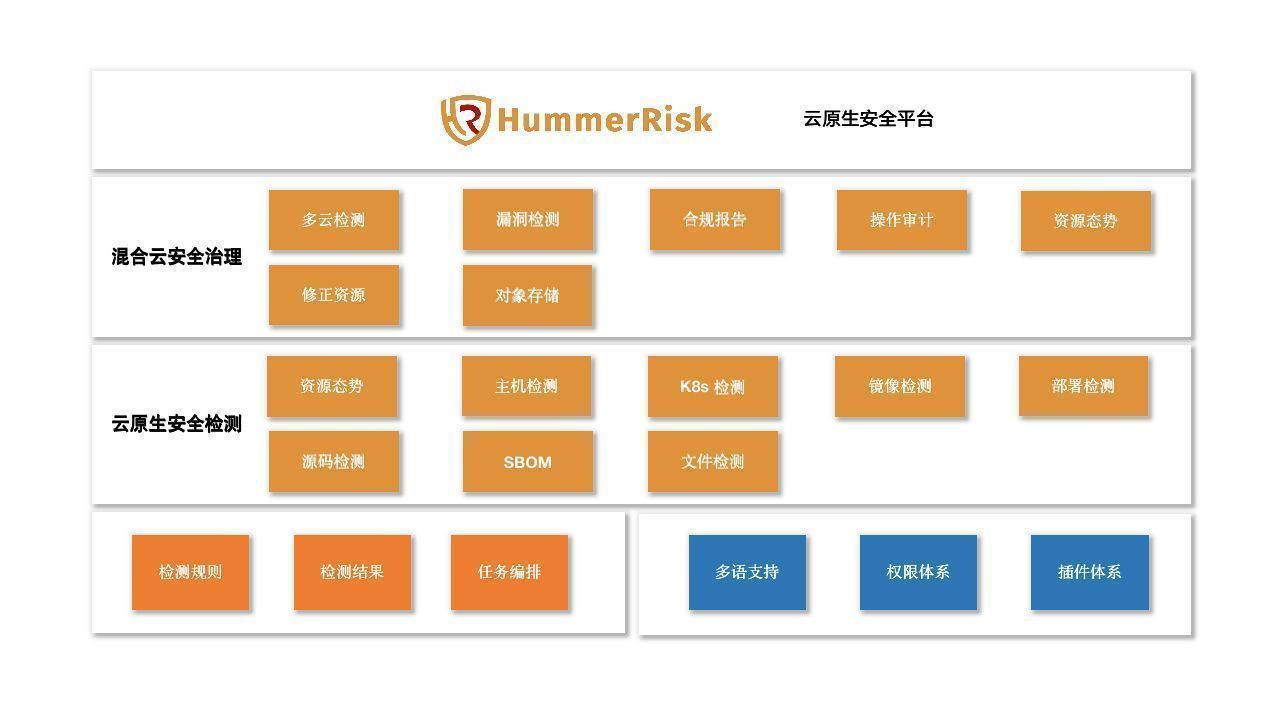
一、下载jpegsrc
1、下载JPEG库的源代码 http://www.ijg.org/files/
2、这里使用最新的jpegsr9e.zip ,别下载错误了(jpegsrc.v9e.tar.gz 是RAM架构的仅支持32位)
3、解压jpegsr9e.zip到d盘,如:D:\jpeg-9e
二、vs2019编译windows x86(x64)架构的lib库
启动Developer Command Prompt for VS 2019.exe,通过命令进入到D:\jpeg-9e:
CD D:\jpeg-9e
直接使用命令(注意vs2019是setup-v16,其他的版本需要查一下):
NMAKE /f makefile.vs setup-v16
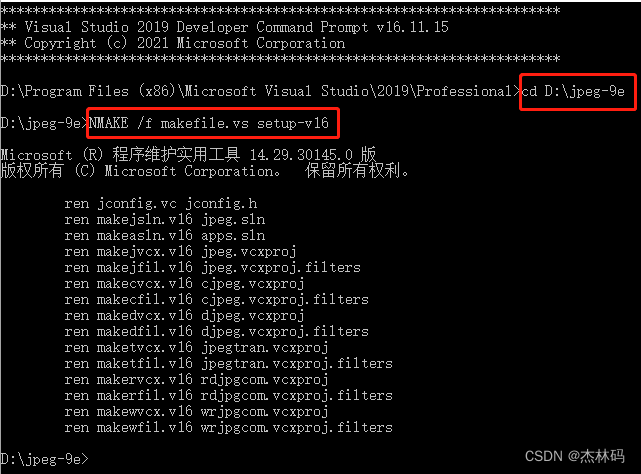
此时在文件夹内出现了jpeg.sln,用vs2019打开,并选择x86或则x64:
编译时需要选择架构类型:
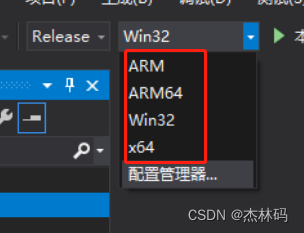
win32和x64代表x86和x64,也可以选择ARM。
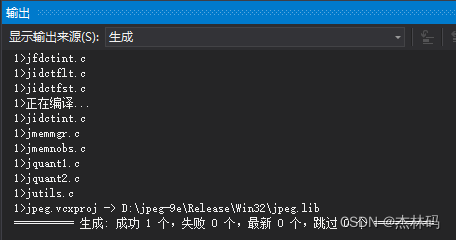
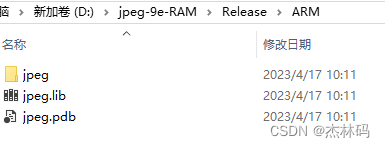
于是生成了:
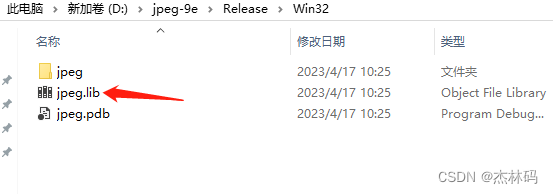
然后通过包含调用lib即可:
#include "jpeglib.h"
大家也可以直接下载vs2019的项目文件:
JPEGLIB windows vs2019项目库下载地址
三、vs2019编译windows ARM架构的lib库
注意如果下错了jpegsrc.v9e.tar.gz ,采用的是ARM架构下的会出现错误:
makefile.vc(11) : fatal error U1052: 未找到文件“win32.mak”
Stop.
此时请将下面的代码通过txt另存为:Win32.Mak,放在D:\jpeg-9e中,然后再执行上面的命令。
# Win32.Mak - Win32 application master NMAKE definitions file for the
# Microsoft Windows SDK programming samples
# Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# This files should be included at the top of all MAKEFILEs as follows:
# !include <Win32.Mak>
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Define APPVER = [ 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.01 | 5.02 | 6.0 | 6.1] prior to including win32.mak to get
# build time checking for version dependencies and to mark the executable
# with version information.
#
# Define TARGETOS = [ WIN95 | WINNT | BOTH ] prior to including win32.mak
# to get some build time checking for platform dependencies.
#
# Define TARGETLANG = [ LANG_JAPANESE | LANG_CHINESE | LANG_KOREAN ] prior
# to including win32.mak to getcompile & link flags for building
# applications to run on Far-East Windows. (This is an optional parameter.
# The system locale is the default.)
#
# Define _WIN32_IE = [ 0x0300 | 0x0400 | 0x0500 | 0x0600] prior to including win32.mak to
# get compile and link flags for building applications and components to
# run on Internet Explorer. (This is an optional parameter. IE 4.0 is
# the default.)
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# NMAKE Options
#
# Use the table below to determine the additional options for NMAKE to
# generate various application debugging, profiling and performance tuning
# information.
#
# Application Information Type Invoke NMAKE
# ---------------------------- ------------
# For No Debugging Info nmake nodebug=1
# For Working Set Tuner Info nmake tune=1
# For Call Attributed Profiling Info nmake profile=1
# For COLE 32->64-bit Porting Tool nmake COLE_64=1
#
# Note: The three options above are mutually exclusive (you may use only
# one to compile/link the application).
#
# Note: creating the environment variables NODEBUG, TUNE, and PROFILE is an
# alternate method to setting these options via the nmake command line.
#
# Note: to use the COLE_64 option, you need to set your build environment
# for 64-bit compilations.
#
# Note: TUNE and PROFILE do nothing for 64bit compilation
#
# Additional NMAKE Options Invoke NMAKE
# ---------------------------- ------------
# For No ANSI NULL Compliance nmake no_ansi=1
# (ANSI NULL is defined as PVOID 0)
#
# =========================================================================
# Build Rules Quick Start
#
# To build one of the following types of executables, use the specified
# compiler and linker command-line options.
#
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# To build: | Compiler Options | Linker options (pick one
# | | line. con = console,
# | | gui = GUI, ole = GUI OLE)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Single threaded | cdebug cflags cvars | ldebug guilflags guilibs
# app with static | | ldebug conlflags conlibs
# CRT | | ldebug guilflags olelibs
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Multithreaded app | cdebug cflags cvarsmt | ldebug guilflags guilibsmt
# with static CRT | | ldebug conlflags conlibsmt
# | | ldebug guilflags olelibsmt
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Single or multi- | cdebug cflags cvarsdll | ldebug guilflags guilibsdll
# threaded app with | | ldebug conlflags conlibsdll
# DLL version of CRT | | ldebug guilflags olelibsdll
# (MSVCRT.DLL) | |
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DLL with static | cdebug cflags cvarsmt | ldebug dlllflags guilibsmt
# CRT* | | ldebug dlllflags conlibsmt
# | | ldebug dlllflags olelibsmt
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DLL with DLL | cdebug cflags cvarsdll | ldebug dlllflags guilibsdll
# version of CRT | | ldebug dlllflags conlibsdll
# (MSVCRT.DLL) | | ldebug dlllflags olelibsdll
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# * Always make DLLs multithreaded because a DLL has no way to know whether
# the calling application has multiple threads, and has no way to prevent
# multithreaded apps from loading it.
#
# To specify an Intel x86 build that defaults to stdcall, add scall to the
# list of compiler options.
#
# =========================================================================
!IFNDEF _WIN32_MAK_
_WIN32_MAK_ = 1
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Get CPU Type - exit if CPU environment variable is not defined
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Win95 does not define PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE - default to i386
!IF "$(PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE)" == ""
CPU=i386
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=x86
!endif
!IF !DEFINED(CPU) || "$(CPU)" == ""
CPU = $(PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE)
!ENDIF # CPU
# if PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE was x86 or X86 change CPU to i386
!IF ( "$(CPU)" == "X86" ) || ( "$(CPU)" == "x86" )
CPU = i386
!ENDIF # CPU == X86
!IF "$(CPU)" != "i386"
!IF "$(CPU)" != "IA64"
!IF "$(CPU)" != "AMD64"
!ERROR Must specify CPU environment variable ( CPU=i386, CPU=IA64, CPU=AMD64)
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Get Target Operating System - Default to WINNT
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
!IFNDEF TARGETOS
TARGETOS = WINNT
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" != "WINNT"
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" != "WIN95"
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" != "BOTH"
!ERROR Must specify TARGETOS environment variable (BOTH, WIN95, WINNT)
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
# default to APPVER of 5.0
!IFNDEF APPVER
APPVER = 5.0
!ENDIF
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "6.1"
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "6.0"
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "5.02"
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "5.01"
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "5.0"
!IF "$(APPVER)" != "4.0"
!ERROR Must specify APPVER environment variable (4.0, 5.0, 5.01, 5.02, 6.0, 6.1)
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!IF "$(APPVER)" =="6.1"
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0700
!ENDIF # _WIN32_IE
!ENDIF # APPVER == 6.1
!IF "$(APPVER)" =="6.0"
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0700
!ENDIF # _WIN32_IE
!ENDIF # APPVER == 6.0
!IF "$(APPVER)" =="5.0"
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0500
!ENDIF # _WIN32_IE
!ENDIF # APPVER == 5.0
!IF "$(APPVER)" =="5.01"
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0600
!ENDIF # _WIN32_IE
!ENDIF # APPVER == 5.01
!IF "$(APPVER)" =="5.02"
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0600
!ENDIF # _WIN32_IE
!ENDIF # APPVER == 5.02
!IFNDEF _WIN32_IE
_WIN32_IE = 0x0400
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Build tool declarations common to all platforms
# Check to see if Cole Porter is used, otherwise use C/C++ compiler
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
!IFDEF COLE_64
cc = Port64
link = Cole & Rem no link when using Cole
implib = Rem no lib when using Cole since the Cole .Objs are text
!ELSE
cc = cl
link = link
implib = lib
!ENDIF
midl = midl
rc = Rc
hc = Start /Wait Hcrtf
mc = Mc
hcvars = -xn
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Platform Dependent Compile Flags - must be specified after $(cc)
#
# Note: Debug switches are on by default for current release
#
# These switches set code generation and debugging options for the compiler.
# They also set macros used for conditional compilation.
#
# The debugging switches allow for source level debugging with WinDebug or
# Microsoft Visual C++.
#
# Common compiler flags:
# -c - compile without linking
# -W3 - Set warning level to level 3 (-W4 for 64-bit compilations)
# -Zi - generate debugging information
# -Od - disable all optimizations
# -Ox - use maximum optimizations
# -Zd - generate only public symbols and line numbers for debugging
# -GS - enable security checks
#
# i386 specific compiler flags:
# -Gz - stdcall (only if scall is added to makefile's compiler build rules)
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# declarations common to all compiler options
ccommon = -c -DCRTAPI1=_cdecl -DCRTAPI2=_cdecl -nologo -GS
# for compatibility with old source code, map {try, except, leave, finally}
# to their proper names (i.e. prefaced by "__")
!IFDEF SEHMAP
ccommon = $(ccommon) -FIsehmap.h
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_JAPANESE"
ccommon = $(ccommon) -DJAPAN -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_CHINESE"
ccommon = $(ccommon) -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_KOREAN"
ccommon = $(ccommon) -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
!IF "$(CPU)" == "i386"
cflags = $(ccommon) -D_X86_=1 -DWIN32 -D_WIN32 -W3
scall = -Gz
!ELSEIF "$(CPU)" == "IA64"
cflags = $(ccommon) -D_IA64_=1 -DWIN64 -D_WIN64 -DWIN32 -D_WIN32
cflags = $(cflags) -W4
scall =
!ELSEIF "$(CPU)" == "AMD64"
cflags = $(ccommon) -D_AMD64_=1 -DWIN64 -D_WIN64 -DWIN32 -D_WIN32
cflags = $(cflags) -W4
scall =
!ENDIF
!IF "$(APPVER)" == "4.0"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0400
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.0"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0500
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.01"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0501
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.02"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0502
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "6.0"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0600
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "6.1"
NMAKE_WINVER = 0x0600
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" == "WINNT"
cflags = $(cflags) -D_WINNT -D_WIN32_WINNT=$(NMAKE_WINVER) -DNTDDI_VERSION=$(NMAKE_WINVER)0000
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" == "WIN95"
cflags = $(cflags) -D_WIN95 -D_WIN32_WINDOWS=$(NMAKE_WINVER) /D_WIN32_DCOM
!ENDIF
# regardless of the TARGET OS, define compile time WINVER to match APPVER macro
cflags = $(cflags) -D_WIN32_IE=$(_WIN32_IE) -DWINVER=$(NMAKE_WINVER)
# Set debugging options
!IF "$(CPU)" != "IA64"
!IFDEF NODEBUG
cdebug = -Zi -Od -DDEBUG
!ELSE IFDEF PROFILE
cdebug = -Gh -Zd -Ox -DNDEBUG
!ELSE IFDEF TUNE
cdebug = -Gh -Zd -Ox -DNDEBUG
!ELSE
cdebug = -Zi -Od -DDEBUG
!ENDIF
!ELSE
!IFDEF NODEBUG
cdebug = -Ox -DNDEBUG
!ELSE
cdebug = -Zi -Od -DDEBUG
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Target Module & Subsystem Dependent Compile Defined Variables - must be
# specified after $(cc)
#
# The following table indicates the various acceptable combinations of
# the C Run-Time libraries LIBC, LIBCMT, and MSVCRT respect to the creation
# of a EXE and/or DLL target object. The appropriate compiler flag macros
# that should be used for each combination are also listed.
#
# Executable Type C Runtime Lib Compiler switch
# -------------------------------------------------------------
# Single threaded app static CRT CVARS *
# Single-threaded app DLL CRT CVARSDLL
# Multi-threaded app static CRT CVARSMT *
# Multi-threaded app DLL CRT CVARSDLL *
#
# Single threaded DLL static CRT CVARS
# Single-threaded DLL DLL CRT CVARSDLL
# Multi-threaded DLL static CRT CVARSMT *
# Multi-threaded DLL DLL CRT CVARSDLL *
#
# * - Denotes the Recommended Configuration
#
# When building single-threaded applications you can link your executable
# with either LIBC, LIBCMT, or MSVCRT, although LIBC will provide the best
# performance.
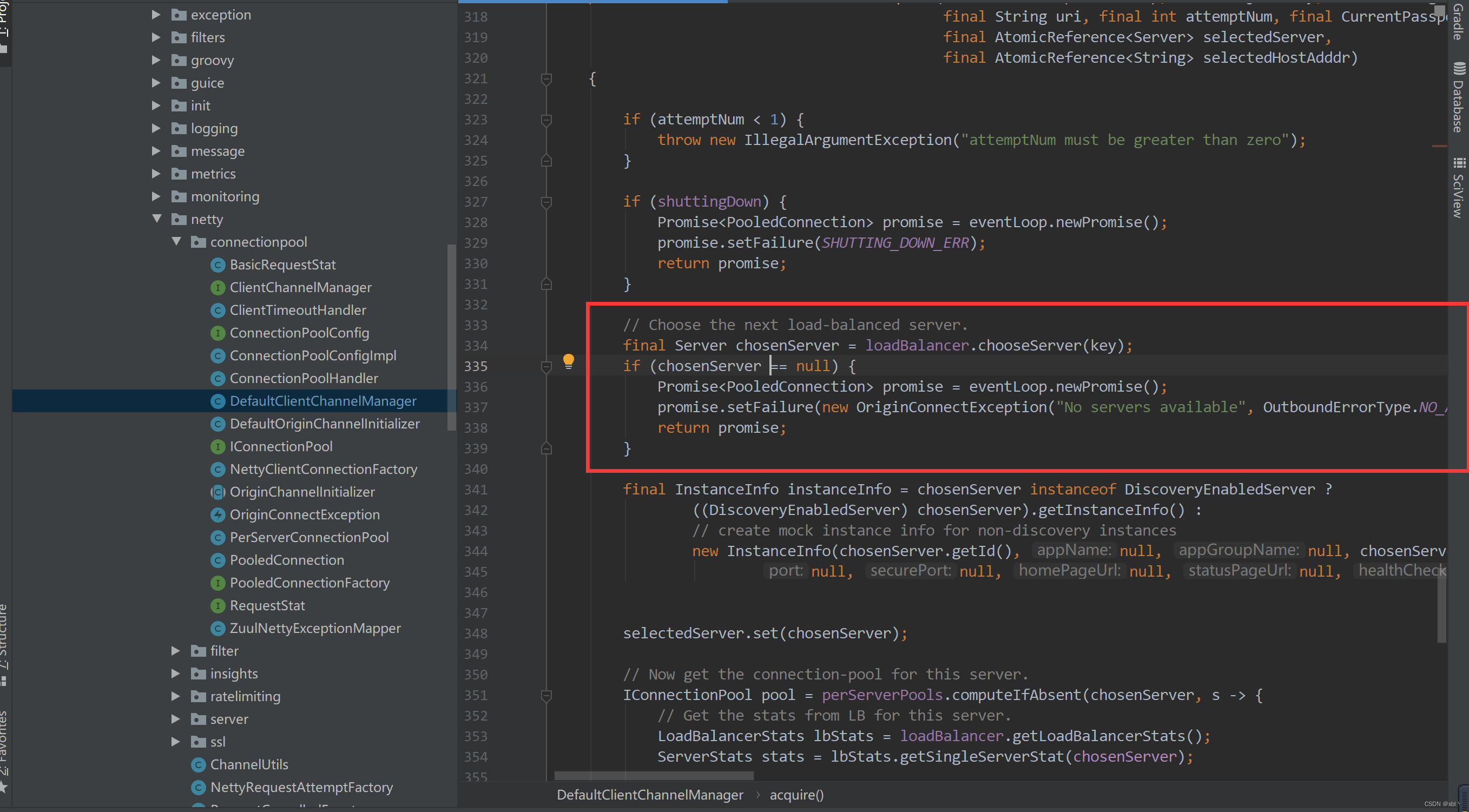
#
# When building multi-threaded applications, either LIBCMT or MSVCRT can
# be used as the C-Runtime library, as both are multi-thread safe.
#
# Note: Any executable which accesses a DLL linked with MSVCRT.LIB must
# also link with MSVCRT.LIB instead of LIBC.LIB or LIBCMT.LIB.
# When using DLLs, it is recommended that all of the modules be
# linked with MSVCRT.LIB.
#
# Note: The macros of the form xDLL are used when linking the object with
# the DLL version of the C Run-Time (that is, MSVCRT.LIB). They are
# not used when the target object is itself a DLL.
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
!IFDEF NO_ANSI
noansi = -DNULL=0
!ENDIF
# for Windows applications that use the C Run-Time libraries
!IFDEF NODEBUG
cvarsmt = $(noansi) -D_MT -MT
cvars = $(cvarsmt)
cvarsdll = $(noansi) -D_MT -D_DLL -MD
!ELSE
cvarsmt = $(noansi) -D_MT -MTd
cvars = $(cvarsmt)
cvarsdll = $(noansi) -D_MT -D_DLL -MDd
!ENDIF
# for compatibility with older-style makefiles
cvarsmtdll = $(cvarsdll)
# for POSIX applications
psxvars = -D_POSIX_
# resource compiler
rcflags = /r
!ifdef NODEBUG
rcvars = -DWIN32 -D_WIN32 -DWINVER=$(NMAKE_WINVER) $(noansi)
!else
rcvars = -DWIN32 -D_WIN32 -DWINVER=$(NMAKE_WINVER) -DDEBUG -D_DEBUG $(noansi)
!endif
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_JAPANESE"
rcflags = $(rcflags) /c932
rcvars = $(rcvars) -DJAPAN -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_CHINESE"
rcvars = $(rcvars) -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
!IF "$(TARGETLANG)" == "LANG_KOREAN"
rcvars = $(rcvars) -DDBCS -DFE_IME
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Platform Dependent MIDL Flags - must be specified after midl
#
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" == "WIN95"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT40
!ELSEIF "$(TARGETOS)" == "WINNT"
!IF "$(APPVER)" == "5.0"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT50
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "6.0"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT60
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "6.1"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT60
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.01"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT51
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.02"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT51
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "4.0"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION=-target NT40
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
!IF "$(CPU)" == "IA64"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION = $(MIDL_OPTIMIZATION) /ia64
!ELSEIF "$(CPU)" == "AMD64"
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION = $(MIDL_OPTIMIZATION) /x64
!ELSE
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION = $(MIDL_OPTIMIZATION) /win32
!ENDIF
!IF ("$(TARGETOS)" == "WINNT" ) && ("$(APPVER)" != "4.0")
MIDL_OPTIMIZATION = $(MIDL_OPTIMIZATION) /robust
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Platform Dependent Link Flags - must be specified after $(link)
#
# Note: $(DLLENTRY) should be appended to each -entry: flag on the link
# line.
#
# Note: When creating a DLL that uses C Run-Time functions it is
# recommended to include the entry point function of the name DllMain
# in the DLL's source code. Also, the MAKEFILE should include the
# -entry:_DllMainCRTStartup$(DLLENTRY) option for the creation of
# this DLL. (The C Run-Time entry point _DllMainCRTStartup in turn
# calls the DLL defined DllMain entry point.)
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# declarations common to all linker options
lflags = $(lflags) /INCREMENTAL:NO /NOLOGO
# declarations for use on Intel x86 systems
!IF "$(CPU)" == "i386"
DLLENTRY = @12
!ENDIF
# declarations for use on Intel Architecture 64-bit systems
!IF "$(CPU)" == "IA64"
DLLENTRY =
!ENDIF
# declarations for use on AMD64 systems
!IF "$(CPU)" == "AMD64"
DLLENTRY =
!ENDIF
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Target Module Dependent Link Debug Flags - must be specified after $(link)
#
# These switches allow the inclusion of the necessary symbolic information
# for source level debugging with WinDebug, profiling and/or performance
# tuning.
#
# Note: Debug switches are on by default.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
!IF "$(CPU)" == "i386"
!IFDEF NODEBUG
ldebug = /RELEASE
!ELSE
ldebug = /DEBUG /DEBUGTYPE:cv
!ENDIF
!ELSE
!IFDEF NODEBUG
ldebug = /RELEASE
!ELSE IFDEF PROFILE
ldebug = /DEBUG:mapped,partial /DEBUGTYPE:coff
!ELSE IFDEF TUNE
ldebug = /DEBUG:mapped,partial /DEBUGTYPE:coff
!ELSE
ldebug = /DEBUG /DEBUGTYPE:cv
!ENDIF
!ENDIF
# for compatibility with older-style makefiles
linkdebug = $(ldebug)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Subsystem Dependent Link Flags - must be specified after $(link)
#
# These switches allow for source level debugging with WinDebug for local
# and global variables. They also provide the standard application type and
# entry point declarations.
#
# Note that on x86 screensavers have a WinMain entrypoint, but on RISC
# platforms it is main. This is a Win95 compatibility issue.
#
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Windows 98 needs subsystem version set to 4.10 for version 5.0 features.
!IF ("$(APPVER)" == "5.0") && (("$(TARGETOS)" == "BOTH") || ("$(TARGETOS)" == "WIN95"))
EXEVER = 4.10
!ELSE
EXEVER = $(APPVER)
!ENDIF
# ---------------------------------------------
# for Windows applications
conlflags = $(lflags) -subsystem:console,$(EXEVER)
guilflags = $(lflags) -subsystem:windows,$(EXEVER)
dlllflags = $(lflags) -entry:_DllMainCRTStartup$(DLLENTRY) -dll
# For screen savers
!IF "$(CPU)" == "i386"
savlflags = $(lflags) -subsystem:windows,$(EXEVER) -entry:WinMainCRTStartup
!ELSE
savlflags = $(lflags) -subsystem:windows,$(EXEVER) -entry:mainCRTStartup
!ENDIF
# for POSIX applications
psxlflags = $(lflags) -subsystem:posix -entry:__PosixProcessStartup
# for compatibility with older-style makefiles
conflags = $(conlflags)
guiflags = $(guilflags)
psxflags = $(psxlflags)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# C Run-Time Target Module Dependent Link Libraries
#
# Note: For POSIX applications, link with $(psxlibs).
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# for POSIX applications
psxlibs = libcpsx.lib psxdll.lib psxrtl.lib oldnames.lib
# optional profiling and tuning libraries
!IF "$(CPU)" != "IA64"
!IFDEF PROFILE
optlibs = cap.lib
!ELSE IFDEF TUNE
optlibs = wst.lib
!ELSE
optlibs =
!ENDIF
!ELSE
optlibs =
!ENDIF
# if building for basic Windows 95, use WinSock1, else use WinSock2
!IF "$(TARGETOS)" == "WIN95"
!IF "$(APPVER)" == "4.0"
winsocklibs = wsock32.lib
!ELSE
winsocklibs = ws2_32.lib mswsock.lib
!ENDIF
!ELSE
winsocklibs = ws2_32.lib mswsock.lib
!ENDIF
# basic subsystem specific libraries, less the C Run-Time
baselibs = kernel32.lib $(optlibs) $(winsocklibs) advapi32.lib
winlibs = $(baselibs) user32.lib gdi32.lib comdlg32.lib winspool.lib
# for Windows applications that use the C Run-Time libraries
conlibs = $(baselibs)
guilibs = $(winlibs)
# for OLE applications
olelibs = ole32.lib uuid.lib oleaut32.lib $(guilibs)
#for backwards compatibility
conlibsmt = $(conlibs)
conlibsdll = $(conlibs)
guilibsmt = $(guilibs)
guilibsdll = $(guilibs)
olelibsmt = $(olelibs)
olelibsdll = $(olelibs)
# for backward compatibility
ole2libs = $(olelibs)
ole2libsmt = $(olelibsmt)
ole2libsdll = $(olelibsdll)
# Visual Basic
bc = vb6
bc_exe = /Make
bc_dll = /Makedll
# Set the Output Directory
!IF ("$(APPVER)" == "6.1")
OUTDIR=SVR2008
!ELSEIF ("$(APPVER)" == "6.0")
OUTDIR=LH
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.0"
OUTDIR=WIN2000
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.01"
OUTDIR=XP32
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "5.02"
OUTDIR=SRV2003
!ELSEIF "$(APPVER)" == "4.0"
OUTDIR=NT4
!ENDIF
!IF "$(CPU)" == "AMD64"
OUTDIR=$(OUTDIR)_X64
!ELSEIF "$(CPU)" == "IA64"
OUTDIR=$(OUTDIR)_64
!ENDIF
#set Prerelease Out directories
!IF "$(SDKPRERELEASE)" == "1"
OUTDIR=PRE_$(OUTDIR)
!ENDIF
#Set DEBUG
!IF "$(NODEBUG)" == ""
OUTDIR=$(OUTDIR)_DEBUG
!ELSE
OUTDIR=$(OUTDIR)_RETAIL
!ENDIF
!IF "$(OS)" == "Windows_NT"
CLEANUP=if exist $(OUTDIR)/$(NULL) rd /s /q $(OUTDIR)
!ELSE
CLEANUP=deltree /y $(OUTDIR)
!ENDIF
VC6MSG=This sample only compiles with Microsoft Visual C++ 6.0. \
To compile this run vcvars32.bat for Visual C++ 6.0, and setenv.bat in $(MSSDK).
WIN64MSG=This sample is currently not supported on the 64 bit platform.
#ENDIF _WIN32_MAK_
!ENDIF
于是可得到如下图结果:
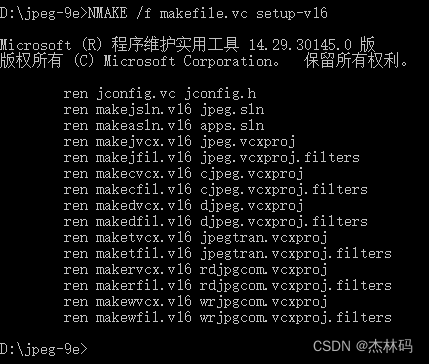
在文件夹中生成了一个:jpeg.sln,用vs2019打开jpeg.sln,得到:
右击jpeg项目名称,点击编译如下图:
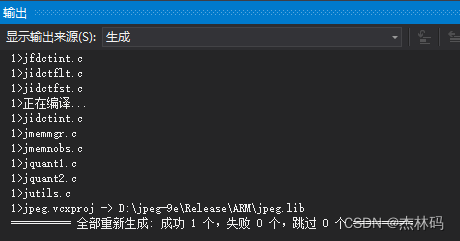
此时生成的是 RAM下的库: