目录
一、介绍
二、前期准备
二、模型
三、训练运行
3.1训练
3.2指定图片进行预测
🍨 本文为[🔗365天深度学习训练营]内部限免文章(版权归 *K同学啊* 所有)
🍖 作者:[K同学啊]
📌 本周任务:
●1. 在DenseNet系列算法中插入SE-Net通道注意力机制,并完成猴痘病识别(数据集链接)
●2. 改进思路是否可以迁移到其他地方呢
●3. 测试集accuracy到达89%(拔高,可选)
一、介绍
论文:(搜名字也能看)Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks.pdf
这篇文章介绍了一种新的神经网络结构单元,称为“Squeeze-and-Excitation”(SE)块,它通过显式地建模通道之间的相互依赖关系来自适应地重新校准通道特征响应。这种方法可以提高卷积神经网络的表示能力,并且可以在不同数据集上实现极其有效的泛化。作者还展示了SE块在现有最先进CNNs中带来了显著的性能提升,而只需稍微增加计算成本。
SE-Net 是 ImageNet 2017(ImageNet 收官赛)的冠军模型,是由WMW团队发布。具有复杂度低,参数少和计算量小的优点。且SENet 思路很简单,很容易扩展到已有网络结构如 Inception 和 ResNet 中。
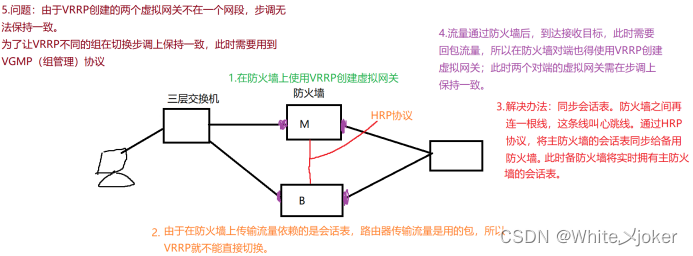
已经有很多工作在空间维度上来提升网络的性能,如 Inception 等,而 SENet 将关注点放在了特征通道之间的关系上。其具体策略为:通过学习的方式来自动获取到每个特征通道的重要程度,然后依照这个重要程度去提升有用的特征并抑制对当前任务用处不大的特征,这又叫做“特征重标定”策略。具体的 SE 模块如下图所示:

首先 Squeeze 操作,我们顺着空间维度来进行特征压缩,此操作通常采用采用 global average pooling 来实现。得到了全局描述特征后,进行 Excitation 操作来抓取特征通道之间的关系。最后是一个 Scale 的操作,我们将 Excitation 的输出的权重看做是经过特征选择后的每个特征通道的重要性,然后通过乘法逐通道加权到先前的特征上,完成在通道维度上的对原始特征的重标定,从而使得模型对各个通道的特征更有辨别能力。
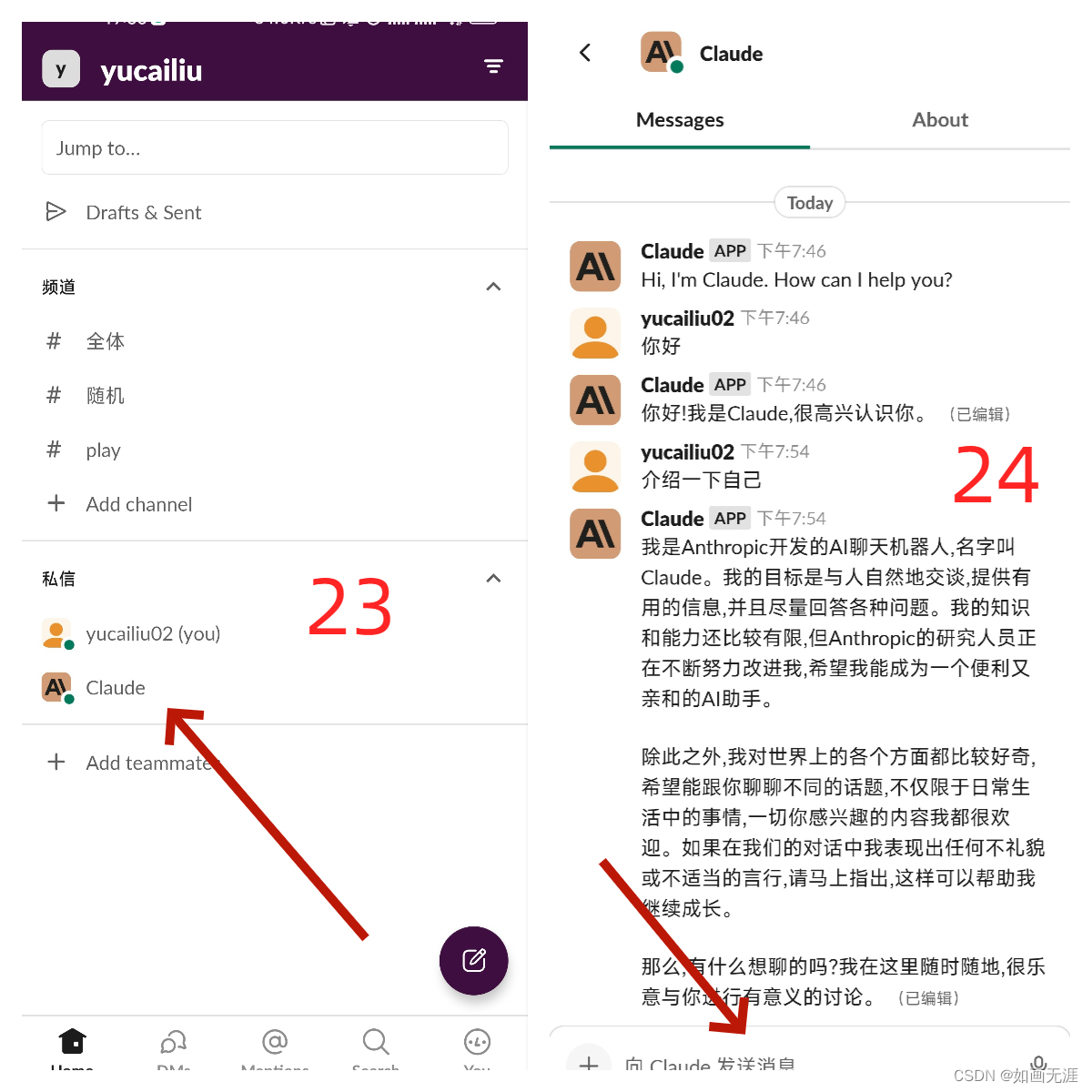
SE模块应用分析:
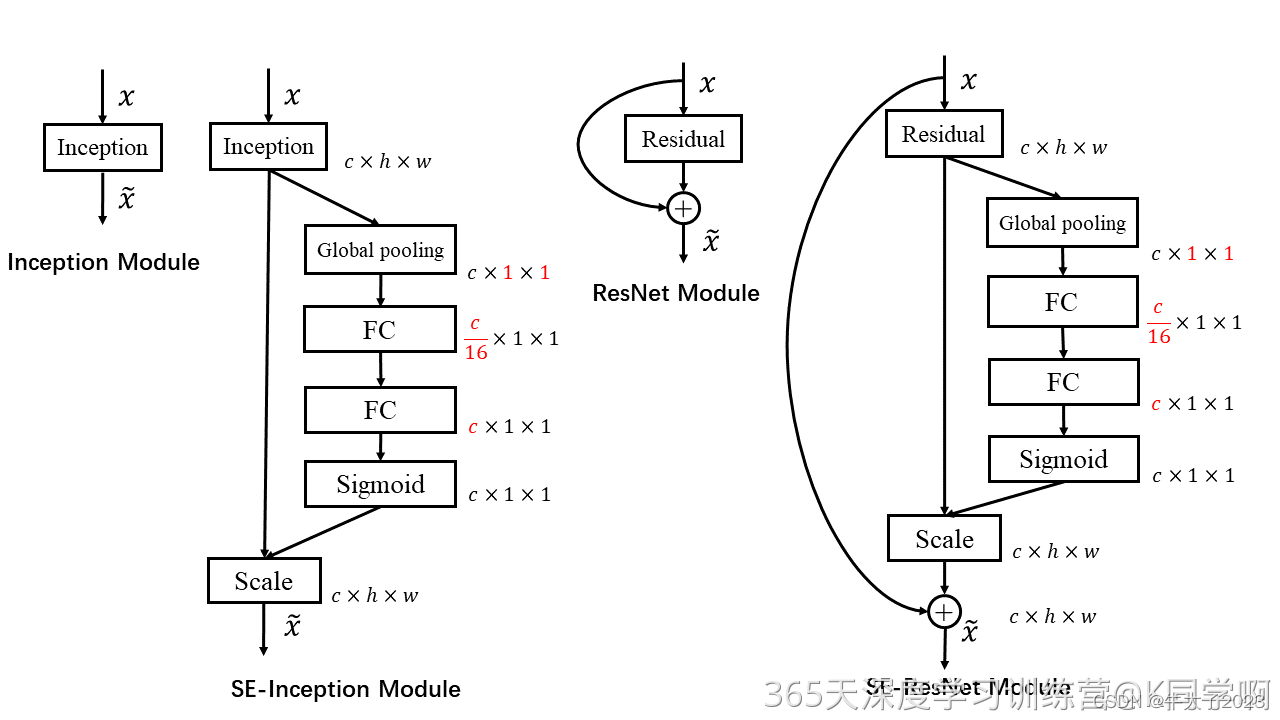
上图分别是将 SE 模块嵌入到 Inception 结构与 ResNet 中的示例,方框旁边的维度信息代表该层的输出,r 表示 Excitation 操作中的降维系数。
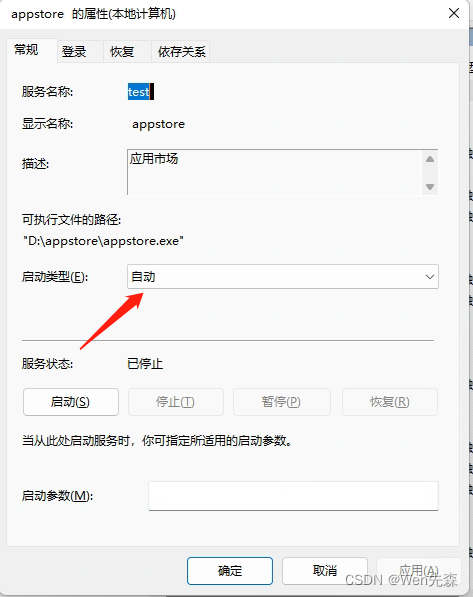
SE模型效果对比:
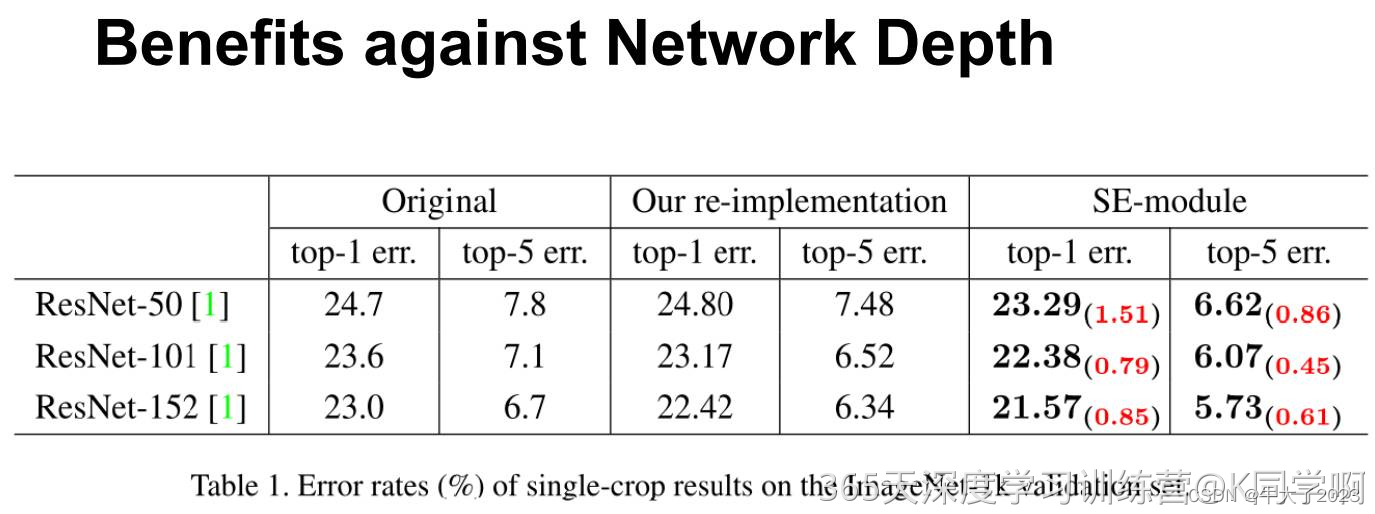
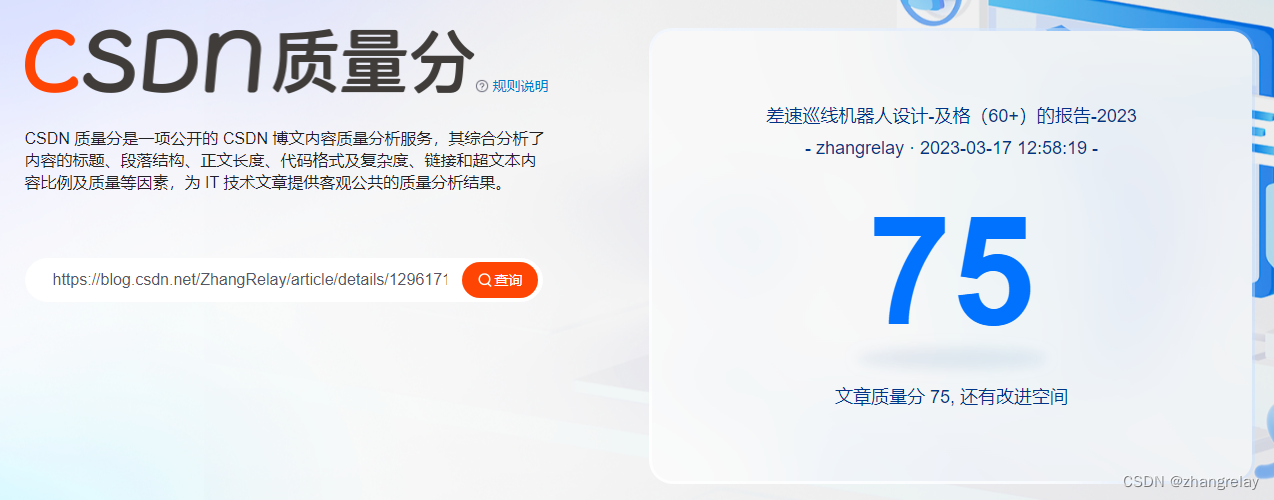
可以看出,SE-ResNets 在各种深度上都远远超过了其对应的没有SE的结构版本的精度,这说明无论网络的深度如何,SE模块都能够给网络带来性能上的增益。值得一提的是,SE-ResNet-50 可以达到和ResNet-101 一样的精度;更甚,SE-ResNet-101 远远地超过了更深的ResNet-152。
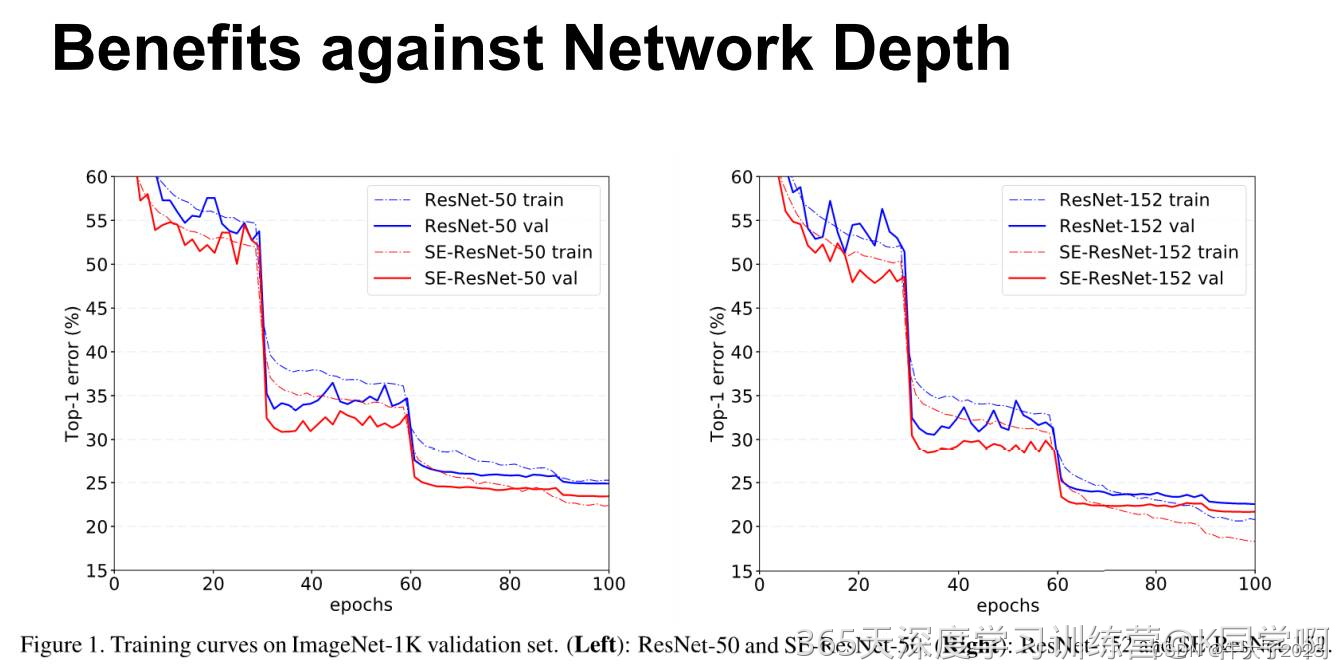
上图展示了ResNet-50 和 ResNet-152 以及它们对应的嵌入SE模块的网络在ImageNet上的训练过程,可以明显地看出加入了SE模块的网络收敛到更低的错误率上。
二、前期准备
大致模板和以前一样,以后不再详细列,距离可见:深度学习第J4周:ResNet与DenseNet结合探索_牛大了2023的博客-CSDN博客
配置gpu+导入数据集
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
data_dir = './data/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[1] for path in data_paths]
print(classeNames)
image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*')))
print("图片总数为:", image_count)数据预处理+划分数据集
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("./data/", transform=train_transforms)
print(total_data.class_to_idx)
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
batch_size = 32
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0)
for X, y in test_dl:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
break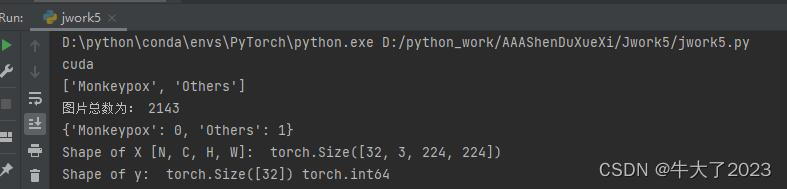
二、模型
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch.utils.checkpoint as cp
def _bn_function_factory(norm, relu, conv):
def bn_function(*inputs):
concated_features = torch.cat(inputs, 1)
bottleneck_output = conv(relu(norm(concated_features)))
return bottleneck_output
return bn_function
class _DenseLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_input_features, growth_rate, bn_size, drop_rate, efficient=False):
super(_DenseLayer, self).__init__()
self.add_module('norm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_input_features)),
self.add_module('relu1', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
self.add_module('conv1', nn.Conv2d(num_input_features, bn_size * growth_rate,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)),
self.add_module('norm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate)),
self.add_module('relu2', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
self.add_module('conv2', nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate, growth_rate,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)),
self.add_module('SE_Block', SE_Block(growth_rate, reduction=16))
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.efficient = efficient
def forward(self, *prev_features):
bn_function = _bn_function_factory(self.norm1, self.relu1, self.conv1)
if self.efficient and any(prev_feature.requires_grad for prev_feature in prev_features):
bottleneck_output = cp.checkpoint(bn_function, *prev_features)
else:
bottleneck_output = bn_function(*prev_features)
new_features = self.SE_Block(self.conv2(self.relu2(self.norm2(bottleneck_output))))
if self.drop_rate > 0:
new_features = F.dropout(new_features, p=self.drop_rate, training=self.training)
return new_features
class _Transition(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, num_input_features, num_output_features):
super(_Transition, self).__init__()
self.add_module('norm', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_input_features))
self.add_module('relu', nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(num_input_features, num_output_features,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False))
self.add_module('pool', nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
class _DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_layers, num_input_features, bn_size, growth_rate, drop_rate, efficient=False):
super(_DenseBlock, self).__init__()
for i in range(num_layers):
layer = _DenseLayer(
num_input_features + i * growth_rate,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
bn_size=bn_size,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
efficient=efficient,
)
self.add_module('denselayer%d' % (i + 1), layer)
def forward(self, init_features):
features = [init_features]
for name, layer in self.named_children():
new_features = layer(*features)
features.append(new_features)
return torch.cat(features, 1)
class SE_Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ch_in, reduction=16):
super(SE_Block, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) # 全局自适应池化
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(ch_in, ch_in // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(ch_in // reduction, ch_in, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c) # squeeze操作
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1) # FC获取通道注意力权重,是具有全局信息的
return x * y.expand_as(x) # 注意力作用每一个通道上
class DenseNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, growth_rate, block_config, num_init_features=24, compression=0.5, bn_size=4, drop_rate=0,
num_classes=10, small_inputs=True, efficient=False):
super(DenseNet, self).__init__()
assert 0 < compression <= 1, 'compression of densenet should be between 0 and 1'
# First convolution
if small_inputs:
self.features = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv0', nn.Conv2d(3, num_init_features, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)),
]))
else:
self.features = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv0', nn.Conv2d(3, num_init_features, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)),
]))
self.features.add_module('norm0', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_init_features))
self.features.add_module('relu0', nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.features.add_module('pool0', nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
ceil_mode=False))
# Each denseblock
num_features = num_init_features
for i, num_layers in enumerate(block_config):
block = _DenseBlock(
num_layers=num_layers,
num_input_features=num_features,
bn_size=bn_size,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
efficient=efficient,
)
self.features.add_module('denseblock%d' % (i + 1), block)
num_features = num_features + num_layers * growth_rate
if i != len(block_config) - 1:
trans = _Transition(num_input_features=num_features,
num_output_features=int(num_features * compression))
self.features.add_module('transition%d' % (i + 1), trans)
num_features = int(num_features * compression)
# self.features.add_module('SE_Block%d' % (i + 1),SE_Block(num_features, reduction=16))
# Final batch norm
self.features.add_module('norm_final', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features))
# Linear layer
self.classifier = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
features = self.features(x)
out = F.relu(features, inplace=True)
out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(out, (1, 1))
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.classifier(out)
return out打印模型:
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)
model = DenseNet(growth_rate=32, block_config=(6,12,24,16), compression=0.5,
num_init_features=64, bn_size=4, drop_rate=0.2,num_classes=4,efficient=True)
out = model(x)
print('out.shape: ', out.shape)
print(out)
model.to(device)
# 统计模型参数量以及其他指标
import torchsummary as summary
summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))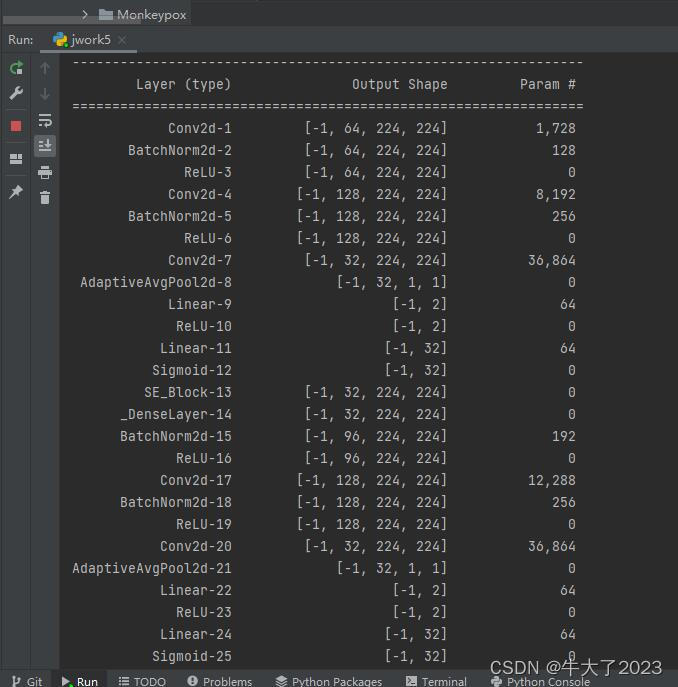
三、训练运行
3.1训练
代码和以前的差不多,不再细说
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss跑十轮并保存模型
import copy
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
epochs = 10
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
best_acc = 0 # 设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 更新学习率(使用自定义学习率时使用)
# adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, learn_rate)
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
# scheduler.step() # 更新学习率(调用官方动态学习率接口时使用)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
# 保存最佳模型到 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch + 1, epoch_train_acc * 100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc * 100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
PATH = './best_model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
print('Done')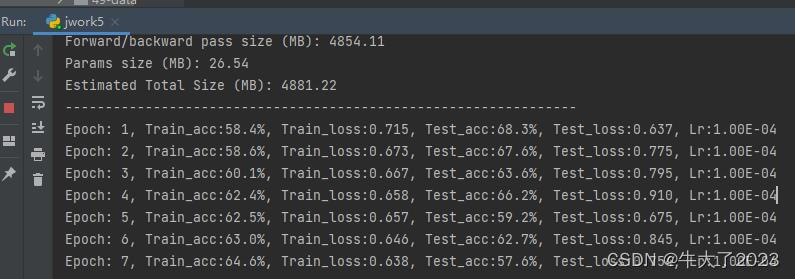
打印训练记录图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # 忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 # 分辨率
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()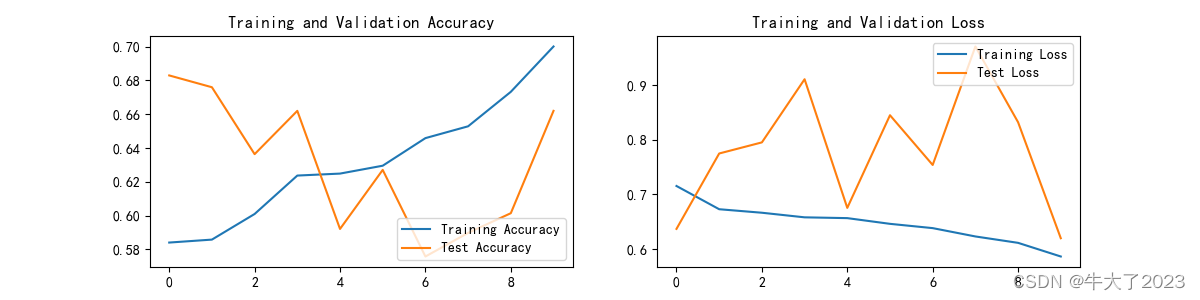
还是这个报错:RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 54.00 MiB (GPU 0; 4.00 G。原因是我的显卡太lj了(3050ti),GPU算力不够,被迫把batchsize从32调低为2了
3.2指定图片进行预测
把训练部分注释掉
from PIL import Image
classes = list(total_data.class_to_idx)
def predict_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_img = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
plt.imshow(test_img) # 展示预测的图片
test_img = transform(test_img)
img = test_img.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(img)
_, pred = torch.max(output, 1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print(f'预测结果是:{pred_class}')
# 预测训练集中的某张照片
predict_one_image(image_path='./data/Monkeypox/M01_01_00.jpg',
model=model,
transform=train_transforms,
classes=classes)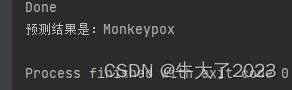

![[oeasy]python0132_[趣味拓展]emoji_表情符号_抽象话_由来_流汗黄豆](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f825b205f79a240e80dff43d6763d507.png)