<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>从面向dom编程到面向数据编程
输入显示列表
const app=Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods:{
handleAddItem(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue='';
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue" />
<button
v-on:click="handleAddItem"
v-bind:title="inputValue">
增加
</button>
<ul>
<todo-item v-for="(item,index) of list" v-bind:content="item" v-bind:index="index"/>
<ul>
</div>
`
});
app.component('todo-item',{
props:['content','index'],
template:'<li>{{index}}--{{content}}</li>'
});
app.mount('#root');
反转字符串
Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
str:'hello world'
}
},
methods:{
handleReverse(){
this.str=this.str.split('').reverse().join('');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{str}}
<button v-on:click="handleReverse">反转字符串</button>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');createApp表示创建一个Vue应用,存储到app变量中
传入的参数表示,这个应用最外层的组件,应该如何展示
MVVM设计模式,M->Model 数据,V->View 视图,VM-> ViewModel视图数据连接
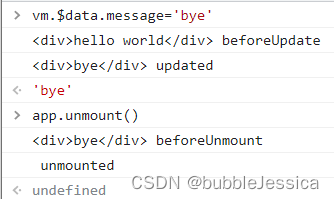
生命周期函数(8个)
// 生命周期函数 在某一时刻自动执行的函数
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: 'hello world'
}
},
beforeCreate(){
// 在实例生成之前自动执行的函数
console.log('beforeCreate');
},
created(){
// 在实例生成之后自动执行的函数
console.log('created');
},
beforeMount(){
// 在组件内容被渲染到页面之前自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeMounted');
},
mounted(){
// 在组件内容被渲染到页面之后自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'mounted');
},
beforeUpdate(){
// 在data中数据发生变化时,自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeUpdate');
},
updated(){
// 在data中数据发生变化时,且重新渲染页面后,自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'updated');
},
beforeUnmount(){
// 当Vue应用(实例)失效时,自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'beforeUnmount');
},
unmounted(){
// 当Vue应用(实例)失效时,且DOM完全销毁之后,自动执行的函数
console.log(document.getElementById('root').innerHTML,'unmounted');
},
template: `<div>{{message}}</div>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');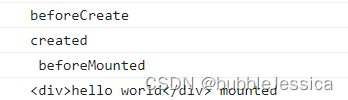
插值表达式{{}}
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: '<strong>hello world</strong>'
}
},
template: `<div>{{message}}</div>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]() 结果却显示包含html标签的变量,这时想要显示加粗的变量,我们需要在模板里加上v-html指令即可
结果却显示包含html标签的变量,这时想要显示加粗的变量,我们需要在模板里加上v-html指令即可
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: '<strong>hello world</strong>'
}
},
template: `<div v-html="message"></div>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root'); ![]()
添加title属性需要添加v-bind指令,此时页面上鼠标悬停在hello world时会出现hello world标题
v-bind:title简写成:title
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: 'hello world'
}
},
template: `<div v-bind:title="message">hello world</div>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');v-bind我们还可以结合输入框使用
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
disable:false
}
},
template: `<input v-bind:disabled="disable"/>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]()
注意:模板可以使用v-once指令使变量只渲染第一次时的值,之后修改变量的值不会跟随变化
事件绑定v-on:click() 简写@click
结合动态属性:[变量]
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:'hello world',
name:'title',
event:'click'
}
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
alert('click');
}
},
template: `<div :[name]="message" @[event]="handleClick">{{message}}</div>`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');阻止默认行为@click.prevent="handleClick"
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:'hello world'
}
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
alert('click');
//e.preventDefault();
}
},
template:
`
<form action="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="handleClick">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');computed计算属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:'hello world'
}
},
computed:{
// 当计算属性依赖的内容发生变化时,方法才会重新执行计算
total(){
return Date.now();
}
},
methods:{
// 只要页面重新渲染,方法就会执行
formatString(string){
return string.toUpperCase();
},
getTotal(){
return Date.now();
}
},
template:
`
<div>{{formatString(message)}} {{total}}</div>
<div>{{formatString(message)}} {{getTotal()}}</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');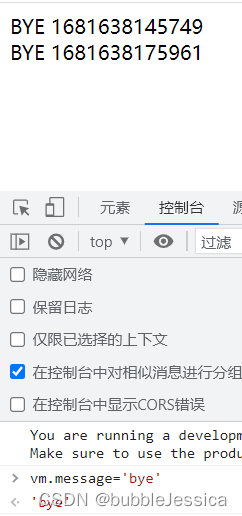
侦听器watch(通常异步操作使用)(监听对应属性)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:'hello world',
count:2,
price:5,
newTotal:10
}
},
// 监听器
watch:{
// 当价格发生变化才会执行的函数
price(current,prev){
this.newTotal= current*this.count;
}
},
computed:{
// 当计算属性依赖的内容发生变化时,方法才会重新执行计算 建议使用因为有缓存、简洁
total(){
return this.price*this.count;
}
},
methods:{
// 只要页面重新渲染,方法就会执行
formatString(string){
return string.toUpperCase();
},
getTotal(){
return this.price*this.count;
}
},
template:
`
<div>{{formatString(message)}} {{total}}</div>
<div>{{formatString(message)}} {{getTotal()}}</div>
<div>{{formatString(message)}} {{newTotal}}</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');改变字符串样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 5</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<style>
.red{
color: red;
}
.green{
color: green;
}
.blue{
color: blue;
}
.brown{
color: brown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 改变样式
// 1字符串/2对象/3数组
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
classString:'green',
classObject:{
'red':true,
'green':true,
'blue':true
},
classArray:['red','blue','green',{brown:true}]
}
},
template:
`
<div :class="classString">Hello World</div>
<div :class="classArray">Hello World</div>
<div :class="classObject">Hello World</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
父元素包括多个子元素注意:$attrs.class使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 5</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<style>
.red{
color: red;
}
.green{
color: green;
}
.blue{
color: blue;
}
.brown{
color: brown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 改变样式
// 1字符串/2对象/3数组
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
classString:'red',
classObject:{
'red':true,
'green':true,
'blue':true
},
classArray:['red','blue','green',{brown:false}]
}
},
template:
`
<div :class="classString">
Hello World
<demo class="green" />
</div>
`
});
app.component('demo',{
template:
`
<div :class="$attrs.class">one</div>
<div>two</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
行内样式使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 5</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<style>
.red{
color: red;
}
.green{
color: green;
}
.blue{
color: blue;
}
.brown{
color: brown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 改变样式
// 1字符串/2对象/3数组
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
classString:'red',
classObject:{
'red':true,
'green':true,
'blue':true
},
classArray:['red','blue','green',{brown:false}],
styleString:'color:yellow;background:orange',
// 行内样式我们使用对象存储可读性更高
styleObject:{
color:'orange',
background:'purple'
}
}
},
template:
`
<div :style="styleObject">
Hello World
</div>
`
});
app.component('demo',{
template:
`
<div :class="$attrs.class">one</div>
<div>two</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
v-if和v-show区别
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
show:false
}
},
template:
`
<div v-if="show">Hello World</div>
<div v-show="show">Bye World</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');
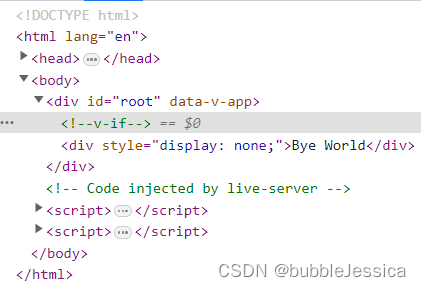
频繁需要修改元素的话我们建议使用v-show,因为不会把元素销毁掉
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
conditionOne:false,
conditionTwo:true
}
},
template:
`
<div v-if="conditionOne">if</div>
<div v-else-if="conditionTwo">else if</div>
<div v-else>else</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');v-for用法
数组和对象使用 注意:v-for优先级比v-if优先级高,所以如果要判断的话需要嵌套标签但是我们发现此时多了个div标签,这里我们使用小技巧将外面的div标签替换为template标签相当于占位符
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
listArray:['dell','lee','teacher'],
listObject:{
firstName:'dell',
lastName:'lee',
job:'teacher'
}
}
},
methods:{
handleAddBtnClick(){
// 1使用数组的变更函数
//this.listArray.push('hello');结尾增加
//this.listArray.pop();结尾删除
//this.listArray.shift();开头删除
//this.listArray.unshift('hello');//开头增加
// this.listArray.reverse();
// 2直接替换数组
// this.listArray=['bye','world'];
// this.listArray=['bye','world'].filter(item=>item==='bye');
// 3更新数组内容
// this.listArray[1]='bye';
this.listObject.age=100;
this.listObject.sex='male';
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<template v-for="(value,key,index) in listObject" :key="index">
<div v-if="key!=='lastName'">
{{value}}--{{key}}--{{index}}
</div>
</template>
<div v-for="item in 10">{{item}}</div>
<button @click="handleAddBtnClick">新增</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');事件
当调用多个函数的时候,我们不能像以前一样直接写引用名,而是需要再加上()逗号分开才生效
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(num,event){
console.log(event.target);
this.counter+=num;
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{counter}}
<button @click="handleBtnClick(2,$event)">新增</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]()
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(){
alert('1');
},
handleBtnClick1(){
alert('2');
},
},
template:
`
<div>
{{counter}}
<button @click="handleBtnClick(),handleBtnClick1()">新增</button>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');阻止冒泡(向外传播)@click.stop
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(){
this.counter+=1;
},
handleDivClick(){
alert('div click');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{counter}}
<div @click="handleDivClick">
<button @click.stop="handleBtnClick">新增</button>
</div>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');点击自己标签才显示@click.self
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick(){
this.counter+=1;
},
handleDivClick(){
alert('div click');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<div @click.self="handleDivClick">
{{counter}}
<button @click="handleBtnClick">新增</button>
</div>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');事件修饰符:注意标签@click.prevent阻止默认行为发生、@click.capture捕获阶段(从外到内)默认是冒泡阶段(从内到外) 、@click.once只能点击一次
按键和鼠标修饰符
按键:enter,tab,delete,esc,up,down,left,right
鼠标:left,right,middle
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleKeyDown(){
console.log('keydown');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<input @keydown.delete="handleKeyDown"/>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
counter: 0
}
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
console.log('click');
}
},
template:
`
<div>
<div @click="handleClick">123</div>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');双向绑定
复选框checkbox和单选框radio
// input,textarea,checkbox,radio
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:[]
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{message}}
jack <input type="checkbox" value="jack" v-model="message"/>
jessica <input type="checkbox" value="jessica" v-model="message"/>
karry <input type="checkbox" value="karry" v-model="message"/>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]()
// input,textarea,checkbox,radio
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:''
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{message}}
jack <input type="radio" value="jack" v-model="message"/>
jessica <input type="radio" value="jessica" v-model="message"/>
karry <input type="radio" value="karry" v-model="message"/>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]()
列表框
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:[],
options:[{
text:'A',value:{value:'A'}
},{
text:'B',value:{value:'B'}
},{
text:'C',value:{value:'C'}
}]
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{message}}
<select v-model="message" multiple>
<option v-for="item in options" :value="item.value">{{item.text}}</option>
</select>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');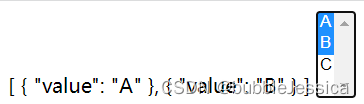
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return{
message:'world',
}
},
template:
`
<div>
{{message}}
<input type="checkbox" v-model="message" true-value="hello" false-value="world"/>
</div>
`
});
const vm=app.mount('#root');![]() world表示没选上的值
world表示没选上的值
注意:v-model.lazy等鼠标移开输入框点击外面一下才会双向绑定 v-model-trim去除字符串首尾空格



![P1829 [国家集训队]Crash的数字表格 / JZPTAB(莫比乌斯反演)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/edc05df29b3e42a4ab72b343557d8209.png)