前言
回想起五年前的一次面试,面试官问@Configuration注解和@Component注解有什么区别?记得当时的回答是:
-
相同点:
@Configuration注解继承于@Component注解,都可以用来通过ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner装载Spring bean的配置信息。 -
不同点:
Component注解为通用组件类模式注解,Configuration注解为配置类模式注解,主要是在做代码分层上的有差别(当然也是从字面意思上理解)。
很显然不是面试官想要到答案,最后还是挂了。回去看了一下注解本身定,Configuration继承于Component,多了个proxyBeanMethods 属性,注释中提到在运行中可以生成子类进行增强,但是类类型必须不是final的,当proxyBeanMethods配置为false的时候不会进行增强。当时也就草率的下了定义,Configuration可以选择是否通过生成代理类进行增强。
进阶
多余的属性是proxyBeanMethods,字面的意思是代理Bean的方法,代理了个什么东西?是如何增强?带着问题写了一段测试代码:
@Component
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(Demo.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
Test test = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Test.class);
System.out.println("spring ioc容器中管理的person对象:" + annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class));
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println("通过bean作用的方法创建对象:" + test.createUser());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println("通过没用bean作用的方法创建对象:" + test.createUserNoMethodBean());
}
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
@Configuration
public static class Test {
@Bean
public Person createUser() {
return createUserNoMethodBean();
}
public Person createUserNoMethodBean(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
return person;
}
}
public static class Person {
private String name;
//get set 省略
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
}
代码输出
spring ioc容器中管理的person对象:Person{name='2a8c8844-c979-4784-942b-af4299d32866'}
通过bean作用的方法创建对象:Person{name='2a8c8844-c979-4784-942b-af4299d32866'}
通过bean作用的方法创建对象:Person{name='2a8c8844-c979-4784-942b-af4299d32866'}
通过没用bean作用的方法创建对象:Person{name='67707608-79bf-44c0-a83a-9ebaa7c17bb1'}
通过没用bean作用的方法创建对象:Person{name='27028430-9f82-4379-993a-6edd884ce145'}
我们调用Test对象创建用户方法,带有bean注解的返回的是同一个对象,并且与注入到spring ioc容器中的person对象是同一个,而且没有通过@Bean注解作用的方法真正执行了。不得不说好神奇。
猜想
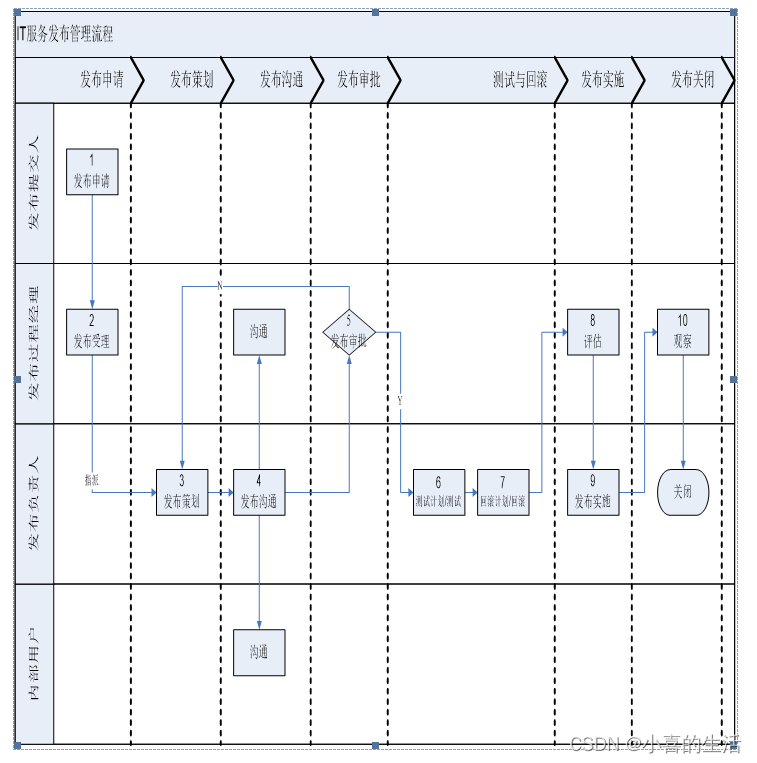
我们先做一个大胆的猜想~ 注解Configuration注解proxyBeanMethods默认为true,也就是说默认会进行代理增强。调用通过bean注解的方法时会进行拦截,并且会舍弃调用真正的目标方法。其中会对带有bean的方法进行代理,对不带有bean的方法进行过滤。拦截带有bean方法返回对象时会从spring ioc容器中进行依赖查找并返回该对象。
如图
- 带有bean方法不需要进行执行目标方法,也就是我们的原始方法;
- 我们需要注入我们的BeanFactory对象,来完成我们带有Bean方法依赖查找;
- 需要对我们的方法进行过滤,需要对特定方法进行回调。
源码
由上一章我们熟悉了Spring ioc容器解析注册的流程,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class类比较重要,前半部分为BeanDefinitionRegistry逻辑,后半部为配置类的增强。
接下来开始查看对给定BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理。跟踪源码到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(beanfactory);
/**
* Prepare the Configuration classes for servicing bean requests at runtime
* by replacing them with CGLIB-enhanced subclasses.
*/
//通过 CGLIB 增强的子类来代替配置类来为 bean 请求提供支持
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory);
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory);
}
this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId);
if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported...
// Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then.
processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
}
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory));
}
继续跟踪到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory)方法中,
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
StartupStep enhanceConfigClasses = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.config-classes.enhance");
Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
Object configClassAttr = beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE);
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = null;
MethodMetadata methodMetadata = null;
if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef;
annotationMetadata = annotatedBeanDefinition.getMetadata();
methodMetadata = annotatedBeanDefinition.getFactoryMethodMetadata();
}
if ((configClassAttr != null || methodMetadata != null) && beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
// Configuration class (full or lite) or a configuration-derived @Bean method
// -> eagerly resolve bean class at this point, unless it's a 'lite' configuration
// or component class without @Bean methods.
AbstractBeanDefinition abd = (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef;
if (!abd.hasBeanClass()) {
boolean liteConfigurationCandidateWithoutBeanMethods =
(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE.equals(configClassAttr) &&
annotationMetadata != null && !ConfigurationClassUtils.hasBeanMethods(annotationMetadata));
if (!liteConfigurationCandidateWithoutBeanMethods) {
try {
abd.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
}
}
}
//判断BeanDefinition的configurationClass是否为full,然后加入集合后续进行特殊处理
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL.equals(configClassAttr)) {
if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" +
beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass");
}
else if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
logger.info("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName +
"' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " +
"is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " +
"return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.");
}
configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef);
}
}
if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty() || NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {
// nothing to enhance -> return immediately
enhanceConfigClasses.end();
return;
}
ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer();
//遍历进行cglib增强子类
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue();
// If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class
beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean class
Class<?> configClass = beanDef.getBeanClass();
Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader);
if (configClass != enhancedClass) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " +
"enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));
}
beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass);
}
}
enhanceConfigClasses.tag("classCount", () -> String.valueOf(configBeanDefs.keySet().size())).end();
在ConfigurationClassEnhancer类中,我们看到增强的具体实现:
/**
* Creates a new CGLIB {@link Enhancer} instance.
*/
//创建cglib的实例。
private Enhancer newEnhancer(Class<?> configSuperClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//为增强类设置父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(configSuperClass);
//为增强类设置接口,该接口继承BeanFactoryAware,在实例化非lazy对象处理中接口回调阶段initializeBean 进行(BeanNameAware ClassLoaderAware BeanFactoryAware 回调),我们能通过BeanFactoryAware 获取我们beanfactory类。
enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class});
enhancer.setUseFactory(false);
//设置beanfactory字段。方便进行依赖查找
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
//具体我们可以看到此处配置的filter 也就是特殊方法才会执行回调,否则调用父类目标方法
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER);
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes());
return enhancer;
}
CALLBACK_FILTER:并不是所有方法进行拦截, 首先需要拦截的是内部调用 @Bean 注解的方法时,进行ioc依赖查找返回;其次是依赖查找依赖的beanfactory字段的赋值;其他方法不进行拦截(当然也可以拦截,直接在调用父类的方法proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args));这样多实现不如不实现,没用!!!。
因为我们多个拦截器,所以我们需要进行组合,选出符合条件的拦截器下标。
/**
* A {@link CallbackFilter} that works by interrogating {@link Callback Callbacks} in the order
* that they are defined via {@link ConditionalCallback}.
*/
private static class ConditionalCallbackFilter implements CallbackFilter {
private final Callback[] callbacks;
private final Class<?>[] callbackTypes;
//初始化的数据为固定顺序
public ConditionalCallbackFilter(Callback[] callbacks) {
this.callbacks = callbacks;
this.callbackTypes = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) {
this.callbackTypes[i] = callbacks[i].getClass();
}
}
@Override
public int accept(Method method) {
//遍历callbacks,首先判断是否符合
for (int i = 0; i < this.callbacks.length; i++) {
Callback callback = this.callbacks[i];
if (!(callback instanceof ConditionalCallback) || ((ConditionalCallback) callback).isMatch(method)) {
return i;
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException("No callback available for method " + method.getName());
}
public Class<?>[] getCallbackTypes() {
return this.callbackTypes;
}
}
// The callbacks to use. Note that these callbacks must be stateless.
private static final Callback[] CALLBACKS = new Callback[] {
new BeanMethodInterceptor(),
new BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor(),
NoOp.INSTANCE
};
private static final ConditionalCallbackFilter CALLBACK_FILTER = new ConditionalCallbackFilter(CALLBACKS);
CALLBACKS 根据ConditionalCallbackFilter#accept(method)``方法逻辑,首先会判断是是继承了ConditionalCallback,然后调用isMatch(method)的方法;组合条件中 NoOp.INSTANCE非ConditionalCallback子类与BeanMethodInterceptor和BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor互斥;BeanMethodInterceptor和BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor`互斥。
BeanMethodInterceptor#isMatch(method);源码
@Override
public boolean isMatch(Method candidateMethod) {
return (candidateMethod.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class &&
!BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor.isSetBeanFactory(candidateMethod) &&
BeanAnnotationHelper.isBeanAnnotated(candidateMethod));
}
接下来创建我们目标类的子类,注册子类的回调:
/**
*为派生子类的设置回调。
*/
private Class<?> createClass(Enhancer enhancer) {
Class<?> subclass = enhancer.createClass();
// Registering callbacks statically (as opposed to thread-local)
// is critical for usage in an OSGi environment (SPR-5932)...
//CALLBACKS为
Enhancer.registerStaticCallbacks(subclass, CALLBACKS);
return subclass;
}
CALLBACKS 为数组,
BeanMethodInterceptor:对于配置类中内部 @Bean 注解的方法的调用将会被拦截器拦截。拦截器的逻辑是判断声明的 Spring bean 在容器中是否已经存在,如果存在则直接返回容器中的 Spring bean。否则真正的配置类的方法创建 Spring bean 实例,避免了多例的出现。主要是解析获取我们beanfactory字段(该字段受益于CALLBACKS第二个元素的赋值),进行依赖查找。
private ConfigurableBeanFactory getBeanFactory(Object enhancedConfigInstance) {
//解析BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD beanfactory字段~
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(enhancedConfigInstance.getClass(), BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD);
Assert.state(field != null, "Unable to find generated bean factory field");
Object beanFactory = ReflectionUtils.getField(field, enhancedConfigInstance);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory has not been injected into @Configuration class");
Assert.state(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory,
"Injected BeanFactory is not a ConfigurableBeanFactory");
return (ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
}
BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor:为我们代理类新增的BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD字段进行赋值。源码如下:
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
//查找我们的BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD字段
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(obj.getClass(), BEAN_FACTORY_FIELD);
Assert.state(field != null, "Unable to find generated BeanFactory field");
//为我们字段进行赋值,args[0]->因为我们BeanFactoryAware接口回调方法为 void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;只有一个参数~
field.set(obj, args[0]);
// Does the actual (non-CGLIB) superclass implement BeanFactoryAware?
// If so, call its setBeanFactory() method. If not, just exit.
//如果父类实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,改方法直接调用父类方法。
if (BeanFactoryAware.class.isAssignableFrom(ClassUtils.getUserClass(obj.getClass().getSuperclass()))) {
return proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
}
return null;
}
NoOp.INSTANCE:这个NoOp表示no operator,即什么操作也不做,代理类直接调用被代理的方法不进行拦截。
配置中当然满足内部bean方法调用时走BeanMethodInterceptor;调用setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory)时走BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor;其他方法走NoOp.INSTANCE。
回到我们ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory)方法中,可以看到BeanDefinition的beanClass属性被赋值我们生成增强的代理子类,
最后来到我们bean的实例化处理方法DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons。至此@Configuration的实现原理和我们猜想大致相同。






![[入门必看]数据结构1.1:数据结构的基本概念](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c3dbbca0e18a4064be7335cd61b266a2.png#pic_center)