目录
I/O多路复用
异步I/O
I/O多路复用
阻塞型I/O 相对于非阻塞型 I/O 来说,最大的优点就是在设备的资源不可用时,进程主动放弃 CPU,让其他的进程运行,而不用不停地轮询,有助于提高整个系统的效率。但是其缺点也是比较明显的,那就是进程阻塞后,不能做其他的操作,这在一个进程要同时对多个设备进行操作时显得非常不方便。比如一个进程既要读取键盘的数据,又要读取串口的数据,那么如果都是用阻塞的方式进行操作的话,如果因为读取键盘而使进程阻塞,即便串口收到了数据,也不能及时获取。解决这个问题的方法有多种,比如多进程、多线程和 I/0 多路复用。在这里我们来讨论 I/O 多路复用的实现,首先回顾一下在应用层中,I/O 多路复用的相关操作。在应用层,由于历史原因,I/O 多路复用有 select、poll 以及 Linux 所特有的epoll 三种方式。这里以poll为例来进行说明,poll 系统调用的原型及相关的数据类型如下。
int poll(struct pollfd *fds,nfds_t nfds,int timeout):
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */
short events; /* requested events */
short revents; /* returned events */
};
POLLIN There is data to read.
POLLOUT Writing now will not block.
POLLRDNORM Equivalent to POLLIN.
POLLWRNORM Equivalent to POLLOUT.poll的第一个参数是要监听的文件描述符集合,类型为指向 struct pollfd 的指针,struct pollfd有3 个成员,fd 是要监听的文件描述符,events 是监听的事件,revents 是返回的事件。常见的事件有 POLLIN、POLLOUT,分别表示设备可以无阻塞地读、写。POLLRDNORM和POLLWRNORM 是在 _XOPEN_SOURCE 宏被定义时所引入的事件POLLRDNORM 通常和POLLIN 等价,POLLWRNORM 和POLLOUT 等价。poll 函数的第二个参数是要监听的文件描述符的个数,第三个参数是毫秒的超时值,负数表示一直监听,直到被监听的文件描述符集合中的任意一个设备发生了事件才会返回。如果有一个程序既要监听键盘,又要监听串口,当用户按下键盘上的键后,将键值转换成字符串后通过串口发送出去,当串口收到了数据后,在屏幕上显示,那么可以使用下面的应用程序来实现.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include "vser.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
struct pollfd fds[2];
char rbuf[32];
char wbuf[32];
struct input_event key;
fds[0].fd = open("/dev/vser0", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fds[0].fd == -1)
goto fail;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
fds[0].revents = 0;
fds[1].fd = open("/dev/input/event1", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fds[1].fd == -1)
goto fail;
fds[1].events = POLLIN;
fds[1].revents = 0;
while (1) {
ret = poll(fds, 2, -1);
if (ret == -1)
goto fail;
if (fds[0].revents & POLLIN) {
ret = read(fds[0].fd, rbuf, sizeof(rbuf));
if (ret < 0)
goto fail;
puts(rbuf);
}
if (fds[1].revents & POLLIN) {
ret = read(fds[1].fd, &key, sizeof(key));
if (ret < 0)
goto fail;
if (key.type == EV_KEY) {
sprintf(wbuf, "%#x\n", key.code);
ret = write(fds[0].fd, wbuf, strlen(wbuf) + 1);
if (ret < 0)
goto fail;
}
}
}
fail:
perror("poll test");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
代码第 22 行至第 32 行,分别以非阻塞方式打开了两个设备文件,并初始化了关心的事件;代码第 35 行调用 poll 进行监听,如果被监听的设备没有一个设备文件可读,那么 poll 将会一直阻塞,直到键盘或串口任意一个设备能够读取数据才返回;poll 返回,如果返回值不为负值,那么意味着肯定至少有一个设备可以读取(因为没有设置超时),代码第 39 行至第 57 行就是判断返回的事件,如果相应的事件发生,则读取数据。如果从串口读取到数据则在标准输出上进行打印;如果在键盘上读到了数据,则判断按键的类型,若为EV_KEY 则将键值转换为字符串,通过串口发送。因为虚拟串口是内环回的,所以发给串口的数据都会返回来。
了解了应用层的实现后,接下来看看驱动是如何实现的.
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/kfifo.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include "vser.h"
#define VSER_MAJOR 256
#define VSER_MINOR 0
#define VSER_DEV_CNT 1
#define VSER_DEV_NAME "vser"
struct vser_dev {
unsigned int baud;
struct option opt;
struct cdev cdev;
wait_queue_head_t rwqh;
wait_queue_head_t wwqh;
};
DEFINE_KFIFO(vsfifo, char, 32);
static struct vser_dev vsdev;
static int vser_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static int vser_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t vser_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
int ret;
unsigned int copied = 0;
if (kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)) {
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.rwqh, !kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
ret = kfifo_to_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);
if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.wwqh);
return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}
static ssize_t vser_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
int ret;
unsigned int copied = 0;
if (kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)) {
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.wwqh, !kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
ret = kfifo_from_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);
if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.rwqh);
return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}
static long vser_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != VS_MAGIC)
return -ENOTTY;
switch (cmd) {
case VS_SET_BAUD:
vsdev.baud = arg;
break;
case VS_GET_BAUD:
arg = vsdev.baud;
break;
case VS_SET_FFMT:
if (copy_from_user(&vsdev.opt, (struct option __user *)arg, sizeof(struct option)))
return -EFAULT;
break;
case VS_GET_FFMT:
if (copy_to_user((struct option __user *)arg, &vsdev.opt, sizeof(struct option)))
return -EFAULT;
break;
default:
return -ENOTTY;
}
return 0;
}
unsigned int vser_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{
int mask = 0;
poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.rwqh, p);
poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.wwqh, p);
if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo))
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM;
return mask;
}
static struct file_operations vser_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = vser_open,
.release = vser_release,
.read = vser_read,
.write = vser_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = vser_ioctl,
.poll = vser_poll,
};
static int __init vser_init(void)
{
int ret;
dev_t dev;
dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);
ret = register_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT, VSER_DEV_NAME);
if (ret)
goto reg_err;
cdev_init(&vsdev.cdev, &vser_ops);
vsdev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
vsdev.baud = 115200;
vsdev.opt.datab = 8;
vsdev.opt.parity = 0;
vsdev.opt.stopb = 1;
ret = cdev_add(&vsdev.cdev, dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
if (ret)
goto add_err;
init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.rwqh);
init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.wwqh);
return 0;
add_err:
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
reg_err:
return ret;
}
static void __exit vser_exit(void)
{
dev_t dev;
dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);
cdev_del(&vsdev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
}
module_init(vser_init);
module_exit(vser_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("name<e-mail>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple character device driver");
MODULE_ALIAS("virtual-serial");
驱动的代码非常简单,代码第 114 行至第 127 行实现了一个 poll 接口函数,代码第136 行让 file_operations 内的 poll 函数指针指向了该接口函数。但是这简单的代码背后的机制却比较复杂,为了让大家更好地理解 I/O 多路复用的实现,下面把 poll 系统调用的过程用图4.1来简单描述一下。
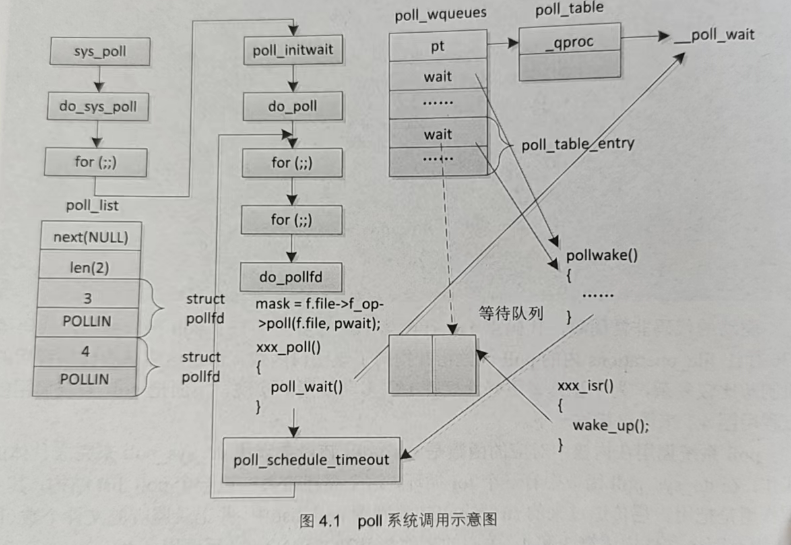
poll 系统调用在内核中对应的函数是 sys_poll,该函数调用 do_sys_poll来完成具体的工作;在do_sys_poll函数中有一个 for 循环,这个循环将会构造一个poll_list 结构,其主要作用是把用户层传递过来的 struct pollfd 复制到 poll_list 中,并记录监听的文件个数(图4.1中有两个文件描述符3和4,关心的事件都是POLLIN);之后调用poll_initwait函数,该函数构造一个poll_wqueues 结构,并初始化其中部分的成员,包括将pt 指针指向一个poll_table 的结构,poll_table 结构中有一个函数指针指 __poll_wait; 接下来调用 do_poll函数,do_poll函数内有两层 for 循环,内层的 for 循环将会遍历poll_list 中的每一个struct pollfd 结构,并对应初始化 poll_wqueues 中的每一个poll_table_entry (关键是要构造一个等待队列节点,然后指定唤醒该节点后调用的函数为 poll_wake),接下来根据 fd 我到对应的file结构,从而调用驱动中的poll 接口函数(图示中为xxx poll),驱动中的poll接口函数将会调用 poll_wait 辅助函数,该函数又会调用之前在初始化 poll_wqueues 时指定的 poll_wait 函数, poll_wait 函数的主要作用是将刚才构造好的等待队列节点加入到驱动的等待队列中;接下来驱动的 poll 接口函数判断资源是否可用,并返回状态给 mask;如果内层循环所调用的每一个驱动的 poll 接口函数都返回,没有相应的事件发生,那么会调用 poll_schedule_timeout 将 poll 系统调用休眠;当设备可用后,通常会产生一个中断(或由另外一个进程的某个操作使资源可用),在对应的中断处理函数中(图示中为xxx isr)将会调用 wake_up 函数(或其变体),将该驱动对应资源的等待队列上的进程唤醒,这时也会把刚才因为 poll 系统调用所加入的节点出队,并调用相应的函数,即poll_wake 函数,该函数负责唤醒因调用 poll_schedule_timeout 函数而休眠的 poll 系统用,poll系统调用唤醒后,回到外层的 for 循环继续执行,这次执行再次遍历所有驱动中的 poll接口函数后,会发现至少有一个关心的事件产生,于是将该事件记录在 struct pollfd的 revents 成员中,然后跳出外层的 for 循环,将内核的 struct pollfd 复制至用户层,poll系统调用最终返回,并返回有多少个被监听的文件有关心的事件产生。
上面的过程比较复杂,而 poll 系统调用又可以随时添加新的要监听的文件描述符,第所以在内核中,相应的数组还有可能动态扩充,从而使整个过程更复杂一些。但是,其宗旨只有一个,那就是遍历所有被监听的设备的驱动中的 poll 接口函数,如果都没有关心的事件发生,那么 poll系统调用休眠,直到至少有一个驱动唤醒它为止。
再来理解驱动中的 poll接口函数的实现就比较简单了,代码第 118 行和第 119 行是将系统调用中构造的等待队列节点加入到相应的等待队列中,代码第 121 行至第 126行根据资源的情况返回设置 mask 的值并返回。驱动中的 poll 接口函数是不会休眠的,休眠发生在 poll系统调用上,这和前面的阻塞型 IO 是不同的。
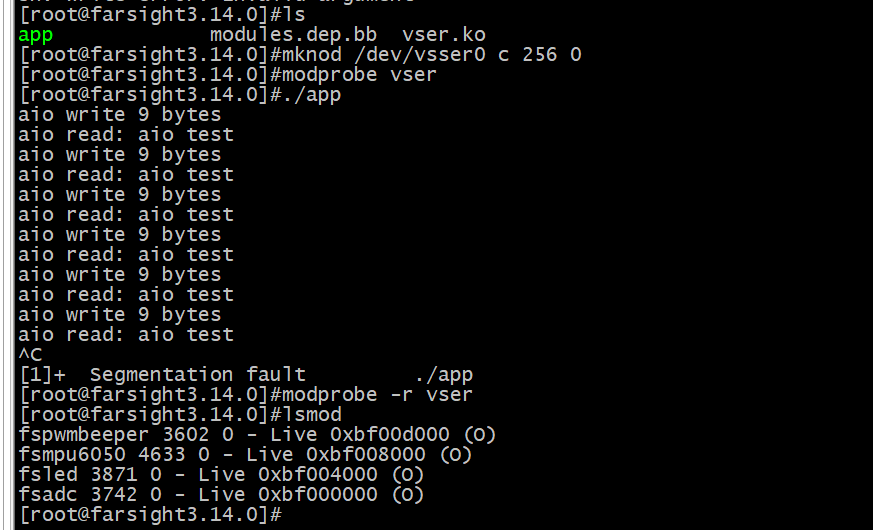
驱动和测试程序编写好后,可以使用下面的命令测试
mknod /dev/vser0 c 256 0
make
./lazy
sudo ./test
按键按下什么就会打印对应的信息这个0x1对应的是回车。在开发板上无效,感觉可能是由于用串口和开发板通信,所以输入文件不是/dev/input/event1.然后把键盘直接插在开发板也不行,因为没有键盘的驱动,就更麻烦了。然后我想可能是没实现对应驱动,但是又不太可能毕竟和开发板子进行通信考得就是串口2.下面仔细看看这个event1到底是来干嘛的。
找了半天根本没找到。也许不叫这个名
算了世上无难事,只要肯放弃。不搞了。反正在Ubuntu上能实现。不过我想到一个思路,再写个驱动,在串口捕获键盘输入时转发一下,先往后学习吧。没准到时候就解决了。
异步I/O
异步I/O是POSIX定义的一组标准接口,Linux 也支持。对于前面的几种I/O模型异步I/O在提交完I/O操作请求后就立即返回,程序不需要等到I/O操作完成再去做别的事情,具有非阻塞的特性。当底层把 I/O 操作完成后,可以给提交者发送信号,或者调用注册的回调函数,告知请求提交者 I/O 操作已完成。在信号处理函数或回调函数中,可以使用异步I/O接口来获得I/O的完成情况,比如获取读写操作返回的字节数或错误码、读取的数据等。一个简单的针对虚拟串口的异步 I/O 应用程序代码如下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <aio.h>
#include "vser.h"
void aiow_completion_handler(sigval_t sigval)
{
int ret;
struct aiocb *req;
req = (struct aiocb *)sigval.sival_ptr;
if (aio_error(req) == 0) {
ret = aio_return(req);
printf("aio write %d bytes\n", ret);
}
return;
}
void aior_completion_handler(sigval_t sigval)
{
int ret;
struct aiocb *req;
req = (struct aiocb *)sigval.sival_ptr;
if (aio_error(req) == 0) {
ret = aio_return(req);
if (ret)
printf("aio read: %s\n", (char *)req->aio_buf);
}
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
int fd;
struct aiocb aiow, aior;
fd = open("/dev/vser0", O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
goto fail;
memset(&aiow, 0, sizeof(aiow));
memset(&aior, 0, sizeof(aior));
aiow.aio_fildes = fd;
aiow.aio_buf = malloc(32);
strcpy((char *)aiow.aio_buf, "aio test");
aiow.aio_nbytes = strlen((char *)aiow.aio_buf) + 1;
aiow.aio_offset = 0;
aiow.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_THREAD;
aiow.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_function = aiow_completion_handler;
aiow.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_attributes = NULL;
aiow.aio_sigevent.sigev_value.sival_ptr = &aiow;
aior.aio_fildes = fd;
aior.aio_buf = malloc(32);
aior.aio_nbytes = 32;
aior.aio_offset = 0;
aior.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_THREAD;
aior.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_function = aior_completion_handler;
aior.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify_attributes = NULL;
aior.aio_sigevent.sigev_value.sival_ptr = &aior;
while (1) {
if (aio_write(&aiow) == -1)
goto fail;
if (aio_read(&aior) == -1)
goto fail;
sleep(1);
}
fail:
perror("aio test");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
EXIT_FAILURE没有成功执行一个程序,其实就是1
代码第 50 行定义了两个分别用于写和读的异步 I/O 控制块,代码第 56 行至第 76行初始化了这两个控制块,主要是文件描述符,用于读写的缓冲区、读写的字节数和异步I/O 完成后的回调函数。代码第 79 行发起一个异步写操作,该函数会立即返回,具体的写操作会在底层的驱动中完成。代码第 81 行又发起了一个异步读操作,该函数也会立即返回,具体的读操作会在底层的驱动中完成。当写完成后,注册的 aiow_completion_handler写完成函数将会被自动调用,该函数通过 aio_error 及 aio_retum 获取了I/O操作的错误码及实际的写操作的返回值。sigval.sival_ptr 是在代码第 67 行赋值的,指向了 I/O控制块aiow。同样,当读完成后,注册的 aior_completion_handler 读完成函数将会被自动调用,除了像写完成操作中可以获取完成状态,还可以从 aio_buf 中获取读取的数据。代码第 83行是模拟其他操作所消耗的时间。需要说明的是,在一次异步操作中,可以将多个 I/O请求合并,从而完成一系列的读写操作,其对应的接口函数是 lio_listio。
驱动代码如下:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/kfifo.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/aio.h>
#include "vser.h"
#define VSER_MAJOR 256
#define VSER_MINOR 0
#define VSER_DEV_CNT 1
#define VSER_DEV_NAME "vser"
struct vser_dev {
unsigned int baud;
struct option opt;
struct cdev cdev;
wait_queue_head_t rwqh;
wait_queue_head_t wwqh;
};
DEFINE_KFIFO(vsfifo, char, 32);
static struct vser_dev vsdev;
static int vser_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static int vser_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t vser_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
int ret;
unsigned int copied = 0;
if (kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)) {
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.rwqh, !kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
ret = kfifo_to_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);
if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.wwqh);
return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}
static ssize_t vser_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
int ret;
unsigned int copied = 0;
if (kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)) {
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.wwqh, !kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
ret = kfifo_from_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);
if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.rwqh);
return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}
static long vser_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != VS_MAGIC)
return -ENOTTY;
switch (cmd) {
case VS_SET_BAUD:
vsdev.baud = arg;
break;
case VS_GET_BAUD:
arg = vsdev.baud;
break;
case VS_SET_FFMT:
if (copy_from_user(&vsdev.opt, (struct option __user *)arg, sizeof(struct option)))
return -EFAULT;
break;
case VS_GET_FFMT:
if (copy_to_user((struct option __user *)arg, &vsdev.opt, sizeof(struct option)))
return -EFAULT;
break;
default:
return -ENOTTY;
}
return 0;
}
static unsigned int vser_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{
int mask = 0;
poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.rwqh, p);
poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.wwqh, p);
if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo))
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM;
return mask;
}
static ssize_t vser_aio_read(struct kiocb *iocb, const struct iovec *iov, unsigned long nr_segs, loff_t pos)
{
size_t read = 0;
unsigned long i;
ssize_t ret;
for (i = 0; i < nr_segs; i++) {
ret = vser_read(iocb->ki_filp, iov[i].iov_base, iov[i].iov_len, &pos);
if (ret < 0)
break;
read += ret;
}
return read ? read : -EFAULT;
}
static ssize_t vser_aio_write(struct kiocb *iocb, const struct iovec *iov, unsigned long nr_segs, loff_t pos)
{
size_t written = 0;
unsigned long i;
ssize_t ret;
for (i = 0; i < nr_segs; i++) {
ret = vser_write(iocb->ki_filp, iov[i].iov_base, iov[i].iov_len, &pos);
if (ret < 0)
break;
written += ret;
}
return written ? written : -EFAULT;
}
static struct file_operations vser_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = vser_open,
.release = vser_release,
.read = vser_read,
.write = vser_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = vser_ioctl,
.poll = vser_poll,
.aio_read = vser_aio_read,
.aio_write = vser_aio_write,
};
static int __init vser_init(void)
{
int ret;
dev_t dev;
dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);
ret = register_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT, VSER_DEV_NAME);
if (ret)
goto reg_err;
cdev_init(&vsdev.cdev, &vser_ops);
vsdev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
vsdev.baud = 115200;
vsdev.opt.datab = 8;
vsdev.opt.parity = 0;
vsdev.opt.stopb = 1;
ret = cdev_add(&vsdev.cdev, dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
if (ret)
goto add_err;
init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.rwqh);
init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.wwqh);
return 0;
add_err:
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
reg_err:
return ret;
}
static void __exit vser_exit(void)
{
dev_t dev;
dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);
cdev_del(&vsdev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
}
module_init(vser_init);
module_exit(vser_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("name <e-mail>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple character device driver");
MODULE_ALIAS("virtual-serial");
以异步读为例,在 vser_aio_read 函数中,最关键的还是调用了之前实现的 vser_read函数,但是 vser_read 函数被调用了nr_segs次,这和分散/聚集操作是类似的,即一次读操作实际上是分多次进行的,每次读取一定的宇节数( iov[i].iov_len),然后分别将读到的数据放入分散的内存区城中 (iov[i].iov_base)。从驱动代码中不难发现,异步 I/O 可以在驱动中阻塞,但是上层的操作却是非阻塞的。相应的编译、测试命令如下。
(编译测试程序时要-lrt不然会报错)