一、项目需求
数据集:姓名和对应的国籍
要求:输入一个姓名,通过模型可以得到TA所属的国籍
数据集下载:name_country_datasets
二、思路步骤分析
①准备数据集
将下载好的数据集解压,放到一个指定的位置,我这边放到了和jupyter同级目录下了

测试集和训练集都只有两列,姓名和所属国籍
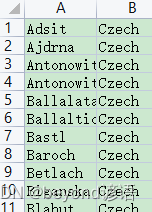
Ⅰ输入数据是姓名,将姓名转换为一个列表,列表中的每一个元素就是姓名的每一个字符

Ⅱ通过ASCII表当成词典进行转换
ASCII表中一个有128个字符,可以将ASCII码理解成一个具有128维的one-hot向量,求出每个字符所对应的ASCII码值
例如第一个是77,本质是一个128维的向量,其中第77位是1,其余都是0
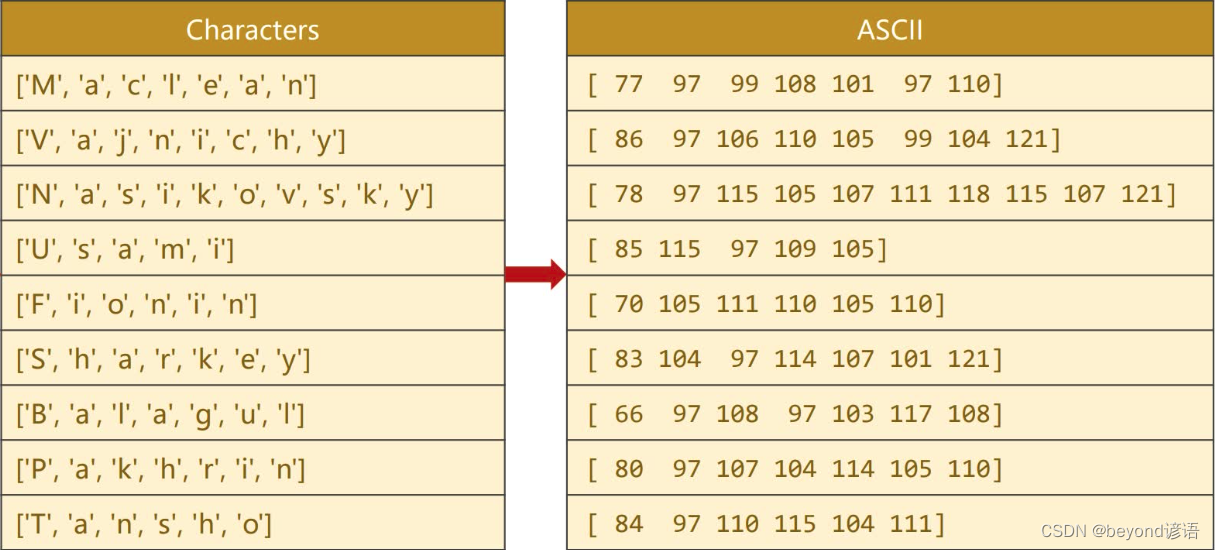
Ⅲ序列长短不一,需要通过padding来维持相同的张量
选出数据集中名字最长的那一个,作为最终的张量长度,然后把其他的名字短的进行填充
Ⅳ输出结果处理
根据数据集中出现的所有国籍,转换成一个分类的索引,生成一个词典即可

1,导包
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import gzip
import csv
import time
import math
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence, pack_padded_sequence, pack_sequence, pad_packed_sequence
2,姓名数据集函数构建
①初始化函数def __init__(self,is_train_set=True):解释:
初始化的时候通过is_train_set指定是否需要训练集,是训练集就读取训练集数据文件,不是的话就读取测试集数据文件
因为是.gz后缀的压缩包故需要通过gzip进行打开,通过csv.reader(f)读取数据集中的数据
rows = list(reader)将csv中的数据集全部读进来,读取每行数据,最终返回的结果为元组(name,country)形式
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]拿到name信息
self.len = len(self.names)记录一下样本的数量
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]拿到country信息
set(self.countries)将列表变成一个集合,因为集合里面不重复,也就是去重
sorted(set(self.countries)) 排序
list(sorted(set(self.countries)))最后变成一个列表形式
②索引函数def __getitem__(self,index):解释:
self.names[index] 拿到姓名
self.countries[index]拿到国籍
self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]根据国籍,从字典中获取对应的索引
countries(key)和index(value)相当于字典中的键值对
姓名是字符串,取出的国籍是索引
③数据集长度函数def __len__(self):解释:
返回数据集的长度
④国籍字典函数def getCounrtyDict(self)::解释:
country_dict = dict()定义一个空字典
for idx,country_name in enumerate(self.country_list,0):遍历
构造键值对country_dict[country_name] = idx
最终构建成一个国籍字典表
⑤根据索引返回国籍字符串函数def idx2country(self,index):解释:
return self.country_list[index]例如输入的是名字,得到分类是9,根据9,来返回对应的字符串,即所属的国籍
⑥总共的国籍数量函数def getCountriesNum(self):解释:
return self.country_num返回国籍数量
完整代码如下:
class NameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,is_train_set=True): #is_train_set 指定是否是训练集
filename = 'names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else 'names_test.csv.gz'
with gzip.open(filename,'rt') as f:#读取数据集
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)#读取每行数据,最终返回的结果为元组(name,country)形式
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]#从rows中去除第0个元素,也就是name
self.len = len(self.names)#记录一下样本的数量
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]
self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries)))#同样,获取country信息,将来作为names的标签进行使用
"""
set(self.countries) #将列表变成一个集合,因为集合里面不重复,也就是去重
sorted(set(self.countries)) #排序
list(sorted(set(self.countries))) #最后变成一个列表形式
"""
self.country_dict = self.getCounrtyDict()#此时的列表中仍是英文名字,需要通过词典转换为序列索引
self.country_num = len(self.country_list)
def __getitem__(self,index):
return self.names[index],self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]
"""
self.names[index] #拿到姓名
self.countries[index] #拿到国籍
self.country_dict[self.countries[index]] #根据国籍,从字典中获取对应的索引
countries(key)和index(value) 相当于字典中的键值对
"""
def __len__(self):
return self.len
def getCounrtyDict(self):
country_dict = dict()#定义一个空字典
for idx,country_name in enumerate(self.country_list,0):#遍历
country_dict[country_name] = idx#构造键值对
return country_dict#返回对应的字典
def idx2country(self,index):#根据索引,返回国籍的字符串
return self.country_list[index]#例如输入的是名字,得到分类是9,根据9,来返回对应的字符串,即所属的国籍
def getCountriesNum(self):#看下到底有多少个国籍
return self.country_num#返回国籍数量
3,数据准备
参数定义
hidden_size = 100#隐藏层是100维度
batch_size = 256#每批256个姓名样本
n_layer = 2#GRU使用了2层
n_epochs = 100#训练100次
n_chars = 128#因为ASCII共128个,故使用张量128来进行表示输入样本
use_gpu = False#不使用GPU
定义训练集和测试集以及对应的dataloader
n_country总共国籍类别的数量,将来决定模型最终的输出维度大小
trainset = NameDataset(is_train_set=True)
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True)
testset = NameDataset(is_train_set=False)
testloader = DataLoader(testset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False)
n_country = trainset.getCountriesNum()#决定模型最终的输出维度大小
4,模型设计
模型大体架构
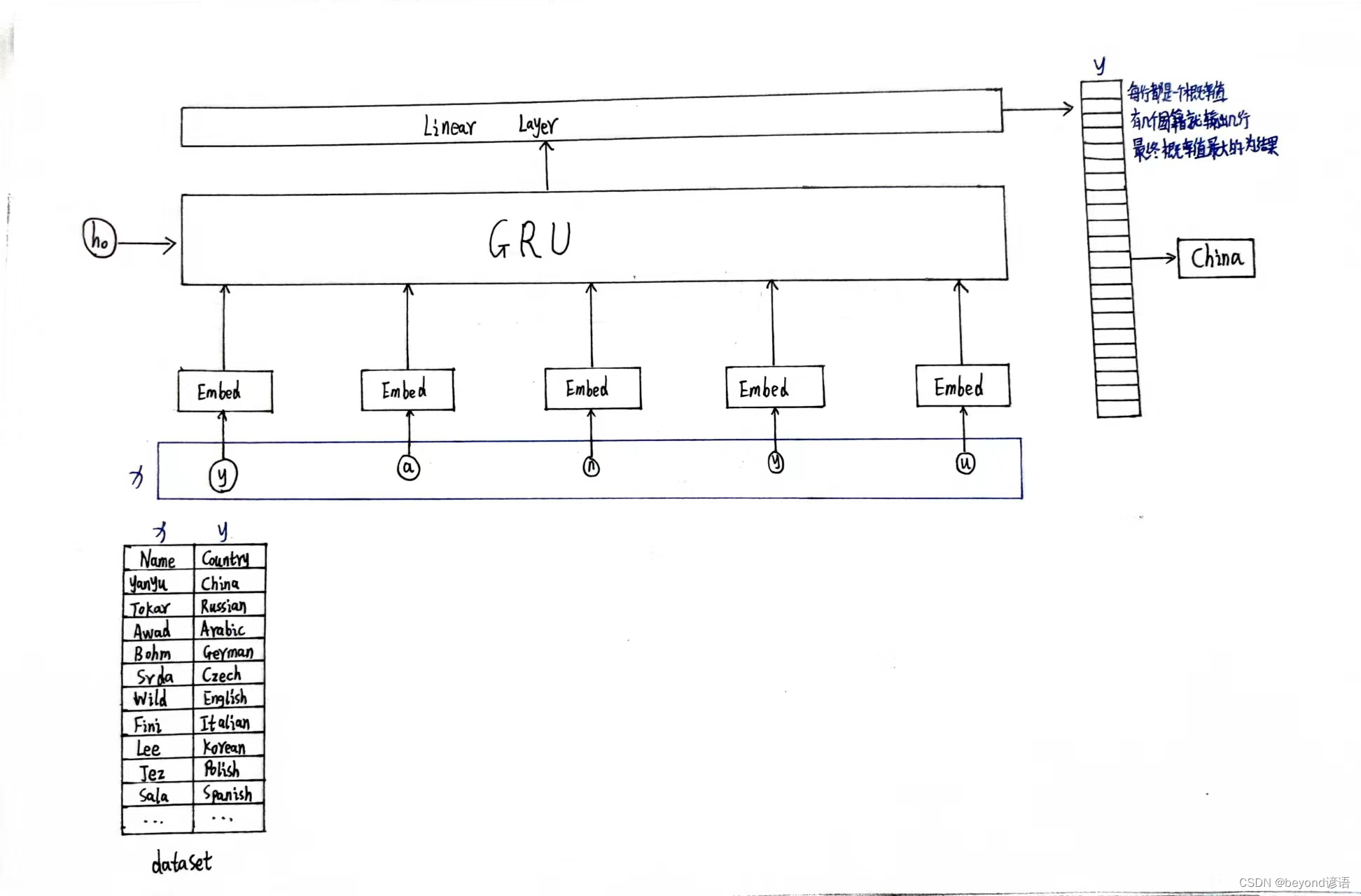
①初始化函数def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size,output_size,n_layers=1,bidirectional=True):解释:
GRU使用:hidden_size、n_layers、bidirectional
embedd嵌入层使用:input_sizeinput_size、hidden_size
embedding层输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize)
embedding层输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
GRU输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
GRU输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize * nDirections)
其中bidirectional确定是否是双向循环神经网络,单向是1,双向是2
在线性层的时候需要将循环神经网络转换为输出的维度
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size*self.n_directions,output_size)
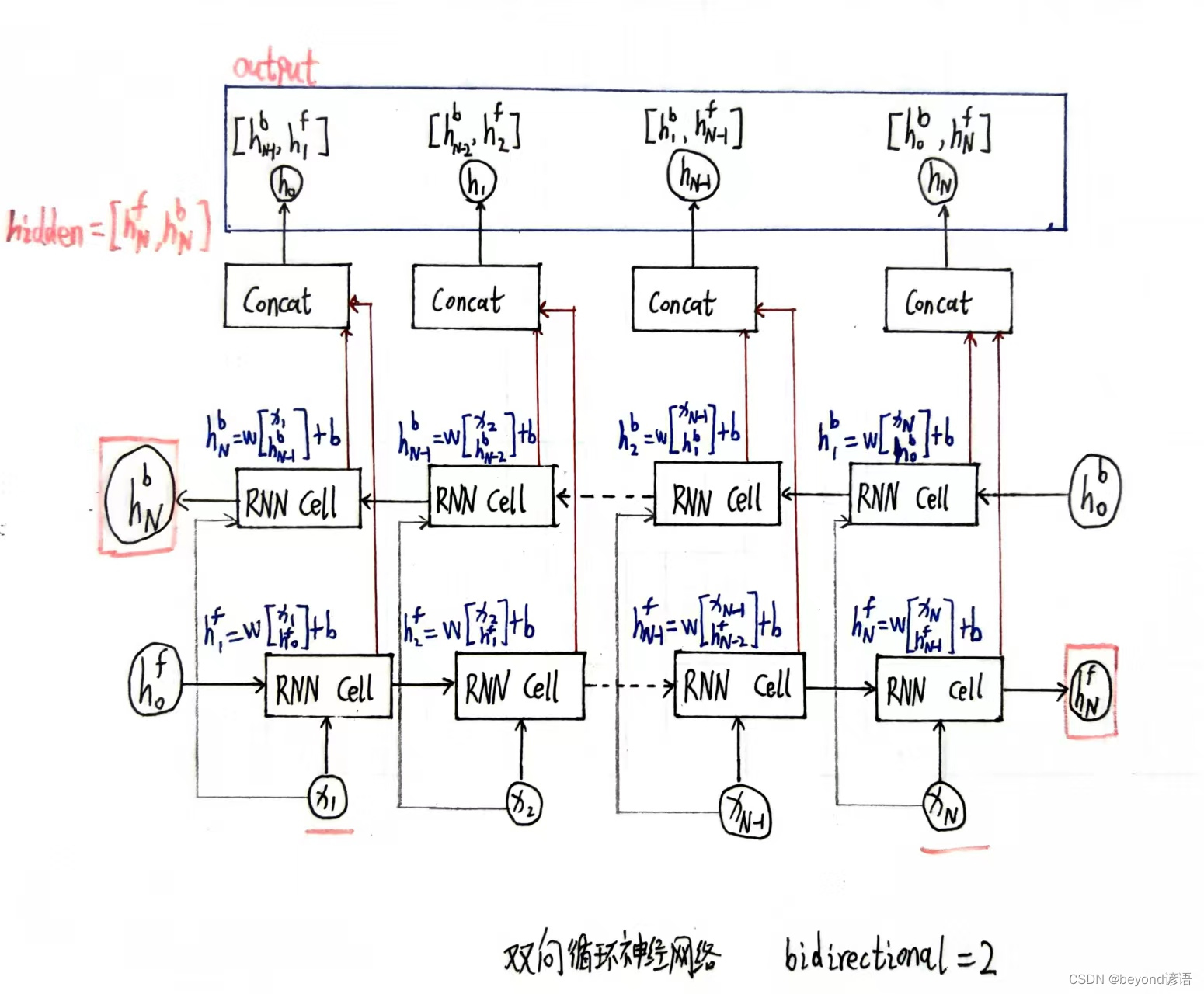
②构建h0函数def _init_hidden(self,batch_size):解释:
根据输入的batchsize来构建全零的初始的隐藏层
③反向传播函数def forward(self,input,seq_lengths):解释:
矩阵转置input = input.t()transpose,将原来的**(batch×seqlen)转换成(seqlen×batch)**
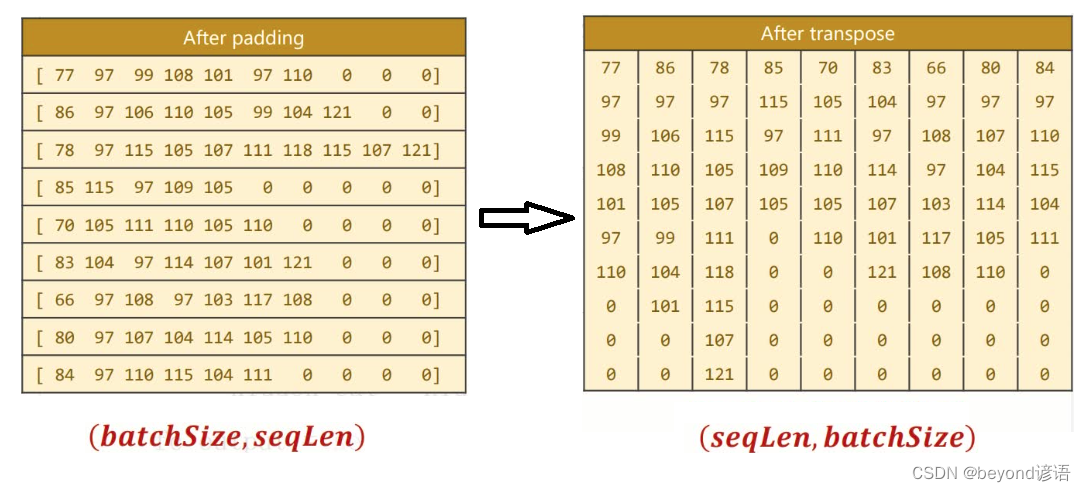
batch_size = input.size(1)保留batchsize,为了方便将来构造最初始的隐藏层
扔到embedding层做嵌入embedding = self.embedding(input)
embedding维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
pack_padded_sequence(embedding,seq_lengths)
gru_input维度为:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
根据判断是否是双向的循环神经网络,最终进行拼接fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat)
完整代码如下:
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size,output_size,n_layers=1,bidirectional=True):
"""
GRU使用:hidden_size、n_layers、bidirectional
embedd嵌入层使用:input_sizeinput_size、hidden_size
"""
super(RNNClassifier,self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1#RNN是单向还是双向,单向是1,双向是2
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size,hidden_size)
"""
embedding层
输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize)
输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
"""
self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size,hidden_size,n_layers,bidirectional=bidirectional)#bidirectional单向还是双向循环神经网络
"""
GRU
输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize * nDirections)
"""
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size*self.n_directions,output_size)
def _init_hidden(self,batch_size):#创建全零的初始的隐藏层
hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions,batch_size,self.hidden_size)
return create_tensor(hidden)
def forward(self,input,seq_lengths):
input = input.t()#矩阵的转置,transpose,将原来的(batch×seqlen)转换成(seqlen×batch)
batch_size = input.size(1)#保留batchsize
hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size)
embedding = self.embedding(input)#embedding维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
gru_input = pack_padded_sequence(embedding,seq_lengths)#gru_input维度为:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
output,hidden = self.gru(gru_input,hidden)
if self.n_directions == 2:
hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1],hidden[-2]],dim=1)
else:
hidden_cat = hidden[-1]
fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat)
return fc_output
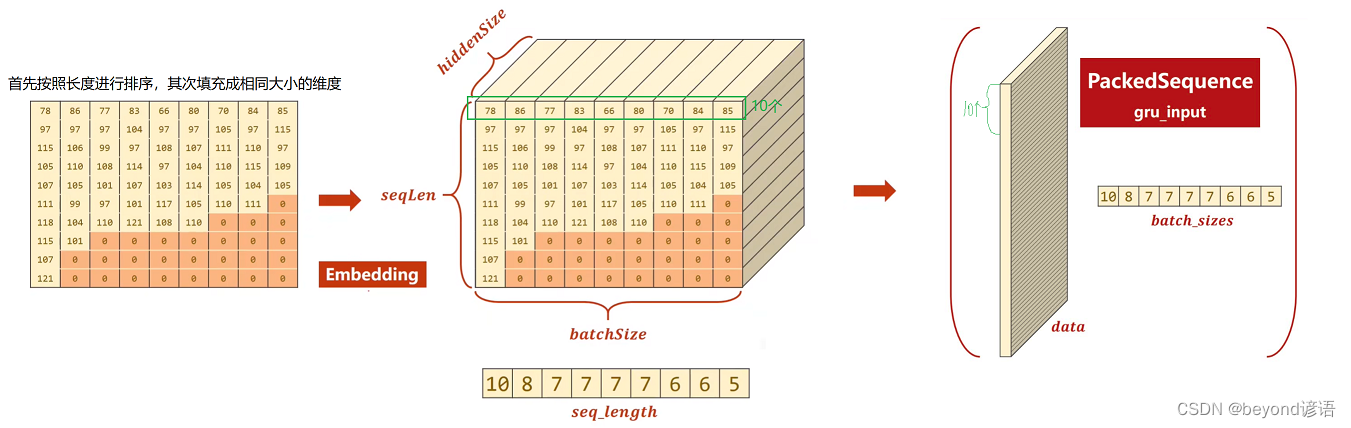
5,制作姓名字典序列
一个是姓名字符串所对应的ASCII码值列表
另一个是存储有用姓名的长度

详细步骤如下:
姓名字符串—>分割每个字符—>根据ASCII码值进行转换—>加边统一维度—>跟根据字符的长度进行排序

①函数name2list(name)解释:
将每个姓名都变成一个列表,给一个字符串姓名,将其值转换为ASCII码值
return arr,len(arr)将来返回的是一个元组,一个是列表本身,一个是列表长度
②函数def create_tensor(tensor):解释:
是否要使用GPU进行训练
③函数def make_tensors(names,countries):解释:
获得姓名序列name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]
转换序列的长度seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths])
先生成一个全零的张量
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences),seq_lengths.max()).long()
通过复制操作,将数据覆盖原先的零
seq_tensor[idx,:seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
按照序列的长度进行排序seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0,descending=True)
返回排完序之后的序列seq_lengths,和排完序之后对应的索引值perm_idx
完整代码如下:
def name2list(name):#将每个姓名都转化为欸一个列表
arr = [ord(c) for c in name]
return arr,len(arr)#返回一个元组,一个是列表本身,一个是列表长度
def create_tensor(tensor):
if use_gpu:
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
tensor = tensor.to(device)
return tensor
def make_tensors(names,countries):
sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names]
name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]
seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths])
countries = countries.long()
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences),seq_lengths.max()).long()#全零
for idx,(seq,seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences,seq_lengths),0):#把值贴上去
seq_tensor[idx,:seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0,descending=True)#按照序列的长度进行排序
seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx]
countries = countries[perm_idx]
return create_tensor(seq_tensor),create_tensor(seq_lengths),create_tensor(countries)
6,训练函数
def trainModel():
total_loss = 0
for i,(names,countries) in enumerate(trainloader,1):
inputs,seq_lengths,target = make_tensors(names,countries)
output = classifier(inputs,seq_lengths)
loss = lossf(output,target)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if i%10 == 0:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch}',end='')
print(f'[{i * len(inputs)}/{len(trainset)}]',end='')
print(f'loss={total_loss / (i*len(inputs))}')
return total_loss
7,测试函数
def testModel():
correct = 0
total = len(testset)
print("evaluating trained model ...")
with torch.no_grad():
for i,(names,countries) in enumerate(testloader,1):
inputs,seq_lengths,target = make_tensors(names,countries)
output = classifier(inputs,seq_lengths)
pred = output.max(dim=1,keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
percent = '%.2f'%(100*correct/total)
print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct}/{total} {percent}%')
return correct/total
8,计时函数
def time_since(since):
s = time.time() - since
# time.time() 返回的是当前时间,秒为单位
# s / 60 变成分钟
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return "%dm %ds"%(m,s)
9,主函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
classifier = RNNClassifier(n_chars,hidden_size,n_country,n_layer) #创建分类器
"""
n_chars 字符数量,输入的是英文字母,需要转换为one-hot向量,也就是整个字母表一共有多少个元素
hidden_size 隐藏层数量,GRU将来输出的隐层的维度
n_country 一共有多少个分类,也就是一共有多少个国家
n_layer 使用几层GRU
"""
if use_gpu: #是否使用GPU
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
classifier.to(device)
lossf = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() #分类问题,使用交叉熵损失函数就够了
optim = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(),lr=0.00001) #优化器使用adam
start = time.time() #计时,看看训练的时间有多长,距离开始训练已经过去了多少时间
print("Training for %d epochs..." %n_epochs)
acc_list = []
for epoch in range(1,n_epochs+1):
trainModel() #训练和测试进行封装到两个函数中
acc = testModel()
acc_list.append(acc) #测试的结果添加到列表中,方便后续的绘图操作
三、项目完整代码实现
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import gzip
import csv
import time
import math
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence, pack_padded_sequence, pack_sequence, pad_packed_sequence
hidden_size = 100#隐藏层是100维度
batch_size = 256#每批256个样本
n_layer = 2#GRU使用了2层
n_epochs = 100#训练100次
n_chars = 128#因为ASCII共128个,故使用张量128来进行表示输入样本
use_gpu = False#不使用GPU
def time_since(since):
s = time.time() - since
# time.time() 返回的是当前时间,秒为单位
# s / 60 变成分钟
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return "%dm %ds"%(m,s)
class NameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,is_train_set=True): #is_train_set 指定是否是训练集
filename = 'names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else 'names_test.csv.gz'
with gzip.open(filename,'rt') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)#读取每行数据,最终返回的结果为元组(name,country)形式
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]#从rows中去除第0个元素,也就是name
self.len = len(self.names)#记录一下样本的数量
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]
self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries)))#同样,获取country信息,将来作为names的标签进行使用
"""
set(self.countries) #将列表变成一个集合,因为集合里面不重复,也就是去重
sorted(set(self.countries)) #排序
list(sorted(set(self.countries))) #最后变成一个列表形式
"""
self.country_dict = self.getCounrtyDict()#此时的列表中仍是英文名字,需要通过词典转换为序列索引
self.country_num = len(self.country_list)
def __getitem__(self,index):
return self.names[index],self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]
"""
self.names[index] #拿到姓名
self.countries[index] #拿到国籍
self.country_dict[self.countries[index]] #根据国籍,从字典中获取对应的索引
countries(key)和index(value) 相当于字典中的键值对
"""
def __len__(self):
return self.len
def getCounrtyDict(self):
country_dict = dict()#定义一个空字典
for idx,country_name in enumerate(self.country_list,0):#遍历
country_dict[country_name] = idx#构造键值对
return country_dict#返回对应的字典
def idx2country(self,index):#根据索引,返回国籍的字符串
return self.country_list[index]#例如输入的是名字,得到分类是9,根据9,来返回对应的字符串,即所属的国籍
def getCountriesNum(self):#看下到底有多少个国籍
return self.country_num#返回国籍数量
trainset = NameDataset(is_train_set=True)
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True)
testset = NameDataset(is_train_set=False)
testloader = DataLoader(testset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False)
n_country = trainset.getCountriesNum()#决定模型最终的输出维度大小
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size,output_size,n_layers=1,bidirectional=True):
"""
GRU使用:hidden_size、n_layers、bidirectional
embedd嵌入层使用:input_sizeinput_size、hidden_size
"""
super(RNNClassifier,self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1#RNN是单向还是双向,单向是1,双向是2
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size,hidden_size)
"""
embedding层
输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize)
输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
"""
self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size,hidden_size,n_layers,bidirectional=bidirectional)#bidirectional单向还是双向循环神经网络
"""
GRU
输入维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
输出维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize * nDirections)
"""
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size*self.n_directions,output_size)
def _init_hidden(self,batch_size):#创建全零的初始的隐藏层
hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions,batch_size,self.hidden_size)
return create_tensor(hidden)
def forward(self,input,seq_lengths):
input = input.t()#矩阵的转置,transpose,将原来的(batch×seqlen)转换成(seqlen×batch)
batch_size = input.size(1)#保留batchsize
hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size)
embedding = self.embedding(input)#embedding维度:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
gru_input = pack_padded_sequence(embedding,seq_lengths)#gru_input维度为:(seqLen,batchsize,hiddensize)
output,hidden = self.gru(gru_input,hidden)
if self.n_directions == 2:
hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1],hidden[-2]],dim=1)
else:
hidden_cat = hidden[-1]
fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat)
return fc_output
def make_tensors(names,countries):
sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names]
name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]
seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths])
countries = countries.long()
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences),seq_lengths.max()).long()#全零
for idx,(seq,seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences,seq_lengths),0):#把值贴上去
seq_tensor[idx,:seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0,descending=True)#按照序列的长度进行排序
seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx]
countries = countries[perm_idx]
return create_tensor(seq_tensor),create_tensor(seq_lengths),create_tensor(countries)
def create_tensor(tensor):
if use_gpu:
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
tensor = tensor.to(device)
return tensor
def name2list(name):#将每个姓名都转化为欸一个列表
arr = [ord(c) for c in name]
return arr,len(arr)#返回一个元组,一个是列表本身,一个是列表长度
def trainModel():
total_loss = 0
for i,(names,countries) in enumerate(trainloader,1):
inputs,seq_lengths,target = make_tensors(names,countries)
output = classifier(inputs,seq_lengths)
loss = lossf(output,target)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if i%10 == 0:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch}',end='')
print(f'[{i * len(inputs)}/{len(trainset)}]',end='')
print(f'loss={total_loss / (i*len(inputs))}')
return total_loss
def testModel():
correct = 0
total = len(testset)
print("evaluating trained model ...")
with torch.no_grad():
for i,(names,countries) in enumerate(testloader,1):
inputs,seq_lengths,target = make_tensors(names,countries)
output = classifier(inputs,seq_lengths)
pred = output.max(dim=1,keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
percent = '%.2f'%(100*correct/total)
print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct}/{total} {percent}%')
return correct/total
if __name__ == '__main__':
classifier = RNNClassifier(n_chars,hidden_size,n_country,n_layer) #创建分类器
"""
n_chars 字符数量,输入的是英文字母,需要转换为one-hot向量,也就是整个字母表一共有多少个元素
hidden_size 隐藏层数量,GRU将来输出的隐层的维度
n_country 一共有多少个分类,也就是一共有多少个国家
n_layer 使用几层GRU
"""
if use_gpu: #是否使用GPU
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
classifier.to(device)
lossf = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() #分类问题,使用交叉熵损失函数就够了
optim = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(),lr=0.00001) #优化器使用adam
start = time.time() #计时,看看训练的时间有多长,距离开始训练已经过去了多少时间
print("Training for %d epochs..." %n_epochs)
acc_list = []
for epoch in range(1,n_epochs+1):
trainModel() #训练和测试进行封装到两个函数中
acc = testModel()
acc_list.append(acc) #测试的结果添加到列表中,方便后续的绘图操作
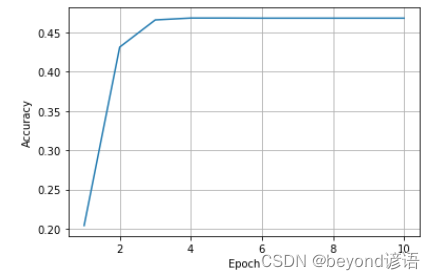
四、绘图
epoch = np.arange(1,len(acc_list)+1,1)
acc_list = np.array(acc_list)
plt.plot(epoch,acc_list)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.grid()
plt.show()









![[ 应急响应基础篇 ] 使用 Process Explorer 进程分析工具分析系统进程(附Process Explorer安装教程)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7bba58ffa6b84b8bb1ad14372ad398f1.png)