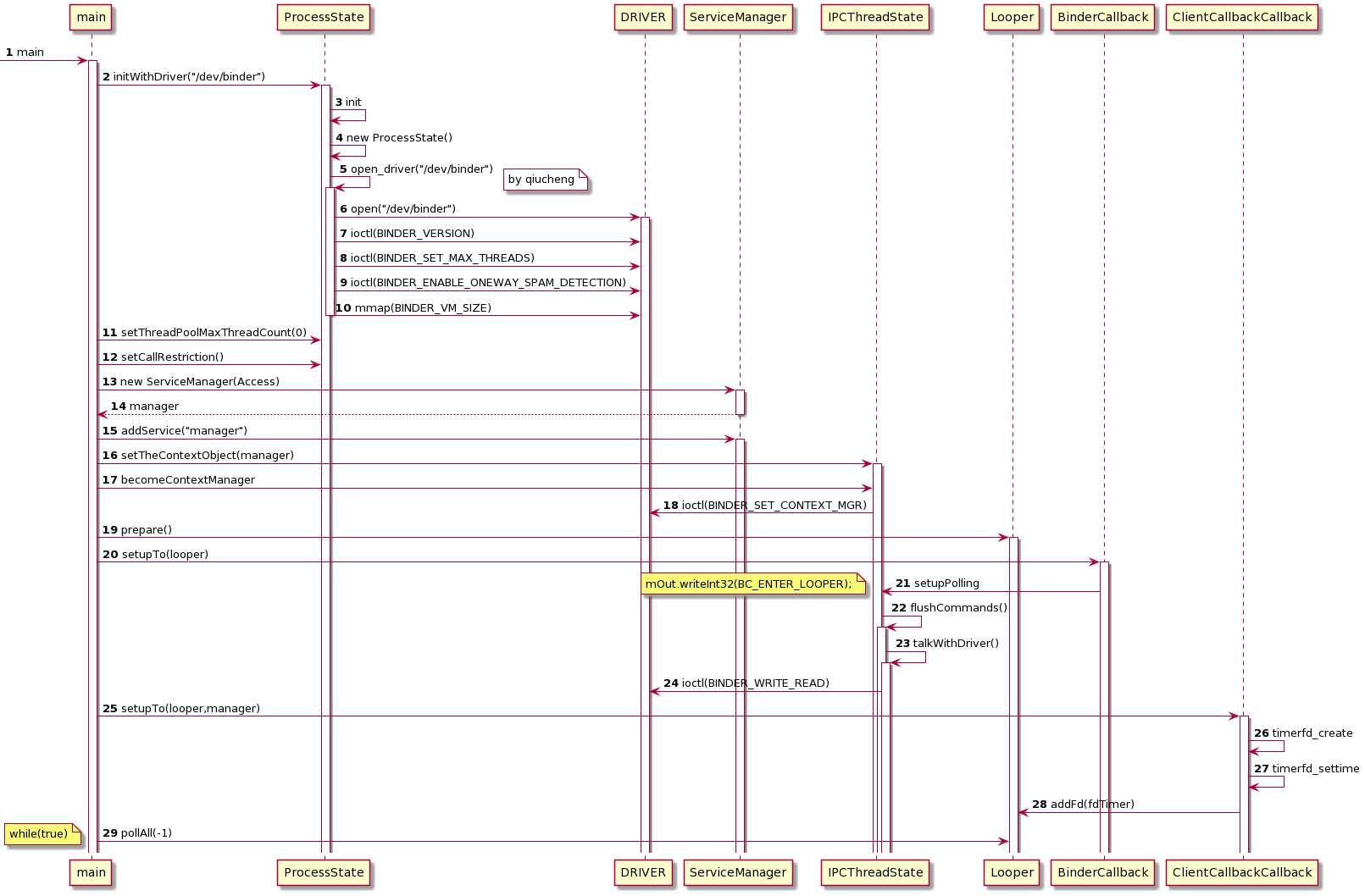
/frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc > 2) {
LOG(FATAL) << "usage: " << argv[0] << " [binder driver]";
}
// 设备驱动名为:"/dev/binder"
const char* driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1] : "/dev/binder";
// 1)调用ProcessState 的 initWithDriver初始化驱动
sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver);
ps->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0);
ps->setCallRestriction(ProcessState::CallRestriction::FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY);
// 2)创建 ServiceManager 对象
sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make(std::make_unique<Access>());
// 注册自己的服务 ServiceManager,将name 和service 保存到map 中
// using ServiceMap = std::map<std::string, Service>;
if (!manager->addService("manager", manager, false /*allowIsolated*/, IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT).isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not self register servicemanager";
}
// 3)设置 ServiceManager为上下文对象:setTheContextObject
IPCThreadState::self()->setTheContextObject(manager);
ps->becomeContextManager();
// 4)开启循环,执行 Looper::prepare
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false /*allowNonCallbacks*/);
// 5)两个回调 callback的方法 setupTo
BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager);
// 6)执行死循环,等待客户端消息
while(true) {
looper->pollAll(-1);
}
// should not be reached
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}1)调用ProcessState 的 initWithDriver初始化驱动
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::initWithDriver(const char* driver)
{
return init(driver, true /*requireDefault*/);
}
======
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::init(const char *driver, bool requireDefault)
{
[[clang::no_destroy]] static sp<ProcessState> gProcess;
[[clang::no_destroy]] static std::mutex gProcessMutex;
if (driver == nullptr) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(gProcessMutex);
return gProcess;
}
[[clang::no_destroy]] static std::once_flag gProcessOnce;
std::call_once(gProcessOnce, [&](){
if (access(driver, R_OK) == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder driver %s is unavailable. Using /dev/binder instead.", driver);
driver = "/dev/binder";
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(gProcessMutex);
// 创建 ProcessState 对象,参数是:"/dev/binder"
gProcess = sp<ProcessState>::make(driver);
});
if (requireDefault) {
// Detect if we are trying to initialize with a different driver, and
// consider that an error. ProcessState will only be initialized once above.
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(gProcess->getDriverName() != driver,
"ProcessState was already initialized with %s,"
" can't initialize with %s.",
gProcess->getDriverName().c_str(), driver);
}
return gProcess;
}创建 ProcessState 对象,参数是:"/dev/binder"
ProcessState::ProcessState(const char *driver)
// 设置 mDriverName 为:"/dev/binder"
: mDriverName(String8(driver))
// 去打开驱动设备,缓存返回的fd 文件描述符
, mDriverFD(open_driver(driver))
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)
, mThreadCountLock(PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER)
, mThreadCountDecrement(PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER)
, mExecutingThreadsCount(0)
, mWaitingForThreads(0)
, mMaxThreads(DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS)
, mStarvationStartTimeMs(0)
, mThreadPoolStarted(false)
, mThreadPoolSeq(1)
, mCallRestriction(CallRestriction::NONE)
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
// mmap the binder, providing a chunk of virtual address space to receive transactions.
// mmap 映射内存,大小为:#define BINDER_VM_SIZE ((1 * 1024 * 1024) - sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE) * 2) 1M - 16k
mVMStart = mmap(nullptr, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
// *sigh*
ALOGE("Using %s failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n", mDriverName.c_str());
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
mDriverName.clear();
}
}打开设备驱动,返回文件描述符
static int open_driver(const char *driver)
{
// 以读写方式打开设备驱动
int fd = open(driver, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd >= 0) {
int vers = 0;
// 调用binder驱动的binder_ioctl 获取binder 版本号
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to obtain version failed: %s", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
// 如果版本不匹配
if (result != 0 || vers != BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION) {
ALOGE("Binder driver protocol(%d) does not match user space protocol(%d)! ioctl() return value: %d",
vers, BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION, result);
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
// 最大的线程数为: 15 ,DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS 15
size_t maxThreads = DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
uint32_t enable = DEFAULT_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION, &enable);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGD("Binder ioctl to enable oneway spam detection failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
} else {
ALOGW("Opening '%s' failed: %s\n", driver, strerror(errno));
}
// 返回文件描述符
return fd;
}2)创建 ServiceManager 对象
sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make(std::make_unique<Access>())
/frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/ServiceManager.cpp
// 保存在 mAccess,Access看起来是和surlinux 相关的
ServiceManager::ServiceManager(std::unique_ptr<Access>&& access) : mAccess(std::move(access)) {
// TODO(b/151696835): reenable performance hack when we solve bug, since with
// this hack and other fixes, it is unlikely we will see even an ephemeral
// failure when the manifest parse fails. The goal is that the manifest will
// be read incorrectly and cause the process trying to register a HAL to
// fail. If this is in fact an early boot kernel contention issue, then we
// will get no failure, and by its absence, be signalled to invest more
// effort in re-adding this performance hack.
// #ifndef VENDORSERVICEMANAGER
// // can process these at any times, don't want to delay first VINTF client
// std::thread([] {
// vintf::VintfObject::GetDeviceHalManifest();
// vintf::VintfObject::GetFrameworkHalManifest();
// }).detach();
// #endif // !VENDORSERVICEMANAGER
}3)设置 ServiceManager为上下文对象:setTheContextObject
IPCThreadState 是单例模式,只有一个对象
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
void IPCThreadState::setTheContextObject(const sp<BBinder>& obj)
{
the_context_object = obj;
}
=====
case BR_TRANSACTION_SEC_CTX:
case BR_TRANSACTION:
{
。。。。
if (tr.target.ptr) {
// We only have a weak reference on the target object, so we must first try to
// safely acquire a strong reference before doing anything else with it.
if (reinterpret_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(
tr.target.ptr)->attemptIncStrong(this)) {
error = reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,
&reply, tr.flags);
reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->decStrong(this);
} else {
error = UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION;
}
} else {
// 下列调用 servicemanager 的 transact
error = the_context_object->transact(tr.code, buffer, &reply, tr.flags);
}4)开启循环,执行 Looper::prepare
/system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
创建 Looper 对象
sp<Looper> Looper::prepare(int opts) {
bool allowNonCallbacks = opts & PREPARE_ALLOW_NON_CALLBACKS;
sp<Looper> looper = Looper::getForThread();
if (looper == nullptr) {
// 创建 Looper 对象
looper = new Looper(allowNonCallbacks);
Looper::setForThread(looper);
}
if (looper->getAllowNonCallbacks() != allowNonCallbacks) {
ALOGW("Looper already prepared for this thread with a different value for the "
"LOOPER_PREPARE_ALLOW_NON_CALLBACKS option.");
}
return looper;
}Looper 构造函数:
Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks)
: mAllowNonCallbacks(allowNonCallbacks),
mSendingMessage(false),
mPolling(false),
mEpollRebuildRequired(false),
mNextRequestSeq(0),
mResponseIndex(0),
mNextMessageUptime(LLONG_MAX) {
// 设置 eventfd
mWakeEventFd.reset(eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC));
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mWakeEventFd.get() < 0, "Could not make wake event fd: %s", strerror(errno));
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
rebuildEpollLocked();
}void Looper::rebuildEpollLocked() {
// Close old epoll instance if we have one.
if (mEpollFd >= 0) {
#if DEBUG_CALLBACKS
ALOGD("%p ~ rebuildEpollLocked - rebuilding epoll set", this);
#endif
mEpollFd.reset();
}
// Allocate the new epoll instance and register the wake pipe.
mEpollFd.reset(epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC));
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mEpollFd < 0, "Could not create epoll instance: %s", strerror(errno));
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.fd = mWakeEventFd.get();
int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd.get(), EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeEventFd.get(), &eventItem);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(result != 0, "Could not add wake event fd to epoll instance: %s",
strerror(errno));
for (size_t i = 0; i < mRequests.size(); i++) {
const Request& request = mRequests.valueAt(i);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd.get(), EPOLL_CTL_ADD, request.fd, &eventItem);
if (epollResult < 0) {
ALOGE("Error adding epoll events for fd %d while rebuilding epoll set: %s",
request.fd, strerror(errno));
}
}
}5)两个回调 callback的方法 setupTo
BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager);
class BinderCallback : public LooperCallback {
public:
static sp<BinderCallback> setupTo(const sp<Looper>& looper) {
sp<BinderCallback> cb = sp<BinderCallback>::make();
int binder_fd = -1;
// 获取到 binder_fd 的值:
IPCThreadState::self()->setupPolling(&binder_fd);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(binder_fd < 0, "Failed to setupPolling: %d", binder_fd);
// 调用 looper->addFd(binder_fd,设置回调为当前的 cb
int ret = looper->addFd(binder_fd,
Looper::POLL_CALLBACK,
Looper::EVENT_INPUT,
cb,
nullptr /*data*/);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(ret != 1, "Failed to add binder FD to Looper");
return cb;
}
int handleEvent(int /* fd */, int /* events */, void* /* data */) override {
IPCThreadState::self()->handlePolledCommands();
return 1; // Continue receiving callbacks.
}
};获取到 binder_fd 的值:mProcess->mDriverFD 就是打开binder 设备驱动的fd,监听驱动 fd
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::setupPolling(int* fd)
{
if (mProcess->mDriverFD < 0) {
return -EBADF;
}
mOut.writeInt32(BC_ENTER_LOOPER);
flushCommands();
*fd = mProcess->mDriverFD;
return 0;
}// 调用 looper->addFd(binder_fd,设置回调为当前的 cb
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
#if DEBUG_CALLBACKS
ALOGD("%p ~ addFd - fd=%d, ident=%d, events=0x%x, callback=%p, data=%p", this, fd, ident,
events, callback.get(), data);
#endif
if (!callback.get()) {
if (! mAllowNonCallbacks) {
ALOGE("Invalid attempt to set NULL callback but not allowed for this looper.");
return -1;
}
if (ident < 0) {
ALOGE("Invalid attempt to set NULL callback with ident < 0.");
return -1;
}
} else {
ident = POLL_CALLBACK;
}
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback;
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0; // reserve sequence number -1
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd.get(), EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &eventItem);
if (epollResult < 0) {
ALOGE("Error adding epoll events for fd %d: %s", fd, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// 将 fd 和 request 结构体保存到 mRequests,可以使用其进行回调 handleEvent 方法
mRequests.add(fd, request);ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager)
class ClientCallbackCallback : public LooperCallback {
public:
static sp<ClientCallbackCallback> setupTo(const sp<Looper>& looper, const sp<ServiceManager>& manager) {
sp<ClientCallbackCallback> cb = sp<ClientCallbackCallback>::make(manager);
int fdTimer = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0 /*flags*/);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(fdTimer < 0, "Failed to timerfd_create: fd: %d err: %d", fdTimer, errno);
itimerspec timespec {
.it_interval = {
.tv_sec = 5,
.tv_nsec = 0,
},
.it_value = {
.tv_sec = 5,
.tv_nsec = 0,
},
};
int timeRes = timerfd_settime(fdTimer, 0 /*flags*/, ×pec, nullptr);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(timeRes < 0, "Failed to timerfd_settime: res: %d err: %d", timeRes, errno);
// 同样调用 Looper 的 addFd
int addRes = looper->addFd(fdTimer,
Looper::POLL_CALLBACK,
Looper::EVENT_INPUT,
cb,
nullptr);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(addRes != 1, "Failed to add client callback FD to Looper");
return cb;
}同样调用 Looper 的 addFd,将 fd 和 request 结构体保存到 mRequests,可以使用其进行回调 handleEvent 方法【在 poollAll 方法去监听回调】
6)执行死循环,等待客户端消息
looper->pollAll(-1)
int Looper::pollAll(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
int result;
do {
result = pollOnce(timeoutMillis, outFd, outEvents, outData);
} while (result == POLL_CALLBACK);
return result;
// 头文件定义:
277 int pollAll(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData);
278 inline int pollAll(int timeoutMillis) {
279 return pollAll(timeoutMillis, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
280 }
// 执行 pollOnce(-1, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)执行 pollOnce(-1, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)
int Looper::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {
int result = 0;
for (;;) {
while (mResponseIndex < mResponses.size()) {
const Response& response = mResponses.itemAt(mResponseIndex++);
int ident = response.request.ident;
if (ident >= 0) {
int fd = response.request.fd;
int events = response.events;
void* data = response.request.data;
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - returning signalled identifier %d: "
"fd=%d, events=0x%x, data=%p",
this, ident, fd, events, data);
#endif
if (outFd != nullptr) *outFd = fd;
if (outEvents != nullptr) *outEvents = events;
if (outData != nullptr) *outData = data;
return ident;
}
}
if (result != 0) {
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - returning result %d", this, result);
#endif
if (outFd != nullptr) *outFd = 0;
if (outEvents != nullptr) *outEvents = 0;
if (outData != nullptr) *outData = nullptr;
return result;
}
result = pollInner(timeoutMillis);
}
}int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - waiting: timeoutMillis=%d", this, timeoutMillis);
#endif
// Adjust the timeout based on when the next message is due.
if (timeoutMillis != 0 && mNextMessageUptime != LLONG_MAX) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
int messageTimeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextMessageUptime);
if (messageTimeoutMillis >= 0
&& (timeoutMillis < 0 || messageTimeoutMillis < timeoutMillis)) {
timeoutMillis = messageTimeoutMillis;
}
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - next message in %" PRId64 "ns, adjusted timeout: timeoutMillis=%d",
this, mNextMessageUptime - now, timeoutMillis);
#endif
}
// Poll.
int result = POLL_WAKE;
mResponses.clear();
mResponseIndex = 0;
// We are about to idle.
mPolling = true;
struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];
// 等待消息
int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd.get(), eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);回调 callback 的 handleEvent 方法
/system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - waiting: timeoutMillis=%d", this, timeoutMillis);
#endif
。。。。
Done: ;
// Invoke pending message callbacks.
mNextMessageUptime = LLONG_MAX;
。。。
// Invoke all response callbacks.
for (size_t i = 0; i < mResponses.size(); i++) {
Response& response = mResponses.editItemAt(i);
if (response.request.ident == POLL_CALLBACK) {
int fd = response.request.fd;
int events = response.events;
void* data = response.request.data;
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKE || DEBUG_CALLBACKS
ALOGD("%p ~ pollOnce - invoking fd event callback %p: fd=%d, events=0x%x, data=%p",
this, response.request.callback.get(), fd, events, data);
#endif
// Invoke the callback. Note that the file descriptor may be closed by
// the callback (and potentially even reused) before the function returns so
// we need to be a little careful when removing the file descriptor afterwards.
// 回调callback 的 handleEvent方法
int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
if (callbackResult == 0) {
removeFd(fd, response.request.seq);
}
// Clear the callback reference in the response structure promptly because we
// will not clear the response vector itself until the next poll.
response.request.callback.clear();
result = POLL_CALLBACK;
}
}
return result;
}安卓12 相对于a10的servicemanager 进程进行了重构.在 Android 11 之前的版本里,SM 是面向 Binder 驱动编程,直接使用 open、mmap、ioctl 等 API 与 Binder 驱动交互。而从 Android 11 开始,SM 放弃使用这些较底层的接口,转向 libbinder 库和 AIDL。标志性的提交如下,该提交奠定了新的 SM 架构基础,此后多次提交对此进行完善填充。
现在的客户端代码流就变成如下三步:
1.用户代码
2.libbinder 代码 binder/IServiceManager.cpp#ServiceManagerShim
3.AIDL 代码 android/os/IServiceManager.cpp#BpServiceManager 接口
所以 libbinder 中的 ServiceManagerShim 起到了一个中转的作用,把请求转给 out 下 AIDL 自动生成的 BpServiceManager。
- BpServiceManager 的实现挪到 out
原来是在 libbinder#IServiceManager.cpp 中手写实现,现在是 AIDL 帮你实现。
当然,该文件中同样自动实现了 BnServiceManager类
代码路径
out/soong/.intermediates/frameworks/native/libs/binder/libbinder/android_arm64_armv8-a_shared/gen/aidl/android/os/IServiceManager.cpp
- 服务端的核心实现在 ServiceManager.cpp
原来是没有 Bn 的,而是一个 binder_loop 方法沟通驱动,现在则是 ServiceManager 继承了 BnServiceManager 来获得代码流。
- waitForService的改动:IServiceCallback.aidl
Waiter 类。新增了 Binder 匿名服务用来向 SM 注册跨进程的回调,当 SM 检测到有服务注册时,会返回通知。
- 服务的客户端数量监听:IServiceCallback.aidl
IServiceCallback.aidl 这个匿名 Binder 服务就是用于该目的,可以监听某个服务的客户端数量。
另外需要特别区分的是,有两个 IServiceManager 。
一个在 libbinder 中,是 android 的 name space,直接被用户 #include<binder/IServiceManager> 使用。
另一个是aidl自动生成的 android os 的 name space,被上面的 libbinder 所使用 #include<android/os/IServiceManager>。
2. defaultServiceManager获取服务的实现
defaultServiceManager方法来获取到 servicemanager 服务。
许多地方都会使用到 defaultServiceManager 方法,如MediaPlayerService 的初始化方法,将其service增加到servicemanager 中管理,以下:
/frameworks/av/media/libmediaplayerservice/MediaPlayerService.cpp
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
void MediaPlayerService::instantiate() {
defaultServiceManager()->addService(
String16("media.player"), new MediaPlayerService());
}看下 defaultServiceManager 在头文件中 binder/IServiceManager.h 有定义
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IServiceManager.h
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager();/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
[[clang::no_destroy]] static sp<IServiceManager> gDefaultServiceManager;
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
{
std::call_once(gSmOnce, []() {
// 创建 AidlServiceManager 对象
sp<AidlServiceManager> sm = nullptr;
while (sm == nullptr) {
// 1. 先看下 ProcessState::self()->getContextObject 获取的对象
// 2. 看下 interface_cast<AidlServiceManager> 返回的值
sm = interface_cast<AidlServiceManager>(ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(nullptr));
if (sm == nullptr) {
ALOGE("Waiting 1s on context object on %s.", ProcessState::self()->getDriverName().c_str());
sleep(1);
}
}
// 创建 ServiceManagerShim 对象
gDefaultServiceManager = sp<ServiceManagerShim>::make(sm);
});
return gDefaultServiceManager;
}
1). 先看下 ProcessState::self()->getContextObject 获取的对象
ProcessState::self() 是获取 ProcessState 对象,创建对象会打开设备驱动,然后mmap一块共享内存,前面有分析
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getContextObject(const sp<IBinder>& /*caller*/)
{
// getStrongProxyForHandle 获取IBinder 对象
sp<IBinder> context = getStrongProxyForHandle(0);
if (context) {
// The root object is special since we get it directly from the driver, it is never
// written by Parcell::writeStrongBinder.
internal::Stability::markCompilationUnit(context.get());
} else {
ALOGW("Not able to get context object on %s.", mDriverName.c_str());
}
return context;
}getStrongProxyForHandle 获取IBinder 对象
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp<IBinder> result;
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
// handle_entry不为空
if (e != nullptr) {
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == nullptr || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
// 传入的handle 的值为 0
if (handle == 0) {
IPCThreadState* ipc = IPCThreadState::self();
CallRestriction originalCallRestriction = ipc->getCallRestriction();
ipc->setCallRestriction(CallRestriction::NONE);
Parcel data;
// 先ping 一下
status_t status = ipc->transact(
0, IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION, data, nullptr, 0);
ipc->setCallRestriction(originalCallRestriction);
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT)
return nullptr;
}
sp<BpBinder> b = BpBinder::create(handle);
// 将 e->binder的值设置为 BpBinder
e->binder = b.get();
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
// 返回的值为BpBinder对象:new BpBinder(0)
result = b;
} else {
// This little bit of nastyness is to allow us to add a primary
// reference to the remote proxy when this team doesn't have one
// but another team is sending the handle to us.
result.force_set(b);
e->refs->decWeak(this);
}
}
return result;
}
// lookupHandleLocked 方法
ProcessState::handle_entry* ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked(int32_t handle)
{
// mHandleToObject 是个动态数组
const size_t N=mHandleToObject.size();
if (N <= (size_t)handle) {
handle_entry e;
// 设置binder 为空
e.binder = nullptr;
e.refs = nullptr;
// 将 handle_entry 结构体保存到 mHandleToObject 中
status_t err = mHandleToObject.insertAt(e, N, handle+1-N);
if (err < NO_ERROR) return nullptr;
}
// 返回 handle_entry
return &mHandleToObject.editItemAt(handle);
}综上:ProcessState::self()->getContextObject 返回的值为:new BpBinder(0)
2). 看下 interface_cast<AidlServiceManager> 返回的值
先看下:interface_cast<>,是如下定义的
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
}返回的置为:AidlServiceManager::asInterface(new BpBinder(0))
安卓12 的BpServiceManager、AidlServiceManager 使用aidl 移动到如下,编译后会自动生成aidl,更加模块化
out/soong/.intermediates/frameworks/native/libs/binder/libbinder/android_arm_armv8-a_shared/gen/aidl/android/os/
IClientCallback.cpp
IServiceCallback.cpp
IServiceManager.cpp
可参考下列文章:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghongzhu/p/15551978.htmlhttps://www.cnblogs.com/wanghongzhu/p/15551978.html
看下 AidlServiceManager 的定义:
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
#include <android/os/IServiceManager.h>
// 赋值为 android/os 的 IServiceManager
using AidlServiceManager = android::os::IServiceManager;
using android::binder::Status;
// libbinder's IServiceManager.h can't rely on the values generated by AIDL
// because many places use its headers via include_dirs (meaning, without
// declaring the dependency in the build system). So, for now, we can just check
// the values here.
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_HIGH == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_HIGH);
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_NORMAL == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_NORMAL);
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT);
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_ALL == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_ALL);
static_assert(AidlServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PROTO == IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
const String16& IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor() const {
return AidlServiceManager::descriptor;
}通过aidl具体生成的路径:
out/soong/.intermediates/frameworks/native/libs/binder/libbinder/android_arm_armv8-a_shared/gen/aidl/android/os/IServiceManager.cpp
生成的代码:
namespace android {
namespace os {
BpServiceManager::BpServiceManager(const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& _aidl_impl)
: BpInterface<IServiceManager>(_aidl_impl){//_aidl_impl 就是 BpBinder(0) 实例
}
--------------------------------------------------
::android::binder::Status BpServiceManager::addService(const ::std::string& name, const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& service, bool allowIsolated, int32_t dumpPriority) {
::android::Parcel _aidl_data;
_aidl_data.markForBinder(remoteStrong());//0、和 Rpc Binder有关
::android::Parcel _aidl_reply;
::android::status_t _aidl_ret_status = ::android::OK;
::android::binder::Status _aidl_status;
//1、写 interface
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_data.writeInterfaceToken(getInterfaceDescriptor());
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//2、写 name
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_data.writeUtf8AsUtf16(name);
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//3、写 binder 对象
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_data.writeStrongBinder(service);
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//4、写 allowIsolated
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_data.writeBool(allowIsolated);
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//5、写 dumpPriority
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_data.writeInt32(dumpPriority);
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//6、借助 BpBinder(0)#transact 来发起 Binder 通信
_aidl_ret_status = remote()->transact(BnServiceManager::TRANSACTION_addService, _aidl_data, &_aidl_reply, 0);
if (UNLIKELY(_aidl_ret_status == ::android::UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION && IServiceManager::getDefaultImpl())) {
return IServiceManager::getDefaultImpl()->addService(name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority);
}
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
//7、如果有返回值就从这个 parcel 包里读
_aidl_ret_status = _aidl_status.readFromParcel(_aidl_reply);
if (((_aidl_ret_status) != (::android::OK))) {
goto _aidl_error;
}
if (!_aidl_status.isOk()) {
return _aidl_status;
}
_aidl_error:
_aidl_status.setFromStatusT(_aidl_ret_status);
return _aidl_status;
}
AidlServiceManager::asInterface 返回的值为 BpServiceManager 对象。这里安卓10不是使用aidl,这里看安卓10的代码:
IServiceManager.cpp - OpenGrok cross reference for /frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
安卓10 的defaultmanager 函数定义为如下:
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != nullptr) return gDefaultServiceManager;
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
while (gDefaultServiceManager == nullptr) {
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(nullptr));
if (gDefaultServiceManager == nullptr)
sleep(1);
}
}
return gDefaultServiceManager;
}interface_cast<IServiceManager> 的值为如下:返回的置为:IServiceManager::asInterface
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
}IServiceManager::asInterface 会在下列去定义:【在编译过程中的预处理中会将宏定义展开,相当于是接口,分别在头文件和实现cpp自动定义和实现方法】
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IServiceManager.h
class IServiceManager : public IInterface
{
public:
// 在头文件中定义了函数
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager)
。。。。
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
// 定义了变量:descriptor,asInterface方法
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \
public: \
static const ::android::String16 descriptor; \
static ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> asInterface( \
const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& obj); \
virtual const ::android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
I##INTERFACE(); \
virtual ~I##INTERFACE(); \
static bool setDefaultImpl(std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> impl); \
static const std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE>& getDefaultImpl(); \
private: \
static std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> default_impl; \
public: 具体的实现在如下:
/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
#define LOG_TAG "ServiceManager"
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
// 实现方法的宏定义
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager");
}; // namespace android
// 具体实现:(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager")
// name为:"android.os.IServiceManager",INTERFACE 为 ServiceManager
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \
// 设置 descriptor变量为:"android.os.IServiceManager"
const ::android::String16 I##INTERFACE::descriptor(NAME); \
const ::android::String16& \
I##INTERFACE::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
return I##INTERFACE::descriptor; \
} \
// asInterface 方法实现:
::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \
const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& obj) \
{ \
::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> intr; \
if (obj != nullptr) { \
intr = static_cast<I##INTERFACE*>( \
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
I##INTERFACE::descriptor).get()); \
if (intr == nullptr) { \
// 创建BpServiceManager 对象,obj就是 new BpBinder(0)
intr = new Bp##INTERFACE(obj); \
} \
} \
return intr; \
} \
std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::default_impl; \
bool I##INTERFACE::setDefaultImpl(std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> impl)\
{ \
if (!I##INTERFACE::default_impl && impl) { \
I##INTERFACE::default_impl = std::move(impl); \
return true; \
} \
return false; \
} \
const std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE>& I##INTERFACE::getDefaultImpl() \
{ \
return I##INTERFACE::default_impl; \
} \
I##INTERFACE::I##INTERFACE() { } \
I##INTERFACE::~I##INTERFACE() { } \
综上:interface_cast<AidlServiceManager> 为 asInterface 方法实现,返回的为对象sm 的值:为:new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0))
BpServiceManager是让客户端去调用的,在安卓10 的 IServiceManager 中有其他方法:
class BpServiceManager : public BpInterface<IServiceManager>
{
public:
explicit BpServiceManager(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl)
{
}
virtual sp<IBinder> getService(const String16& name) const
{
sp<IBinder> svc = checkService(name);
if (svc != nullptr) return svc;
const bool isVendorService =
strcmp(ProcessState::self()->getDriverName().c_str(), "/dev/vndbinder") == 0;
const long timeout = uptimeMillis() + 5000;
if (!gSystemBootCompleted && !isVendorService) {
// Vendor code can't access system properties
char bootCompleted[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("sys.boot_completed", bootCompleted, "0");
gSystemBootCompleted = strcmp(bootCompleted, "1") == 0 ? true : false;
}
// retry interval in millisecond; note that vendor services stay at 100ms
const long sleepTime = gSystemBootCompleted ? 1000 : 100;
int n = 0;
while (uptimeMillis() < timeout) {
n++;
ALOGI("Waiting for service '%s' on '%s'...", String8(name).string(),
ProcessState::self()->getDriverName().c_str());
usleep(1000*sleepTime);
sp<IBinder> svc = checkService(name);
if (svc != nullptr) return svc;
}
ALOGW("Service %s didn't start. Returning NULL", String8(name).string());
return nullptr;
}
virtual sp<IBinder> checkService( const String16& name) const
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeString16(name);
remote()->transact(CHECK_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
return reply.readStrongBinder();
}
virtual status_t addService(const String16& name, const sp<IBinder>& service,
bool allowIsolated, int dumpsysPriority) {
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeString16(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
data.writeInt32(allowIsolated ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt32(dumpsysPriority);
status_t err = remote()->transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode() : err;
}
virtual Vector<String16> listServices(int dumpsysPriority) {
Vector<String16> res;
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeInt32(n++);
data.writeInt32(dumpsysPriority);
status_t err = remote()->transact(LIST_SERVICES_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
if (err != NO_ERROR)
break;
res.add(reply.readString16());
}
return res;
}
};
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager");

![[POJ - 1015]Jury Compromise(01背包问题)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3b941abd187949c7ab8a76a3748da066.png)