一 相关概念
在分布式服务架构下,一个 Web 请求从网关流入,有可能会调用多个服务对请求进行处理,拿到最终结果。在这个过程中每个服务之间的通信又是单独的网络请求,无论请求流经的哪个服务除了故障或者处理过慢都会对前端造成影响。
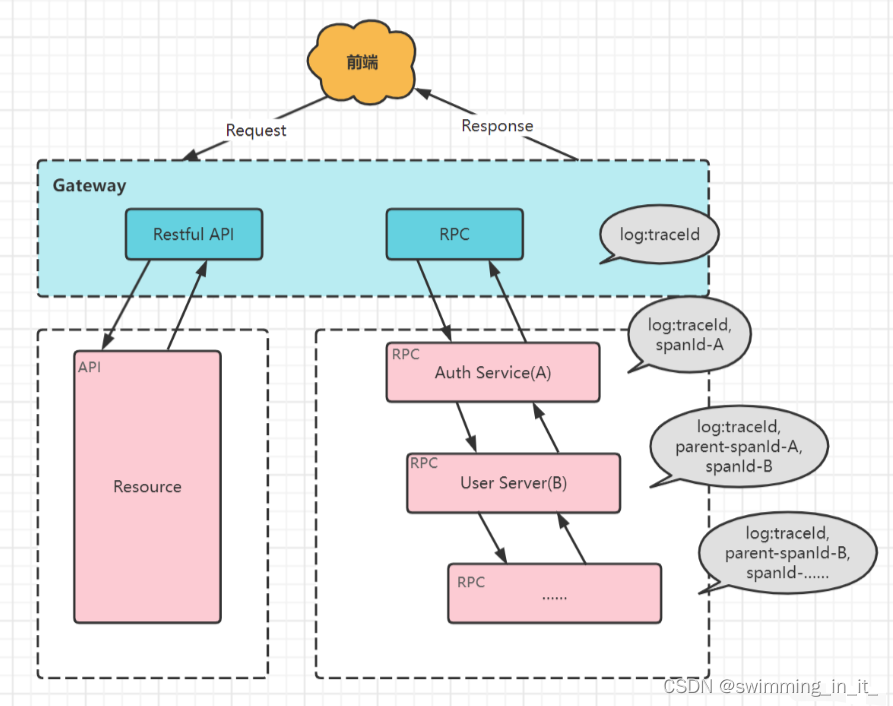
在分布式链路追踪中有两个重要的概念:跟踪(trace)和 跨度(span)。trace 是请求在分布式系统中的整个链路视图,span 则代表整个链路中不同服务内部的视图,span 组合在一起就是整个 trace 的视图。
- traceId:用于标识某一次具体的请求ID。当用户的请求进入系统后,会在RPC调用网络的第一层生成一个全局唯一的traceId,并且会随着每一层的RPC调用,不断往后传递,这样的话通过traceId就可以把一次用户请求在系统中调用的路径串联起来。
- spanId:用于标识某一次RPC调用在分布式请求中的位置。请求到达每个服务后,服务都会为请求生成spanId。
- parent-spanId:用于标识上游RPC调用在分布式请求中的位置。请求到达每个服务后,随请求一起从上游传过来的上游服务的 spanId 会被记录成 parent-spanId,或者叫 pspanId。当前服务生成的 spanId 随着请求一起,在传到下游服务时,这个 spanId 又会被下游服务当作 parent-spanId 记录。
- MDC:(Mapped Diagnostic Context)映射诊断环境,是 log4j 和 logback 提供的一种方便在线多线程条件下记录日志的功能,可以看成是一个与当前线程绑定的 ThreadLocal。
public class MDC {
// 添加 key-value
public static void put(String key, String val) {...}
// 根据 key 获取 value
public static String get(String key) {...}
// 根据 key 删除映射
public static void remove(String key) {...}
// 清空
public static void clear() {...}
}
二 实现方式
2.1 设置TraceId
2.1.1 使用filter过滤器设置traceId
新建一个过滤器,实现Filter,重写init,doFilter,destroy方法,设置traceId放在doFilter中,在destroy中调用MDC.clear()方法。
@Slf4j
@WebFilter(filterName = "traceIdFilter",urlPatterns = "/*")
public class traceIdFilter implements Filter {
/**
* 日志跟踪标识
*/
private static final String TRACE_ID = "TRACE_ID";
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
MDC.put(TRACE_ID, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
filterChain.doFilter(request, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
MDC.clear();
}
}
2.1.2 使用Interceptor拦截器设置traceId
定义一个拦截器,重写preHandle方法,在方法中通过MDC设置traceId
/**
* MDC设置traceId拦截器
*
* @author china
*/
@Component
public abstract class TraceIdInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
private static final String UNIQUE_ID = "TRACE_ID";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) {
MDC.put(UNIQUE_ID, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
MDC.clear();
}
}
2.1.3 使用JWT token过滤器的项目
springboot项目经常使用spring security+jwt来做权限限制,在这种情况下,我们通过新建filter过滤器来设置traceId,那么在验证token这部分的日志就不会带上traceId,因此我们需要把代码放在jwtFilter中。
/**
* token过滤器 验证token有效性
*
* @author china
*/
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
/**
* 日志跟踪标识
*/
private static final String TRACE_ID = "TRACE_ID";
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
MDC.put(TRACE_ID, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(request);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(loginUser) && StringUtils.isNull(SecurityUtils.getAuthentication())) {
tokenService.verifyToken(loginUser);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser, null, loginUser.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
MDC.clear();
}
}
2.2 logback.xml配置traceId
与之前的相比只是添加了[%X{TRACE_ID}], [%X{***}]是一个模板,中间属性名是我们使用MDC put进去的。
#之前
<property name="log.pattern" value="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{20} - [%method,%line] - %msg%n" />
#增加traceId后
<property name="log.pattern" value="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{20} - [%method,%line] - [%X{TRACE_ID}] - %msg%n" />
2.3 扩展
2.3.1 补充异步方法带入上下文的traceId
异步方法会开启一个新线程,我们想要是异步方法和主线程共用同一个traceId,首先先新建一个任务适配器MdcTaskDecorator:
public class MdcTaskDecorator implements TaskDecorator
/**
* 使异步线程池获得主线程的上下文
* @param runnable
* @return
*/
@Override
public Runnable decorate(Runnable runnable) {
Map<String,String> map = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
return () -> {
try{
MDC.setContextMap(map);
runnable.run();
} finally {
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
}
然后,在线程池配置中增加executor.setTaskDecorator(new MdcTaskDecorator())的设置
/**
* 线程池配置
*
* @author china
**/
@EnableAsync
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
private int corePoolSize = 50;
private int maxPoolSize = 200;
private int queueCapacity = 1000;
private int keepAliveSeconds = 300;
@Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
executor.setTaskDecorator(new MdcTaskDecorator());
// 线程池对拒绝任务(无线程可用)的处理策略
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}
最后,在业务代码上使用@Async开启异步方法即可
@Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor")
void testSyncMethod();
2.3.1 在接口放回中,增加traceId返回
在笔者项目中,接口返回都使用了一个叫AjaxResult自定义类来包装,所以只需要把这个类的构造器中增加traceId返回即可,相对简单。
/**
* 日志跟踪标识
*/
private static final String TRACE_ID = "TRACE_ID";
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象,使其表示一个空消息。
*/
public AjaxResult() {
super.put(TRACE_ID, MDC.get(TRACE_ID));
}
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象
*
* @param code 状态码
* @param msg 返回内容
*/
public AjaxResult(int code, String msg) {
super.put(CODE_TAG, code);
super.put(MSG_TAG, msg);
super.put(TRACE_ID, MDC.get(TRACE_ID));
}
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象
*
* @param code 状态码
* @param msg 返回内容
* @param data 数据对象
*/
public AjaxResult(int code, String msg, Object data) {
super.put(CODE_TAG, code);
super.put(MSG_TAG, msg);
super.put(TRACE_ID, MDC.get(TRACE_ID));
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(data)) {
super.put(DATA_TAG, data);
}
}
三 MDC的实现方式
3.1 InheritableThreadLocal
在代码开发中,经常使用 ThreadLocal来保证在同一个线程中共享变量。在 ThreadLocal 中,每个线程都拥有了自己独立的一个变量,线程间不存在共享竞争发生,并且它们也能最大限度的由CPU调度,并发执行。显然这是一种以空间来换取线程安全性的策略。
但是,ThreadLocal有一个问题,就是它只保证在同一个线程间共享变量,也就是说如果这个线程起了一个新线程,那么新线程是不会得到父线程的变量信息的。因此,为了保证子线程可以拥有父线程的某些变量视图,JDK提供了一个数据结构,InheritableThreadLocal。
javadoc 文档对 InheritableThreadLocal 说明:
该类扩展了 ThreadLocal,为子线程提供从父线程那里继承的值:在创建子线程时,子线程会接收所有可继承的线程局部变量的初始值,以获得父线程所具有的值。通常,子线程的值与父线程的值是一致的;但是,通过重写这个类中的 childValue 方法,子线程的值可以作为父线程值的一个任意函数。
当必须将变量(如用户 ID 和 事务 ID)中维护的每线程属性(per-thread-attribute)自动传送给创建的所有子线程时,应尽可能地采用可继承的线程局部变量,而不是采用普通的线程局部变量。
代码对比可以看出两者区别:
- ThreadLocal:
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* Method childValue is visibly defined in subclass
* InheritableThreadLocal, but is internally defined here for the
* sake of providing createInheritedMap factory method without
* needing to subclass the map class in InheritableThreadLocal.
* This technique is preferable to the alternative of embedding
* instanceof tests in methods.
*/
T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
- InheritableThreadLocal
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* Computes the child's initial value for this inheritable thread-local
* variable as a function of the parent's value at the time the child
* thread is created. This method is called from within the parent
* thread before the child is started.
* <p>
* This method merely returns its input argument, and should be overridden
* if a different behavior is desired.
*
* @param parentValue the parent thread's value
* @return the child thread's initial value
*/
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the table.
* @param map the map to store.
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
这个是开发时一般使用的类,直接copy父线程的变量
public class CopyOnInheritThreadLocal extends
InheritableThreadLocal<HashMap<String, String>> {
/**
* Child threads should get a copy of the parent's hashmap.
*/
@Override
protected HashMap<String, String> childValue(
HashMap<String, String> parentValue) {
if (parentValue == null) {
return null;
} else {
return new HashMap<String, String>(parentValue);
}
}
}
为了支持InheritableThreadLocal的父子线程传递变量,JDK在Thread中,定义了ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals 属性。该属性变量在线程初始化的时候,如果父线程的该变量不为null,则会把其值复制到ThreadLocal。
从上面的代码实现,还可以看到,如果我们使用原生的 InheritableThreadLocal类则在子线程中修改变量,可能会影响到父线程的变量值,及其他子线程的值。因此,一般我们推荐没有特殊情况,最好使用CopyOnInheritThreadLocal类,该实现是新建一个map来保持值,而不是直接使用父线程的引用。
参考文档:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33204709/article/details/125358252
https://blog.csdn.net/t194978/article/details/123012783
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37556444/article/details/100142429