1.什么是真正的传输线?(What is a real transmission line?)
答:真正的传输线由任意两条延长一定长度的导体组成。将一根导线标记为信号路径,将另一根导线标记为返回路径。
A real transmission line is composed of any two conductors with some extended length. One
conductor you label as the signal path and the other conductor as the return path.
2.理想的传输线模型与理想的 R、L 或 C 模型有何不同?(How is an ideal transmission line model different from an ideal R, L, or C model?)
答:在低频下,理想的传输线输入阻抗与简单 L 或 C 元件的阻抗匹配,具体取决于远端是开路还是短路。但是,在超出某个频率的频率下,L 或 C 模型的行为会大大偏离理想的传输线。
这意味着 L 或 C 元件可以很好地近似于低频下的理想传输线模型。但在高频下很难和理想传输线模型近似。理想的传输线模型是一种全新的电路元件,其特性与单个 L 或 C 元件完全不同,这在非常高的频率下会变得很明显。
At low frequency, the ideal transmission line input impedance matches the impedance of a simple L or C element depending on if the far end is open or shorted. But, at frequencies beyond some frequency, the behaviors of the L or C model drastically departs from the ideal transmission line.
This means the L or C elements are good approximations to an ideal transmission line model at low frequency. They are terrible approximations to an ideal transmission line at higher frequency. An ideal transmission line model is a brand-new circuit element with properties that are completely different from a single L or C element, which becomes apparent at very high frequency.
3.什么是GND?为什么它对于信号完整性应用来说是一个令人困惑的词?(What is ground? Why is it a confusing word for signal-integrity applications?)
答:术语“接地”仅应用于指代所有其他电压都参考的电路中的单个参考点。接地点不应承载任何电流。在有电流流动的平面上,并非平面上标记为地的所有点都具有相同的电压。这使得难以将地平面用作参考平面。接地一词在业界经常被误用,并与返回路径相混淆。返回路径是承载返回电流的导体。它可以是任何直流电压,并且通常从一个区域到另一个区域具有不同的电压。
The term ground should only be used to refer to the single reference point in a circuit from which all other voltages are referenced. The ground point should not carry any current.
On a plane with current flowing, not all points on the plane labeled as ground are the same voltage. This makes it difficult to use a ground plane as a reference enplane.
The term ground is often misused in the industry and confused with return path. The return path is the conductor that carries the return current. It can be at any DC voltage, and often has a different voltage across it form one region to another.
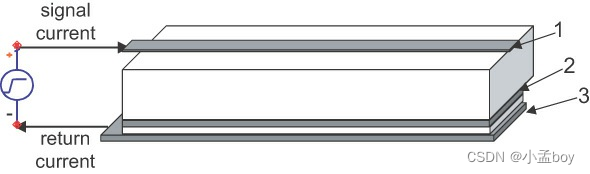
4.底盘和地球有什么区别?(What is the difference between chassis and earth ground?)
答:接地,通常被称为安全接地,实际上是与地面的连接。在所有标记为接地的点与附近插入地面的铜管之间都有一条低电阻路径。该管道定义了一个连接到地球的公共参照点,其他点可以作为参照。只要所有的点都连接到同一个接地,它们将处于相同的电压,并且某一点受到电击的可能性较小。
机箱接地是与仪器或设备的外部金属外壳的连接。在塑料外壳的情况下,没有底盘接地。出于安全原因,UL 要求将底盘接地连接到大地。这降低了用户因机箱接地电压差异很大而受到电击的风险。
Earth ground, often referred to as safety ground, is literally a connection to the ground. There is a lowresistance path between all points labeled as earth ground to a copper pipe sticking into the ground somewhere nearby. This pipe defines a common reference point tied to the Earth from which other points can be references. As long as all points connect to the same earth ground, they will be at the same voltage and there is less chance of someone getting a shock.
Chassis ground is the connection to the external metal housing of an instrument or device. In the case of a plastic enclosure, there is no chassis ground. For safety reasons, the UL requires that chassis ground be connected to earth ground. This reduces the risk of a user getting a shock due to widely different chassis ground voltages.
5.线上的电压和线上的信号有什么区别?(What is the difference between the voltage on a line and the signal on a line?)
如果探头在信号和返回路径上的相邻点之间接触,则传输线上的电压将由示波器测量。这是一个标量电压,因为无法测量该电压的传播特性。它只是信号和返回路径之间的总电压。
信号是沿着线路传播的电压。它有一个与之相关的方向。当测量信号的电压时,其幅度可以与信号的幅度相同,但没有测量到关于信号传播方向的信息。
当传输线上有多个信号传播时,就会出现真正的区别。两个信号可能在传输线上以相反的方向传播。在一点测量时,测得的电压是两个电压之和。它可能小于、大于或等于两个信号电压,具体取决于它们的特定属性。
The voltage on a transmission line is what would be measured by a scope if the probes were touching between the signal and an adjacent point on the return path. This is a scalar voltage in the sense there is no measure of the propagating nature of this voltage. It is just the total voltage between the signal and return path.
The signal is the voltage that is propagating down the line. It has a direction associated with it. When the voltage of a signal is measured, the magnitude can be the same as the magnitude of the signal, but there is no information measured about the direction of propagation of the signal.
The real difference arises when there are multiple signals propagating on the transmission line. Two signals may be propagating in opposite directions on the transmission line. When measured at one point, the voltage measured is the sum of the two voltages. It could be less than, greater than, or the same as the two signal voltages, depending on their specific properties.
6.什么是均匀传输线,为什么这是首选的互连设计?(What is a uniform transmission line and why is this the preferred interconnect design?)
均匀的传输线意味着传输线的横截面在传输线的长度上下是相同的。这意味着线路的瞬时阻抗是相同的。设计信号视为瞬时阻抗
上下线路相同意味着信号将在没有反射和失真的情况下传播,从而提高信号质量。
如果传输线不均匀,就会出现阻抗变化,导致反射和信号失真。
A uniform transmission line means the cross section of the transmission line is the same up and down the length of the line. This means the instantaneous impedance of the line is the same. Engineering the instantaneous impedance the signal sees as the
same up and down the line means the signal will propagate with no reflections and no distortions, improving the signal quality.
If the transmission line is not uniform, there will be impedance changes that will cause reflections and signal distortions.
7.电子在导线中的传播速度有多快?(How fast do electrons travel in a wire?)
令人惊讶的是,即使在窄导线中有多达1A的电流,电子的速度也非常小,大约为1cm/sec。这意味着信号不是电子的运动,而是不断变化的电场和磁场的传播。
这就像一个装满弹珠的管子。如果你把一个弹珠往一端推,另一个弹子会在压力波在弹珠之间向下流动所需的时间内把另一端推出。弹珠沿着管道向下移动的速度很慢,但弹珠运动的冲击速度很快。
Surprisingly, even with as much as 1 A of current in a narrow wire, the speed of the electrons is really small, on the order of 1 cm/sec. This means that it is not the motion of the electrons which is the signal, but the propagating of the changing electric and magnetic fields.
It is like the case of a tube filled with marbles. If you push one marble in one end, another will push out the far end in the time it takes for the pressure wave to flow down between the marbles. The speed of the marble moving down the tube is slow, but the speed of the impact of the motion of the marble is very fast.
8.传导电流、极化电流和位移电流之间的区别是什么?(What is the difference between conduction current, polarization current, and displacement current?)
传导电流是导体中自由电荷的流动。在施加直流电压的情况下可以有直流电流流动。
极化电流是当束缚电荷的极化发生变化时在绝缘体中流动的电流。这实际上是一种电荷运动,但它们仅限于附着在电介质分子上。它们只会在材料的极化发生变化时流动,也就是外部电场发生变化时。这些电流是瞬态的,与 dE/dt 成正比。
位移电流是当电场发生变化时在空气中流动的电流。麦克斯韦将位移电流称为由于以太中电荷的极化变化而流动的电流。今天,你不必调用以太,而是将位移电流描述为电场变化时流动的电流,作为时空结构中电场的一个特征。
Conduction current is the flow of free charges in a conductor. There can be DC current flow with a DC voltage applied.
Polarization current is the current that flows in an insulator when the polarization of bound charges changes. This is literally a motion of charges, but they are restricted to staying attached to the molecules of the dielectric. They will only flow when the polarization of the material changes, which is when the extern E field changes. These currents are transient and are proportional to dE/dt.
Displacement current is the current that flows in the air when the electric field changes. Maxwell called the displacement current the current that flows due to the changing polarization of the charges in the ether. Today, you do not have to invoke the ether, but describe displacement current, as a current that flows when the electric field changes, as a feature of electric fields built into the fabric of space time.
9.什么是互连信号速度的良好经验法则?(What is a good rule of thumb for the speed of a signal on an interconnect?)
在空气中,信号的速度或光速为 12 英寸/纳秒。当通过介电常数为 Dk 的电介质传播时,变化的电场(即光)的速度随着 Dk 的平方根而减慢。
大多数互连材料的典型 Dk 约为 4。这意味着典型层压互连基板上的信号速度约为 12/sqrt(4) = 6 英寸/纳秒。
这是互连信号速度的一个很好的经验法则,大约 6 英寸/纳秒。
In air, the speed of a signal, or the speed of light, is 12 inches/nsec. When propagating through a dielectric with dielectric constant Dk, the speed of the changing electric field, which is light, slows down with the square root of the Dk.
The typical Dk for most interconnect materials is about 4. This means the speed of a signal on a typical laminate interconnect substrate is about 12/sqrt(4) = 6 inches/nsec.
This is a good rule of thumb for the speed of a signal on an interconnect, about 6 inches/nsec.
10.对于 50 欧姆微带线的纵横比,什么是好的经验法则?(What is a good rule of thumb for the aspect ratio of a 50-Ohm microstrip?)
对于 FR4 基板,50 欧姆传输线的线宽与电介质厚度之比为 2/1。
With an FR4 substrate, the ratio of the line width to dielectric thickness of a 50-Ohm transmission line is 2/1.