目录
1. Neural Networks
1.1 Visualizing the data
1.2 Model representation
1.3 Feedforward and cost function
1.4 Regularized cost function
2. Backpropagation
2.1 Sigmoid gradient
2.2 Random initialization
2.3 Backpropagation
2.4 Gradient Checking
2.5 Regularized Neural Networks
2.6 Learning parameters using fmincg
1. Neural Networks
内容:我们将使用反向传播来学习神经网络所需的参数(权重)。
1.1 Visualizing the data
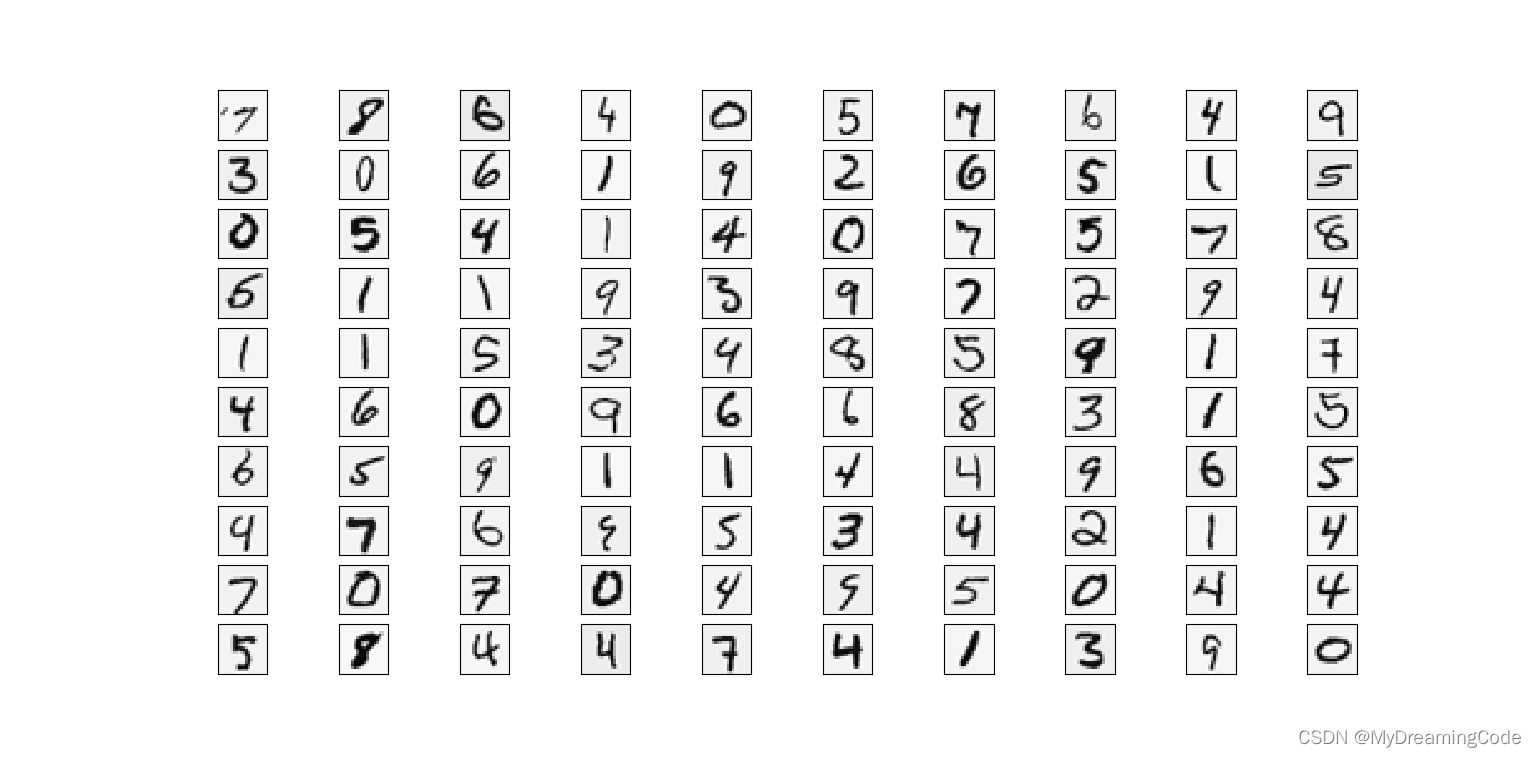
内容:一共有5000个训练集,X为5000×400维度,每行样本数据表示一个由20×20像素组成的手写数字识别图像。y为每个样本的真实标签(注意:0对应的标签为10),维度为5000×1。
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
print(X.shape, y.shape, Theta1.shape, Theta2.shape)
# (5000, 400) (5000, 1) (25, 401) (10, 26)
plot.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
def Plot(X):
sample_idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(X.shape[0]), 100) # 从0-4999中随机抽取100个数
sample_image = X[sample_idx, :]
fig, axisArr = plt.subplots(nrows=10, ncols=10, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10, 10))
for r in range(10):
for c in range(10):
axisArr[r, c].matshow(sample_image[r * 10 + c].reshape(20, 20).T, cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
from plot import * # 绘图
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
Plot(X)
1.2 Model representation
内容:Theta1:25×401 Theta2:10 ×26

1.3 Feedforward and cost function
内容:根据已给出的Theta1和Theta2进行前向传播以及计算代价函数。特别注意,这里真实标签y需要重新编码一下,可更新为5000×10维度的矩阵,用于计算代价函数。
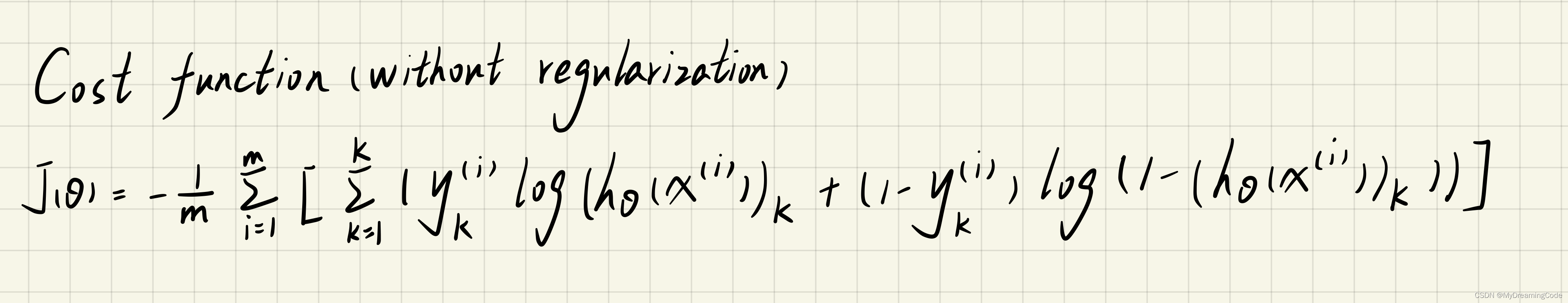
sigmoid.py
import numpy as np
def Sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
forward_propagate.py
import numpy as np
from sigmoid import *
def forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X):
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=np.ones(X.shape[0]), axis=1)
a1 = X
z2 = a1 * Theta1.T
a2 = Sigmoid(z2)
a2 = np.insert(a2, 0, values=np.ones(a2.shape[0]), axis=1)
z3 = a2 * Theta2.T
h_theta = Sigmoid(z3)
return h_theta
cost_function.py
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from forward_propagate import * # 前向传播
def costFunction(Theta1, Theta2, X, y):
X = np.matrix(X)
Theta1 = np.matrix(Theta1)
Theta2 = np.matrix(Theta2)
m = X.shape[0]
h_theta = forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X)
# 对y标签进行编码,使其变成5000×10维度的矩阵
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
# print(y[0], y_onehot[0, :]) # [10] [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
first = np.sum(np.multiply(y_onehot, np.log(h_theta)), axis=1)
second = np.sum(np.multiply(1 - y_onehot, np.log(1 - h_theta)), axis=1)
J_theta = -np.sum(first + second) / m
return J_theta
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
from plot import * # 绘图
from cost_function import * # 代价函数
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
print(costFunction(Theta1, Theta2, X, y))
0.2876291651613189
1.4 Regularized cost function
内容:将代价函数进行正则化
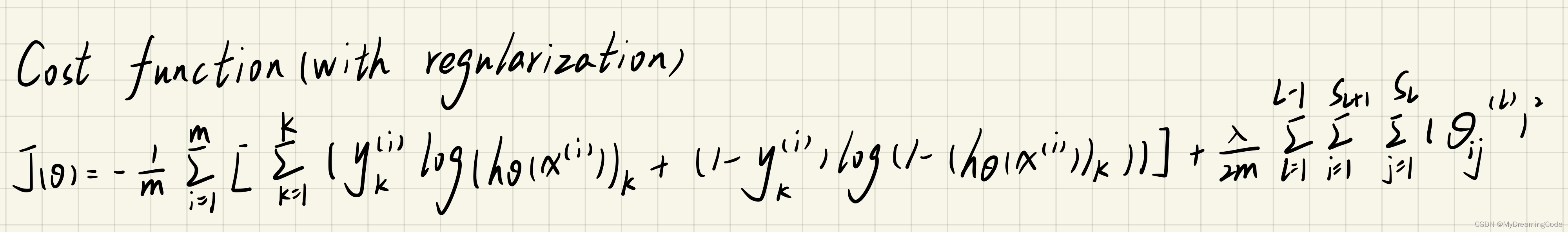
cost_function_reg.py
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from forward_propagate import * # 前向传播
def costFunctionReg(Theta1, Theta2, X, y, learningRate):
X = np.matrix(X)
Theta1 = np.matrix(Theta1)
Theta2 = np.matrix(Theta2)
m = X.shape[0]
h_theta = forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X)
# 对y标签进行编码,使其变成5000×10维度的矩阵
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
first = np.sum(np.multiply(y_onehot, np.log(h_theta)), axis=1)
second = np.sum(np.multiply(1 - y_onehot, np.log(1 - h_theta)), axis=1)
reg = np.sum(np.power(Theta1[:, 1:], 2)) + np.sum(np.power(Theta2[:, 1:], 2))
J_theta = -np.sum(first + second) / m + learningRate * reg / (2 * m)
return J_theta
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
from plot import * # 绘图
from cost_function_reg import * # 代价函数
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
learningRate = 1
print(costFunctionReg(Theta1, Theta2, X, y, learningRate))
0.38376985909092365
2. Backpropagation
内容:利用反向传播来计算神经网络代价函数的梯度,从而将代价函数值最小化。
2.1 Sigmoid gradient
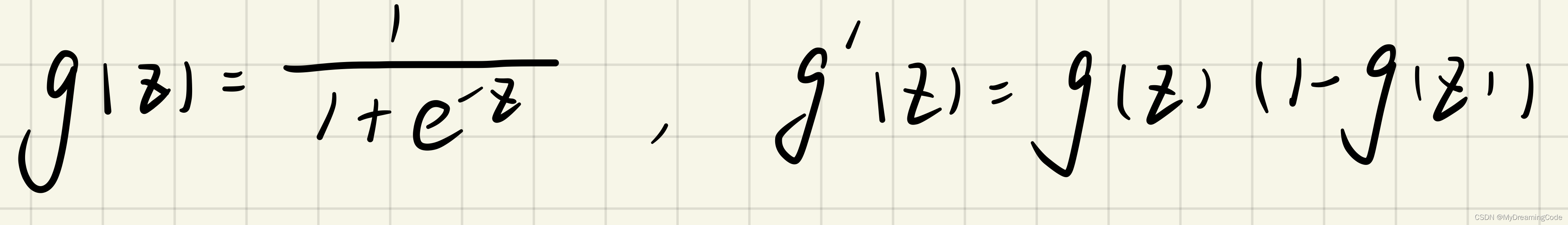
sigmoid_gradient.py
import numpy as np
from sigmoid import *
def sigmoidGradient(z):
return np.multiply(Sigmoid(z), 1 - Sigmoid(z))
# print(sigmoidGradient(0)) # 0.25
2.2 Random initialization
内容:初始化theta的值。Lin为l层的单元数,Lout为l+1层的单元数。
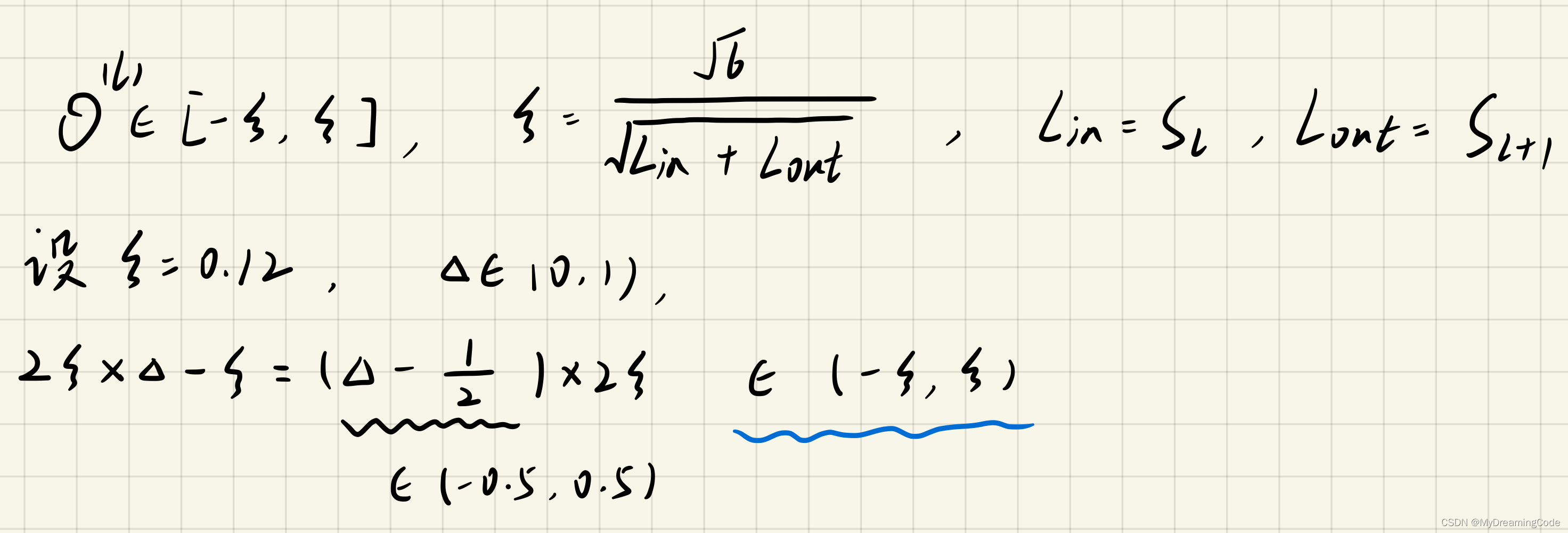
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
from plot import * # 绘图
from cost_function_reg import * # 代价函数
import numpy as np
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
learningRate = 1
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
# np.random.random(size):size指所生成随机数0-1的维度大小
# 这里设范围为[-0.12,0.12]
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
# print(params)
# [-0.09845394 0.07595105 0.05357422 ... -0.11991807 -0.08736149
# -0.09793505]
2.3 Backpropagation
内容: 求误差项,误差项用于衡量此节点对于最后的输出误差的贡献度。
a. 正向传播

b. 反向传播

forward_propagate.py(增加了返回项)
import numpy as np
from sigmoid import *
def forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X):
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=np.ones(X.shape[0]), axis=1)
a1 = X
z2 = a1 * Theta1.T
a2 = Sigmoid(z2)
a2 = np.insert(a2, 0, values=np.ones(a2.shape[0]), axis=1)
z3 = a2 * Theta2.T
h_theta = Sigmoid(z3)
return a1, z2, a2, z3, h_theta
注意:
1. 在计算误差项时,Z2需要变成26×1(维度)
2. 在训练集上算整体的误差项,所以要在for循环中使用delta_l=delta_l+..
back_propagation.py
import numpy as np
from forward_propagate import * # 正向传播
from sigmoid_gradient import * # 激活函数的导数
def backPropagation(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y):
X = np.matrix(X)
y = np.matrix(y)
m = X.shape[0]
Theta1 = np.matrix(np.reshape(params[:hidden_size * (input_size + 1)], (hidden_size, input_size + 1)))
Theta2 = np.matrix(np.reshape(params[hidden_size * (input_size + 1):], (num_labels, hidden_size + 1)))
# 1. feedforward->z、a、h
a1, z2, a2, z3, h_theta = forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X)
# print(a1.shape, z2.shape, a2.shape, h_theta.shape)
# (5000, 401) (5000, 25) (5000, 26) (5000, 10)
# 1.初始化梯度以及代价函数
J = 0
delta1 = np.zeros(Theta1.shape)
delta2 = np.zeros(Theta2.shape)
# print(delta1.shape, delta2.shape) # (25, 401) (10, 26)
# 2.计算代价函数
first_term = np.sum(np.multiply(y, np.log(h_theta)))
second_term = np.sum(np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - h_theta)))
J = -(first_term + second_term) / m
# 3.反向传播计算出误差项(在训练集上算整体的误差项,故要用delta=delta+..)、梯度
for i in range(m):
a1i = a1[i, :] # (1,401)
z2i = z2[i, :] # (1,25)
a2i = a2[i, :] # (1,26)
h_thetai = h_theta[i, :] # (1,10)
yi = y[i, :] # (1,10)
d_error3 = h_thetai - yi # (1,10)
# 将z2的维度变成26×1
z2i = np.insert(z2i, 0, values=np.ones(1)) # (1,26)
# 求隐藏层的误差项
d_error2 = np.multiply((Theta2.T * d_error3.T).T, sigmoidGradient(z2i)) # (1,26)
# 求整个训练集的梯度delta1与delta2
delta1 = delta1 + (d_error2[:, 1:]).T * a1i
delta2 = delta2 + d_error3.T * a2i
delta1 = delta1 / m
delta2 = delta2 / m
return J, delta1, delta2
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from back_propagation import * # 反向传播
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
backPropagation(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot)
2.4 Gradient Checking
内容:用于检查梯度是否正确。

2.5 Regularized Neural Networks
内容:正则化神经网络,即在之前的式子中加入正则项。
注意:用于偏置项的那一列不需要正则化。
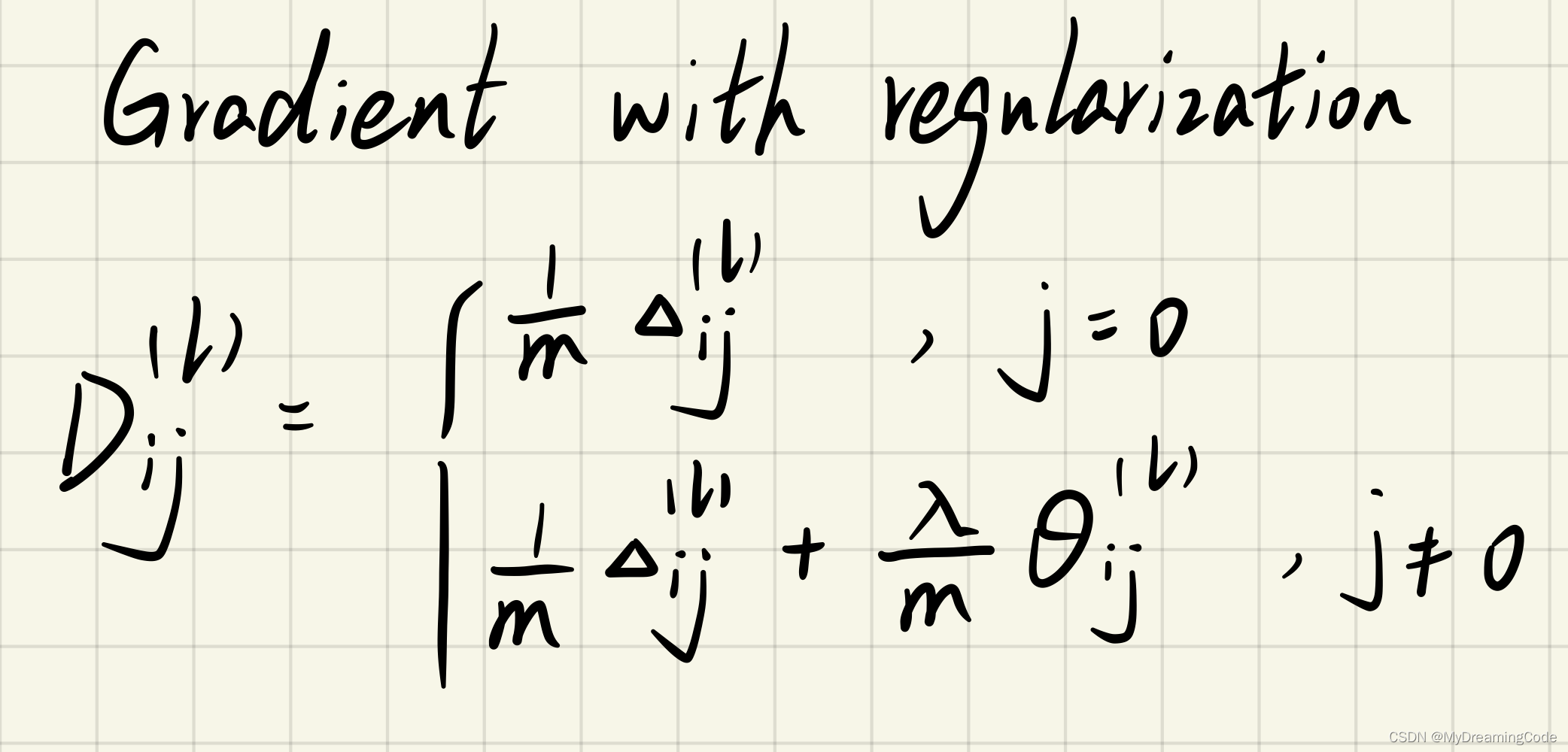
back_propagation_reg.py
import numpy as np
from forward_propagate import * # 正向传播
from sigmoid_gradient import * # 激活函数的导数
def backPropagationReg(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y, learningRate):
X = np.matrix(X)
y = np.matrix(y)
m = X.shape[0]
Theta1 = np.matrix(np.reshape(params[:hidden_size * (input_size + 1)], (hidden_size, input_size + 1)))
Theta2 = np.matrix(np.reshape(params[hidden_size * (input_size + 1):], (num_labels, hidden_size + 1)))
# 1. feedforward->z、a、h
a1, z2, a2, z3, h_theta = forwardPropagate(Theta1, Theta2, X)
# print(a1.shape, z2.shape, a2.shape, h_theta.shape)
# (5000, 401) (5000, 25) (5000, 26) (5000, 10)
# 1.初始化梯度以及代价函数
J = 0
delta1 = np.zeros(Theta1.shape)
delta2 = np.zeros(Theta2.shape)
# print(delta1.shape, delta2.shape) # (25, 401) (10, 26)
# 2.计算代价函数
first_term = np.sum(np.multiply(y, np.log(h_theta)))
second_term = np.sum(np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - h_theta)))
J = -(first_term + second_term) / m
# 3.反向传播计算出误差项(在训练集上算整体的误差项,故要用delta=delta+..)、梯度
for i in range(m):
a1i = a1[i, :] # (1,401)
z2i = z2[i, :] # (1,25)
a2i = a2[i, :] # (1,26)
h_thetai = h_theta[i, :] # (1,10)
yi = y[i, :] # (1,10)
d_error3 = h_thetai - yi # (1,10)
# 将z2的维度变成26×1
z2i = np.insert(z2i, 0, values=np.ones(1)) # (1,26)
# 求隐藏层的误差项
d_error2 = np.multiply((Theta2.T * d_error3.T).T, sigmoidGradient(z2i)) # (1,26)
# 求整个训练集的梯度delta1与delta2
delta1 = delta1 + (d_error2[:, 1:]).T * a1i
delta2 = delta2 + d_error3.T * a2i
delta1 = delta1 / m
delta2 = delta2 / m
# 3.添加正则项(用于偏置项的那一列不需要正则化)
delta1[:, 1:] = delta1[:, 1:] + (learningRate * Theta1[:, 1:]) / m
delta2[:, 1:] = delta2[:, 1:] + (learningRate * Theta2[:, 1:]) / m
# np.ravel:用于将多维数组变成一维数组
# np.concatenate((a,b)):用于将多个数组拼接
grad = np.concatenate((np.ravel(delta1), np.ravel(delta2)))
return J, grad
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from back_propagation_reg import * # 反向传播
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
learningRate = 1
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
backPropagationReg(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate)
2.6 Learning parameters using fmincg
内容:使用fmincg得到参数最优解。
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from scipy.optimize import minimize # 提供最优化算法函数
from back_propagation_reg import * # 反向传播
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
learningRate = 1
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
backPropagationReg(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate)
# 1.fun:目标函数
# 2.x0:初始的猜测
# 3.args=():优化的附加参数
# 4.method:要使用的方法名称,这里使用的TNC(截断牛顿算法)
# 5.jac=True,则假定fun会返回梯度以及目标函数,若为False,则将以数字方式估计梯度
# 6.options={..},带字典类型进去,maxiter指最大迭代次数
fmin = minimize(fun=backPropagationReg, x0=params,
args=(input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate), method='TNC', jac=True,
options={'maxiter': 250})
print(fmin) # x-解决方案
message: Max. number of function evaluations reached
success: False
status: 3
fun: 0.1509371037493068
x: [ 1.432e-01 -5.233e-03 ... -5.369e-01 -2.709e-01]
nit: 22
jac: [ 1.612e-04 -1.047e-06 ... -9.244e-05 -9.776e-05]
nfev: 250
用优化后的参数来进行预测(精确度可达98%):
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report # 常用的输出模型评估报告方法
from scipy.optimize import minimize # 提供最优化算法函数
from back_propagation_reg import * # 反向传播
from forward_propagate import * # 前向传播
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
learningRate = 1
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
backPropagationReg(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate)
fmin = minimize(fun=backPropagationReg, x0=params,
args=(input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate), method='TNC', jac=True,
options={'maxiter': 250})
X = np.matrix(X)
thetafinal1 = np.matrix(np.reshape(fmin.x[:(input_size + 1) * hidden_size], (hidden_size, input_size + 1)))
thetafinal2 = np.matrix(np.reshape(fmin.x[(input_size + 1) * hidden_size:], (num_labels, hidden_size + 1)))
a1, z2, a2, z3, h_theta = forwardPropagate(thetafinal1, thetafinal2, X)
# 对于argmax,axis=1,是在行中比较,选出最大的列索引
y_pred = np.array(np.argmax(h_theta, axis=1) + 1)
print(classification_report(y, y_pred))
# precision recall f1-score support
# 精确率 召回率 调和平均数 支持度(指原始的真实数据中属于该类的个数)
precision recall f1-score support
1 0.98 0.99 0.99 500
2 0.99 0.98 0.99 500
3 0.99 0.98 0.98 500
4 0.99 0.99 0.99 500
5 0.99 0.99 0.99 500
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 500
7 0.99 0.99 0.99 500
8 0.99 1.00 1.00 500
9 0.99 0.98 0.98 500
10 0.99 1.00 0.99 500accuracy 0.99 5000
macro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 5000
weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 5000
3. Visualizing the hidden layer
内容:将隐藏层(25个单元)所表达的东西可视化出来。
plot.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
def Plot(X):
sample_idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(X.shape[0]), 100) # 从0-4999中随机抽取100个数
sample_image = X[sample_idx, :]
fig, axisArr = plt.subplots(nrows=10, ncols=10, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10, 10))
for r in range(10):
for c in range(10):
axisArr[r, c].matshow(sample_image[r * 10 + c].reshape(20, 20).T, cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
plt.show()
def plotHidden(theta):
fig, axisArr = plt.subplots(nrows=5, ncols=5, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(8, 8))
# 1.matplotlib.pyplot.matshow(A,cmap),A-"矩阵"(一个矩阵元素对应一个图像像素),cmap-一种颜色映射方式
# 2.matplotlib.cm为色表,binary为灰度图像标准色表,matshow为可绘制矩阵的函数
# 3.xticks(),若传入空列表则不显示x轴
for r in range(5):
for c in range(5):
axisArr[r][c].matshow(theta[r * 5 + c].reshape(20, 20), cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入MATLAB格式数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder # 数据预处理
from scipy.optimize import minimize # 提供最优化算法函数
from back_propagation_reg import * # 反向传播
from plot import * # 可绘制隐藏层
data = loadmat('ex4data.mat')
X, y = data['X'], data['y']
weights = loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
Theta1, Theta2 = weights['Theta1'], weights['Theta2']
# 初始化值
input_size = 400
hidden_size = 25
num_labels = 10
learningRate = 1
params = (np.random.random(size=hidden_size * (input_size + 1) + num_labels * (hidden_size + 1)) - 0.5) * 2 * 0.12
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
backPropagationReg(params, input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate)
fmin = minimize(fun=backPropagationReg, x0=params,
args=(input_size, hidden_size, num_labels, X, y_onehot, learningRate), method='TNC', jac=True,
options={'maxiter': 250})
X = np.matrix(X)
thetafinal1 = np.matrix(np.reshape(fmin.x[:(input_size + 1) * hidden_size], (hidden_size, input_size + 1)))
thetafinal2 = np.matrix(np.reshape(fmin.x[(input_size + 1) * hidden_size:], (num_labels, hidden_size + 1)))
plotHidden(thetafinal1[:, 1:]) # 不带偏置项
注意: 在运用神经网络的过程中,需要正则化,否则可能会引起过拟合现象。





![[Netty源码] ByteBufAllocator内存管理器相关问题 (十一)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b8146c9d0f284aa68618e3deb89c4290.png)