题目详情
Given a sequence of K integers { N1, N2, ..., NK }. A continuous subsequence is defined to be { Ni, Ni+1, ..., Nj } where 1≤i≤j≤K. The Maximum Subsequence is the continuous subsequence which has the largest sum of its elements. For example, given sequence { -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 }, its maximum subsequence is { 11, -4, 13 } with the largest sum being 20.
Now you are supposed to find the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies two lines. The first line contains a positive integer K (≤10000). The second line contains K numbers, separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, output in one line the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence. The numbers must be separated by one space, but there must be no extra space at the end of a line. In case that the maximum subsequence is not unique, output the one with the smallest indices i and j (as shown by the sample case). If all the K numbers are negative, then its maximum sum is defined to be 0, and you are supposed to output the first and the last numbers of the whole sequence.
Sample Input:
10
-10 1 2 3 4 -5 -23 3 7 -21
Sample Output:
10 1 4
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
200 ms
内存限制
64 MB
简单翻译:
对于给定数组,不仅要找到最大子序和,还要找到最大子序和对应的开头与结尾的元素,其中如果数组全是负数就返回0与锁哥数组的开头与结尾元素
第一次写错误:
(1)要求的是最大子序和对应的开头与结尾的元素,一开始就返回的是下标
(2)没有看清如果数组全是负数就返回0与锁哥数组的开头与结尾元素
(3)没有考虑好如果数组全是负数与数组里只有负数和0的情况
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
int K;
cin >> K;
int a[K];
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int maxSum = INT_MIN;
int sum = 0;
int end = 0, maxEnd = 0;
int start = 0, maxStart = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
sum += a[i];
end = i;
if(sum < 0) {
sum = 0;
end = start = i + 1;
}
else {
if(maxSum < sum) {
maxSum = sum;
maxEnd = end;
maxStart = start;
}
}
}
if(maxSum == INT_MIN) { //如果maxSum还是INT_MIN,说明数组里全是负数
cout << 0 << ' ';
cout << a[0] << ' ';
cout << a[K - 1] << endl;
}
else {
cout << maxSum << ' ';
cout << a[maxStart] << ' ';
cout<< a[maxEnd] << endl;
}
}题目详情
给定K个整数组成的序列{ N1, N2, ..., NK },“连续子列”被定义为{ Ni, Ni+1, ..., Nj },其中 1≤i≤j≤K。“最大子列和”则被定义为所有连续子列元素的和中最大者。例如给定序列{ -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 },其连续子列{ 11, -4, 13 }有最大的和20。现要求你编写程序,计算给定整数序列的最大子列和。
本题旨在测试各种不同的算法在各种数据情况下的表现。各组测试数据特点如下:
- 数据1:与样例等价,测试基本正确性;
- 数据2:102个随机整数;
- 数据3:103个随机整数;
- 数据4:104个随机整数;
- 数据5:105个随机整数;
输入格式:
输入第1行给出正整数K (≤100000);第2行给出K个整数,其间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中输出最大子列和。如果序列中所有整数皆为负数,则输出0。
输入样例:
6
-2 11 -4 13 -5 -2
输出样例:
20思路一:贪心
时间复杂度O(N)
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
int K;
cin >> K;
int num[K];
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
cin >> num[i];
}
int sum = 0;
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
sum += num[i];
if(sum < 0) {
sum = 0;
}
else {
if(sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
}
}
}
cout << maxSum;
return 0;
}
思路二:递归分治
主要思路:
1. 将序列从中间分为左右两个序列
2. 递归求得两子列的最大和sumLeft与sumRight
3.从中分点向左右扫描找到跨过分界线的最大子列和sumMiddle
4.取最大值
实际操作时递归三部曲:
1.参数与返回值:
参数:num数组,返回当前子列和最大值
2.终止条件:
左右端点重合
3.单层递归逻辑:
单纯左侧与单纯右侧简单,难的是跨中间点
跨中间点其实也用到了贪心的想法,即分成两部分,分别找左[left, middle]与右[middle + 1, right]的最大值,然后加起来就是跨中间点最大值
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int layer = 0;
int Max3(int A, int B, int C) { //这个函数是用来比较左中右里最大值
return A > B ? A > C ? A : C : B > C ? B : C;
/*
A > B ? A > C ? A : C :
这一部分首先判断 A 是否大于 B,如果是,则继续判断 A 是否大于 C,如果是,则返回 A,否则返回 C。
如果 A 不大于 B,则执行下一个部分:
B > C ? B : C
这一部分首先判断 B 是否大于 C,如果是,则返回 B,否则返回 C。
*/
}
int findMaxMiddleSum(vector<int> &num, int left, int right, int middle) { //这个函数是用来找“中”(跨越中间分界点)的最大值
int leftSideSum = 0, leftSideMaxSum = 0;
for(int i = middle; i >= left; i--) {
leftSideSum += num[i];
if(leftSideSum > leftSideMaxSum) {
leftSideMaxSum = leftSideSum;
}
}
int rightSideSum = 0, rightSideMaxSum = 0;
for(int i = middle + 1; i <= right; i++) {
rightSideSum += num[i];
if(rightSideSum > rightSideMaxSum) {
rightSideMaxSum = rightSideSum;
}
}
return leftSideMaxSum + rightSideMaxSum;
}
int recursion(vector<int> &num, int left, int right) {
//递归终止条件
// cout << "left = " << left << endl;
// cout << "right = " << right << endl;
// cout << "layer = " << ++layer << endl;
if(left == right) {
if(num[left] > 0) {
return num[left];
}
else return 0;
}
//单层递归逻辑
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
// cout << "middle = " << middle << endl;
int leftSum = recursion(num, left, middle);
int rightSum = recursion(num, middle + 1, right);
int middleSum = findMaxMiddleSum(num, left, right, middle);
return Max3(leftSum, rightSum, middleSum);
}
int main(void) {
int K;
cin >> K;
vector<int> num(K, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
cin >> num[i];
}
// for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// cout << num[i] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// cout << "-------------------------" << endl;
int maxSum = recursion(num, 0, K - 1);
cout << maxSum;
return 0;
}时间复杂度分析:
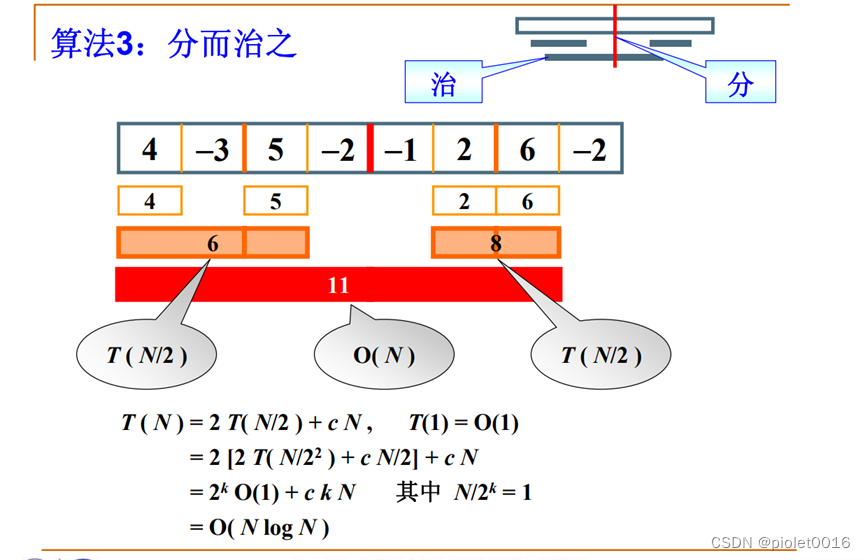
N代表长度
N = 2 ^ k
k = logN
T(N) = N * O(1) + c * O(NlogN)
空间复杂度
递归的空间复杂度=递归深度*每次递归的空间复杂度。每次递归边界变为一半,最后结束递归时N/2^k=1,递归深度k=log2 N,S(N)=O(NlogN)




![[C++]string类的模拟实现和相关函数的详解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/09548998183944cbb11ce6a81246ad60.png#pic_center)