文章目录
- 包装类
- 包装类层次结构
- 基本类型包装类
- 特殊包装类
- 数组
- 一维数组
- 多维数组
- 可变长参数
- 字符串
- String类
- StringBuilder类
- 内部类
- 成员内部类
- 静态内部类
- 局部内部类
- 匿名内部类
- Lambda表达式
- 方法引用
- 异常机制
- 自定义异常
- 抛出异常
- 异常的处理
- 常用工具类
- 数学工具类
- 随机数
- 数组工具类
包装类
包装类层次结构
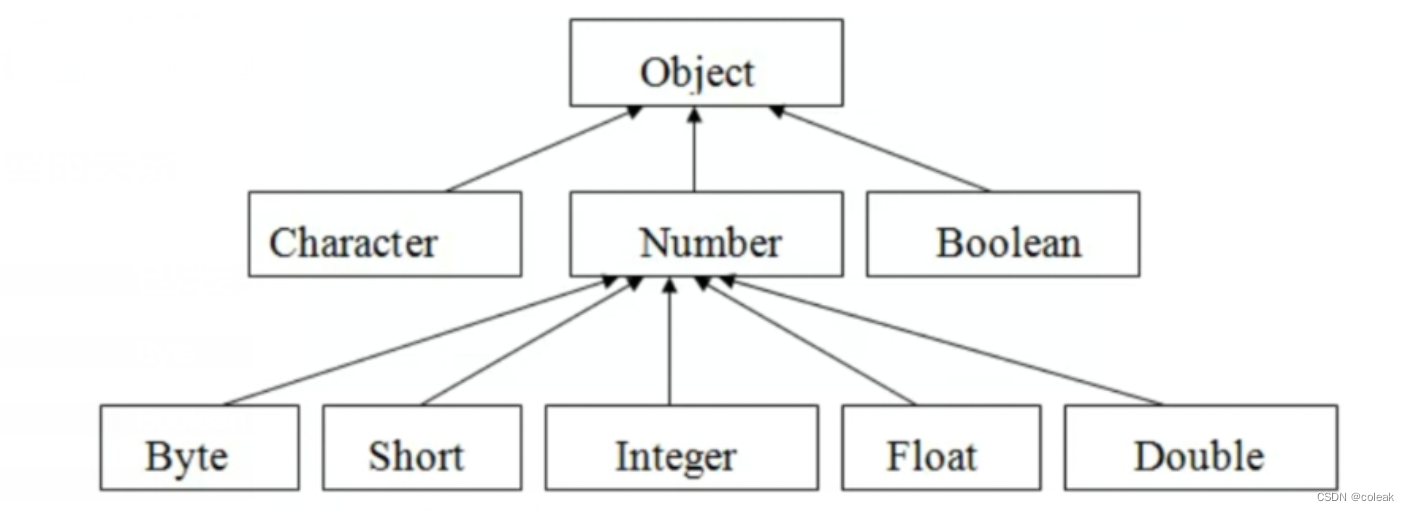
基本类型包装类
package com.test.entity;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = new Integer(10);
Integer b = new Integer(10);
System.out.println(a == b);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 10, b = 10;
System.out.println(a == b);
}
package com.test.entity;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 128, b = 128;
System.out.println(a == b);
}
}
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
//这里会有一个IntegerCache,如果在范围内,那么会直接返回已经提前创建好的对象
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
false
true
false
IntegerCache会默认缓存-128~127之间的所有值,将这些值提前做成包装类放在数组中存放
package com.test.entity;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = Integer.valueOf("5555");
System.out.println(i);
Integer j = Integer.parseInt("5555");
System.out.println(j);
}
}
package com.test.entity;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = Integer.decode("036");
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(166));
}
}
30
a6
特殊包装类
package com.test.entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal i = BigDecimal.valueOf(10);
i = i.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(3), 100, RoundingMode.CEILING);
//计算10/3的结果,精确到小数点后100位
//RoundingMode是舍入模式,就是精确到最后一位时,该怎么处理,这里CEILING表示向上取整
System.out.println(i);
BigInteger j = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.MAX_VALUE);
j = j.pow(100); //来个100次方吧
System.out.println(j);
}
}
数组
一维数组
package com.test.entity;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[]{1,2,43,5};
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//foreach
for (int a:array){
System.out.print(a+" ");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = new String[10];
Object[] array = arr; //引用类型的数组同样支持向上转型
Object[] arr = new Object[10];
String[] array = (String[]) arr; //引用类型数组也支持向下转型
}
多维数组
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] arr = new int[][]{{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{ //要遍历一个二维数组,那么我们得一列一列一行一行地来
for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
可变长参数
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
test("co","le","ak","66");
}
public static void test(String... strings){ //strings这个变量就是一个String[]类型的
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.print(string); //遍历打印数组中每一个元素
}
}
}
字符串
String类
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "Hello World";
String str2 = "Hello World";
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
}
}
直接使用双引号创建的字符串,如果内容相同,为了优化效率,那么始终都是同一个对象
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Hello World");
String str2 = new String("Hello World");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); //字符串的内容比较,一定要用equals
}
}
false
true
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello World";
String[] strings = str.split(" ");
for (String string : strings)
{
System.out.println(string);
}
String sub = str.substring(6, 8); //分割字符串,返回新的子串对象,这里返回67字符
System.out.println(sub);
}
}
Hello
World
Wo
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "Hello World";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
for (char aChar : chars)
{
System.out.println(aChar);
}
char[] chars2 = new char[]{'c', 'o', 'l'};
String str2 = new String(chars2);
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
StringBuilder类
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); //一开始创建时,内部什么都没有
builder.append("AAA"); //我们可以使用append方法来讲字符串拼接到后面
builder.append("BBB");
System.out.println(builder); //当我们字符串编辑完成之后,就可以使用toString转换为字符串了
builder.delete(2, 5); //删除234这个范围内的字符
System.out.println(builder.toString());
}
}
AAABBB
AAB
内部类
成员内部类
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test a = new Test("小明");
Test.Inner inner = a.new Inner(); //依附于a创建的对象,那么就是a的
inner.test("coleak");
}
}
package com.test.entity;
public class Test {
private final String name;
public Test(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public class Inner {
String name;
public void test(String name)
{
System.out.println("方法参数的name = "+name); //就近原则
System.out.println("成员内部类的name = "+this.name); //表示内部类对象
System.out.println("成员内部类的name = "+Test.this.name);
//如果需要指定为外部的对象,那么需要在前面添加外部类型名称
}
}
}
方法参数的name = coleak
成员内部类的name = null
成员内部类的name = 小明
静态内部类
package com.test.entity;
public class Test {
private final String name;
public Test(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public static class Inner {
public void test(){
System.out.println("我是静态内部类!");
}
}
}
package com.test.entity;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test.Inner inner = new Test.Inner();
inner.test();
}
}
仅使用静态内部类时,不会加载外部类,而是直接加载内部类,完成内部静态类的初始化和构造方法
局部内部类
public class Test {
public void hello(){
class Inner{ //局部内部类跟局部变量一样,先声明后使用
public void test(){
System.out.println("我是局部内部类");
}
}
Inner inner = new Inner(); //局部内部类直接使用类名就行
inner.test();
}
}
匿名内部类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Student student = new Student(); //抽象类和接口均无法实例化
// student.test();
}
}
public abstract class Student {
public abstract void test();
protected String a="coleak";
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student() {
int b;
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println("我是匿名内部类的实现!");
}
};
student.test();
}
}
coleak
我是匿名内部类的实现!
Lambda表达式
如果一个接口中有且只有一个待实现的抽象方法,那么我们可以将匿名内部类简写为Lambda表达式
package com.test.entity;
public interface Study {
String stu(String str);
static int num=10;
}
import com.test.entity.Study;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Study study = (a) ->
{
System.out.println(Study.num);
return "我是学习方法!"+" "+a;
};
System.out.println(study.stu("coleak"));
}
}
10
我是学习方法! coleak
方法引用
package com.test.entity;
public interface Study {
int sum(int a, int b);
}
import com.test.entity.Study;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Study study = (a, b) -> a + b;
Study study = (a, b) -> Integer.sum(a, b); //直接使用Integer提供求和方法
System.out.println(study.sum(10, 20));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Study study = Integer::sum; //双冒号来进行方法引用,静态方法使用 类名::方法名 的形式
System.out.println(study.sum(10, 20));
}
public static int sum(int a, int b) { return a + b; } public static void main(String[] args){ Main main = new Main(); Study study = String::new; }
异常机制
自定义异常
异常两大类,编译时异常,运行时异常
抛出异常
当别人调用我们的方法时,如果传入了错误的参数导致程序无法正常运行,这时我们就可以手动抛出一个异常来终止程序继续运行下去,同时告知上一级方法执行出现了问题。
我们在重写方法时,如果父类中的方法表明了会抛出某个异常,只要重写的内容中不会抛出对应的异常我们可以直接省去:
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(test(30,4));
System.out.println(test(30,0));
System.out.println("coleak");
}
public static int test(int a, int b) throws Exception{
if(b == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("被除数不能为0"); //使用throw关键字来抛出异常
return a / b;
}
}
异常的处理
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try { //使用try-catch语句进行异常捕获
Object object = null;
object.toString();
} catch (NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace(); //打印栈追踪信息
System.out.println("异常错误信息:"+e.getMessage()); //获取异常的错误信息
}
System.out.println("程序继续正常运行!");
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
test(10); //必须要进行异常的捕获,否则报错
}
private static void test(int a) throws IOException { //明确会抛出IOException
throw new IOException();
}
}
如果已经是主方法了,那么就相当于到顶层了,此时发生异常再往上抛出的话,就会直接交给JVM进行处理,默认会让整个程序终止并打印栈追踪信息。
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
int[] arr = new int[1];
arr[1] = 100; //这里发生的是数组越界异常,它是运行时异常的子类
} catch (RuntimeException e){ //使用运行时异常同样可以捕获到
System.out.println("捕获到异常");
}
}
}
如果我们要捕获的异常,是某个异常的父类,那么当发生这个异常时,同样可以捕获到
try {
//....
}
catch (NullPointerException e){}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e){}
catch (RuntimeException e){}
try {
//....
} catch (NullPointerException | IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //用|隔开每种类型即可
}
当代码可能出现多种类型的异常时,我们希望能够分不同情况处理不同类型的异常,就可以使用多重异常捕获
try {
//....
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
System.out.println("lbwnb"); //无论是否出现异常,都会在最后执行
}
无论是否出现异常,都会在最后执行任务,可以交给
finally语句块来处理
try语句块至少要配合catch或finally中的一个
常用工具类
数学工具类
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Math也是java.lang包下的类,所以说默认就可以直接使用
System.out.println(Math.pow(5, 3.5)); //我们可以使用pow方法直接计算a的b次方
Math.abs(-1); //abs方法可以求绝对值
Math.max(19, 20); //快速取最大值
Math.min(2, 4); //快速取最小值
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9)); //求一个数的算术平方根
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Math.sin(Math.PI / 2); //求π/2的正弦值,这里我们可以使用预置的PI进行计算
Math.cos(Math.PI); //求π的余弦值
Math.tan(Math.PI / 4); //求π/4的正切值
System.out.println(Math.asin(1)); //求arcsin1的值
Math.acos(1);
Math.atan(0);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Math.log(Math.E); //e为底的对数函数,其实就是ln,我们可以直接使用Math中定义好的e
Math.log10(100); //10为底的对数函数
//利用换底公式,我们可以弄出来任何我们想求的对数函数
double a = Math.log(4) / Math.log(2); //这里是求以2为底4的对数,log(2)4 = ln4 / ln2
System.out.println(a);
}
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.log(Math.E)); //e为底的对数函数,其实就是ln,我们可以直接使用Math中定义好的e
System.out.println(Math.log10(100)); //10为底的对数函数
//利用换底公式,我们可以弄出来任何我们想求的对数函数
double a = Math.log(4) / Math.log(2); //这里是求以2为底4的对数,log(2)4 = ln4 / ln2
System.out.println(a);
}
}
1.0
2.0
2.0
随机数
import java.util.Random;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random(); //创建Random对象
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
System.out.print(random.nextInt(100)+" ");
//nextInt方法可以指定创建0 - x之内的随机数
}
}
}
数组工具类
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 4, 5, 8, 2, 0, 9, 7, 3, 6};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
Arrays.sort(arr); //可以对数组进行排序,将所有的元素按照从小到大的顺序排放
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
int[] arr2 = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(arr2, 66);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
int[] target = Arrays.copyOf(arr, 10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(target)); //拷贝数组的全部内容,并生成一个新的数组对象
System.out.println(arr == target);
int[] target2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 3, 5); //也可以只拷贝某个范围内的内容
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(target2));
int[] target3 = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(arr, 2, target3, 4, 5); //使用System.arraycopy进行搬运
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(target3));
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(target3, 5));
int[][] array = new int[][]{{2, 8, 4, 1}, {9, 2, 0, 3}};
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(array));
int[][] a = new int[][]{{2, 8, 4, 1}, {9, 2, 0, 3}};
int[][] b = new int[][]{{2, 8, 4, 1}, {9, 2, 0, 3}};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a, b)); //equals仅适用于一维数组
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(a, b));
}
}
[1, 4, 5, 8, 2, 0, 9, 7, 3, 6]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[66, 66, 66, 66, 66, 66, 66, 66, 66, 66]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
false
[3, 4]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0]
7
[[2, 8, 4, 1], [9, 2, 0, 3]]
false
true