文章目录
- 6.日期类的实现
- 构造函数
- 赋值运算符 “=”
- 前置++、后置++
- 日期 - 日期
- 日期类实现—代码汇总
- 流插入
- 流提取
- 7.const成员
- const 与 权限放大
- 8.取地址及const取地址操作符重载
6.日期类的实现
#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d);
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 析构函数
~Date();
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d);
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d);
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d);
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d);
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d);
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d);
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
构造函数
- 需要检查一下日期是否非法
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (day > GetMonthDay(year, month) || day < 0
|| month < 0 || month > 12)//检查日期
{
cout << "日期非法" << endl;
}
else
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
}
赋值运算符 “=”
- 支持连续赋值,需要有返回值
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (*this == d)//如果时自己给自己赋值就不用进行下列操作了,直接返回即可
return *this;
_day = d._day;
_month = d._month;
_year = d._year;
return *this;
}
前置++、后置++
- 默认前置++
Date& operator++() - 对于后置++:编译器加了一个参数,构成函数重载
Date operator++(int),这里只能是int,这是一个规定
调用前置++和后置++实际上:
Date d1(2023,4,1); ++d1; 👉 d1.operator++(); d1++; 👉 d1.operator++(0);//编译器处理
这两个函数实现是 复用 了其他的操作符重载函数:
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);//调用拷贝构造
*this += 1;
return tmp;//调用拷贝构造,实际上返回的是tmp的一份临时拷贝
}
ps.自定义类型,建议尽量选择用前置++/ - -,效率更高
日期 - 日期
在不考虑的效率的情况下,采用计数的方式计算两个日期之间相差的天数。
计数:让小(早)日期不断++,直到等于大(晚)日期,加了多少次,就相隔多少天,注意:this指针指向左操作数
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int count = 0;
while (max != min)
{
++min;
++count;
}
return count * flag;
}
日期类实现—代码汇总
#include "Date.h"
// 获取某年某月的天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int array[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2)
{
if ((year % 400 == 0) || ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)))
{
++array[2];
}
return array[2];
}
else
{
return array[month];
}
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (day > GetMonthDay(year, month) || day < 0
|| month < 0 || month > 12)
{
cout << "日期非法" << endl;
}
else
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{
_day = d._day;
_month = d._month;
_year = d._year;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (*this == d)
return *this;
_day = d._day;
_month = d._month;
_year = d._year;
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
Date::~Date()
{
_day = _month = _day = 0;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
return *this -= (-1 * day);
_day += day;
int MonthDay = GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
while (_day > MonthDay)
{
_day -= MonthDay;
++_month;
if (_month > 12)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
MonthDay = GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
return tmp += day;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
int MonthDay = GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
while (_day < 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month < 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
MonthDay = GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_day += MonthDay;
}
return *this;
}
// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
return tmp -= day;
}
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year < d._year)
return false;
if (_year > d._year)
return true;
if (_month < d._month)
return false;
if (_month > d._month)
return true;
if (_day < d._day)
return false;
if (_day > d._day)
return true;
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _day == d._day
&& _month == d._month
&& _year == d._year;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int count = 0;
while (max != min)
{
++min;
++count;
}
return count * flag;
}
流插入
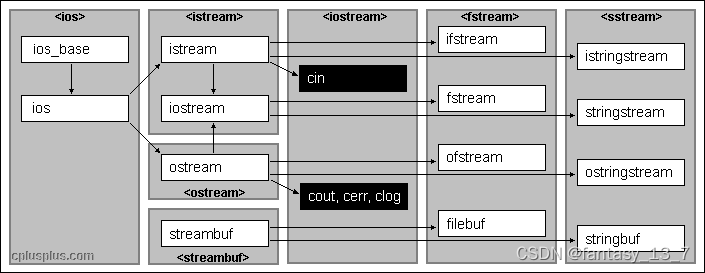
iostream 为 Input/Output Stream 的缩写,即是输入/输出流。「流」是一连串从I/O设备读写的字符。
cout:Object of class ostream (cout是ostream类的对象)
理解为:
class ostream
{
void operator<<()
{……}
}
ostream cout;
所以:
int i = 1;
cout << i;👉cout.operator<<(i);
- cout是如何自动识别类型的?👇函数重载(下图,函数名相同,参数类型不同构成函数重载)

∴ cout 是 运算符重载+函数重载
- 在日期类中实现一个流插入操作符重载:
//函数定义:
void Date::operator<<(ostream& out)
{
out << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
//函数调用
void TestDate8()
{
Date d1(2023, 4, 19);
d1 << cout; 👉 d1.operator<<(cout);
}
int main()
{
TestDate8();
return 0;
}
分析:上述函数定义中的out 只是一个ostream类的实例化对象的“别名”可以随便取。
调用函数的过程中,隐含的参数 this指针传输Date类的对象→d1,作为左操作数 ,ostream类的对象作为 操作符 << 的右操作数
由此,函数调用写作:d1 << cout;
- 这个函数调用的写法很别扭,如何改变?
→不作成员函数,作全局函数- 但是,作全局函数,Date类的成员变量是 private 无法访问
→1. 写 Getyear……成员函数 获取 类的成员变量(Java常用)
→2.友元函数(C++常用)
- 但是,作全局函数,Date类的成员变量是 private 无法访问
在class Date中声明:
class Date
{
public:
//流插入
friend void operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
函数定义:
//流插入
void operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;
}
//函数调用:
cout << d1; 👉 operator<<(cout,d1);
- 另外,<< 可以连续插入:(如下代码)→所以该函数需要有返回值
int i = 0, j = 1;
cout << i << j <<endl;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);//在类中声明
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;
return out;
}
Date d1(2023, 4, 19);
Date d2(2022, 2, 2);
cout << d1 << d2;

- C++ 为什么要用运算符重载输出?👉printf 无法打印自定义类型
流提取
和流插入类似
//流提取
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
7.const成员
const 与 权限放大

将const修饰的“成员函数”称之为const成员函数,const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改。
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
- const对象不可以调用非const成员函数 → “权限放大”
- 非const对象可以调用const成员函数 → “权限缩小”
8.取地址及const取地址操作符重载
class Date
{
public :
Date* operator&()
{
return this ;
}
const Date* operator&()const
{
return this ;
}
private :
int _year ; // 年
int _month ; // 月
int _day ; // 日
};
这两个默认成员函数一般不用重新定义 ,编译器默认会生成。
这两个运算符一般不需要重载,使用编译器生成的默认取地址的重载即可,只有特殊情况,才需
要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容。
END






![[计算机图形学]几何:网格处理(前瞻预习/复习回顾)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d6a5f9c260034cd2a5b8c9c39821107f.png)