Jenkins从配置到实践
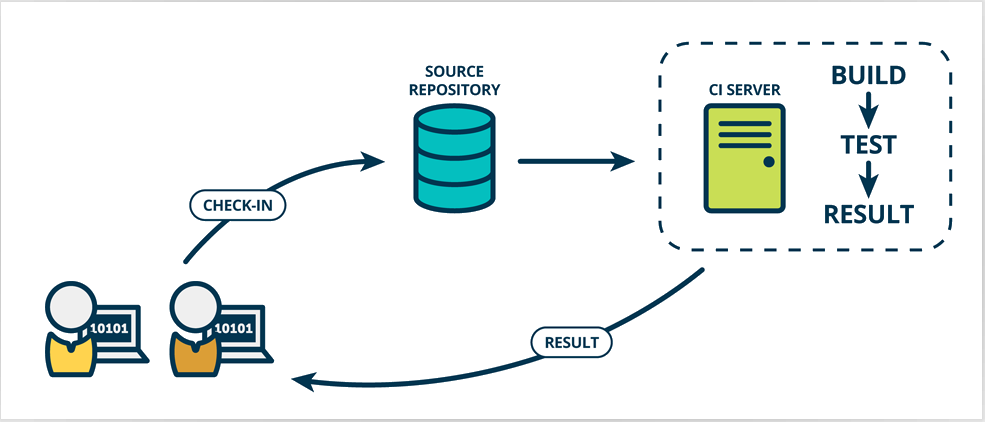
1 持续集成 Continuous integration(CI)
1.1 什么是持续集成?
持续集成Continuous integration(CI)是一种软件开发实践,即团队开发成员经常集成他们的工作,通常每个成员至少集成一次,也就意味着每天可能会发生多次集成。每次集成都通过自动化的构建(包括编译,发布,自动化测试)来验证,从而尽快地发现集成错误。许多团队发现这个过程可以大大减少集成的问题,让团队能够更快的开发内聚的软件。
1.2 持续集成的原则
- 需要版本控制工具来保障团队成员提交的代码不会导致集成失败。常用的版本控制工具有svn、git等。
- 开发人员需要及时向版本控制库中提交代码,也需要经常性地从版本控制库中更新代码到本地。
- 需要有专门的集成服务器来执行集成构建。
根据项目的实际情况,集成构建可以通过代码仓库中代码的变动(如push事件、merge事件等)来自动触发构建,也可以定时启动构建,如每半小时构建一次。
- 必须保证构建的成功。
如果构建失败,则修复构建过程中的错误将是优先级最高的工作。一旦修复,需手动启动一次构建。
- 一个自动构建过程,包括自动编译、分发、部署和测试等。
- 一个代码仓库,即需要版本控制工具来保障代码的可维护性,同时作为构建过程的素材库。
- 一个持续集成服务器。
2 Jenkins介绍
2.1 Jenkins简介
Jenkins,原名 Hudson,2011 年改为现在的名字。它是一个开源的实现持续集成的软件工具。
Jenkins只是一个平台,真正运作的都是插件。这就是Jenkins流行的原因,因为Jenkins什么插件都有。
Jenkins官网:https://www.jenkins.io/
2.2 Jenkins自动化部署实现原理
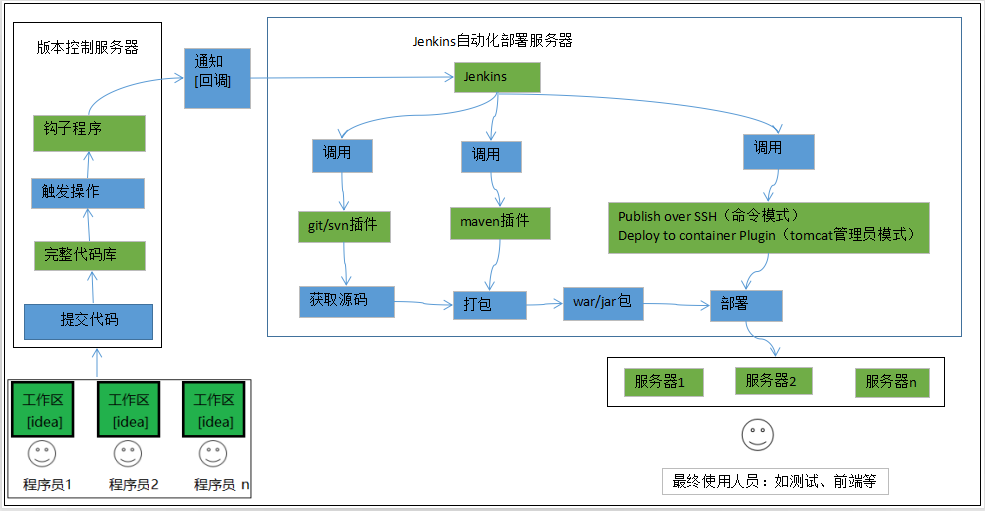
3 Jenkins部署环境
基本环境
JDK:Jenkins是Java语言开发的,因需要JDK环境。Git/SVN:因一般代码是放在Git/SVN服务器上的,我们需要拉取代码。Maven:因一般Java程序是由Maven工程,需要Maven打包。
服务器准备
| 应用名称 | IP地址 | 子网掩码 | 网关 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | 192.168.3.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 | 1核CPU 1G内存 20G磁盘 |
| Gitlab | 192.168.3.6 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 | 4核CPU 6G内存 20G磁盘 |
| Tomcat | 192.168.3.8 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 | 1核CPU 1G内存 20G磁盘 |
说明:操作系统使用Centons7。
静态ip地址设置
# 在CentOS 7上配置静态ip
1.以root用户登录,修改网络配置
[root@jenkins ~]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
BOOTPROTO="static" #是否自动获取,static是静态地址
ONBOOT=yes #开机加载
IPADDR="192.168.3.3"
NETMASK="255.255.255.0"
GATEWAY="192.168.3.1"
2.配置 DNS
[root@jenkins ~]# vi /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 192.168.3.1
nameserver 114.114.114.114
nameserver 8.8.8.8
3.重启网卡,使静态ip的配置文件生效
[root@jenkins ~]# service network restart
注:若克隆的Linux虚拟机,则通过“编辑虚拟机设置 -> 网络适配器 -> 高级”重新生成克隆的机器MAC地址。
# 在ubuntu 22.04上配置静态ip
1.以root用户登录,修改网络配置
[root@jenkins ~]# sudo vim /etc/netplan/01-network-manager-all.yaml
# Let NetworkManager manage all devices on this system
network:
ethernets:
ens33:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
addresses:
- 192.168.3.8/24
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.3.1
nameservers:
addresses:
- 114.114.114.114
- 8.8.8.8
version: 2
renderer: NetworkManager
3.使静态ip的配置文件生效
[root@jenkins ~]# sudo netplan apply
主机名修改
1.主机名修改
[root@jenkins ~]# vi /etc/hosts
192.168.3.3 jenkins
2.重启Linux
[root@jenkins ~]# shutdown -r now
用户及用户组创建
在Linux系统下创建appop用户及appop组;使用root用户登录,执行以下命令:
# 创建appop组
[root@jenkins ~]# groupadd appop
# 创建appop用户
[root@jenkins ~]# useradd appop -g appop
# 设置appop用户密码
[root@jenkins ~]# passwd appop
更改用户 appop 的密码 。
新的 密码:
问题描述:普通用户输入一些系统命令后出现:不在sudoers文件中,此事将被报告。这是因为当前操作用户的权限不够。
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo su -
我们信任您已经从系统管理员那里了解了日常注意事项。
总结起来无外乎这三点:
#1) 尊重别人的隐私。
#2) 输入前要先考虑(后果和风险)。
#3) 权力越大,责任越大。
[sudo] appop 的密码:
appop 不在 sudoers 文件中。此事将被报告。
问题解决:
1.输入命令“ll -h /etc/sudoers”,查看/etc/sudoers文件权限,如果只读权限,修改为可写权限。
[root@jenkins ~]# ll -h /etc/sudoers
-r--r-----. 1 root root 4.3K 9月 30 2020 /etc/sudoers
2.输入修改权限命令:"chmod u+w /etc/sudoers"
[root@jenkins ~]# chmod u+w /etc/sudoers
[root@jenkins ~]# ll -h /etc/sudoers
-rw-r-----. 1 root root 4.3K 9月 30 2020 /etc/sudoers
3.输入编辑命令“vi /etc/sudoers”,在文件中找到root ALL=(ALL) ALL这一行,在该行下以同样的参数添加提升权限的用户信息。
[root@jenkins ~]# vi /etc/sudoers
## Allow root to run any commands anywhere
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
appop ALL=(ALL) ALL
4.返回到命令页面,输入回复权限的命令:
[root@jenkins ~]# chmod 440 /etc/sudoers
5.输入命令:"sudo su -",切换到root用户。
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo su -
[sudo] appop 的密码:
上一次登录:三 8月 17 12:43:43 CST 2022从 192.168.3.173pts/1 上
[root@jenkins ~]#
输入系统操作命令,发现普通用户已有了权限提升,问题解决。
3.1 GitLab
GitLab官方网站:https://about.gitlab.com/
3.1.1 安装需求
GitLab安装需求说明:https://docs.gitlab.cn/jh/install/requirements.html
CPU
推荐的最低 CPU 硬件要求:
- 4 核 是推荐的最小核数,支持多达 500 名用户
- 8 核支持多达 1000 名用户
内存
推荐的最低内存硬件要求:
- 4GB RAM 是必需的最小内存,支持多达 500 名用户
- 8GB RAM 支持多达 1000 名用户
注:通常建议服务器上至少有 2GB 的 swap 存储空间,即使您已有足够可用的 RAM。
3.1.2安装方式
方式一:在ssh下安装GitLab
GitLab官方安装文档:https://gitlab.cn/install/?version=ce
安装依赖
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo yum install -y curl policycoreutils-python openssh-server perl
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo systemctl enable sshd
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo systemctl start sshd
配置镜像
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo curl -fsSL https://packages.gitlab.cn/repository/raw/scripts/setup.sh | /bin/bash
开始安装
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo EXTERNAL_URL="http://192.168.3.9" yum install -y gitlab-jh
除非您在安装过程中指定了自定义密码,否则将随机生成一个密码并存储在 /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password 文件中(出于安全原因,24 小时后,此文件会被第一次 gitlab-ctl reconfigure 自动删除,因此若使用随机密码登录,建议安装成功初始登录成功之后,立即修改初始密码)。使用此密码和用户名 root 登录。
方式二:使用Docker安装GitLab
GitLab官方安装文档:https://docs.gitlab.cn/jh/install/docker.html
注:系统内核至少在3.10以上 uname -r 命令可查看系统内核版本
安装docker
1.卸载旧的版本
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
2.需要的安装包
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
3.设置镜像的仓库
# 默认是国外的,很慢!!!
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 推荐使用阿里云的,十分快
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
4.更新yum软件包索引
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum makecache fast
5.安装docker相关引擎、docker-ce社区版、docker-ee企业版
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
6.启动docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl start docker
7.配置开机启动项:
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl enable docker
8.使用docker version查看是否安装成功
[appop@tomcat ~]$ docker version
9.配置镜像加速器
修改daemon配置文件/etc/docker/daemon.json来使用加速器
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://gw5py7zq.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
注:阿里云镜像加速器地址获取链接 https://cr.console.aliyun.com/cn-hangzhou/instances/mirrors
10.重启服务
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
11.重启docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl restart docker
12.hello-world
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo docker run hello-world
使用 Docker Engine 安装极狐GitLab
1.添加容器
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo docker run --detach \
--hostname 192.168.3.6 \
--publish 443:443 --publish 80:80 \
--name gitlab \
--restart always \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/config:/etc/gitlab:Z \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/logs:/var/log/gitlab:Z \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/data:/var/opt/gitlab:Z \
--shm-size 256m \
registry.gitlab.cn/omnibus/gitlab-jh:latest
2.查看已存在的容器
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo docker ps
3.关闭容器
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo docker stop gitlab
4.启动容器
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo docker start gitlab
打开浏览器,访问:http://192.168.3.6
- 当首次运行出现502错误的时候,排查两个原因:
1.内存至少需要4g,建议6g以上
2.稍微等待几分钟后,再刷新一下可能就好了
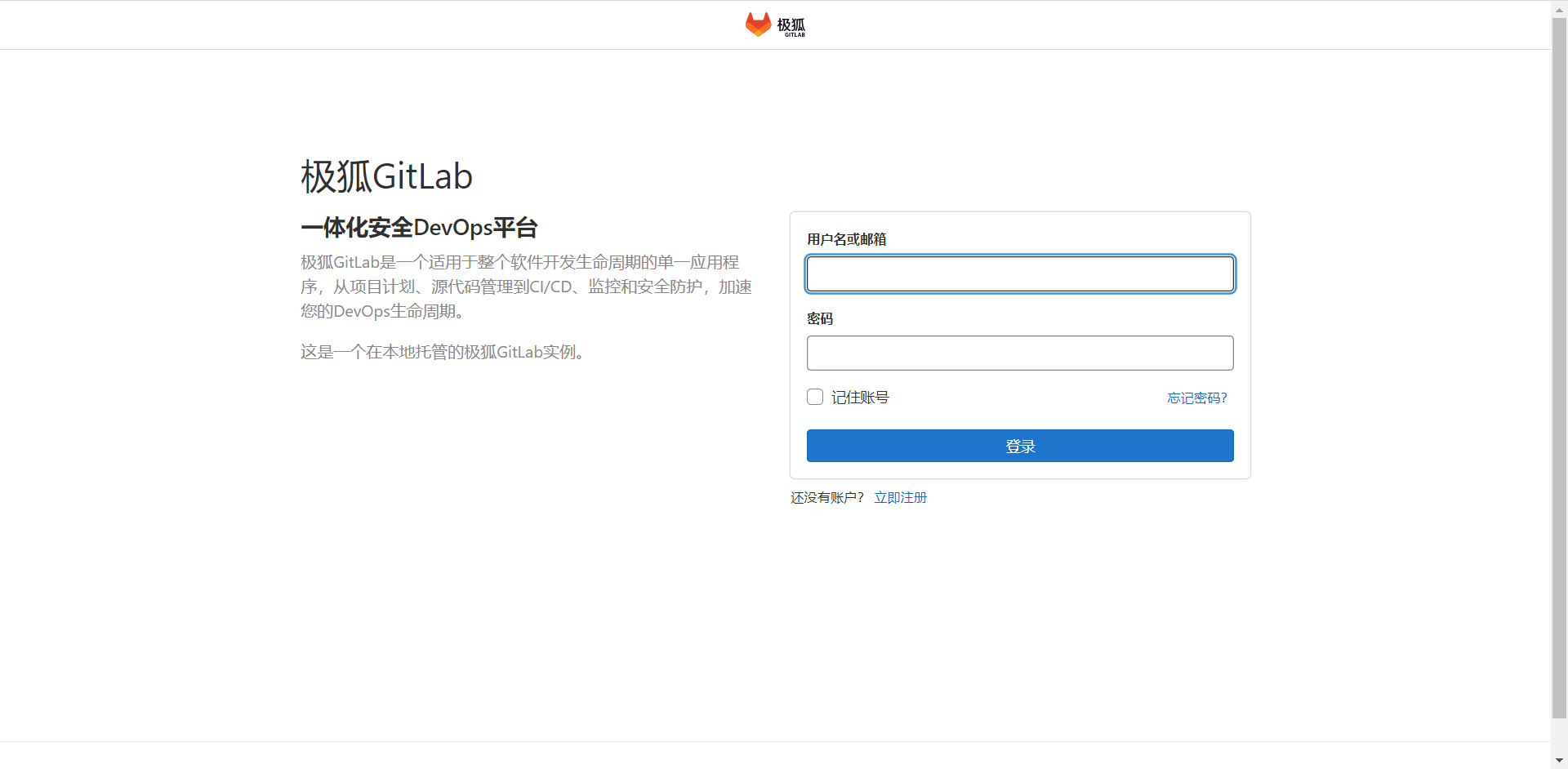
登录极狐GitLab
查看root用户密码:
1.进入容器
[appop@gitlab ~]$ sudo docker exec -it gitlab /bin/bash
2.查看root用户密码
root@192:/# cat /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
# WARNING: This value is valid only in the following conditions
# 1. If provided manually (either via `GITLAB_ROOT_PASSWORD` environment variable or via `gitlab_rails['initial_root_password']` setting in `gitlab.rb`, it was provided before database was seeded for the first time (usually, the first reconfigure run).
# 2. Password hasn't been changed manually, either via UI or via command line.
#
# If the password shown here doesn't work, you must reset the admin password following https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/security/reset_user_password.html#reset-your-root-password.
Password: emhRJuC33vCea41OmIojD+ZZ7nWT8DxNS68oXCrT0wc=
# NOTE: This file will be automatically deleted in the first reconfigure run after 24 hours.
# 注:密码存在/etc/gitlab/initial_root_password文件中,登录后需修改密码,不然24小时后会失效。
在极狐GitLab登录页面上,输入用户名和密码,单击_登录_,登录至极狐GitLab。
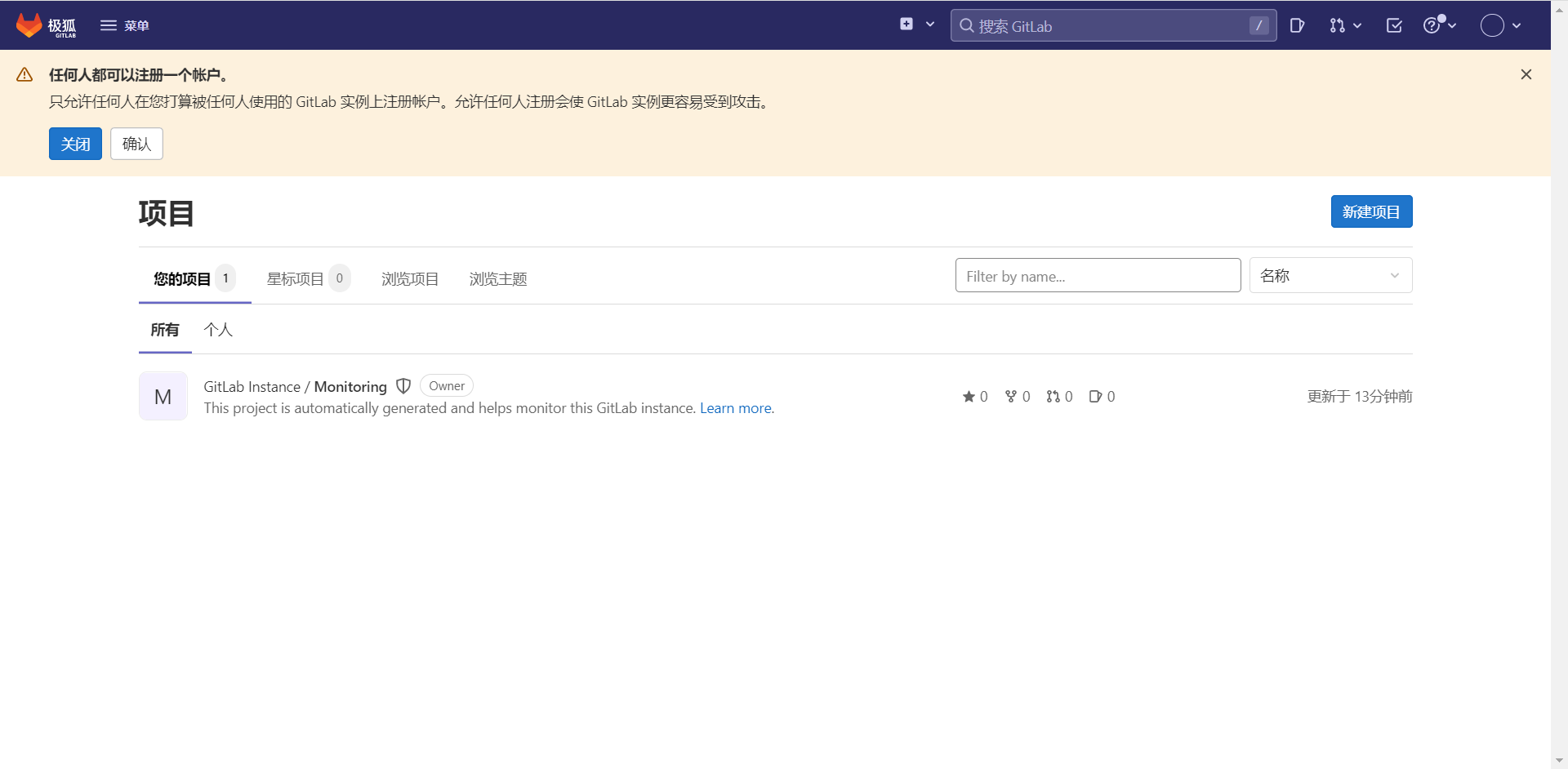
修改GitLab帐户密码
单击_个人中心 >> 编辑个人资料 >> 密码_,更改administrator密码。
3.1.3 GitLab常用命令
gitlab-ctl start # 启动所有 gitlab 组件
gitlab-ctl stop # 停止所有 gitlab 组件
gitlab-ctl restart # 重启所有 gitlab 组件
gitlab-ctl status # 查看服务状态
gitlab-ctl reconfigure # 启动服务
vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb # 修改默认的配置文件
gitlab-ctl tail # 查看日志
3.1.4 GitLab仓库创建
登录到GitLab。
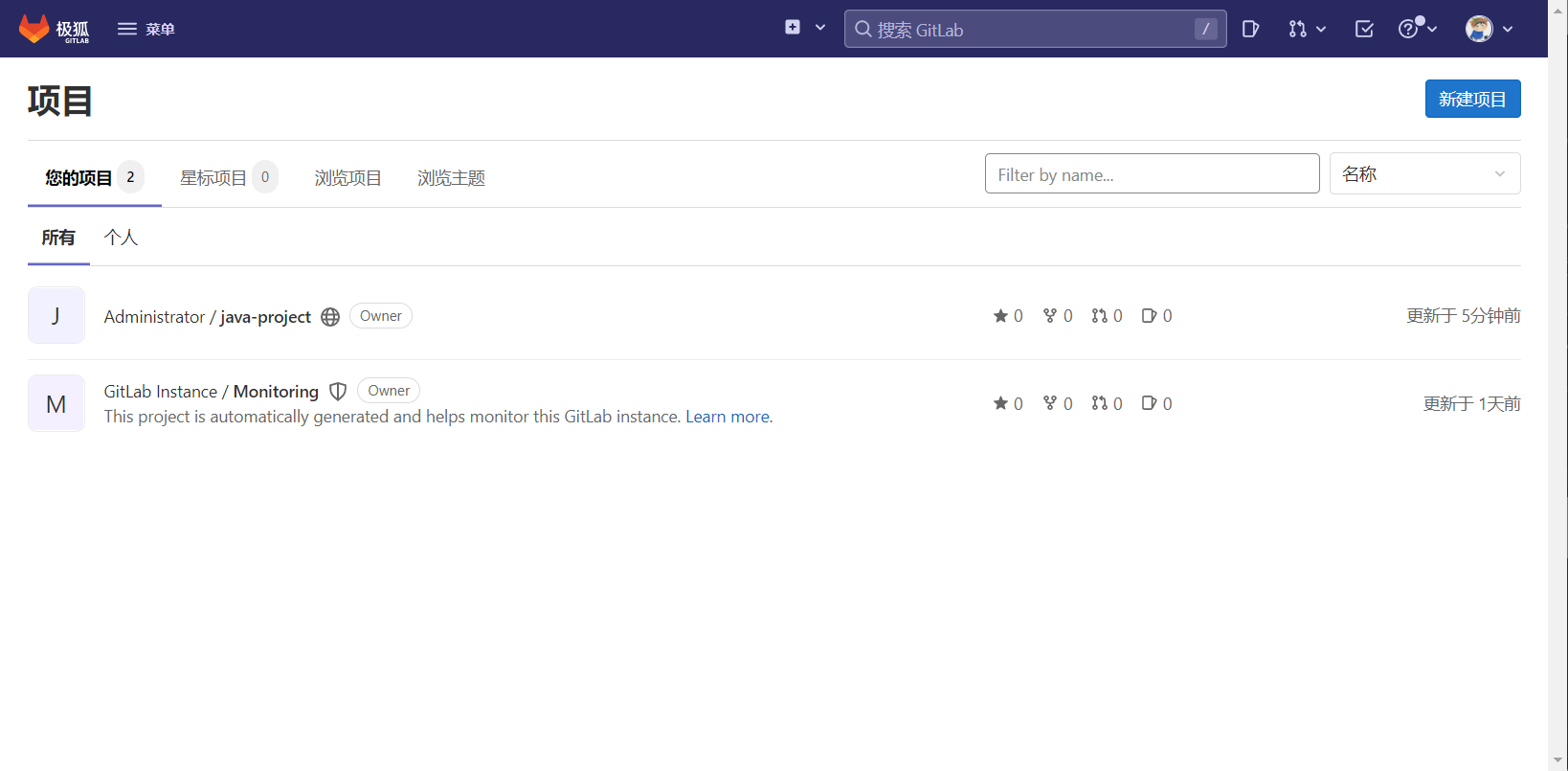
点击新建项目,进入创建新项目界面。
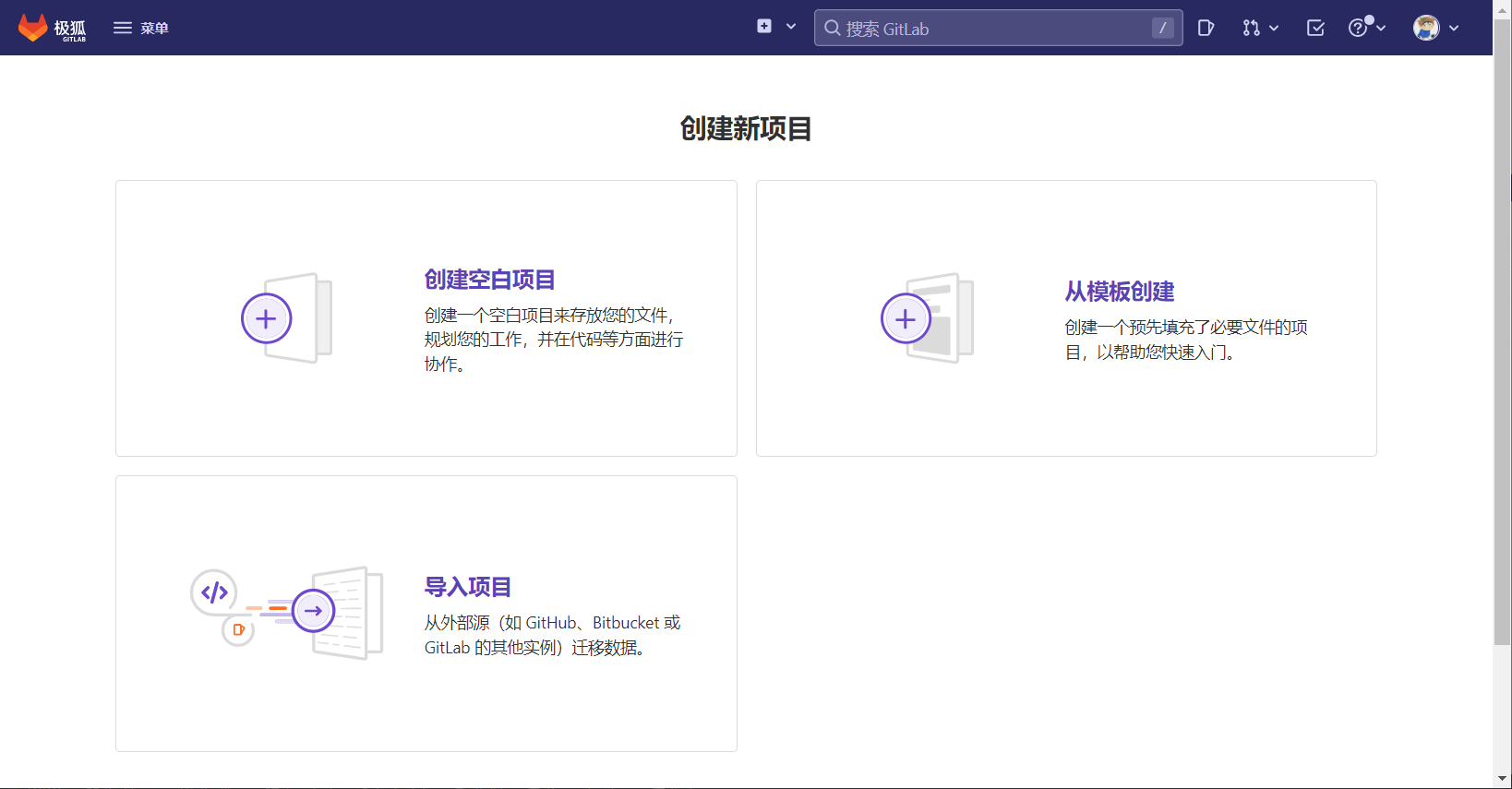
点击创建空白项目,填写相关信息。
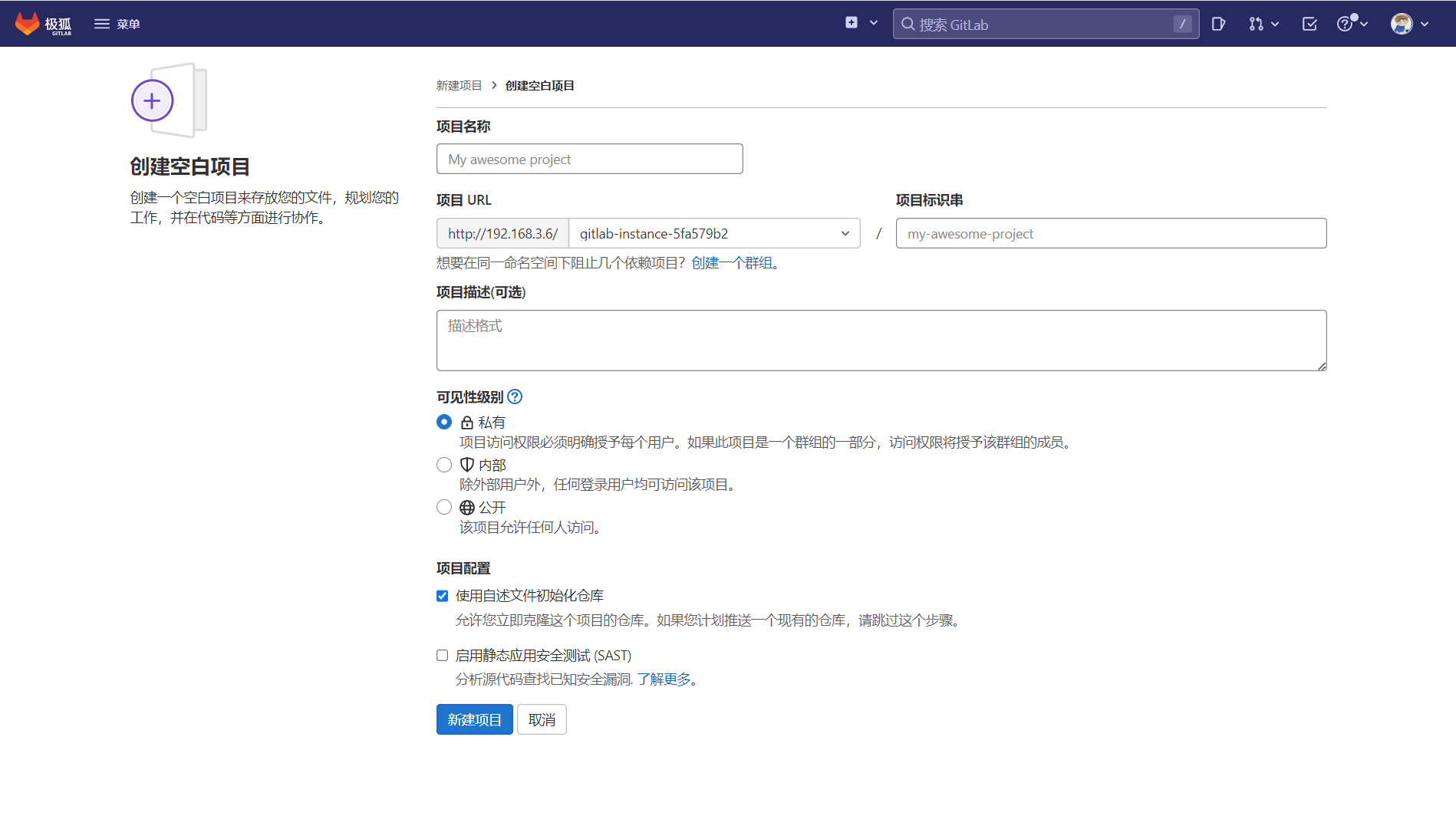
3.1.5 IDEA集成GitLab
- 在IDEA的Settings >> Plugins中,检查GitLab插件是否安装。
- 打开IDEA菜单栏:VCS >> Create Git Repository。
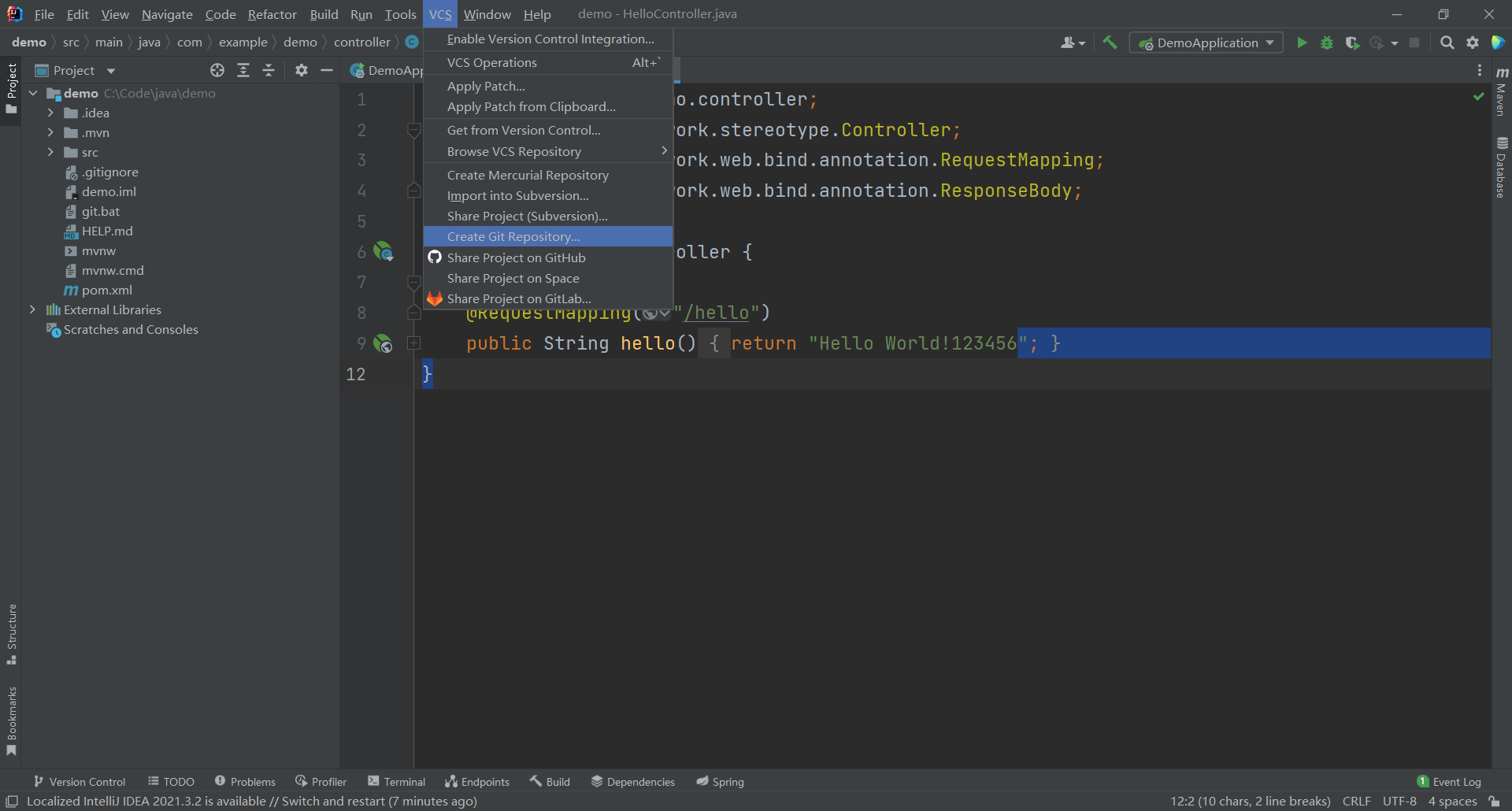
Create Git Repository弹出框,项目目录最好不要改变。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MHUbAtfb-1661161953769)(https://gitee.com/chenjingwei1618/my-project/raw/master/img/202208192305005.png)]
点击Ok后,项目目录下多了一个.git隐藏文件夹。
这个时候选中项目右键,多出一个git菜单。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-vfqh3m3X-1661161953770)(https://gitee.com/chenjingwei1618/my-project/raw/master/img/202208192305786.png)]
- 执行git >> Add操作,图标由红色变成绿色。
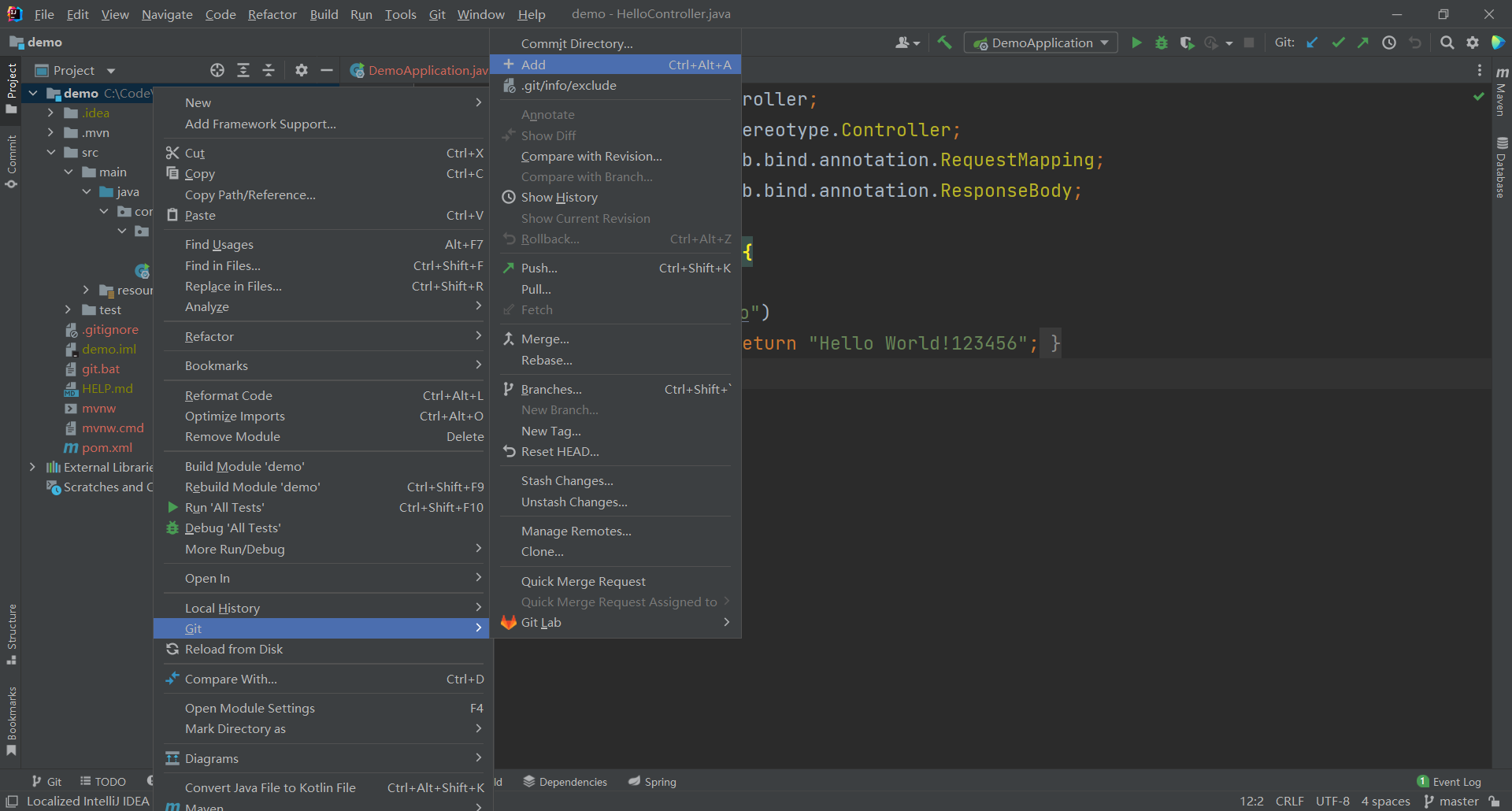
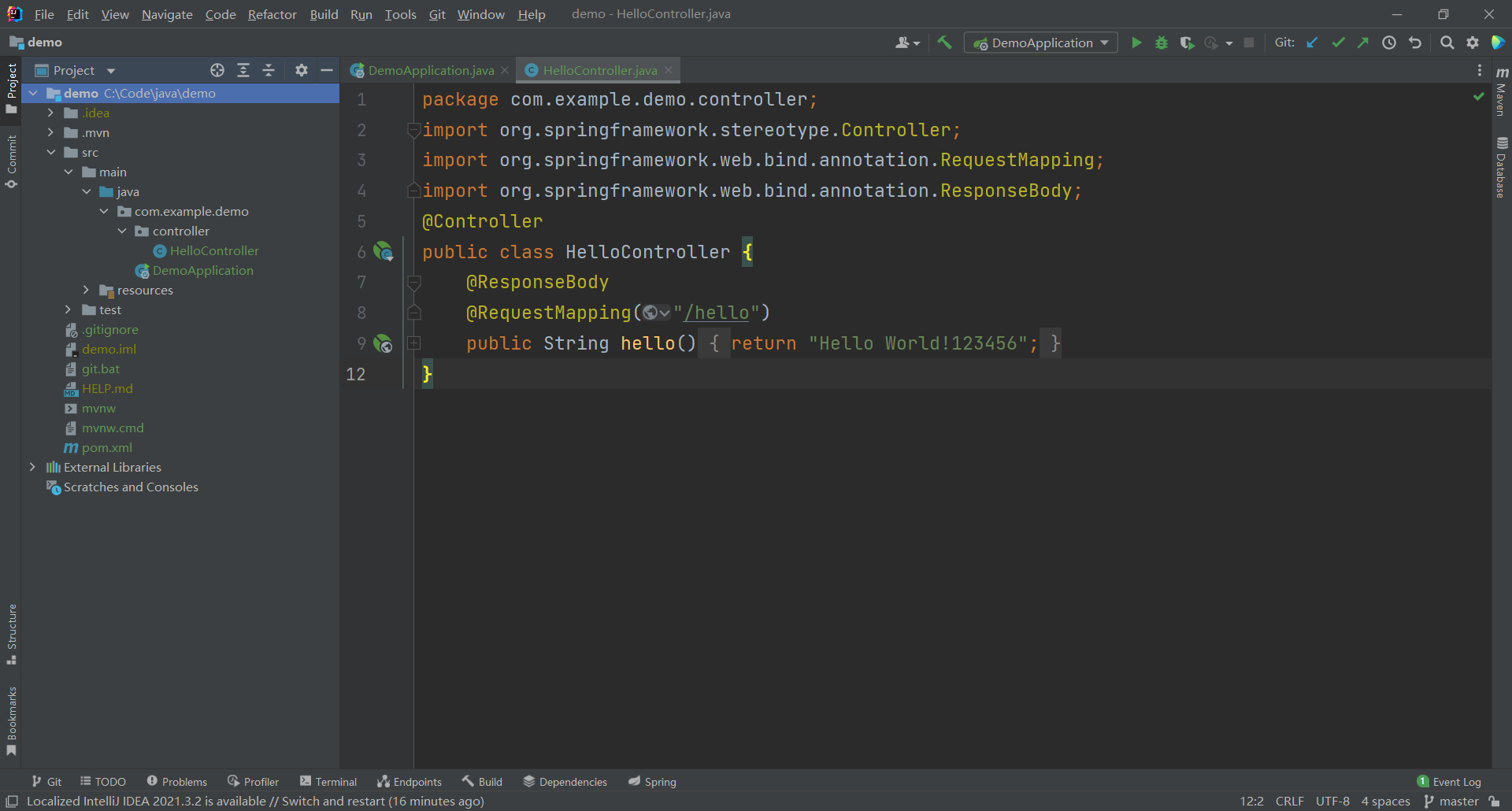
- 执行git >> commit操作。
commit后,图标由绿色变成黑色。

- 执行git >> push操作。
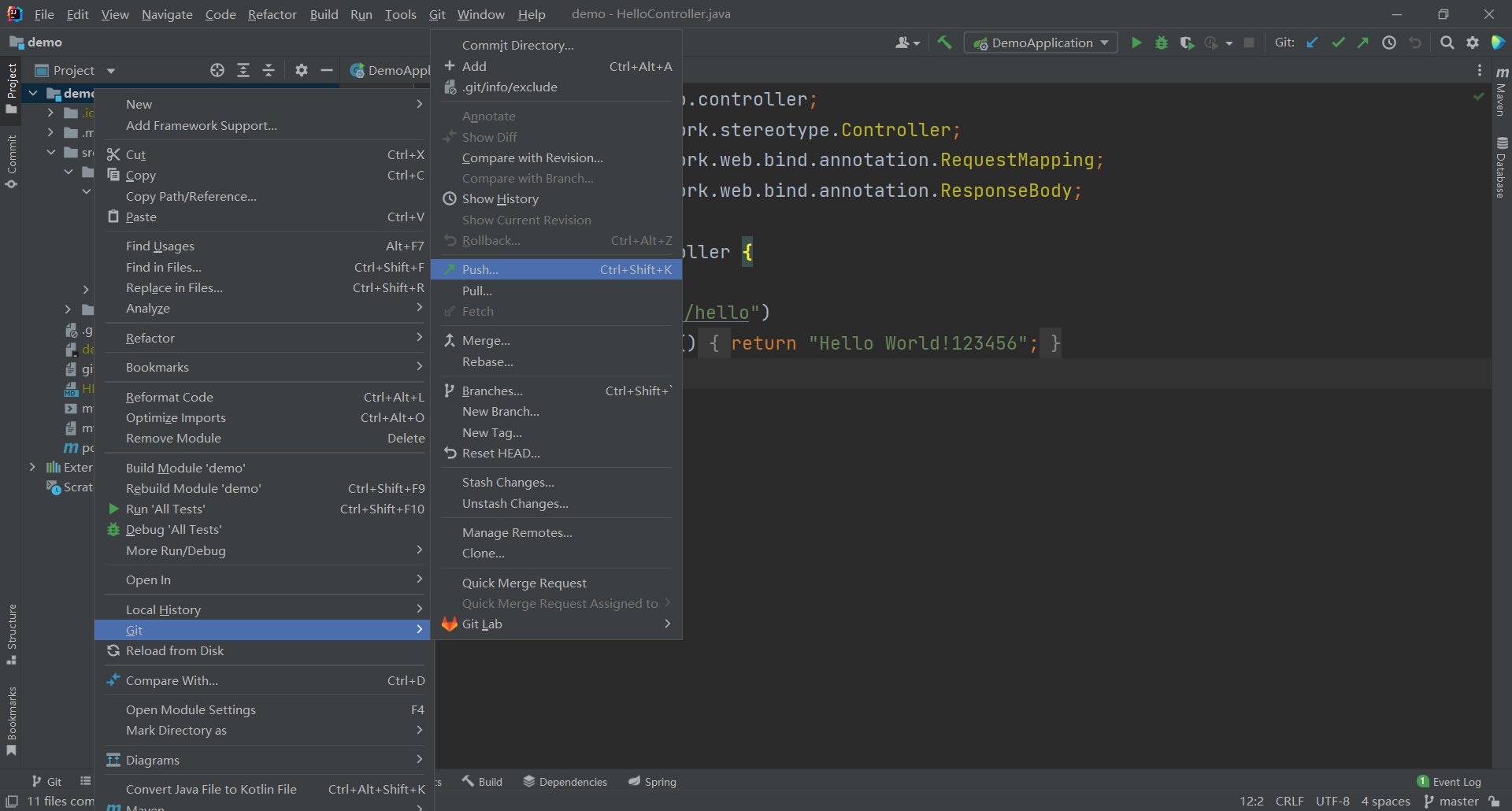
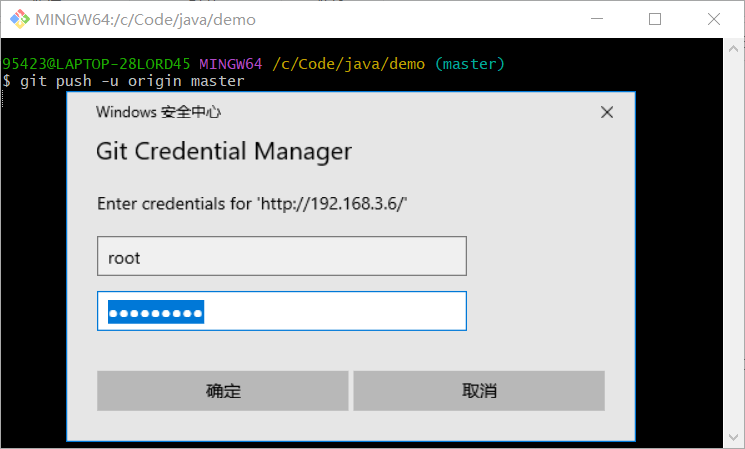
第一次push需要配置:
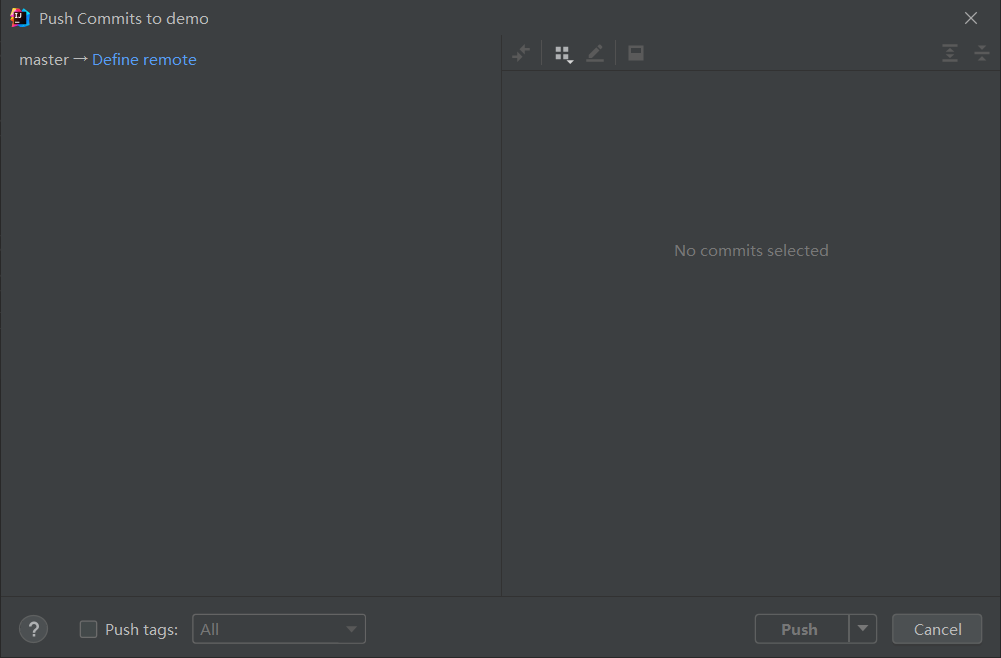
点击Define remote,并把GitLab服务器上project的http地址复制到URL。
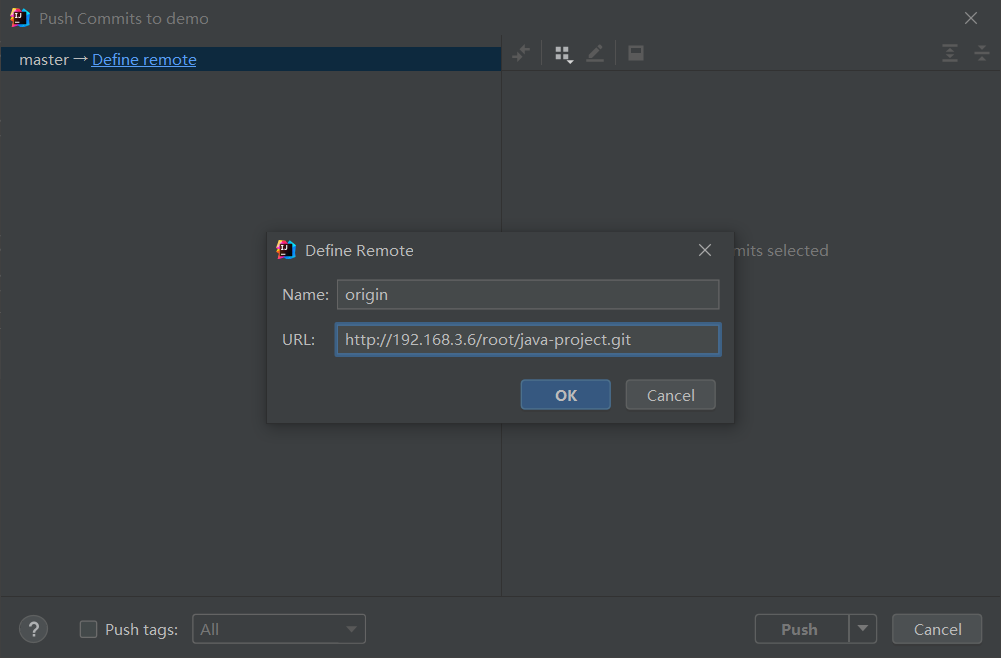
点击Ok后,执行push操作,将代码push到远程GitLab仓库上。
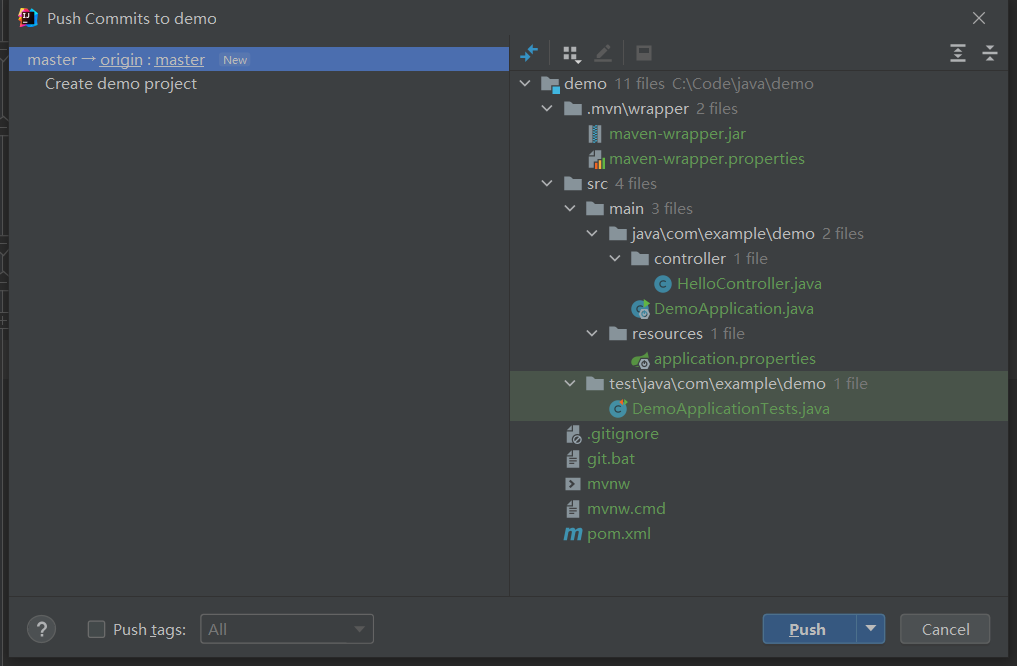
IDEA报错了:
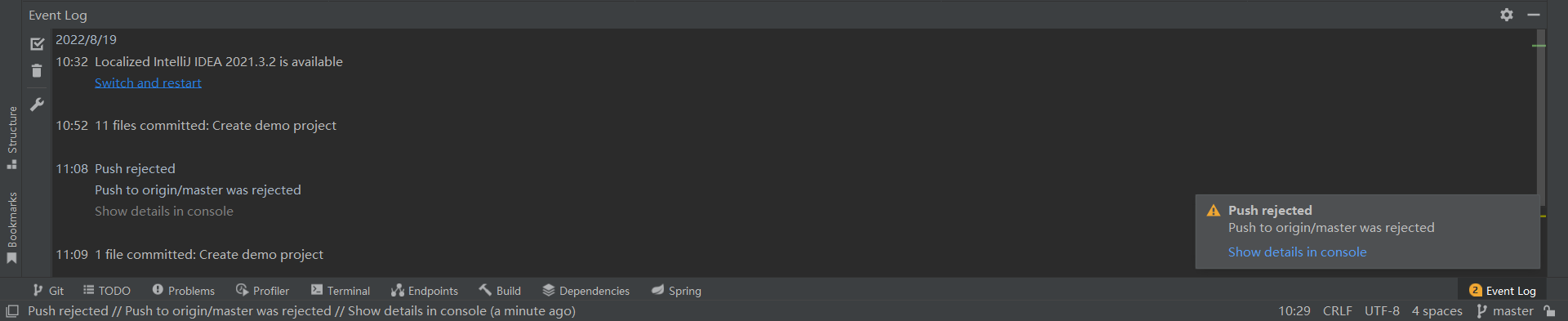
11:07:54.968: [demo] git -c credential.helper= -c core.quotepath=false -c log.showSignature=false push --progress --porcelain origin refs/heads/master:refs/heads/master --set-upstream
error: failed to push some refs to 'http://192.168.3.6/root/java-project.git'
hint: Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do
To http://192.168.3.6/root/java-project.git
hint: not have locally. This is usually caused by another repository pushing
! refs/heads/master:refs/heads/master [rejected] (fetch first)
hint: to the same ref. You may want to first integrate the remote changes
Done
# 意思是远程仓库和本地仓库文件不一致,也就是冲突了.
解决问题:
进入项目所在的本地目录,右键 -> Git Bash Here,在git bash窗口中输入命令:
git pull origin master --allow-unrelated-histories
git pull origin master
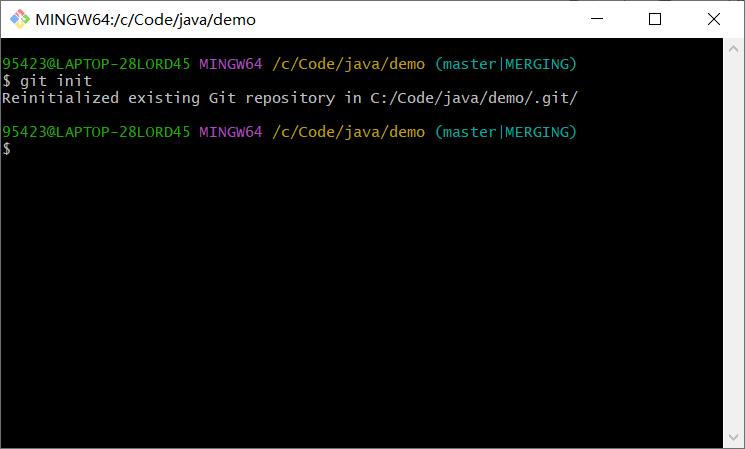
git init
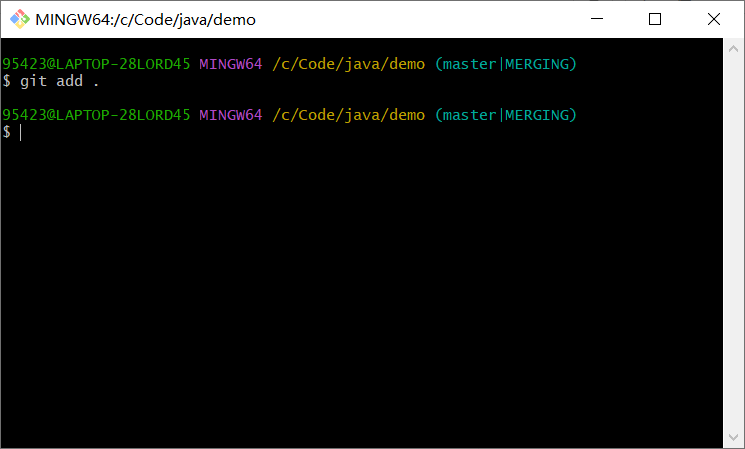
git add .
git commit -m 'test'
git push -u origin master

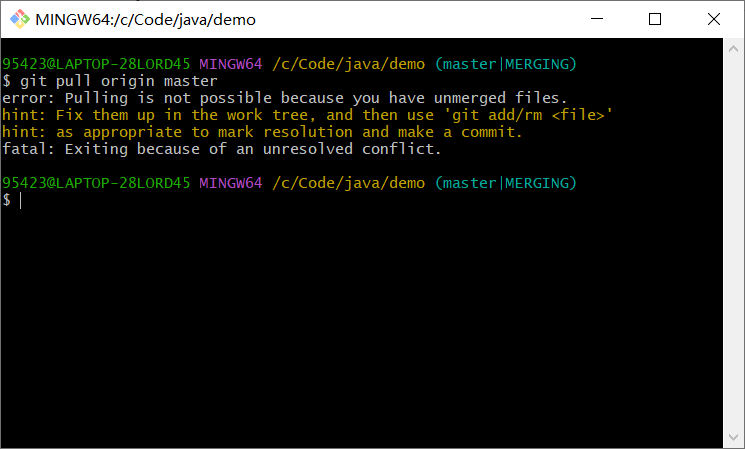


3.2 Jenkins
Jenkins官方网站:https://www.jenkins.io
3.2.1 安装需求
机器要求:
- 256 MB 内存,建议大于 512 MB
- 10 GB 的硬盘空间(用于 Jenkins 和 Docker 镜像)
软件配置:
- Java 8 ( JRE 或者 JDK 都可以)
3.2.2 Jenkins安装
安装JDK1.8
1.下载JDK1.8安装包
官网下载地址:https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
2.解压JDK安装包:通过Xshell进入到服务器的控制台,进入后的当前目录为:/home/appop,把jdk安装文件拷贝到当前录下。进行JDK安装包的解压:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ tar –zxvf jdk-8u341-linux-x64.tar.gz
3.配置环境变量:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ vi ~/.bashrc
在该文件中增加以下配置并保存:
export JAVA_HOME=/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341
export CLASSPATH=${JAVA_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
然后键入命令: source ~/.bashrc让配置文件中的配置立即生效
问题描述:-bash: export: `/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341': 不是有效的标识符
错误原因:export JAVA_HOME=/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341的 “=”左右两边不能有空格。
4.验证JDK版本
[appop@jenkins ~]$ java -version
# linux系统设置环境变量的配置文件:
1、/etc/profile
2、/etc/environment
3、~/.profile
4、~/.bashrc
说明:/etc下的两个配置文件是全局性质的,对所有用户起作用;~/下的两个文件是对当前用户起作用的;一般情况下在`~/.bashrc`中添加修改环境变量就行,然后`source ~/.bashrc`一下,其他几个配置文件尽量不要改动。
下载Jenkins并将jenkins.war上传至所在服务器/home/appop目录下
1.下载jenkins.war安装包
官网下载地址:https://www.jenkins.io/zh/download/
[appop@jenkins ~]$ ll -h
-rw-rw-r--. 1 appop appop 91196986 8月 17 12:39 jenkins.war
打开终端进入到下载目录,运行jenkins
[appop@jenkins ~]$ nohup java -jar jenkins.war --httpPort=8080 >jenkins.log 2>&1 &
注:首次启动war包会在/home/appop/.jenkins生成配置文件。
开放8080端口
# 查看firewall的状态:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --state
[sudo] appop 的密码:
running
出现Active: active (running)切高亮显示则表示是启动状态。
出现 Active: inactive (dead)灰色表示停止,看单词也行。
# 开放80端口:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
# 重新加载防火墙配置(修改防火墙配置后,要重新加载防火墙配置或重启防火墙服务):
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
安装后设置向导
当您第一次访问新的Jenkins实例时,系统会要求您使用自动生成的密码对其进行解锁。
打开浏览器,访问 http://192.168.3.3:8080,并等待 解锁 Jenkins 页面出现。
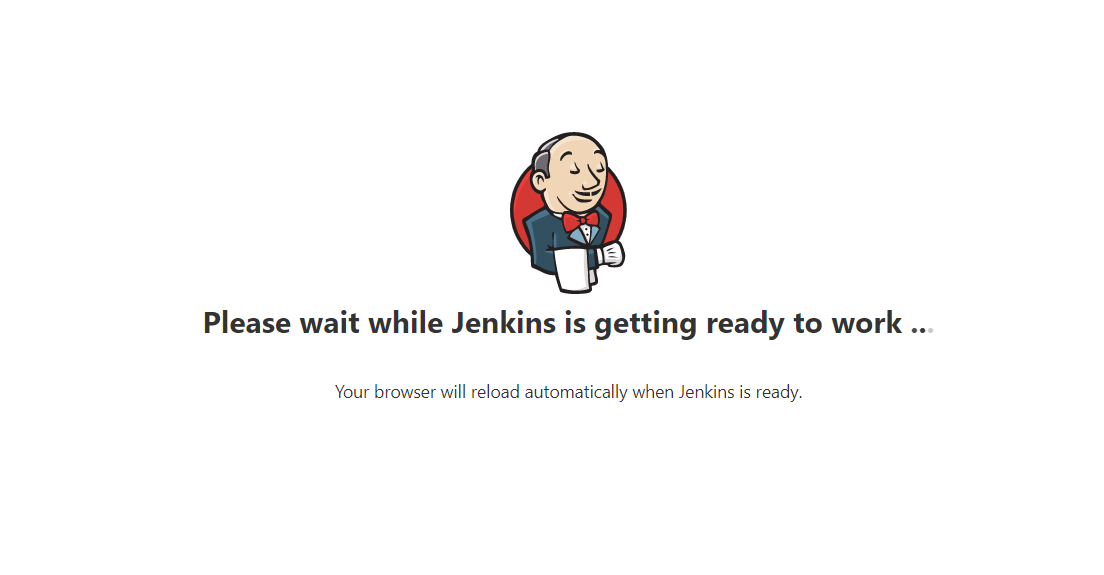
在 解锁Jenkins 页面上,将此 密码 粘贴到管理员密码字段中,然后单击 继续 。
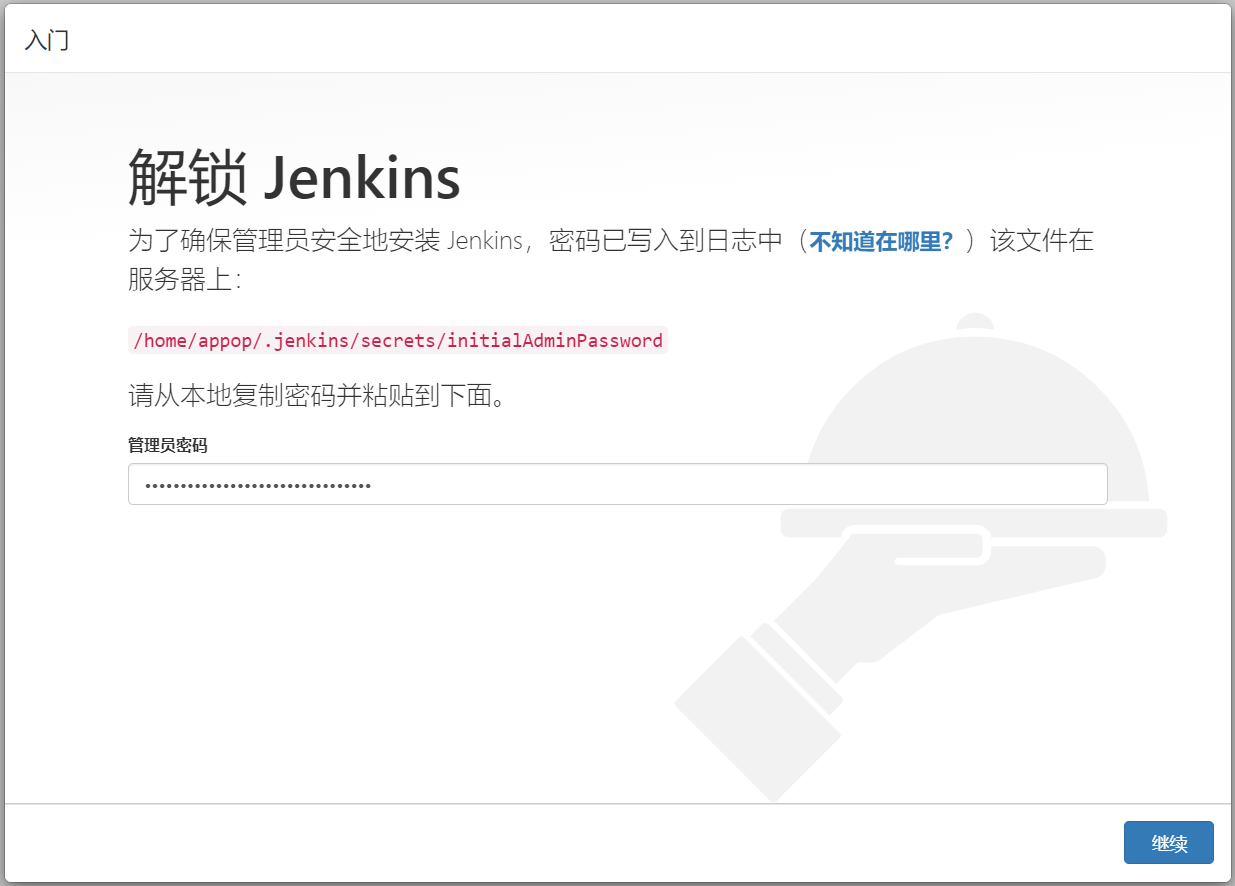
从Jenkins控制台日志输出中,复制自动生成的字母数字密码(在两组*之间):
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
Jenkins initial setup is required. An admin user has been created and a password generated.
Please use the following password to proceed to installation:
6eb1599e8bb44e08b05cbbc422b199f1
This may also be found at: /home/appop/.jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
# 注:密码文件第一次使用后会自动删除
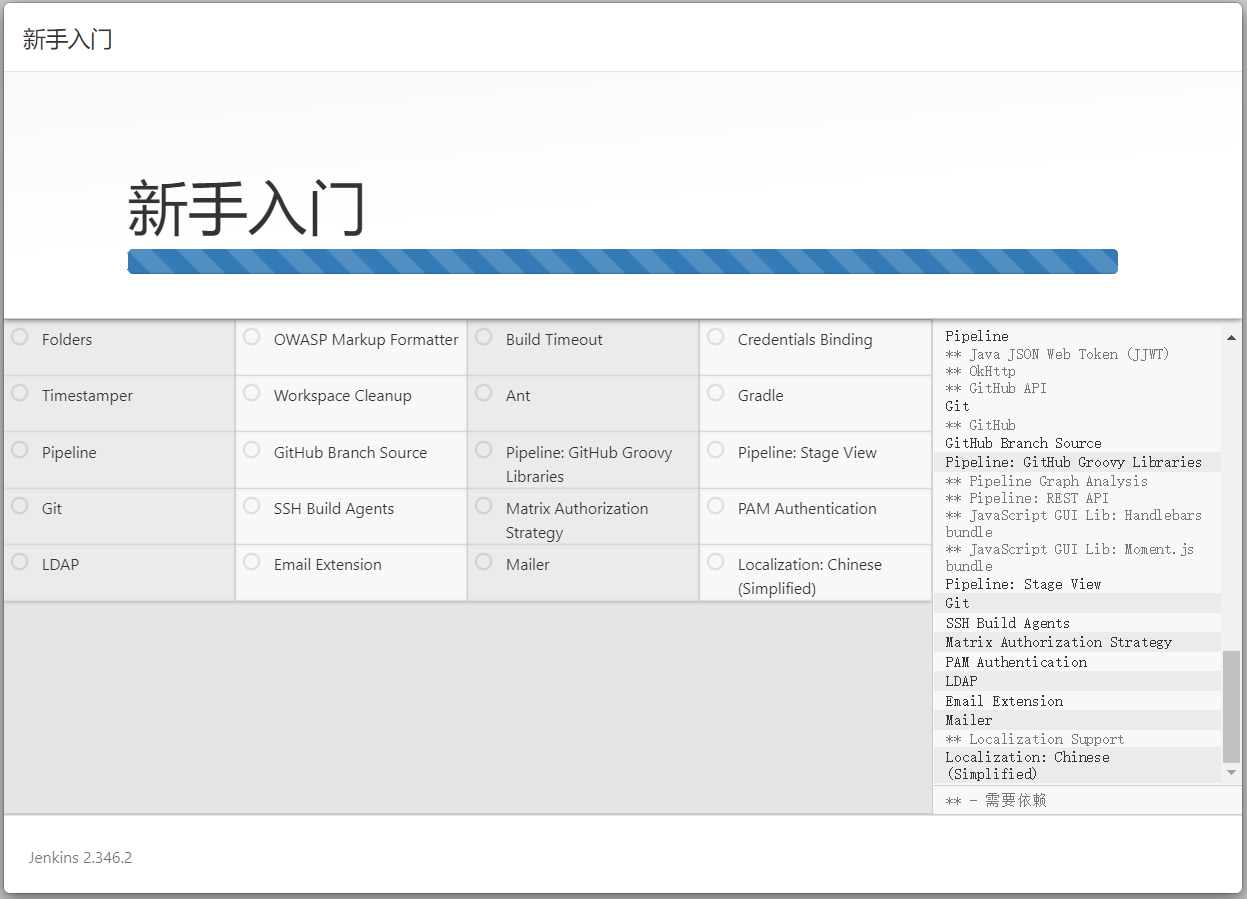
解锁 Jenkins之后,在 Customize Jenkins 页面内, 您可以安装任何数量的有用插件作为您初始步骤的一部分。两个选项可以设置:
- 安装建议的插件 - 安装推荐的一组插件,这些插件基于最常见的用例.
- 选择要安装的插件 - 选择安装的插件集。当你第一次访问插件选择页面时,默认选择建议的插件。

选择"安装Jenkins社区推荐的插件"。
jenkins插件安装完成后,Jenkins要求我们创建第一个管理员账户。填入相关信息,并单击 保存并完成 按钮,Jenkins即可初始化完成。


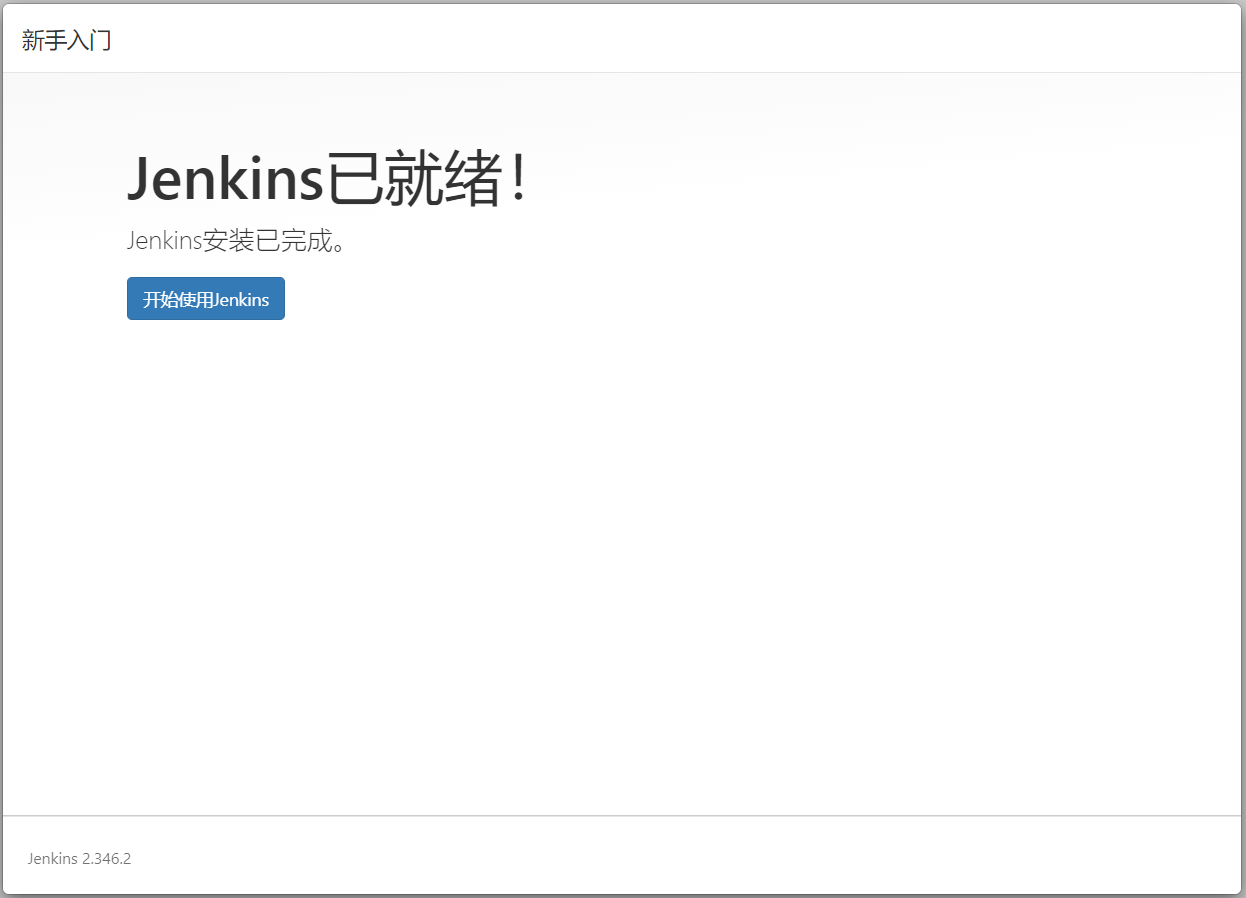
当 Jenkins已就绪! 出现时,单击开始使用 Jenkins。
3.2.3 Maven安装
Maven官方网站:https://maven.apache.org/
< 下载后复制到Jenkins所在服务器解压缩即可 >
1.将apache-maven-3.8.6-bin.tar.gz上传至所在服务器/home/appop目录下
[appop@jenkins ~]$ ll -h
-rw-rw-r--. 1 appop appop 8676320 8月 17 12:39 apache-maven-3.8.6-bin.tar.gz
2.将apache-maven-3.8.6-bin.tar.gz进行解压缩,并移至/usr/local/maven
[appop@jenkins ~]$ tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.8.6-bin.tar.gz
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo mv apache-maven-3.8.6 /usr/local/maven
问题描述:mv: 无法将"apache-maven-3.8.6" 移动至"/usr/local/maven": 权限不够
3.确认maven是否安装成功
[appop@jenkins ~]$ /usr/local/maven/bin/mvn -v
Apache Maven 3.8.6 (84538c9988a25aec085021c365c560670ad80f63)
Maven home: /usr/local/maven
Java version: 1.8.0_341, vendor: Oracle Corporation, runtime: /home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341/jre
Default locale: zh_CN, platform encoding: UTF-8
OS name: "linux", version: "3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"
4.Maven阿里云镜像配置
[appop@jenkins conf]$ sudo vi /usr/local/maven/conf/settings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
distributed with this work for additional information
regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
software distributed under the License is distributed on an
"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations
under the License.
-->
<!--
| This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels:
|
| 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user,
| and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml.
|
| NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option:
|
| -s /path/to/user/settings.xml
|
| 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven
| users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven
| installation). It's normally provided in
| ${maven.conf}/settings.xml.
|
| NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option:
|
| -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml
|
| The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at
| getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default
| values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided.
|
|-->
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<!-- localRepository
| The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts.
|
| Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository
<localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository>
-->
<localRepository>${user.home}/.m2/repository</localRepository>
<!-- interactiveMode
| This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false,
| maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for
| the parameter in question.
|
| Default: true
<interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode>
-->
<!-- offline
| Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build.
| This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others.
|
| Default: false
<offline>false</offline>
-->
<!-- pluginGroups
| This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e.
| when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers
| "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list.
|-->
<pluginGroups>
<!-- pluginGroup
| Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup.
<pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup>
-->
<pluginGroup>org.mortbay.jetty</pluginGroup>
</pluginGroups>
<!-- proxies
| This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network.
| Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy
| specification in this list marked as active will be used.
|-->
<proxies>
<!-- proxy
| Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network.
|
<proxy>
<id>optional</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<username>proxyuser</username>
<password>proxypass</password>
<host>proxy.host.net</host>
<port>80</port>
<nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts>
</proxy>
-->
</proxies>
<!-- servers
| This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system.
| Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server.
|-->
<servers>
<!-- server
| Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by
| a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below).
|
| NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are
| used together.
|
<server>
<id>deploymentRepo</id>
<username>repouser</username>
<password>repopwd</password>
</server>
-->
<!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate.
<server>
<id>siteServer</id>
<privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey>
<passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase>
</server>
-->
<server>
<id>releases</id>
<username>ali</username>
<password>ali</password>
</server>
<server>
<id>Snapshots</id>
<username>ali</username>
<password>ali</password>
</server>
</servers>
<!-- mirrors
| This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories.
|
| It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts.
| However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored
| it to several places.
|
| That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that
| repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred
| server for that repository.
|-->
<mirrors>
<!-- mirror
| Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that
| this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used
| for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors.
|
<mirror>
<id>mirrorId</id>
<mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf>
<name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name>
<url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url>
</mirror>
-->
<mirror>
<!--This sends everything else to /public -->
<id>nexus</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</mirror>
<mirror>
<!--This is used to direct the public snapshots repo in the
profile below over to a different nexus group -->
<id>nexus-public-snapshots</id>
<mirrorOf>public-snapshots</mirrorOf>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots/</url>
</mirror>
<mirror>
<!--This is used to direct the public snapshots repo in the
profile below over to a different nexus group -->
<id>nexus-public-snapshots1</id>
<mirrorOf>public-snapshots1</mirrorOf>
<url>https://artifacts.alfresco.com/nexus/content/repositories/public/</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<!-- profiles
| This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify
| the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine-
| specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment.
|
| For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where
| your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is
| dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin.
|
| As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles
| section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially
| relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property,
| or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a
| value of '1.4' might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of '1.4.2_07'.
| Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line.
|
| NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact
| repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration
| variables for plugins in the POM.
|
|-->
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>development</id>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>central</id>
<url>http://central</url>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>central</id>
<url>http://central</url>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</profile>
<profile>
<!--this profile will allow snapshots to be searched when activated-->
<id>public-snapshots</id>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>public-snapshots</id>
<url>http://public-snapshots</url>
<releases><enabled>false</enabled></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>public-snapshots</id>
<url>http://public-snapshots</url>
<releases><enabled>false</enabled></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</profile>
</profiles>
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>development</activeProfile>
<activeProfile>public-snapshots</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
<!-- activeProfiles
| List of profiles that are active for all builds.
|
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
<activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
-->
</settings>
3.2.4 Git安装
< 在Jenkins所在服务器上安装git >
为了Jenkins能够拉取代码,需要安装Git环境。
在Linux/Centos服务器上,如果使用的git版本过低,使用的时候可能会由于低版本不支持遇到各种问题。部署Gitlab+Maven+Jenkins持续集成环境,但在Jenkins中新建项目的源码管理"Repository URL"中添加git地址环节出现了问题,信息为"Failed to connect to repository : Error performing command: git ls-remote -h http://×××××××××.git HEAD"。
原因分析:这是由于git客户端版本过低造成的!
Jenkins本机默认使用"yum install -y git" 安装的git版本比较低,应该自行安装更高版本的git。
更新yum源
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo yum update
查看jenkins本机的git版本
[appop@jenkins ~]$ git --version
git version 1.8.3.1
卸载本机低版本的git,自行安装更高版本的git
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo yum remove -y git //或者使用"rpm -e --nodeps git"命令进行卸载
[appop@jenkins ~]$ git --version
-bash: /usr/bin/git: No such file or directory
接着进行git版本升级操作
# 下载并安装高版本的git
1.安装git相关的依赖包:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo yum install curl-devel expat-devel gettext-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel gcc perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker
2.到git官网查看最新的版本,并进行git下载:
https://git-scm.com/download/
3.打开文件夹,用于存放下载的git包:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ cd /usr/local/src
4.解压:
[appop@jenkins src]$ sudo tar -xvf git-2.32.0.tar.xz
5.打开解压好的git文件夹:
[appop@jenkins src]$ cd git-2.32.0
6.编译
[appop@jenkins git-2.32.0]$ sudo make prefix=/usr/local/git all
7.安装git
[appop@jenkins git-2.32.0]$ sudo make prefix=/usr/local/git install
8.配置环境变量
[appop@jenkins git-2.32.0]$ vi ~/.bashrc
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/git/bin
然后键入命令: source /etc/profile让配置文件中的配置立即生效
[appop@jenkins ~]$ source ~/.bashrc
9.验证git版本
[appop@jenkins git-2.32.0]$ git --version
git version 2.32.0
3.3 Tomcat
安装JDK1.8
1.下载JDK1.8安装包
官网下载地址:https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
2.解压JDK安装包:通过Xshell进入到服务器的控制台,进入后的当前目录为:/home/appop,把jdk安装文件拷贝到当前录下。进行JDK安装包的解压:
[appop@tomcat ~]$ tar –zxvf jdk-8u341-linux-x64.tar.gz
3.配置环境变量:
[appop@tomcat ~]$ vi ~/.bashrc
在该文件中增加以下配置并保存:
export JAVA_HOME=/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341
export CLASSPATH=${JAVA_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
然后键入命令: source ~/.bashrc让配置文件中的配置立即生效
问题描述:-bash: export: `/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341': 不是有效的标识符
错误原因:export JAVA_HOME=/home/appop/jdk1.8.0_341的 “=”左右两边不能有空格。
4.验证JDK版本
[appop@tomcat ~]$ java -version
# linux系统设置环境变量的配置文件:
1、/etc/profile
2、/etc/environment
3、~/.profile
4、~/.bashrc
说明:/etc下的两个配置文件是全局性质的,对所有用户起作用;~/下的两个文件是对当前用户起作用的;一般情况下在`~/.bashrc`中添加修改环境变量就行,然后`source ~/.bashrc`一下,其他几个配置文件尽量不要改动。
下载tomcat并将apache-tomcat-10.0.23.tar.gz上传至所在服务器/home/appop目录下
1.下载apache-tomcat-10.0.23.tar.gz安装包
官网下载地址:https://tomcat.apache.org/
[appop@tomcat ~]$ ll -h
-rw-rw-r--. 1 appop appop 12M 8月 17 21:16 apache-tomcat-10.0.23.tar.gz
打开终端进入到下载目录,解压Tomcat安装包
[appop@tomcat ~]$ tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-10.0.23.tar.gz
Tomcat服务启动、停止
[appop@tomcat ~]$ cd apache-tomcat-10.0.23/bin/
# Tomcat服务启动
[appop@tomcat bin]$ sh startup.sh
# Tomcat服务停止:
[appop@tomcat bin]$ sh shutdown-force.sh
开放8080端口
# 查看firewall的状态:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --state
[sudo] appop 的密码:
running
出现Active: active (running)切高亮显示则表示是启动状态。
出现 Active: inactive (dead)灰色表示停止,看单词也行。
# 开放80端口:
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
# 重新加载防火墙配置(修改防火墙配置后,要重新加载防火墙配置或重启防火墙服务):
[appop@jenkins ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
打开浏览器,访问:http://192.168.3.8:8080/

3.4 邮箱授权码
在Jenkins设置邮件提醒前,需先获取邮箱授权码。这里使用163邮箱:
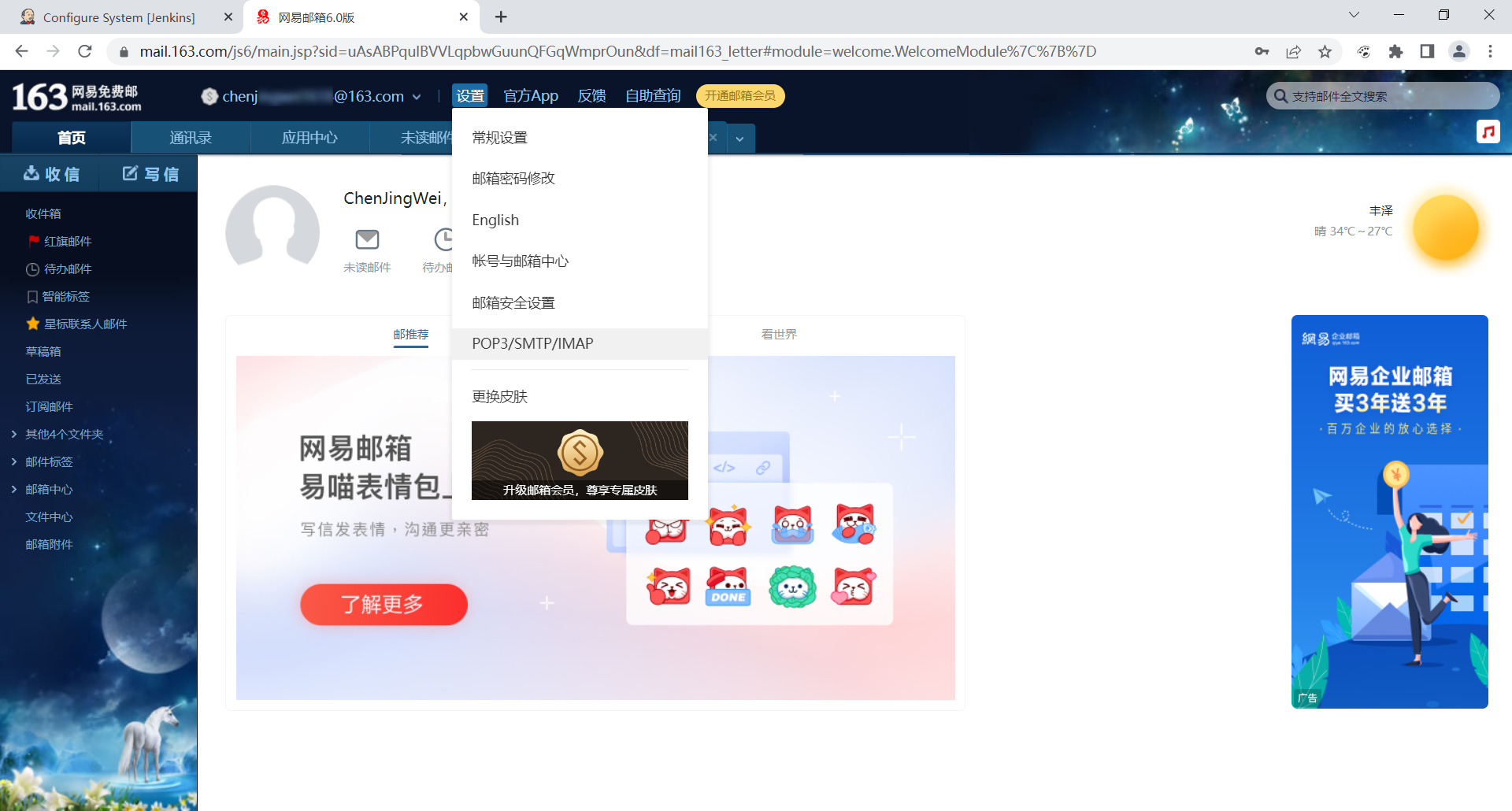
登录163邮箱后,在"设置"找到"POP3/SMTP/IMAP",开启SMTP服务。
使用手机扫描二维码快速发送短信,然后点击“我已发送”进行验证。

成功开启SMTP服务,在第三方客户端登录时,登录密码输入以下授权密码。
4 Jenkins 配置
4.1 Global Tool Configuration (全局工具配置 )
**Global Tool Configuration (全局工具配置 )**主要对一些常用工具的名称、版本、路径和配置文件进行设定。
在面板左侧的导航栏中点击“系统管理”,进入到“管理Jenkins”界面,选择界面中的System Configuration —> Global Tool Configuration后进入到“全局工具配置”界面,依次对Maven配置、JDK、Git、Maven等进行配置。
4.1.1 Maven配置
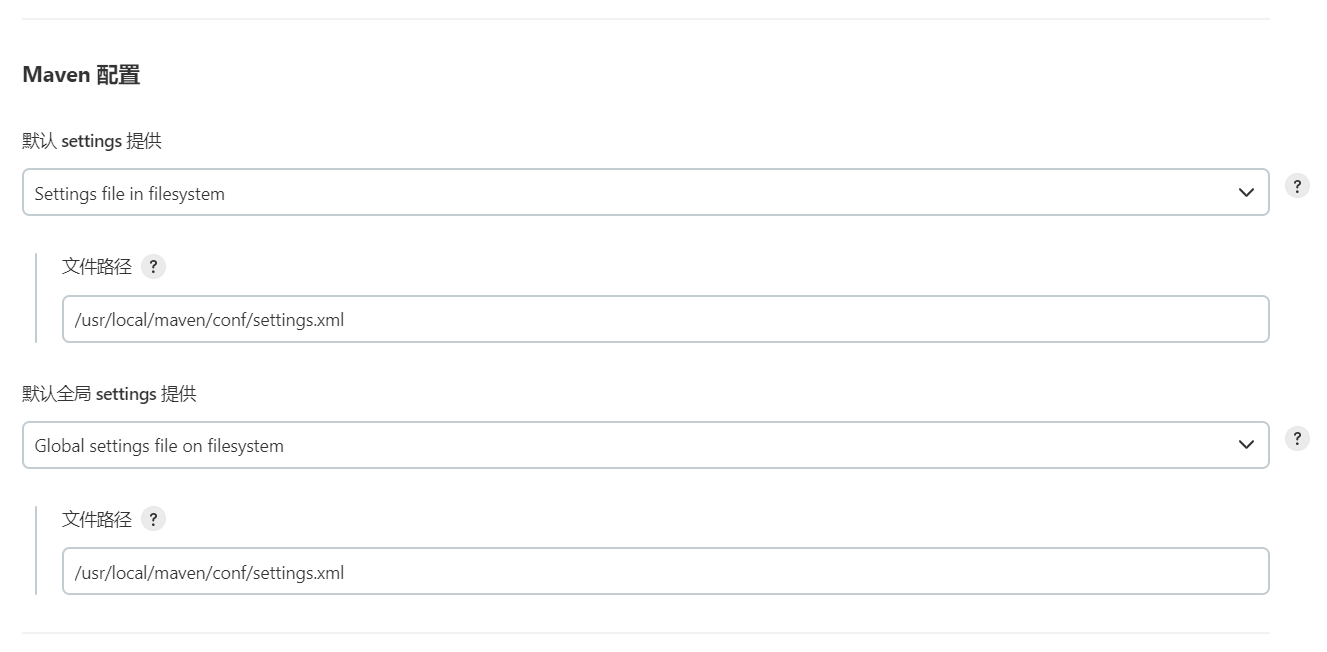
主要用于Maven的主配置文件settings.xml的设定。
settings.xml包含仓库镜像、本地镜像和认证信息等。
一般默认的路径有两种:Global Maven Settings — ${M2_HOME}/conf/settings.xml;
User Maven Settings — ${user.HOME}/.m2/settings.xml。
如果两个文件都存在,会对内容进行合并,优先应用当前目录下settings.xml中的设定。
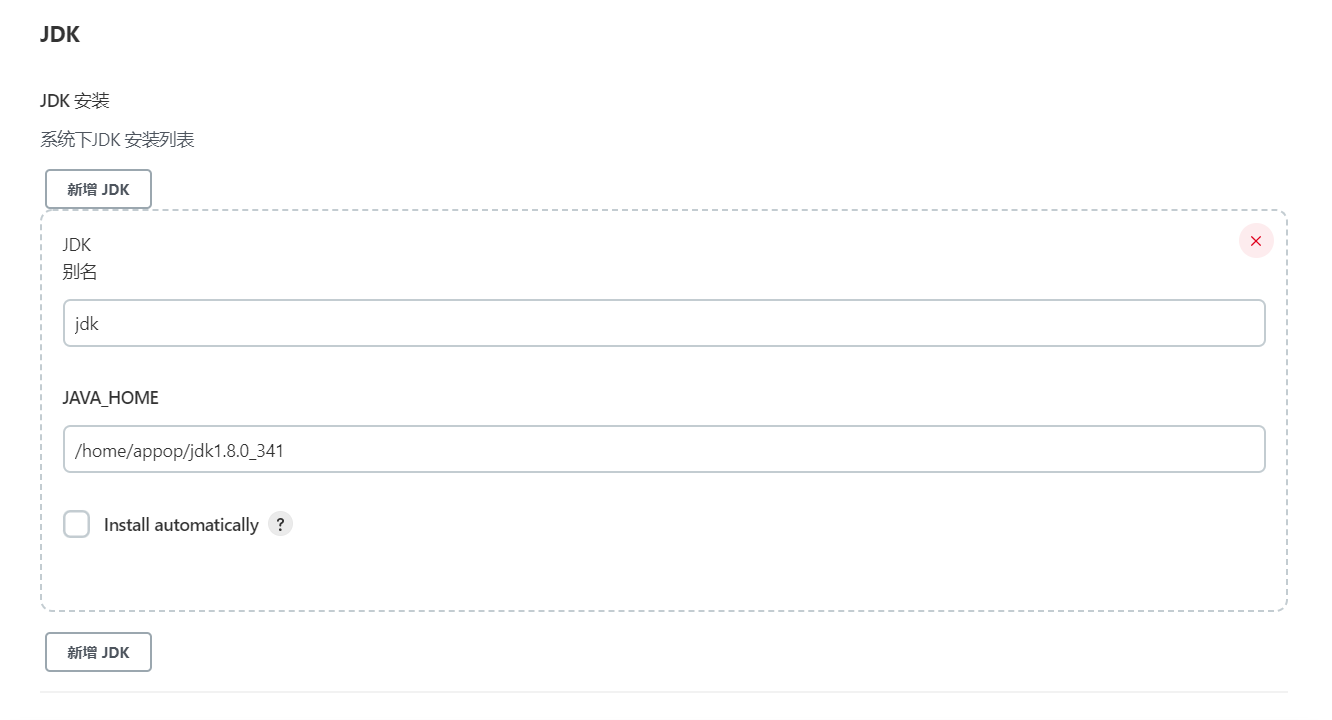
4.1.2 JDK
如果已经安装过JDK,这里需要配置JDK的JAVA_HOME。
4.1.3 Git
Git的配置也很重要,因为大多数的任务都要获取Git仓库中的代码,所以这里需要配置Git的执行路径。
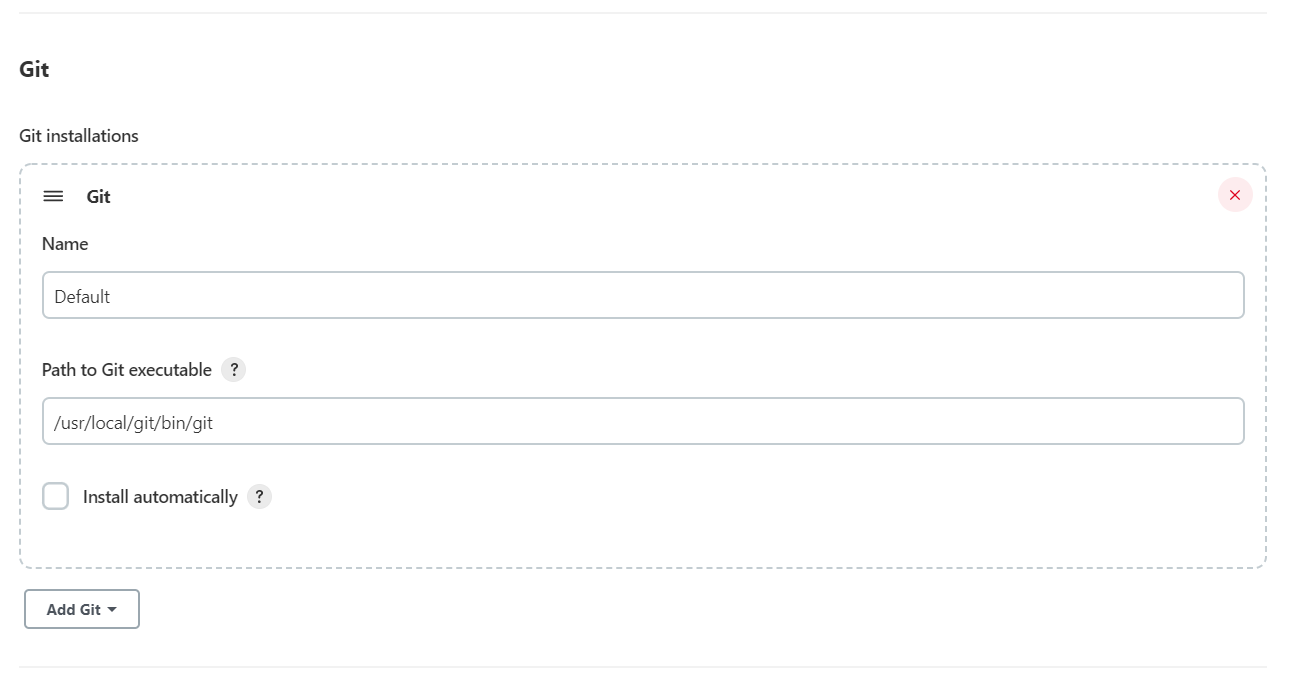
注:git的安装目录获取方式:whereis git ,要精确到 /bin/git。
4.1.4 Maven
主要用于配置Maven的主目录,可以添加多个,用Name来区分。如果系统中已经安装Maven,这里直接填写MAVEN_HOME对应的路径,Jenkins会在Master节点上进行检查,查看该目录是否有效。

4.2 Manager Plugin(插件管理)
Jenkins提供了大量的插件,这些插件使Jenkins能实现很多复杂的功能。下面列出了部分持续集成所需的插件:
- Email Extension Plugin:邮件通知插件。例如,构建失败或成功后可以发送相关信息到指定的邮箱。
- Publish Over SSH:用于远程服务器发布,将编译生成的jar、war等文件推送到远程服务器中指定的目录。
- Maven Integration:Maven集成插件,缺少此插件则新建任务时没有Maven Project选项。
- GitLab:用于从指定的代码仓库中拉取需要构建的代码。
- Sonar scanner:用于构建前或构建后对代码进行扫描。
- Git parameter:基于Git的参数化构建。
- HTML Publisher plugin:用于在Jenkins中配置HTML格式的报告。
- Groovy Label Assignment plugin:用于执行Groovy代码。
- NodeJS plugin:配置JavaScript的运行环境,作为前端代码的打包工具或构建工具。
- Build Authorization Token Root:开启Token构建方式,可用于匿名构建。
- Blue Ocean:是pipeline的可视化UI。同时兼容经典的自由模式的job。Jenkins Pipeline从头开始设计,但仍与自由式作业兼容,Blue Ocean减少了经典模式下的混乱并为团队中的每个成员增加了清晰度。
检查必要的插件是否已安装,若未安装,则可手动安装相关插件。
4.2.1 安装Maven Integration插件
进入 Manage Jenkins >> Manage Plugins 中,单击“可选插件”选项卡,在输入框中填写需要安装的插件名字_Maven Integration_。
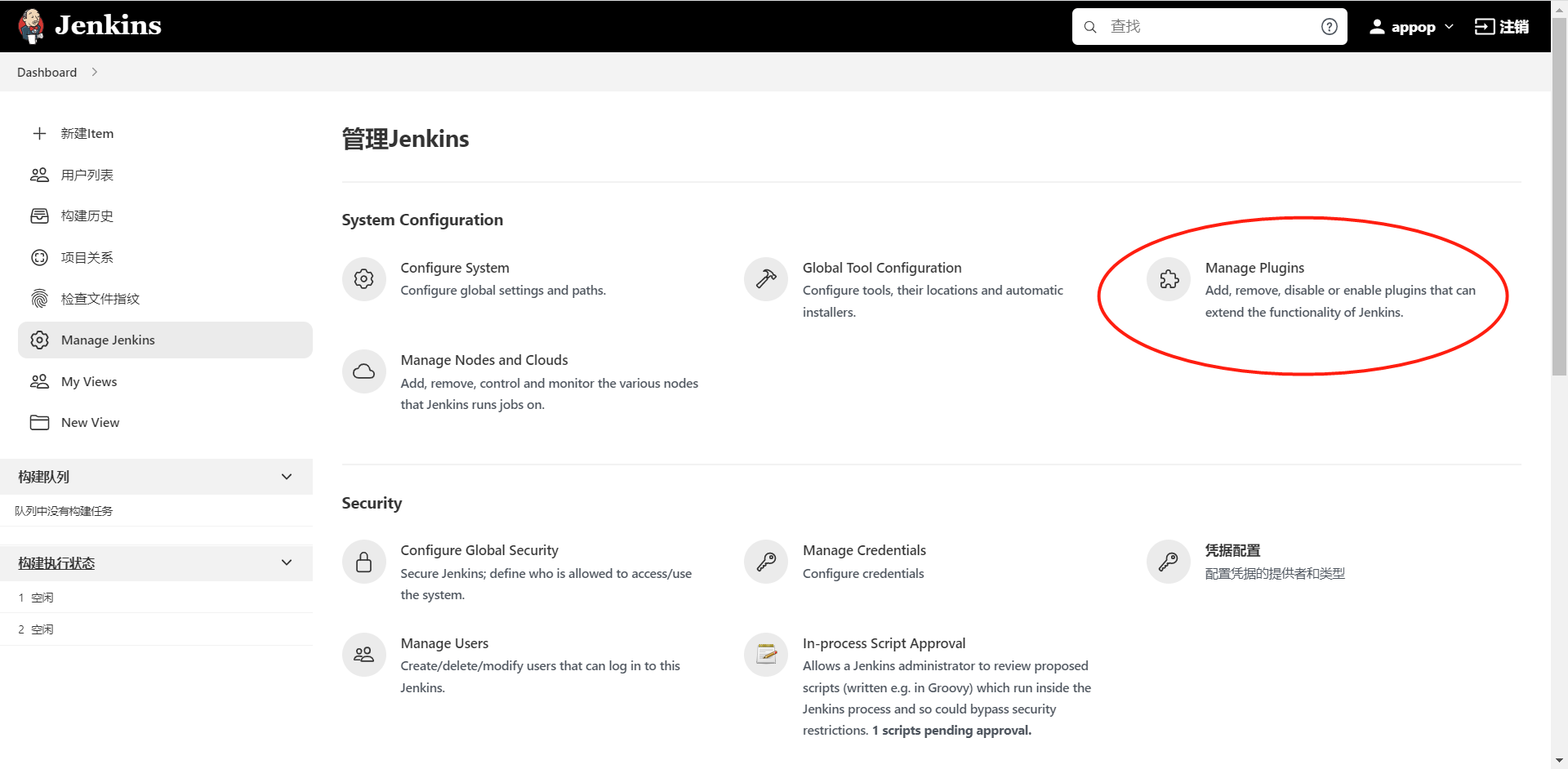

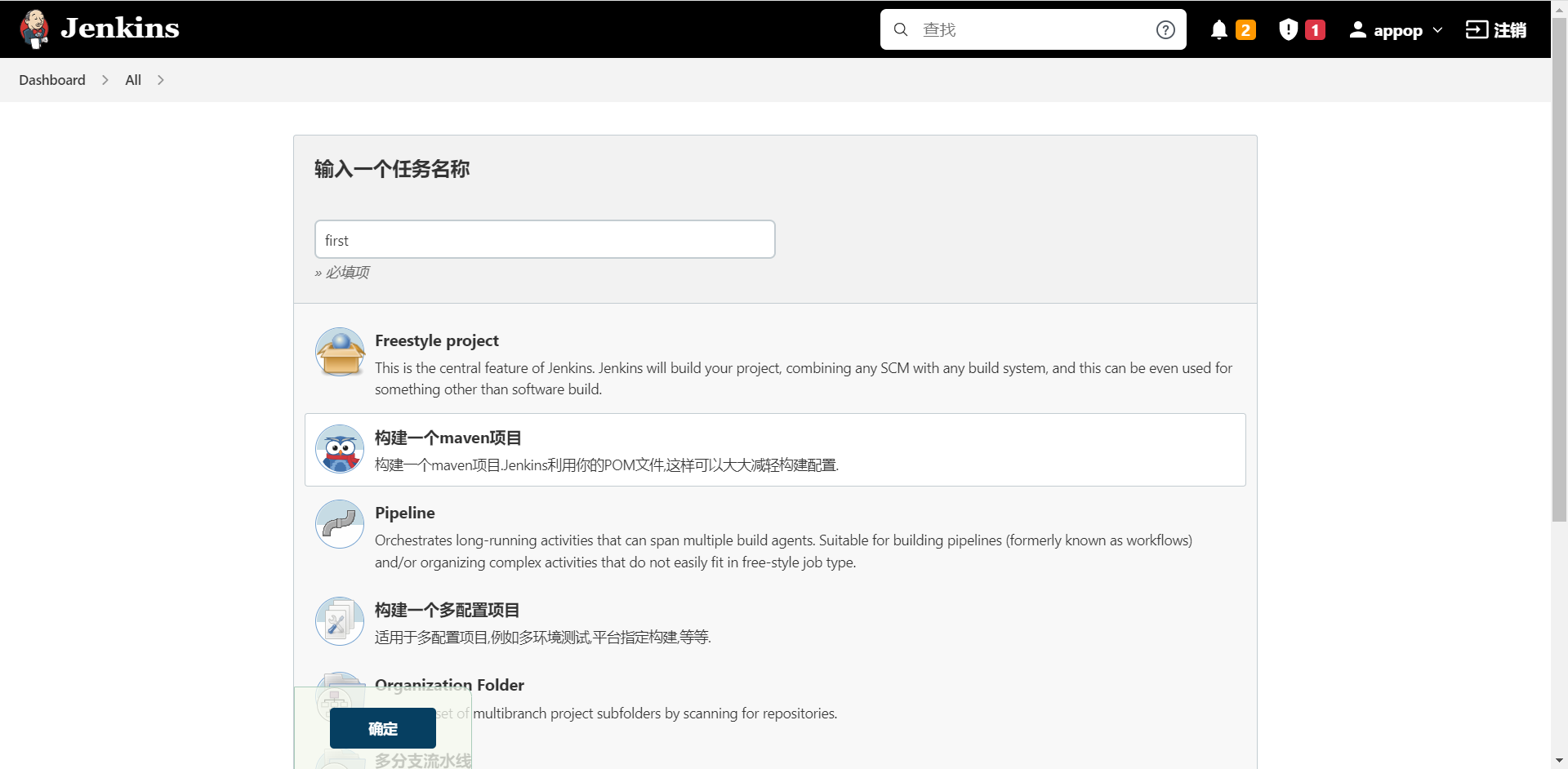
安装好Maven Integration插件,在新建Item时,才有"构建一个maven项目"选项,可用于Maven项目创建。
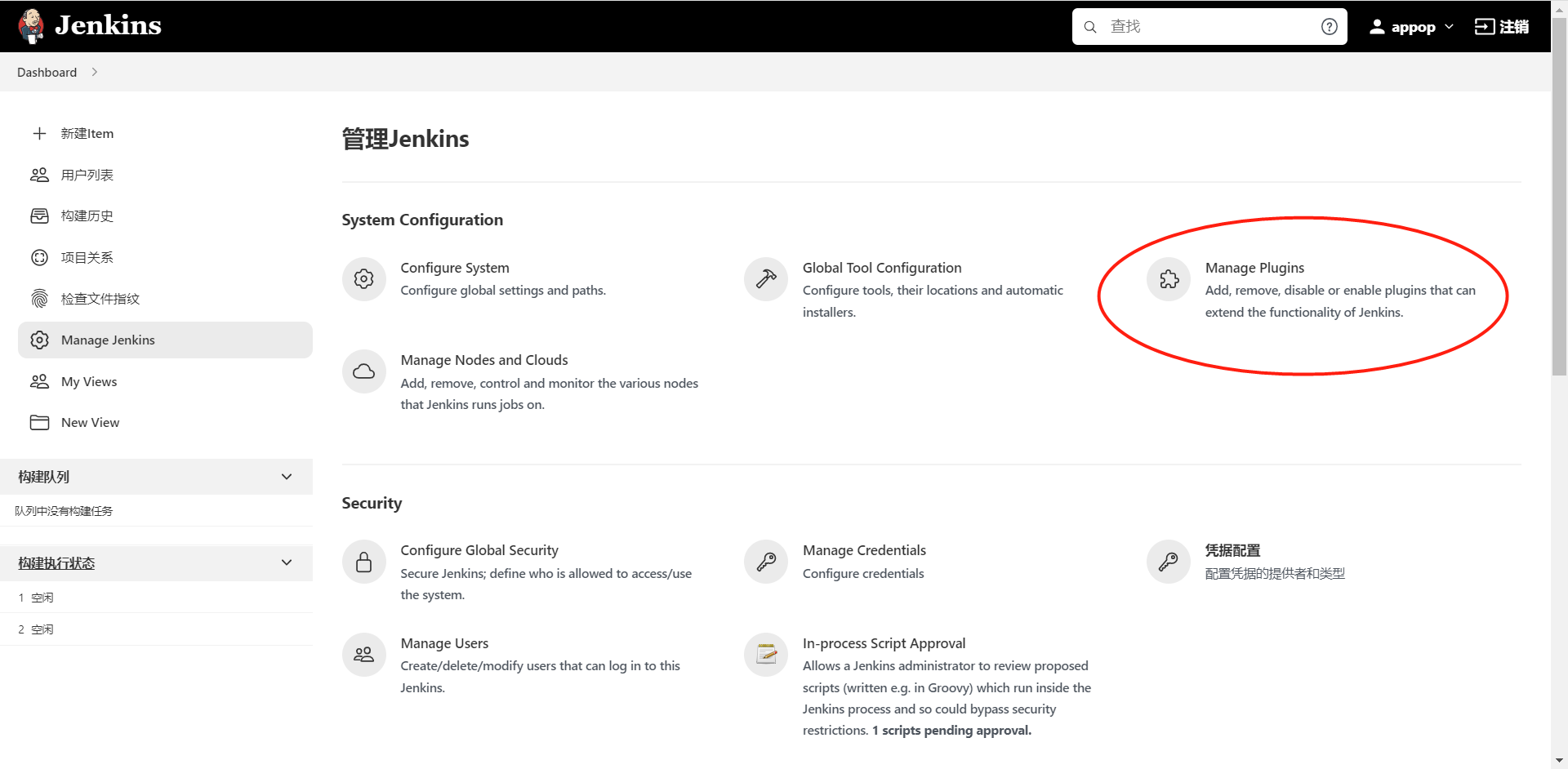
4.2.2 安装Publish over SSH插件
进入 Manage Jenkins >> Manage Plugins 中,单击“可选插件”选项卡,在输入框中填写需要安装的插件名字_Publish over SSH_。
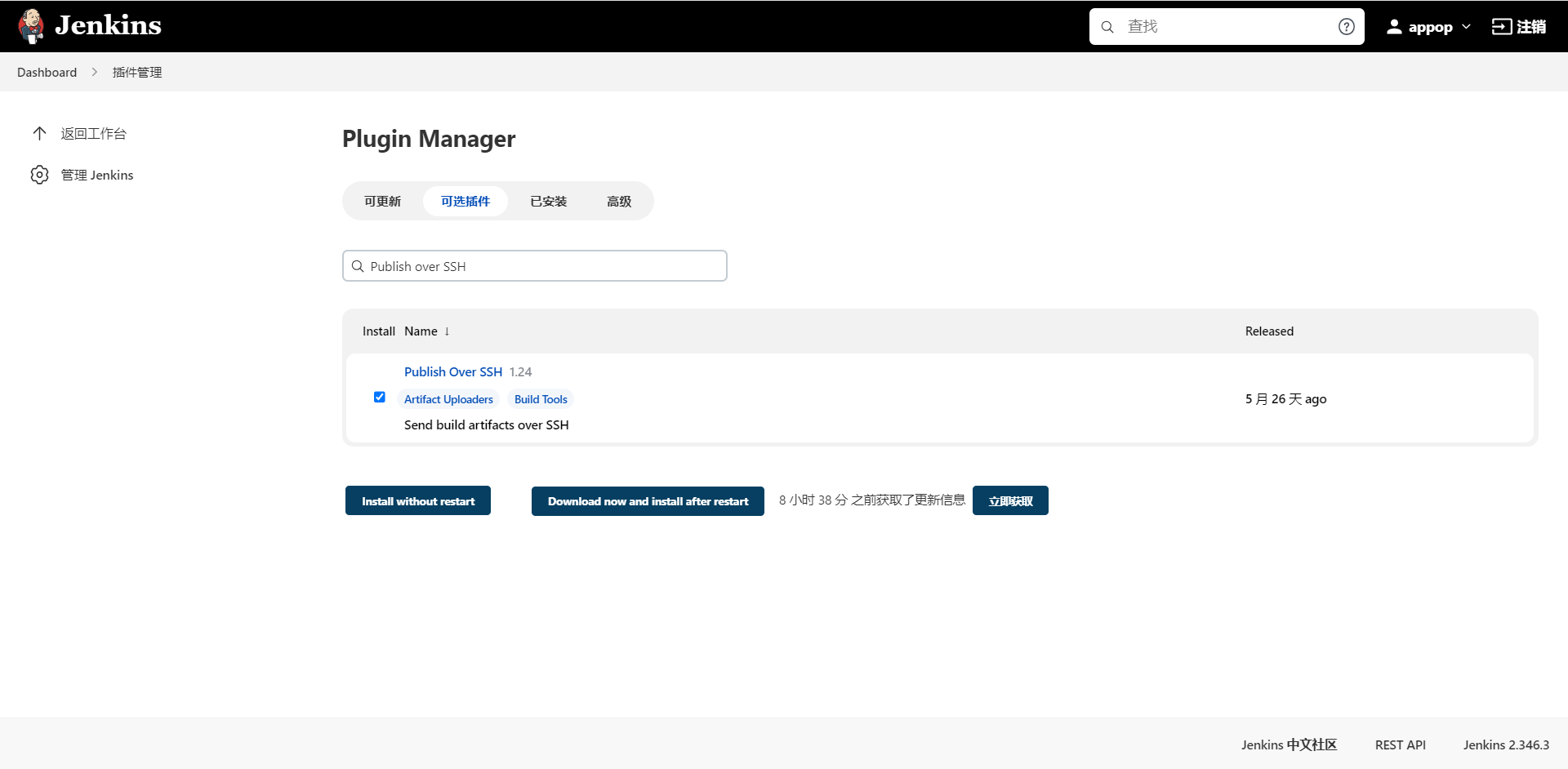
安装好Publish over SSH插件,可用于远程服务器发布,将编译生成的jar、war等文件推送到远程服务器中指定的目录。
4.2.3 安装Build Authorization Token Root插件
进入 Manage Jenkins >> Manage Plugins 中,单击“可选插件”选项卡,在输入框中填写需要安装的插件名字_Build Authorization Token Root_。
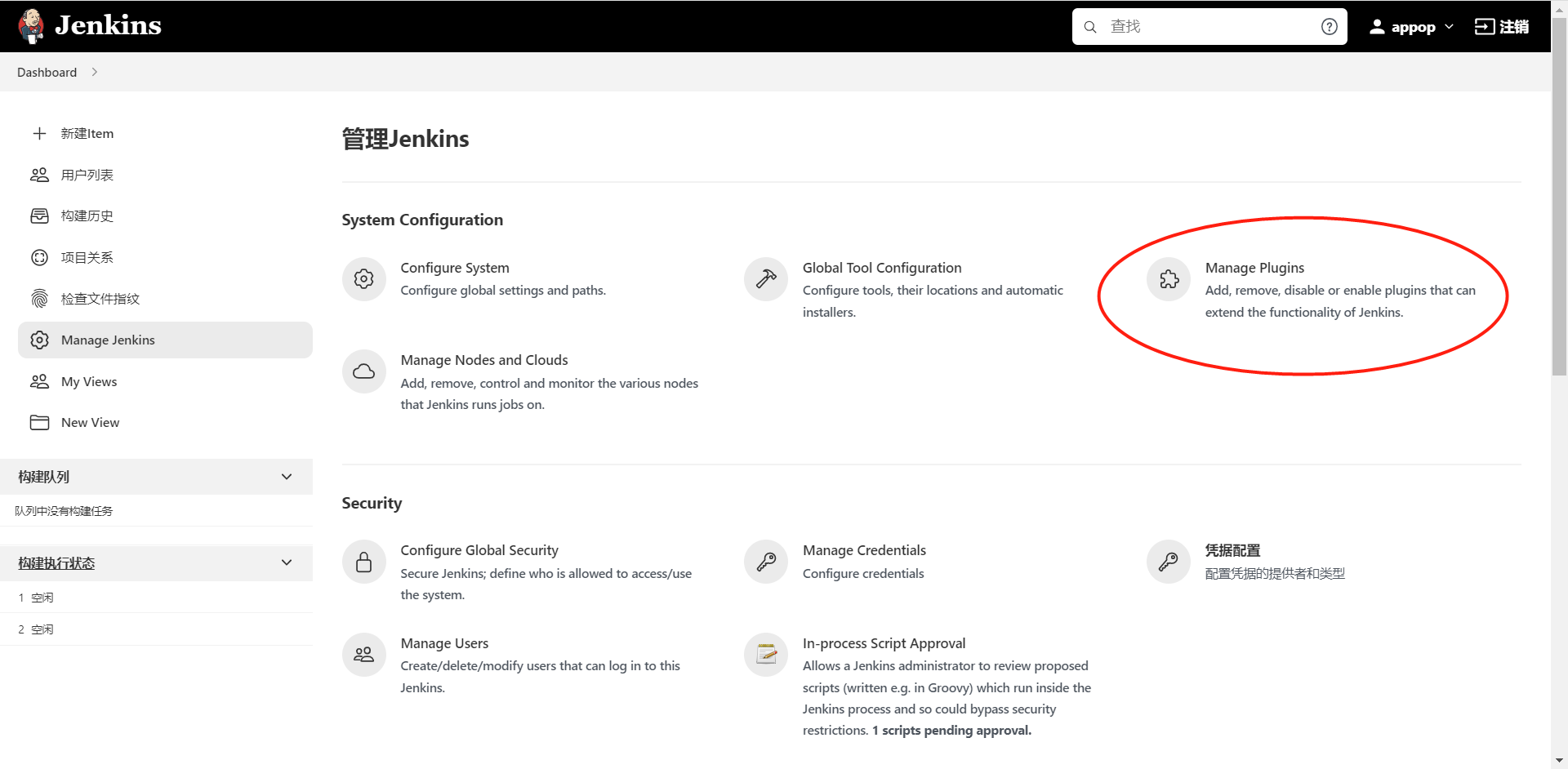
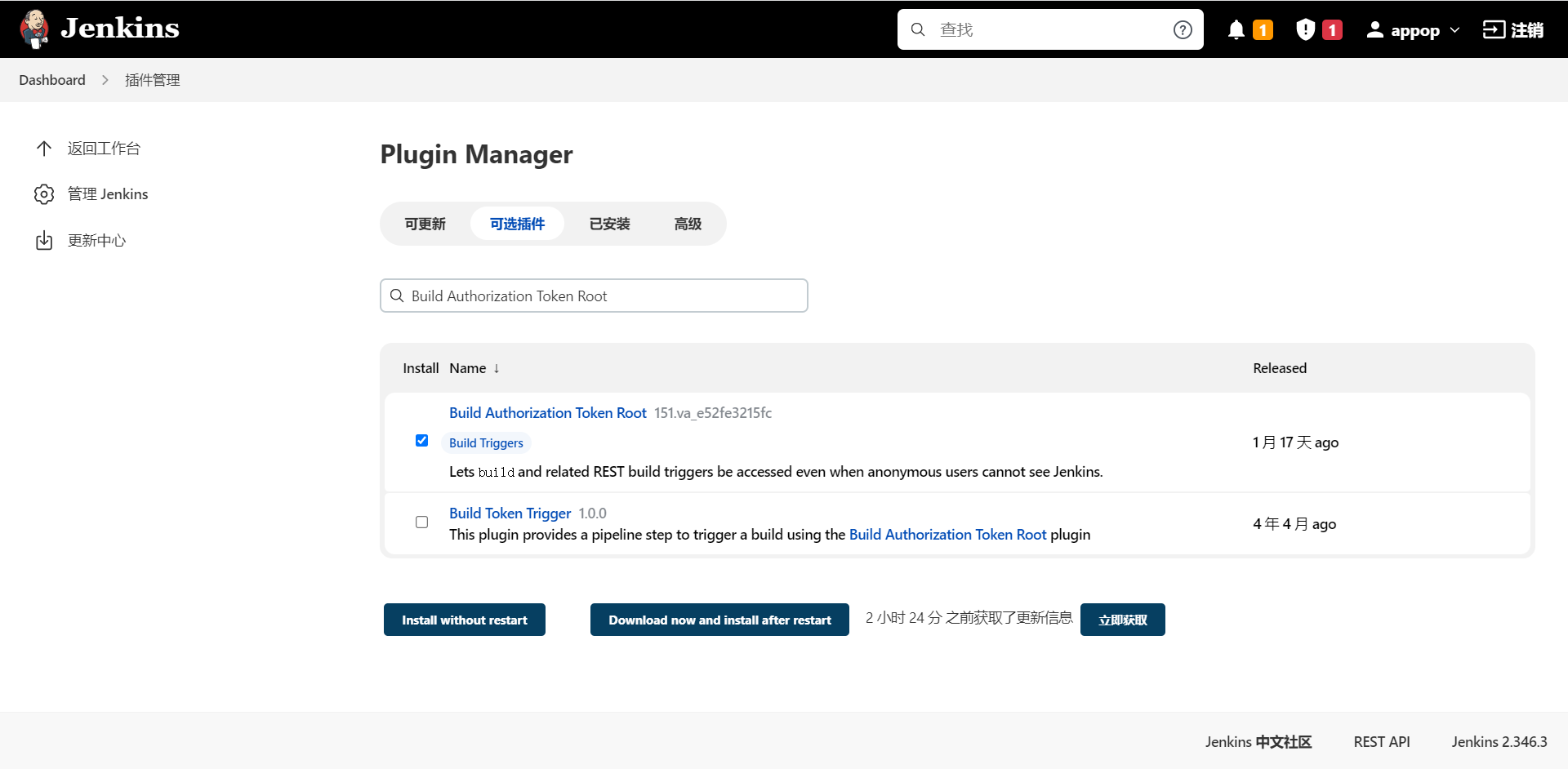
安装好Publish over SSH插件,可用于匿名构建,如:GitLab钩子自动构建项目。
4.2.4 安装Blue Ocean 插件
进入 Manage Jenkins >> Manage Plugins 中,单击“可选插件”选项卡,在输入框中填写需要安装的插件名字_Blue Ocean_。

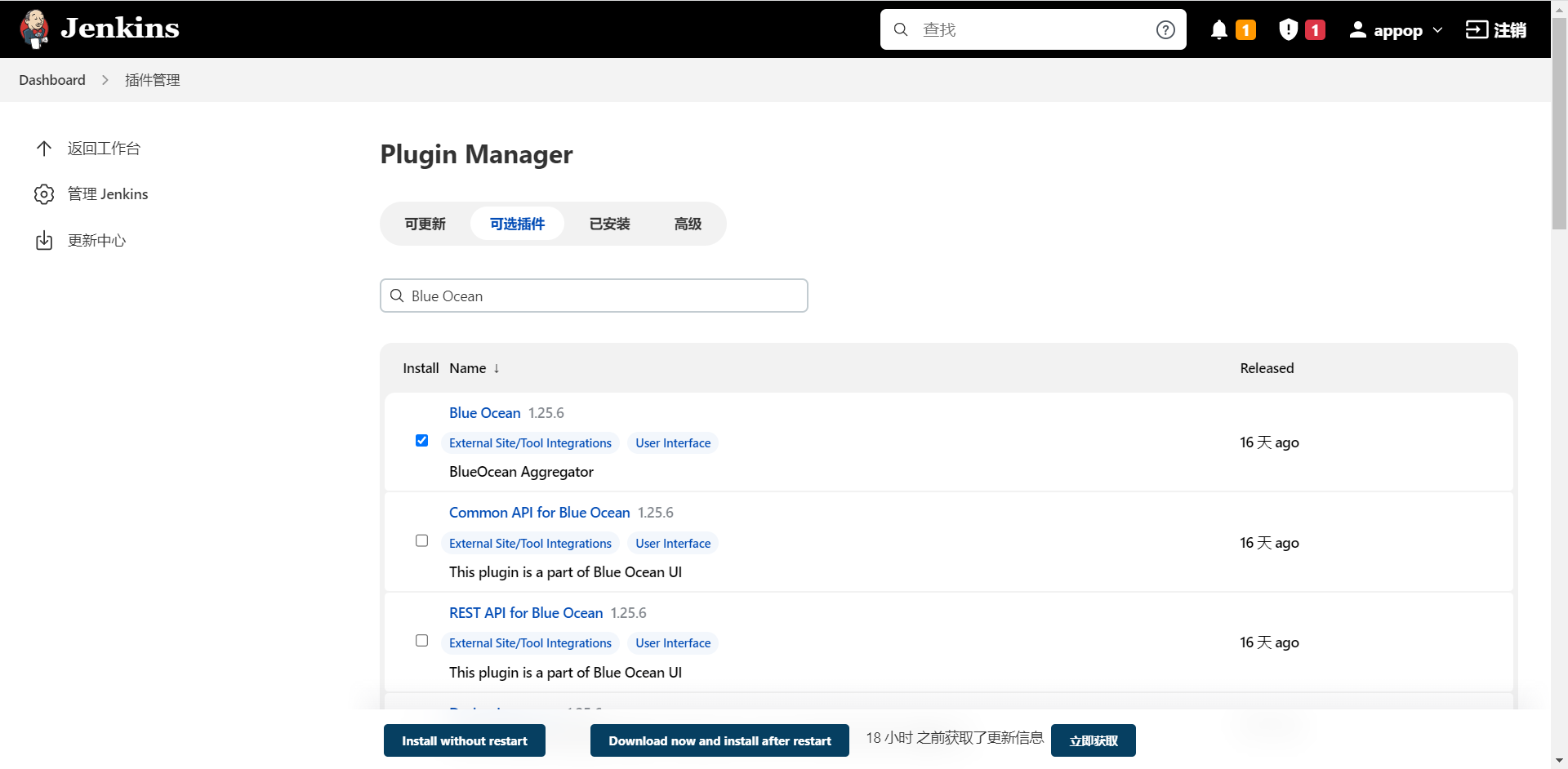
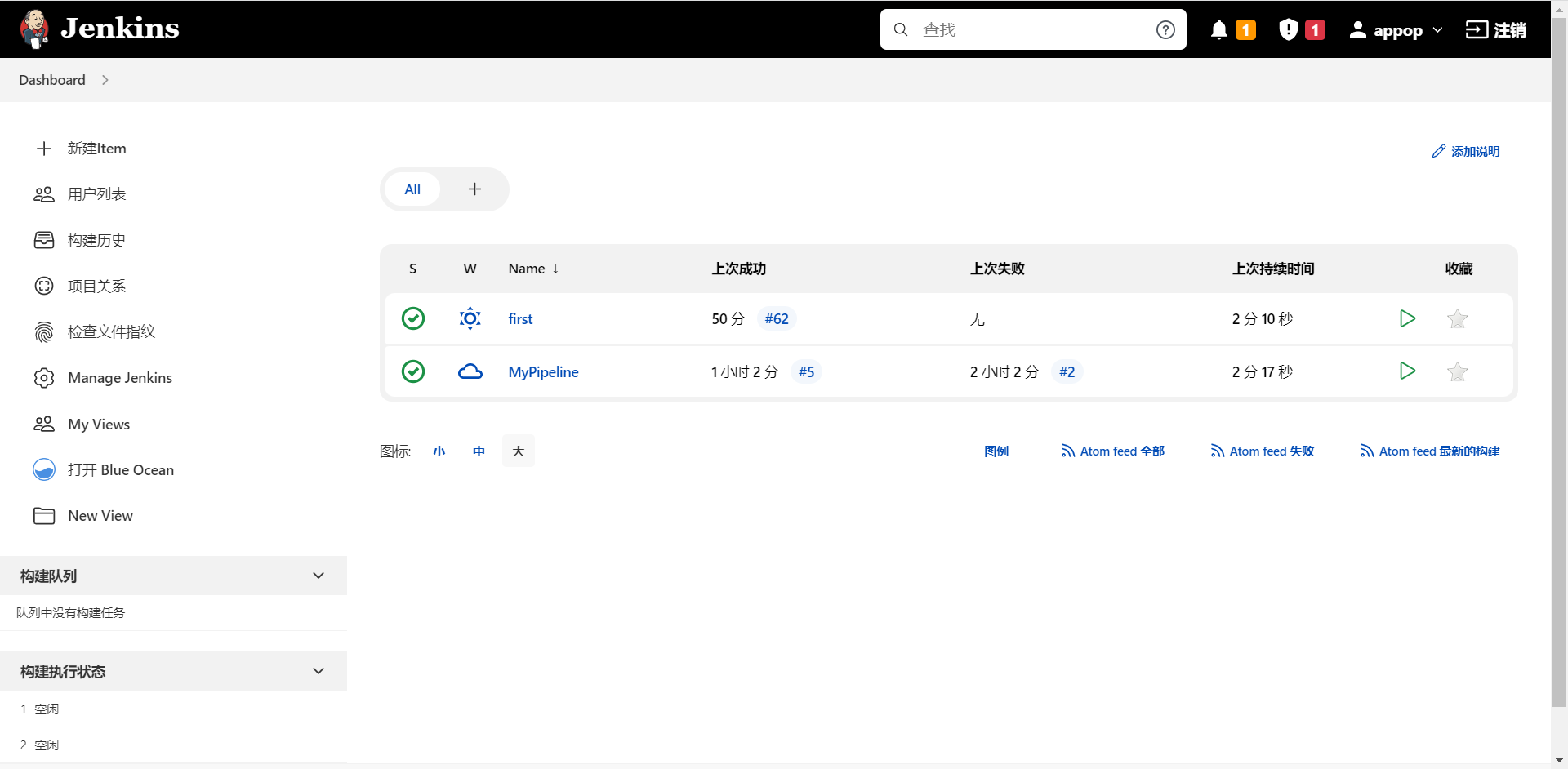
安装好Blue Ocean插件,在面板左侧的导航栏中,才有"打开Blue Ocean"选项。
4.3 Configure System(系统设置)
在Jenkins主面板左侧的导航栏中选择“Manage Jenkins”,进入到“管理Jenkins”界面,点击此界面中“系统设置”选项,进入到“配置”界面,设置完成后点击保存即可,为后面我们配置自动化部署做准备。

4.3.1 Publish over SSH
Publish over SSH:若要将构建后生成的jar包(后端)或dist目录文件(前端)推送到远程服务器中,需配置此模块。可以配置多台远程服务器,在此我们选择用户名和密码来连接远程服务器。
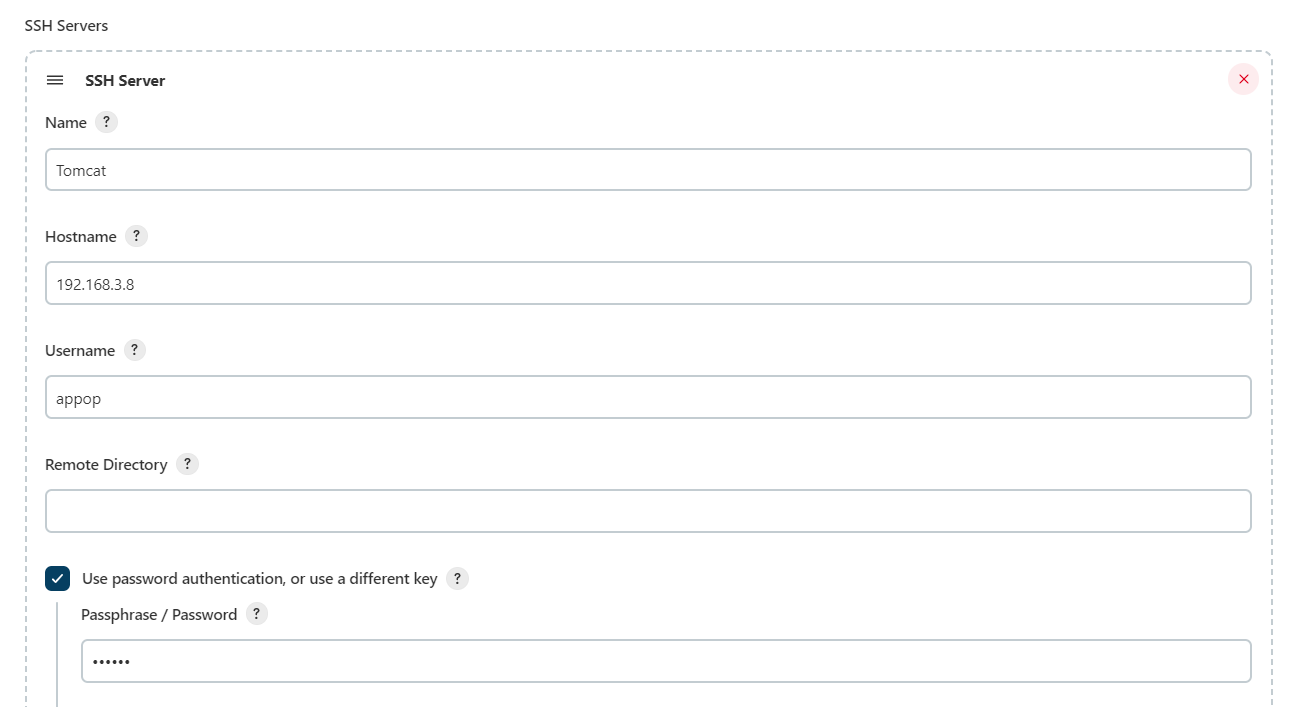
- Name:自定义一个名称。在Job中使用Publish over SSH插件时,此名称将出现在“SSH Server”中“Name”选项的下拉列表中
- Hostname:远程服务器的主机名或IP地址
- Username:远程服务器的用户名
- Remote Directory:远程服务器上真实存在的目录,而且“Username”指定的用户要有访问此文件夹的权限,插件将把文件推送到此目录下
- Use password authentication,or use a different key:勾选此选项,并在“Passphrase/Password”中输入与Username匹配的密码

配置完后点击“Test Configuration”,测试是否可以连接成功。
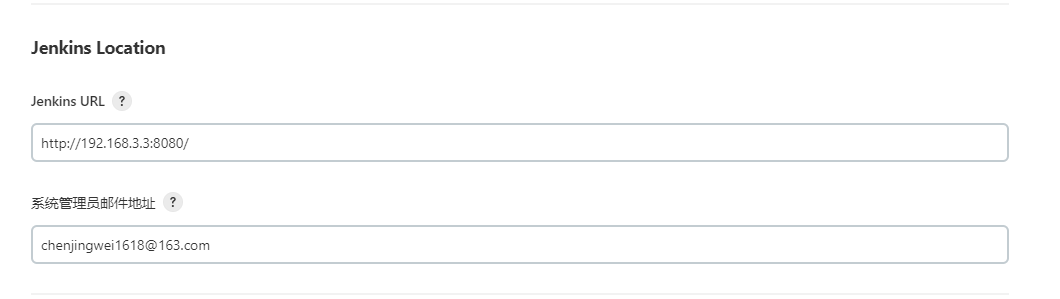
4.3.2 Jenkins Location
Jenkins URL是指定安装Jenkins的HTTP地址,这个值用来在邮件中生产Jenkins链接。此项是有必要的,因为Jenkins无法探测到自己的URL地址。
系统管理员邮箱地址:填写发送邮件的账号,否则无法发送邮件。
4.3.3 邮件通知
进入Jenkins,依次点击Manage Jenkins >> Configure System >> 邮件通知 >> 高级。

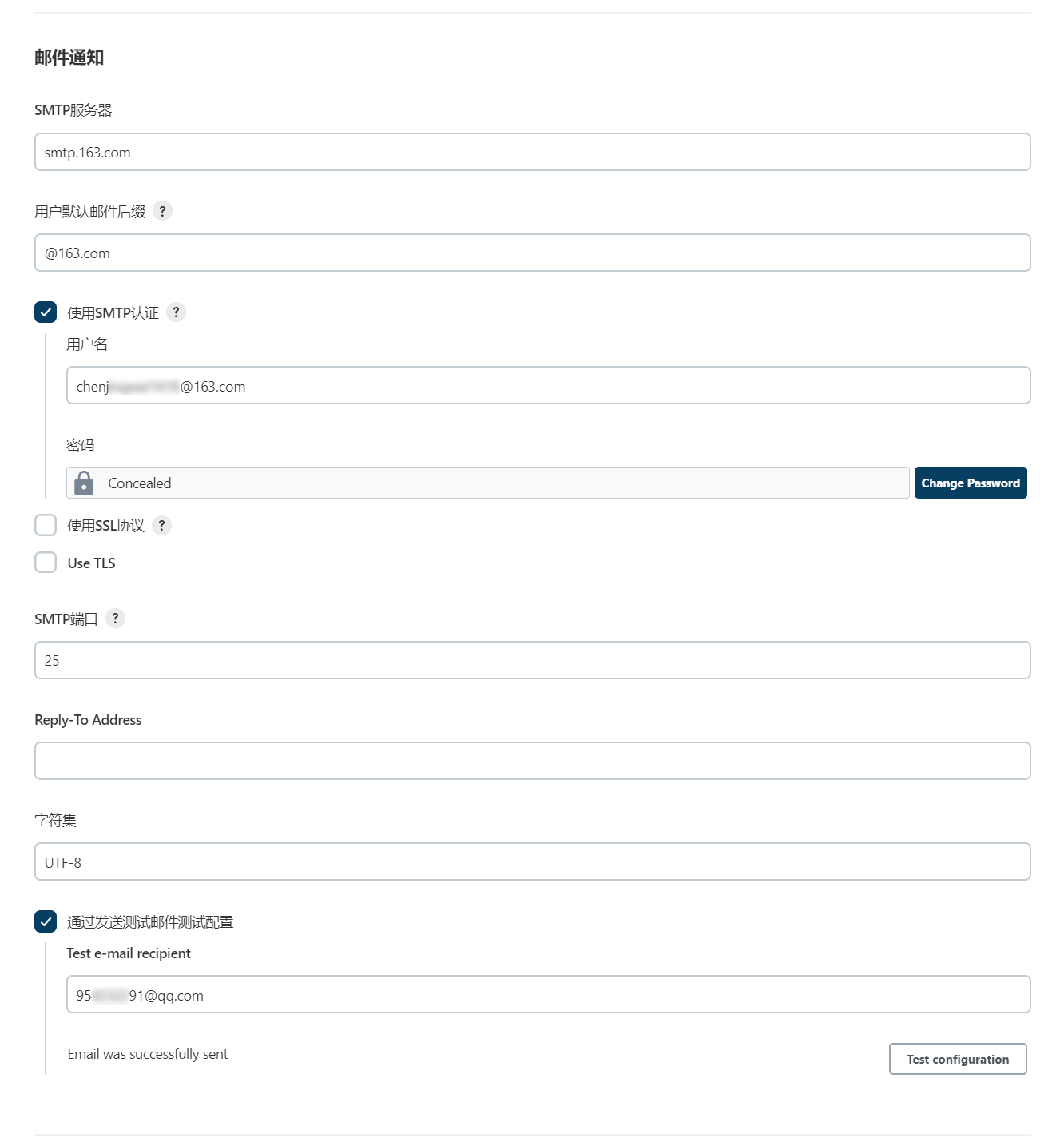
- SMTP Server:SMTP服务器的地址;
- SMPT Port:SMTP的端口号,默认为25;
- Default user E-mail suffix:默认的邮箱后缀;
- SMTP Username:即在Jenkins Location模块中填写的“系统管理员邮件地址”;
- SMTP Password:“系统管理员邮件地址”所对应的密码,需填写获取的邮箱授权码;
4.4.4 Extended E-mail Notification
在Jenkins的使用中邮件提醒是一个常用功能,Jenkins默认安装了 Mailer Plugin插件用于实现此功能,但 Mailer Plugin功能简单不能满足一些复杂需求,如:自定义邮件标题、内容等。Extended E-mail Notification(ext mail)是一个功能更为齐全,使用也更为复杂的插件。
进入Jenkins,依次点击Manage Jenkins >> Configure System >> Extended E-mail Notification >> 高级。


- SMTP Server:SMTP服务器的地址;
- SMPT Port:SMTP的端口号,默认为25;
- SMTP Username:即在Jenkins Location模块中填写的“系统管理员邮件地址”;
- SMTP Password:“系统管理员邮件地址”所对应的密码;
- Default user E-mail suffix:默认的邮箱后缀;
- Default Content Type:默认的邮件内容格式;
- Default Recipients:默认收件人的邮箱地址(可填写多个,中间用英文逗号隔开即可);
- Default Subject:邮件标题。例如,$PROJECT_NAME - Build # $BUILD_NUMBER - $BUILD_STATUS!。其中,$PROJECT_NAME为构建项目名称,$BUILD_NUMBER为构建编号,$BUILD_STATUS为构建状态.
5 创建Maven项目
构建一个maven项目.Jenkins利用你的POM文件,这样可以大大减轻构建配置。
5.1 新建Item
进入Jenkins主界面,在面板左侧的导航栏中点击“新建任务”,进入“新建任务”界面后,在“任务名称”文本框中输入一个合法的名称(该名称最好能简短、清晰地描述所要构建的项目,且不能与已有的任务名称重合),然后选择“构建一个Maven项目”,点击左下角的“确定”按钮,进入任务配置界面。

5.2 General
在“General”选项卡下勾选“丢弃旧的构建”,填写需要保留的构建天数和构建的最大个数。若不及时清理旧的构建,则会消耗服务器的磁盘空间。“保持构建天数” 和"保持构建的最大个数"是可以自定义的,需要根据实际情况确定一个合理的值。

5.3 源码管理
源码管理就是配置你代码的存放位置。在“源码管理”模块中选择Git。
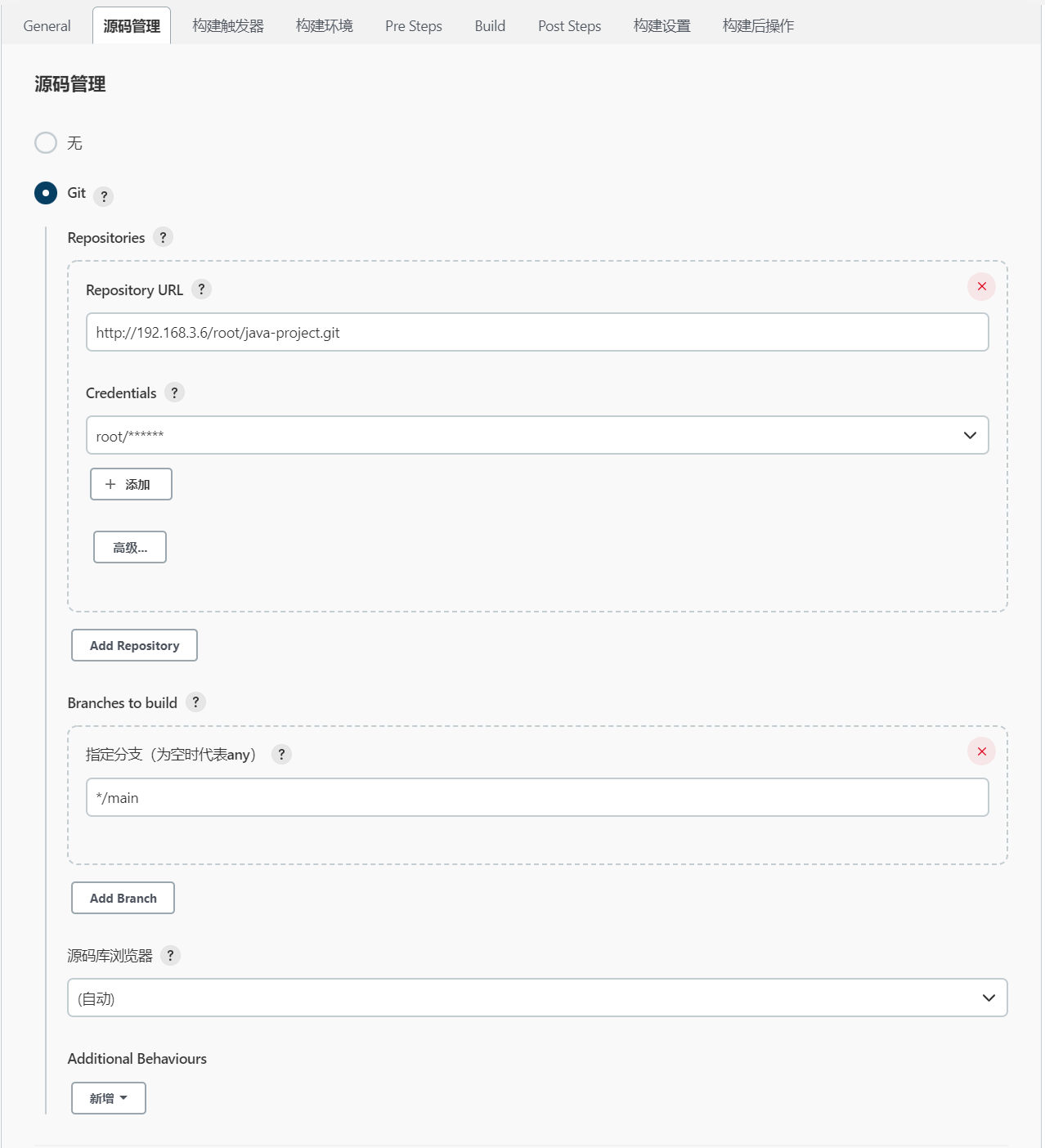
Repository URL:要构建的项目在GitLab中的HTTP地址。首先进入到所要构建的项目在GitLab中的主界面,在项目的URL下拉选框中选择“HTTP”,并点击右侧的“复制”按钮,将复制的HTTP地址粘贴到“Repository URL”文本框中即可。

Credentials:凭证。点击右侧的“添加”按钮,选择“Jenkins”选项后会弹出一个“添加凭据”弹窗。
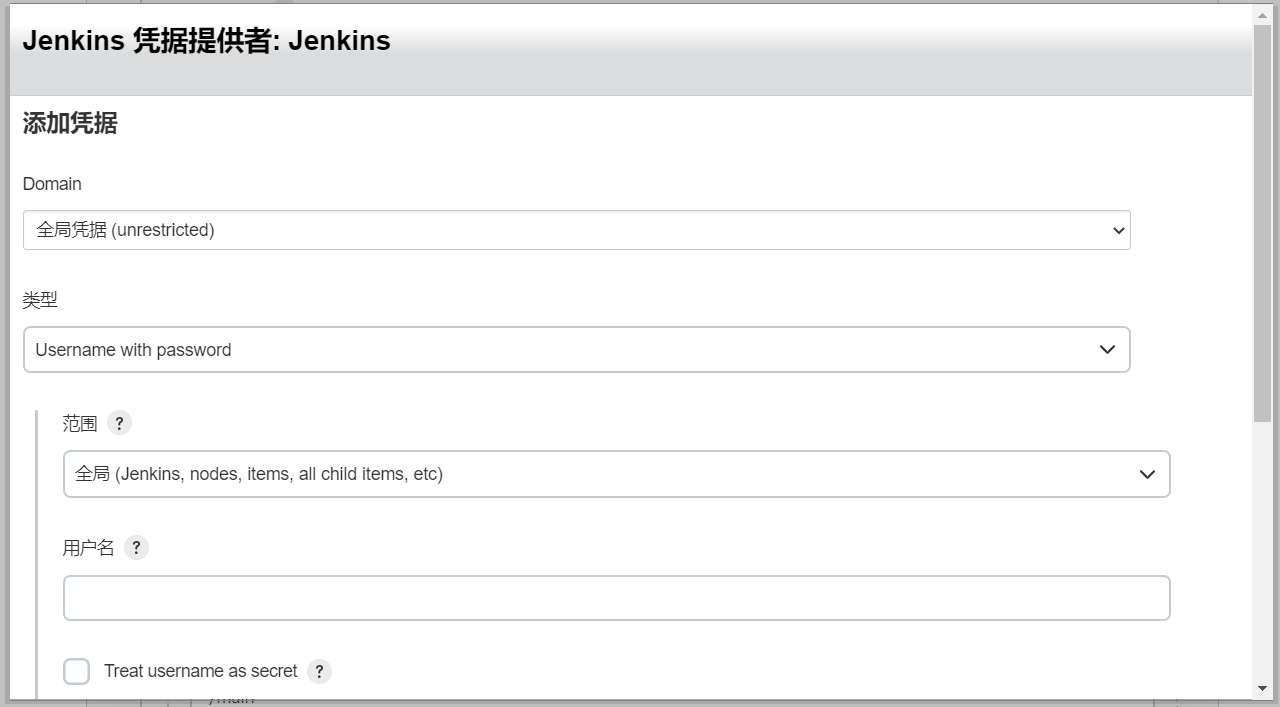
添加凭据时,类型选择“Username with password”,然后在“用户名”文本框中输入GitLab的登陆账户,“密码”文本框中输入与账户相匹配的密码,“ID”文本框中填入自定义的名称,但不能与已有的凭据ID重合。填写完毕后,点击“添加”按钮,所添加的凭据就会出现在“Credentials”的下拉选框中,在选框中选择相应的凭据即可。
Branches to build:构建的分支。*/master表示master分支,也可以设置为其他分支。
5.4 构建触发器
构建触发器,顾名思义,就是构建任务的触发器。
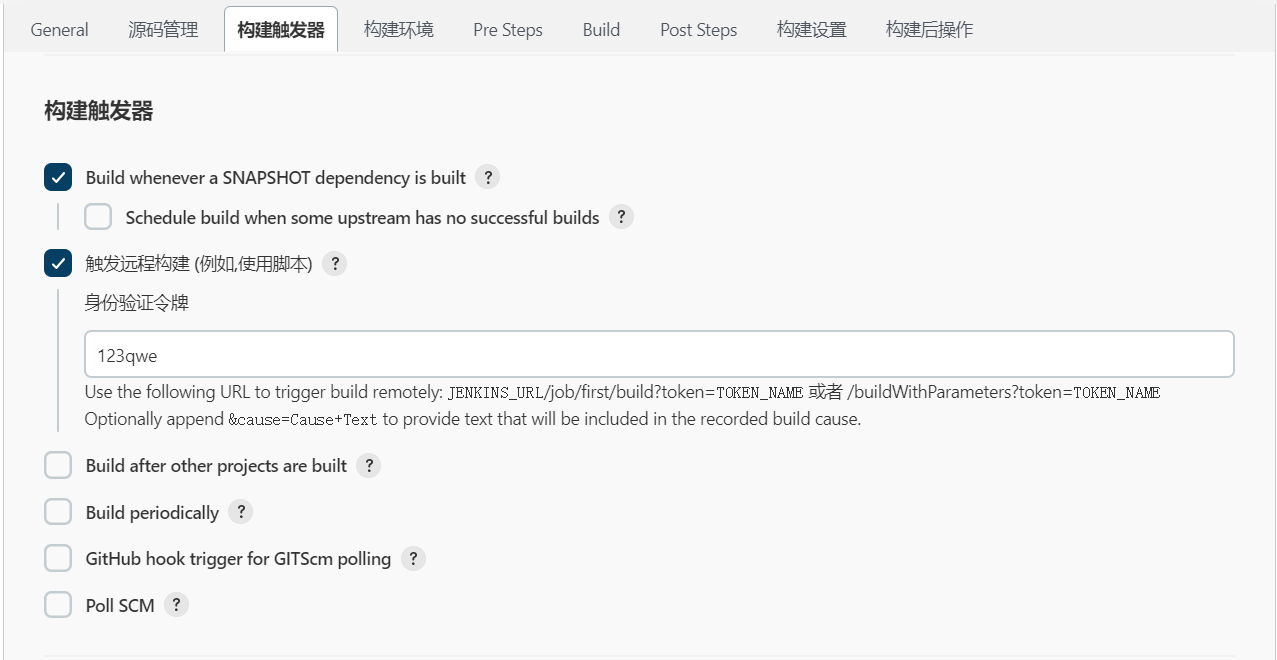
# 几种构建方式:
- 快照依赖构建/Build whenever a SNAPSHOT dependency is built
- 当依赖的快照被构建时执行本job
- 触发远程构建 (例如,使用脚本)
- 远程调用本job的restapi时执行本job
- job依赖构建/Build after other projects are built
- 当依赖的job被构建时执行本job
- 定时构建/Build periodically
- 使用cron表达式定时构建本job
- 向GitHub提交代码时触发Jenkins自动构建/GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling
- Github-WebHook出发时构建本job
- 定期检查代码变更/Poll SCM
- 使用cron表达式定时检查代码变更,变更后构建本job
5.4.1 触发远程构建
触发远程构建(例如,使用脚本): 该选项会提供一个接口,可以用来在代码层面触发构建。
即:源码改动后,执行push或者merge操作时,自动可以使用GitLab的Webhooks回调钩子调起Jenkins的启动任务接口。
GitLab钩子自动构建项目
- 在构建触发器中配置接口和token

Build Authorization Token Root插件安装成功后,到GitLab设置Webhooks。
- Webhooks设置
进入java-project项目,通过“设置-Webhooks”进行配置。其中:
网址:http://192.168.3.3:8080/buildByToken/build?job=first&token=123qwe
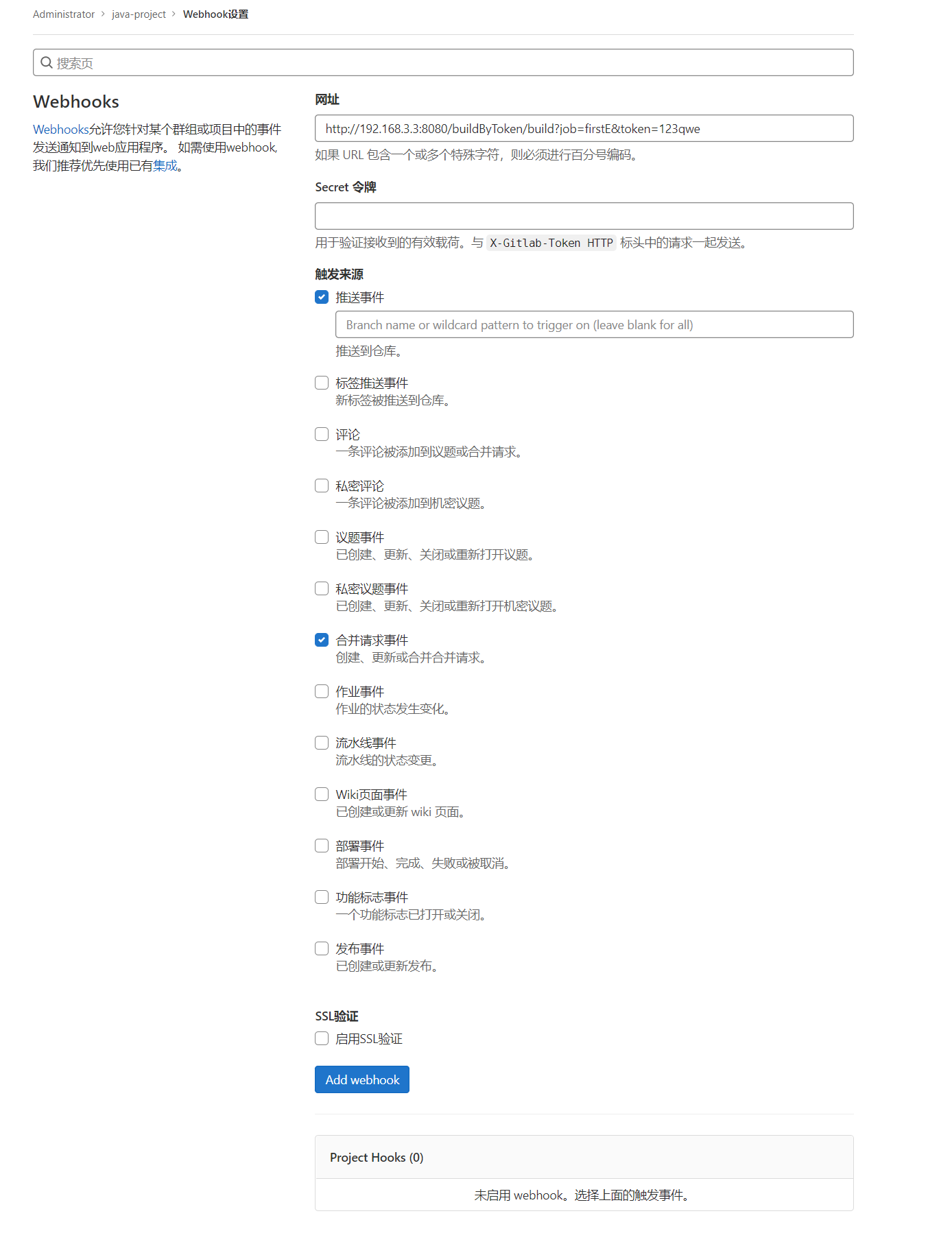
问题描述:Url is blocked: Requests to the local network are not allowed
问题解决:通过“菜单-管理员-设置-网络”,将“出站请求”中<允许来自 web hooks 和服务对本地网络的请求>勾选上,并保存更改。

构建验证:

5.4.2 定时构建 Build periodically
Build periodically: 周期性的构建。很好理解,就是每隔一段时间进行构建。
日程表类似 linux crontab书写格式。如下图的设置,表示每小时进行一次构建。
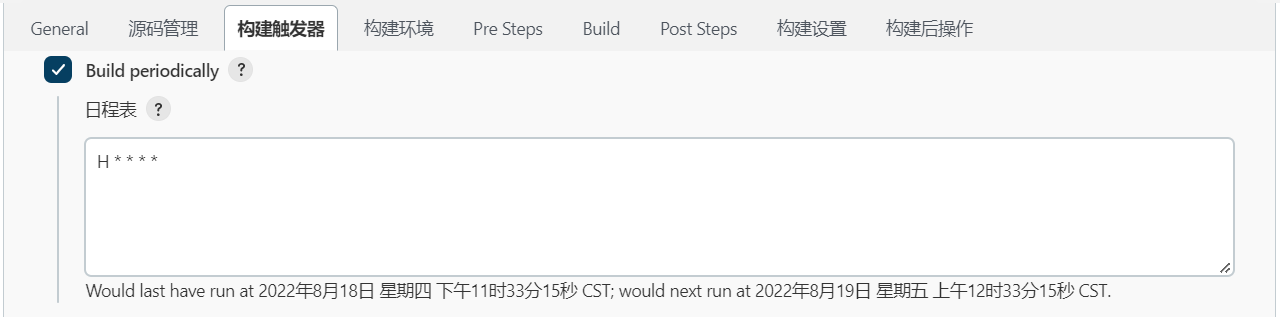
标准cron:https://crontab.guru
Jenkins cron不是标准的cron表达式
第一颗 * 表示每个小时的第几分钟,取值0~59
H * * * *
H:每小时执行一次
第二颗 * 表示小时,取值0~23
* 15 * * * 表示每天下午3点
* 1 * * * 表示每天凌晨1点
第三颗 * 表示一个月的第几天,取值1~31
* 1 5 * * 表示每月5日凌晨1点
第四颗 * 表示第几月,取值1~12
* 15 5 1 * 表示每年几月执行
第五颗 * 表示一周中的第几天,取值0~7,其中0和7代表的都是周日
/ 表示每隔多长时间,比如 */10 * * * * 表示 每隔10分钟。
H hash散列值,以job名取值,获取到以job名为入参的唯一值,相同名称值也相同,这个偏移量会和实际时间相加,获得一个真实的运行时间。
意义在于:不同的项目在不同的时间运行,即使配置的值是一样的,比如 都是`15 * * * * ` ,表示每个小时的第15分钟开始执行任务,那么会造成同一时间内在Jenkins中启动很多job,换成`H/15 * * * *`,那么在首次启动任务时,会有随机值参与进来,有的会在17分钟启动 有的会在19分钟启动,随后的启动时间也是这个值。这样就能错开相同cron值的任务执行了。
H的值也可以设置范围:
H * * * * 表示一小时内的任意时间
*/10 * * * * 每10分钟
H/10 * * * * 每10分钟,可能是7,17,27,起始时间hash,步长不变
45 3 * * 1-6 每个周一至周六,凌晨3点45 执行1次
45 3-5 * * 1-6 每个周一至周六,凌晨3点45 ,凌晨4点45,凌晨5点45 各执行1次
H(40-48) 3-5 * * 1-6 在40~48之间取值 其他同上
45 3-5/2 * * 1-6 每个周一至周六,凌晨3点45 ,凌晨5点45 各执行1次
45 0-6/2 * * 1-6 * * 1-6 0点开始,每间隔2小时执行一次 0:45、2:45、4:45
5.4.3 源码变更构建 Poll SCM
使用Poll SCM 方式与Build periodically一样。
会主动定期检查代码托管服务器上是否有变化,一旦发生变化执行job构建。
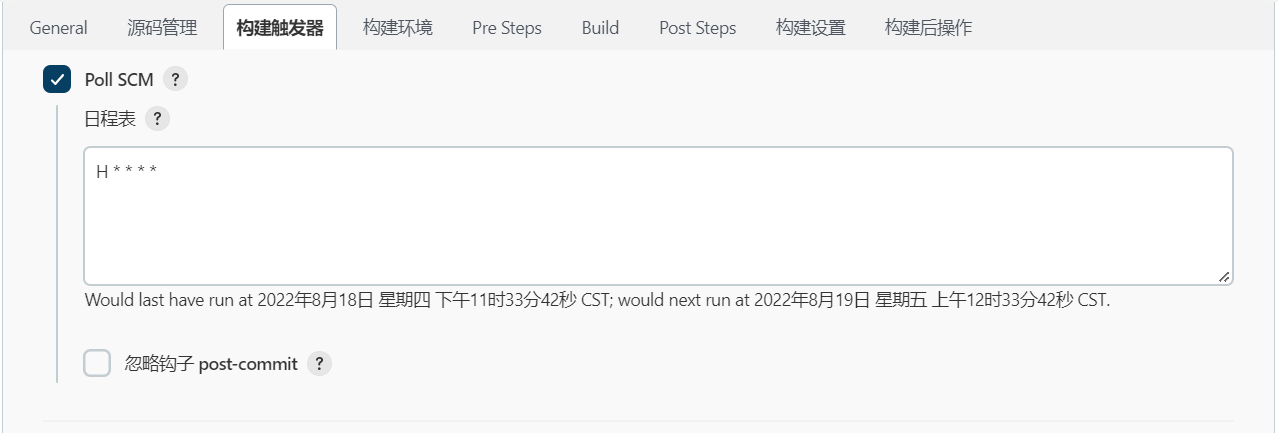
5.5 Pre Steps
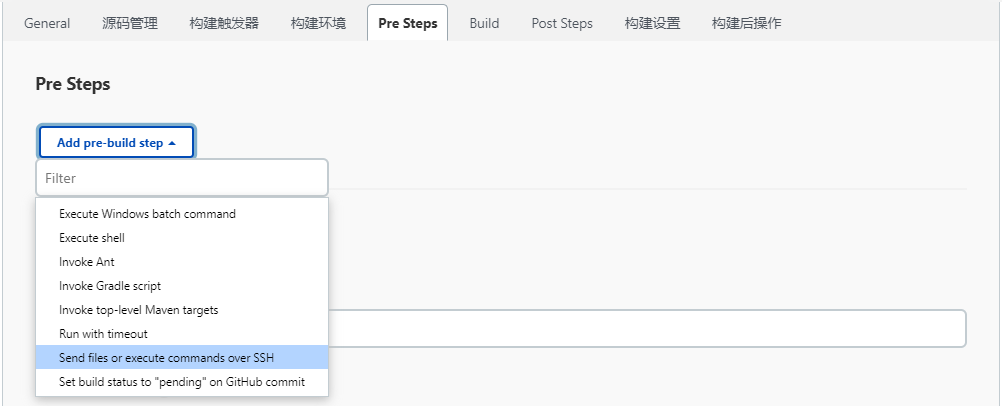
配置运行前清理
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Pre Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。

在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Exec command”选项:./clean.sh demo
clean.sh脚本文件在Tomcat服务器上创建,具体如下:
#!/bin/bash
#删除历史数据
rm -rf xxoo
appname=$1
#获取传入的参数
echo "arg:$1"
#获取正在运行的jar包pid
pid=`ps -ef | grep $1 | grep 'java -jar' | awk '{printf $2}'`
echo $pid
#如果pid为空,提示一下,否则,执行kill命令
if [ -z $pid ];
#使用-z 做空值判断
then
echo "$appname not started"
else
kill -9 $pid
echo "$appname stoping...."
check=`ps -ef | grep -w $pid | grep java`
if [ -z $check ];
then
echo "$appname pid:$pid is stop"
else
echo "$appname stop failed"
fi
fi
5.6 Build
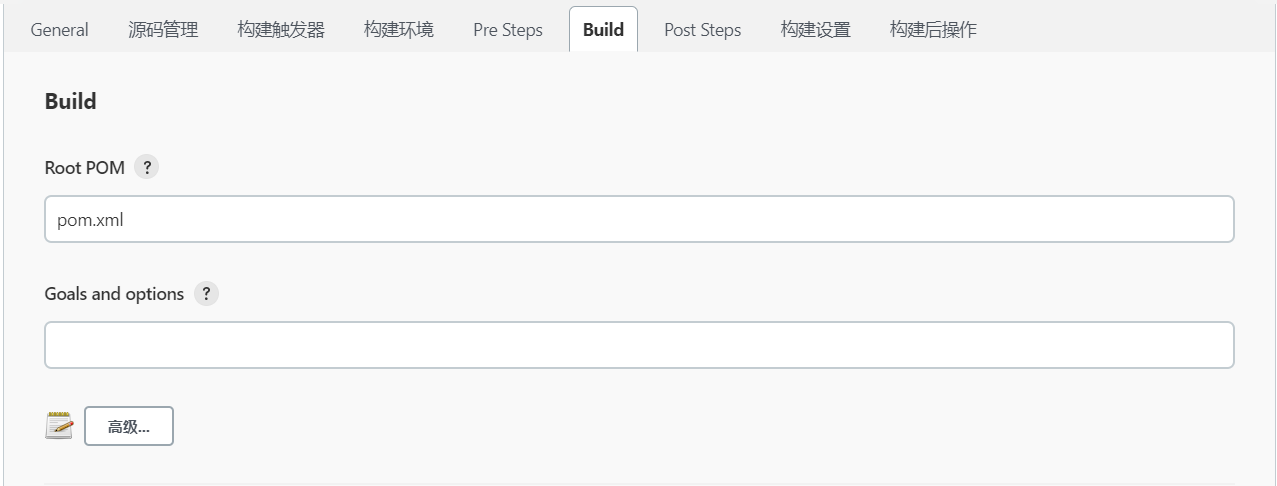
- Root POM:最上层pom.xml文件的路径,这里是相对于${WORKSPACE}的路径。如果不做设置,默认是在工作目录的根目录下,填写pom.xml即可。如果不是默认路径,例如,在${WORKSPACE}/my-project/pom.xml下,这里写上/my-project/pom.xml。
- Goals and options:这里就是mvn指令后面的部分,如clean package,也可以带参数。比如,要跳过单元测试,就使用-Dmaven.test.skip=true。
5.7 Post Steps
Send files or execute commands over SSH配置
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Post Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。
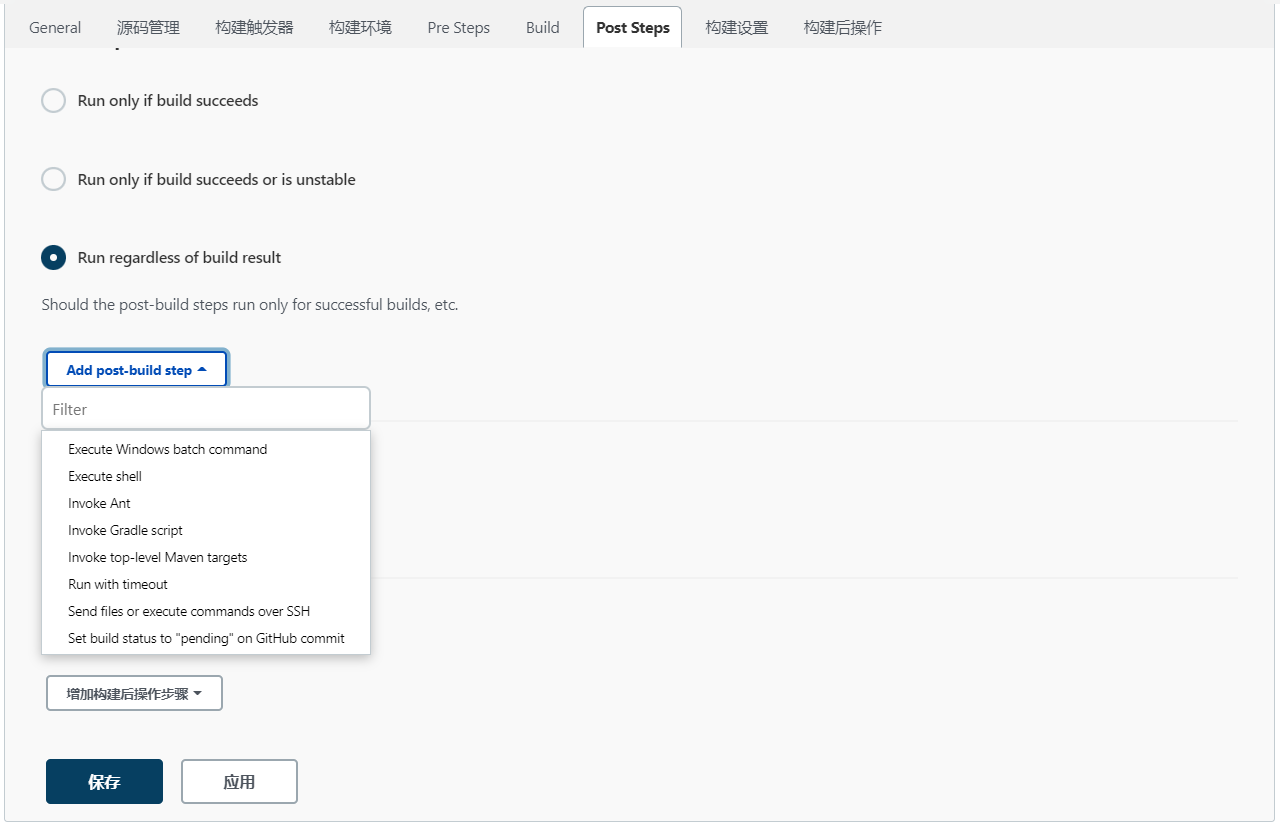
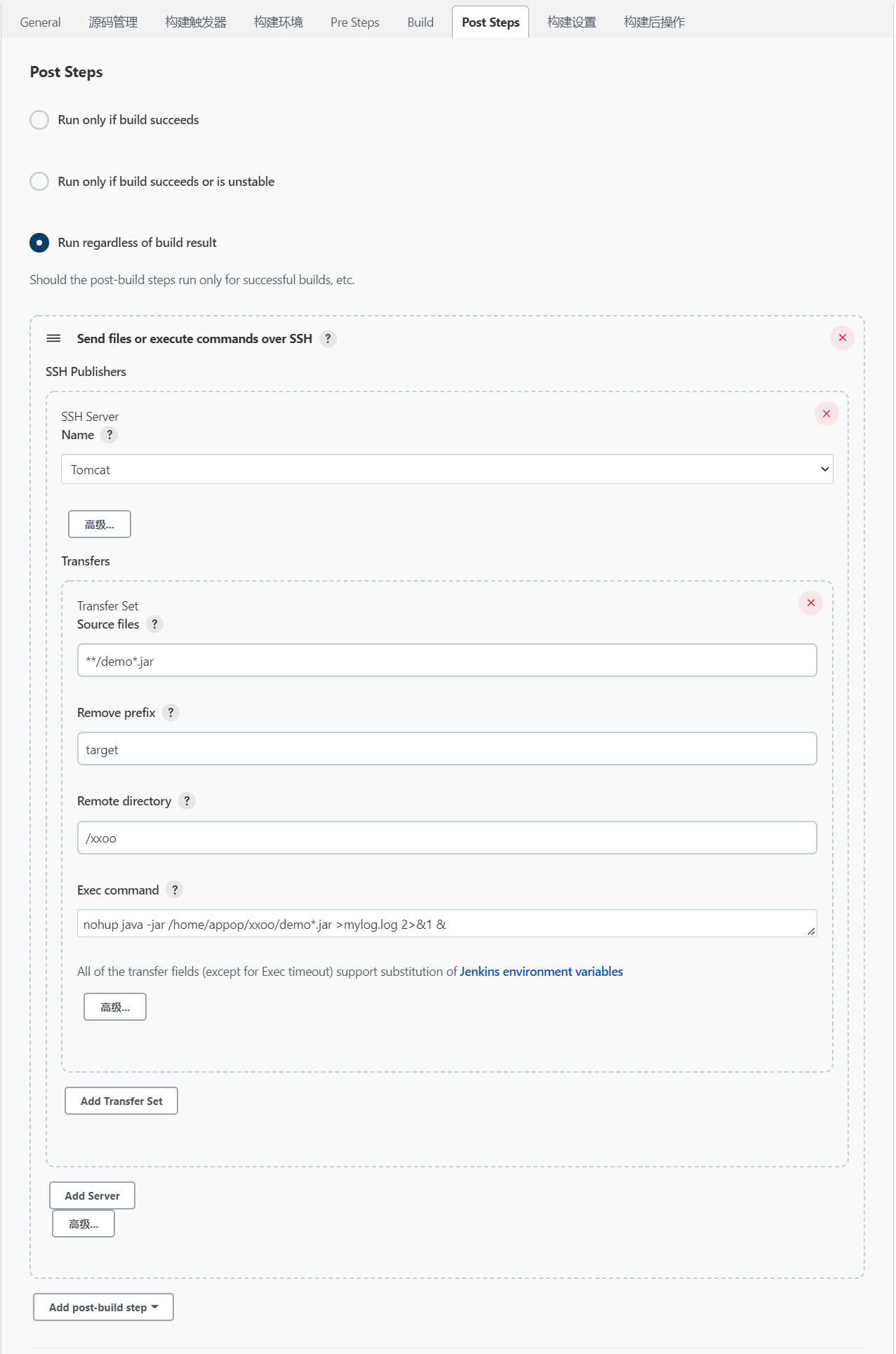
在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Source files”、“Remove prefix”、“Remote directory”和“Exec command”选项:
# Source files
**/demo*.jar
# Remove prefix
target
# Remote directory
/xxoo
# Exec command
nohup java -jar /home/appop/xxoo/demo*.jar >mylog.log 2>&1 &
- Name:选择在Jenkins“系统管理--->系统设置”中设置的SSH Server的名字;
- Source files:拷贝到远程服务器上的文件。需要上传的文件必须位于当前的workspace中,否则会上传失败。如果只执行命令而不需要传输文件时,此处可为空;
- Remove prefix:在“Source files”配置的路径中要移除的前缀。在Source files文本框中填入的地址,会默认在服务器下创建相同的目录,所以要将我们不需要的前缀在这里剔除掉,只传输XXX.jar;
- Remote directory:远程服务器接收文件的目录,此目录是相对于“SSH Server”中的“Remote directory”的,如果不存在将会自动创建;
- Exec command:文件传输任务执行完毕后,在远程服务器上执行的脚本(可填写脚本所在目录)。
# shell的日志输出
nohup java -jar /home/appop/xxoo/demo*.jar >mylog.log 2>&1 &
- 数据流重定向:就是将某个命令执行后应该要出现在屏幕上的数据传输到其他地方
1.标准输入(stdin):代码为0,使用<或<<;
2.标准输出(stdout):代码为1,使用>或>>;
3.标准错误输出(stderr):代码为2,使用2>或2>>
> 覆盖写
>> 追加写
超时机制
输出命令时一定要注意不要让窗口卡主,不然Jenkins会认为一直没完成。

5.8 构建后操作
在“构建后操作步骤”中添加"Editable Email Notification"。
在“增加构建后操作步骤”下拉选框中选择“Editable Email Notification”,选择后会在“构建后操作”中出现“Editable Email Notification”模块。

- Project Recipient List:收件人的邮箱地址。若有多个收件人时用英文逗号隔开。也可使用系统配置中的默认设置:$DEFAULT_RECIPIENTS。
- Default Subject:邮件主题。可使用系统配置中的默认设置:$DEFAULT_SUBJECT。
- Default Content:邮件内容。可使用系统配置中的默认设置:$DEFAULT_CONTENT。
5.9 立即构建
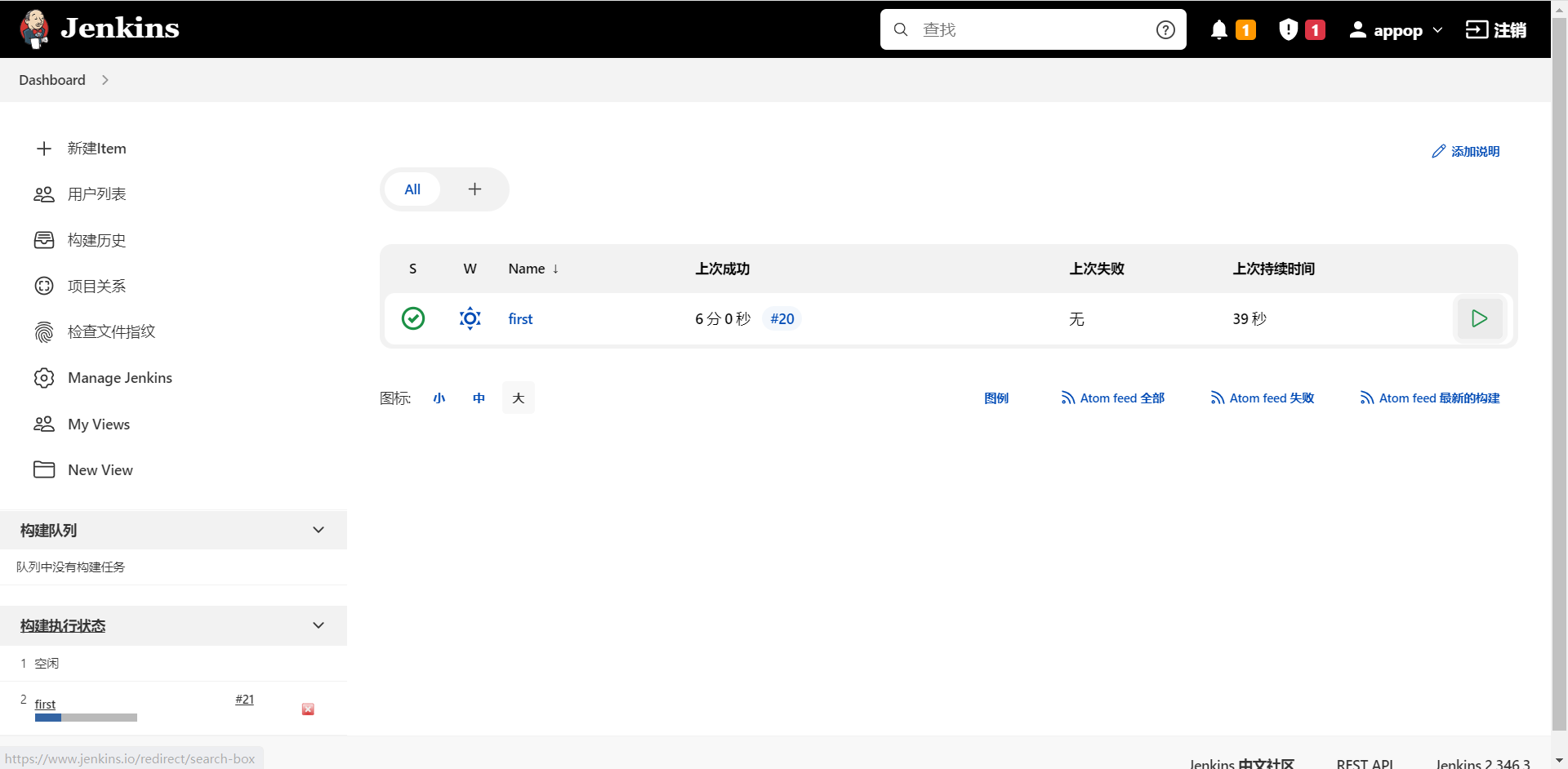
- 配置完成后,点击构建项目,执行构建。
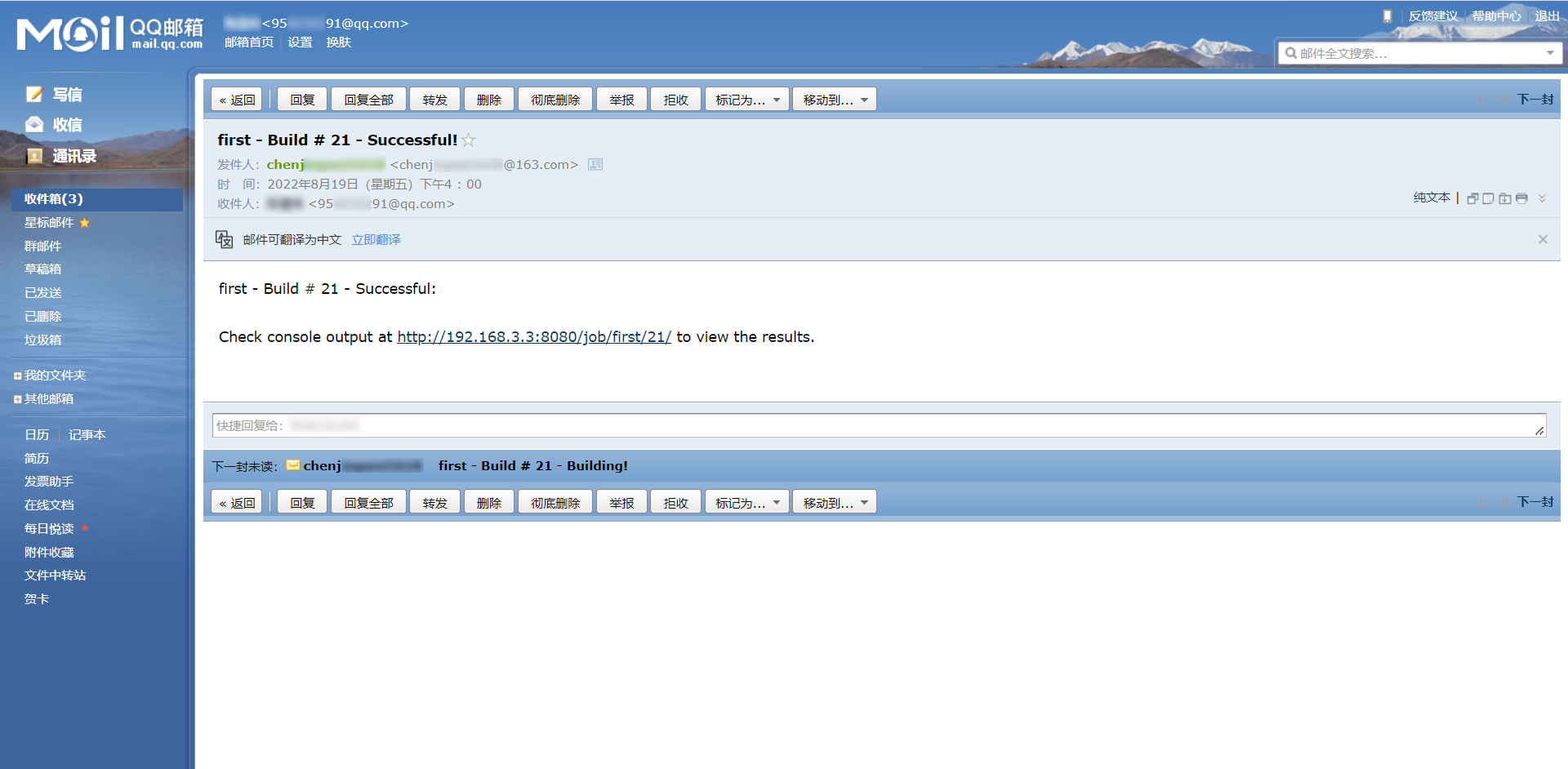
- 构建成功后,会接收到构建成功的邮件。
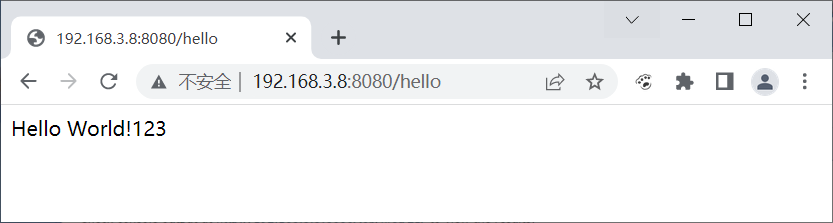
- 构建成功后,浏览器上访问,看是否能正常访问。
6 自动化部署到docker容器中
安装docker
1.卸载旧的版本
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
2.需要的安装包
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
3.设置镜像的仓库
# 默认是国外的,很慢!!!
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 推荐使用阿里云的,十分快
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
4.更新yum软件包索引
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum makecache fast
5.安装docker相关引擎、docker-ce社区版、docker-ee企业版
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo yum install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
6.启动docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl start docker
7.配置开机启动项:
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl enable docker
8.使用docker version查看是否安装成功
[appop@tomcat ~]$ docker version
9.配置镜像加速器
修改daemon配置文件/etc/docker/daemon.json来使用加速器
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://gw5py7zq.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
10.重启服务
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
11.重启docker
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo systemctl restart docker
12.hello-world
[appop@tomcat ~]$ sudo docker run hello-world
6.1 使用外部jar包完成自动化部署
运行镜像
[appop@tomcat docker]$ sudo docker run -d -p 8080:8080 --name demo-out -v /home/appop/xxoo/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar:/app.jar java:8 java -jar app.jar
- 问题描述:Docker 拉取镜像失败 :unauthorized: authentication required,使用阿里云镜像加速器,没效果。
解决方案:使用date命令,查看系统时间和当前时间是否一致,如果不一致,就需要使用ntp同步标准时间,ntp:网络时间协议(network time protol)。
安装:sudo yum install -y ntp
同步:sudo ntpdate pool.ntp.org
# timedatectl命令:
1.查看时区
timedatectl
2.查看时区列表
timedatectl list-timezones
3.将硬件时钟调整为与本地时钟一致, 0 为设置为 UTC 时间
timedatectl set-local-rtc 1
4.设置系统时区
timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
5.手动修改时间方法
timedatectl set-time "yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS"
或者使用date命令修改时间
date -s "yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS"
如:date -s '2016-06-21 21:50:00'
- 问题描述:Error: Invalid or corrupt jarfile xxx.jar
解决方案:使用docker启动的容器默认是用的root权限,但是docker中的root只是相当于普通用户,所以需要给挂载的目录或者文件开启权限。
#开启目录权限
chmod a+rwx “需要挂载的目录”
eg:chmod a+rwx /home/appop/xxoo #这边需要挂载的目录是/home/appop/xxoo
#开启docker挂载权限
sudo chmod a+rw /var/run/docker.sock
进入容器查看容器中是否有对应的jar包
[appop@tomcat docker]$ sudo docker exec -it demo-out /bin/bash
Pre Step配置
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Pre Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。
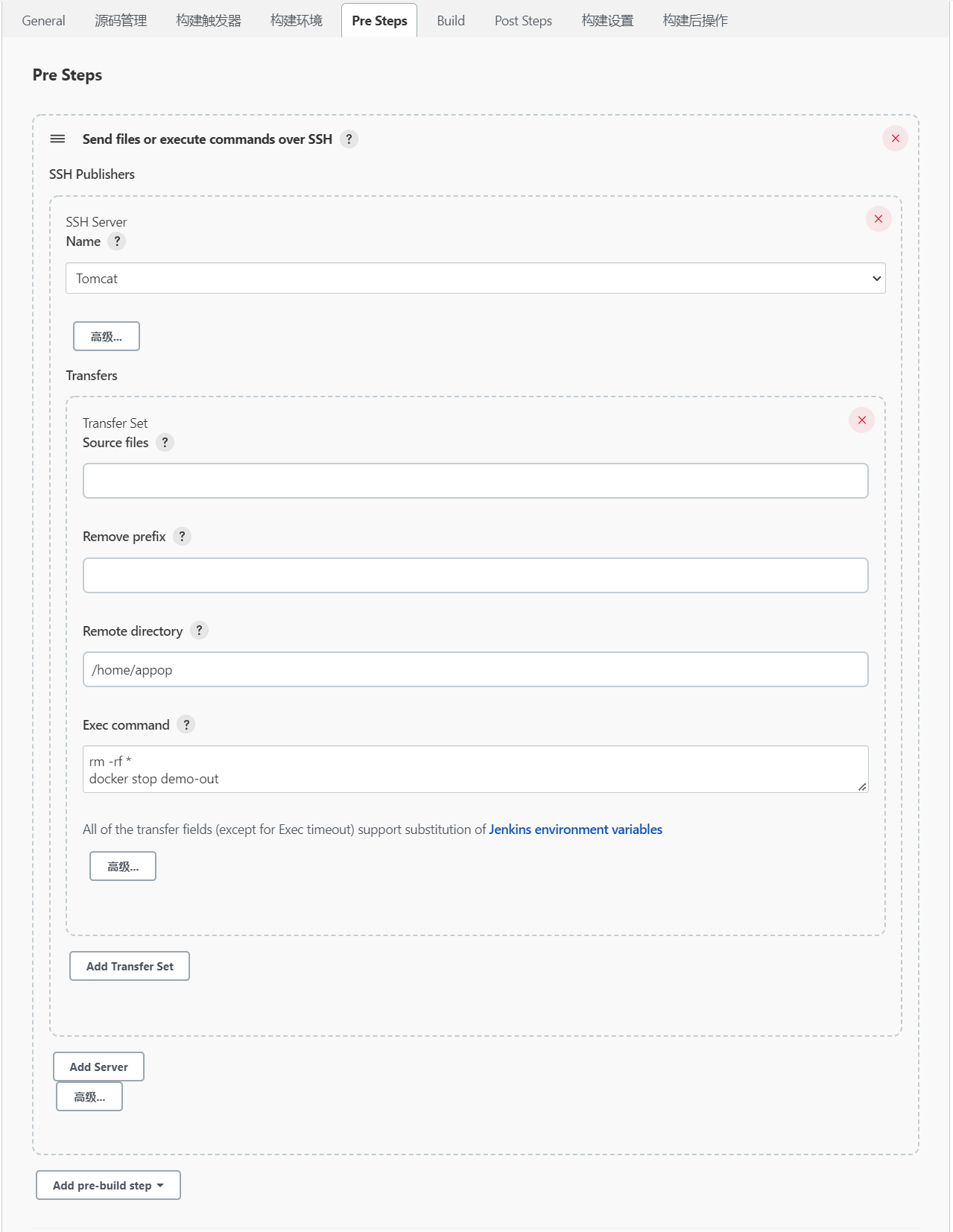
在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Remote directory”和“Exec command”选项:
# Remote directory:
/home/appop
# Exec command:
rm -rf /xxoo
docker stop demo-out
Post Steps配置
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Post Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。

在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Source files”、“Remove prefix”、“Remote directory”和“Exec command”选项:
# Source files
**/demo*.jar
# Remove prefix
target
# Remote directory
/xxoo
# Exec command:
docker start demo-out
立即构建
-
配置完成后,点击构建项目,执行构建。
-
构建成功后,会接收到构建成功的邮件。
-
构建成功后,浏览器上访问,看是否能正常访问。
6.2 自动化部署构建Docker镜像运行jar
在IDEA编写Dockerfile文件并push到GitLab仓库
- 打开IDEA,在demo下创建Dockerfile文件
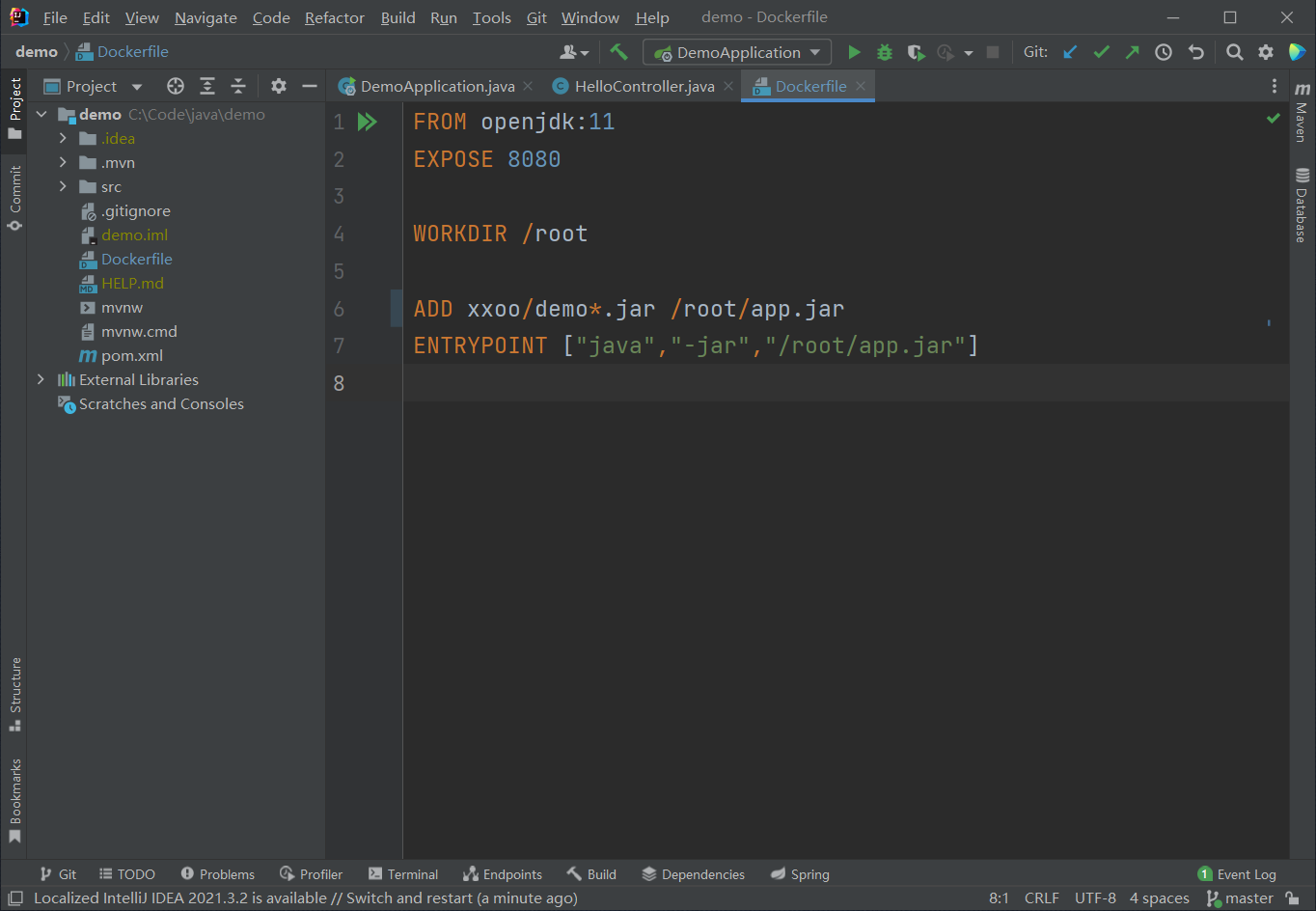
Dockerfile:
FROM java:8
EXPOSE 8080
WORKDIR /root
ADD xxoo/demo*.jar /root/app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/root/app.jar"]
- Dockerfile文件编写完成后,将其push到GitLab仓库
Pre Steps配置
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Pre Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。

在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Remote directory”和“Exec command”选项:
# Remote directory:
/home/appop
# Exec command:
rm -rf *
docker stop demo
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)
Post Steps配置
在“Add post-build step”下拉选框中选择“Send files or execute commands over SSH”,选择后会在“Post Steps”中出现“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块。
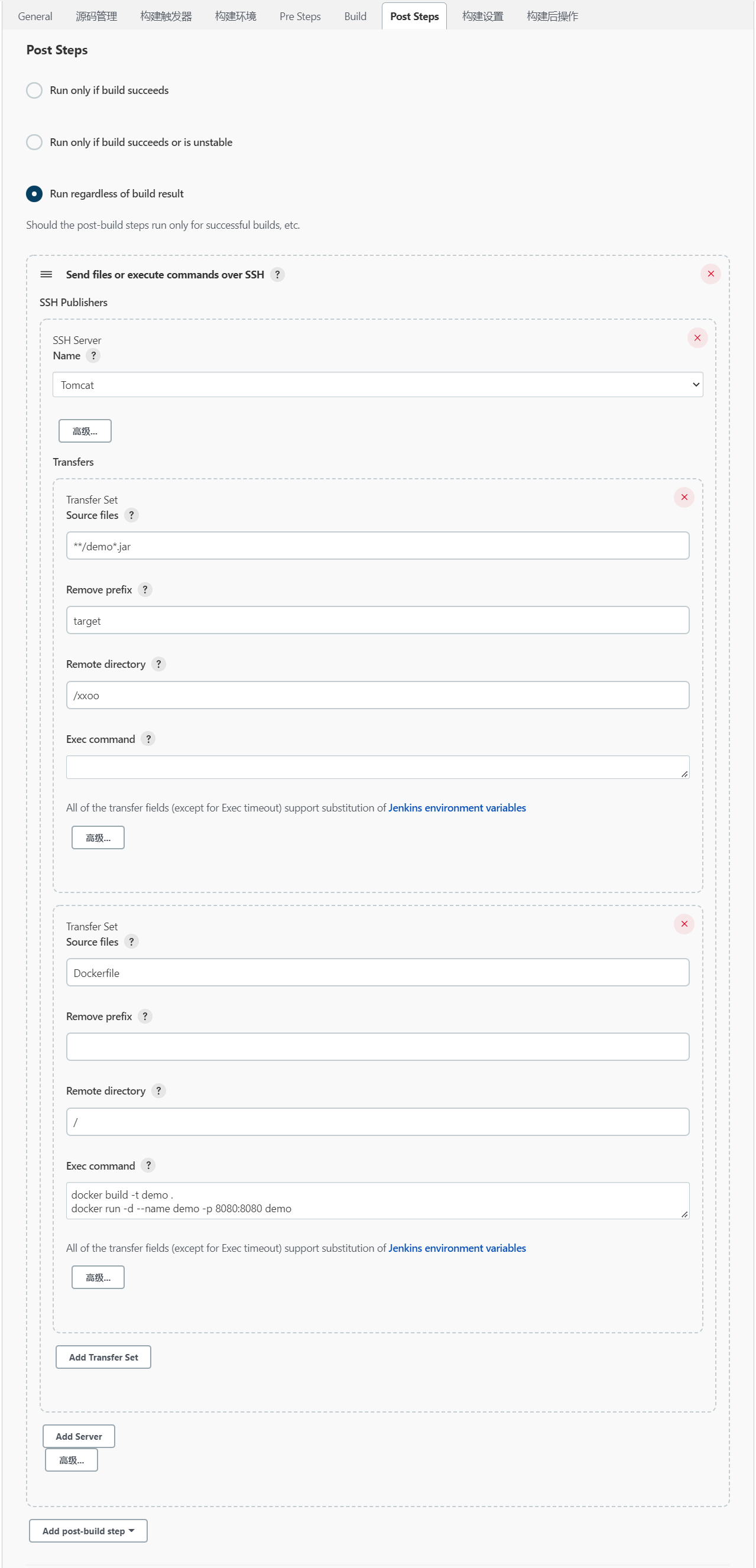
在“Send files or execute commands over SSH”模块中,设置“Source files”、“Remove prefix”、“Remote directory”和“Exec command”选项:
# Source files
Dockerfile
# Remote directory:
/
# Exec command:
docker build -t demo .
docker run -d --name demo -p 8080:8080 demo
立即构建
-
配置完成后,点击构建项目,执行构建。
-
构建成功后,会接收到构建成功的邮件。
-
构建成功后,浏览器上访问,看是否能正常访问。
7 流水线Pipeline
流水线(Pipeline)是 Jenkins 的一套插件。流水线既能作为任务的本身,也能作为Jenkinsfile。
使用流水线可以让我们的任务从ui手动操作,转换为代码化,像docker的Dockerfile一样,从shell命令到配置文件,更适合大型项目,可以让团队其他开发者同时参与进来,同时也可以编辑开发Jenkinswebui不能完成的更复杂的构建逻辑,作为开发者可读性也更好。
7.1 新建Item
进入Jenkins主界面,在面板左侧的导航栏中点击“新建任务”,进入“新建任务”界面后,在J“任务名称”文本框中输入一个合法的名称(该名称最好能简短、清晰地描述所要构建的项目,且不能与已有的任务名称重合),然后选择“Pipeline”,点击左下角的“确定”按钮,进入任务配置界面。

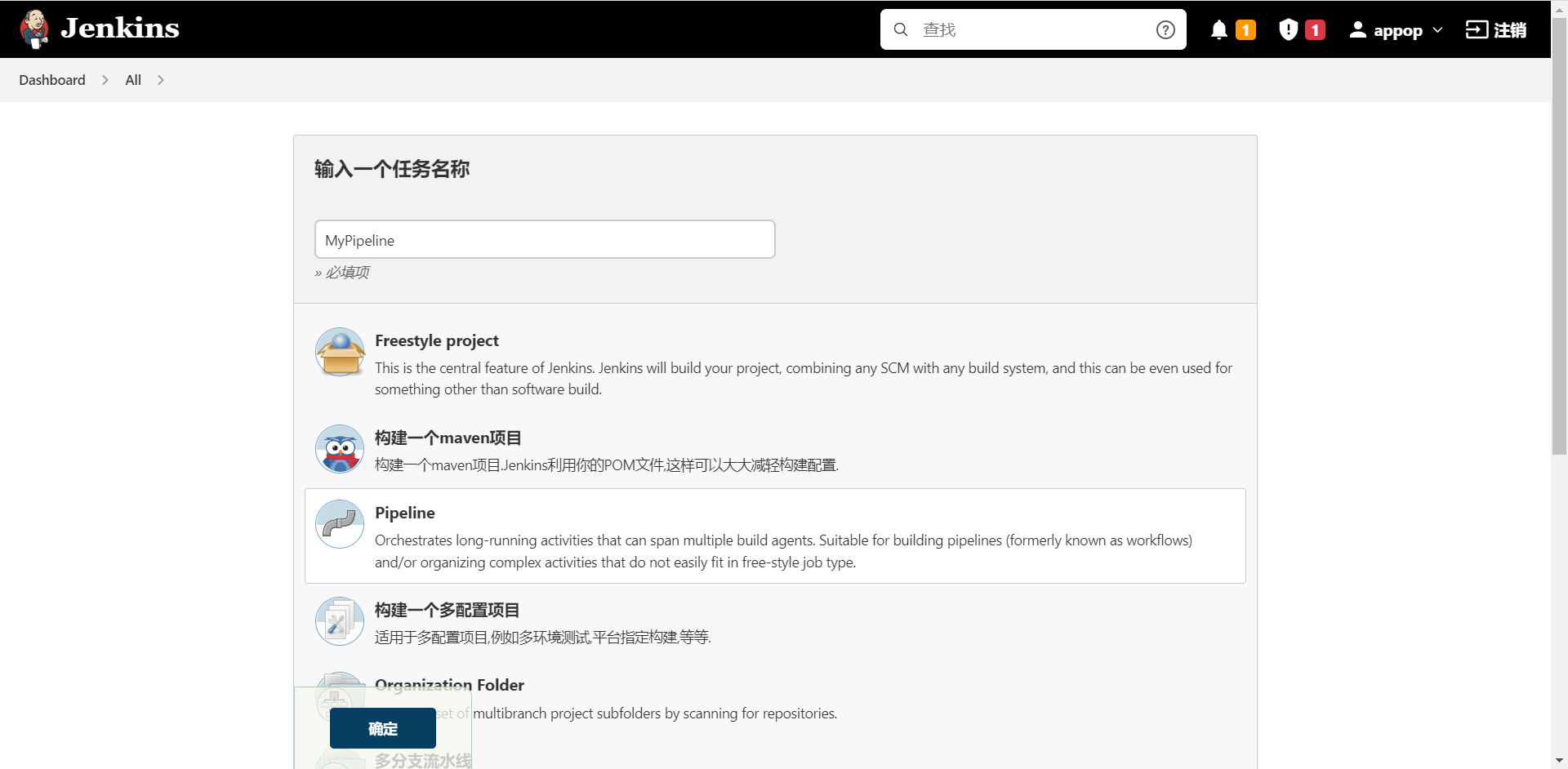

7.2 General
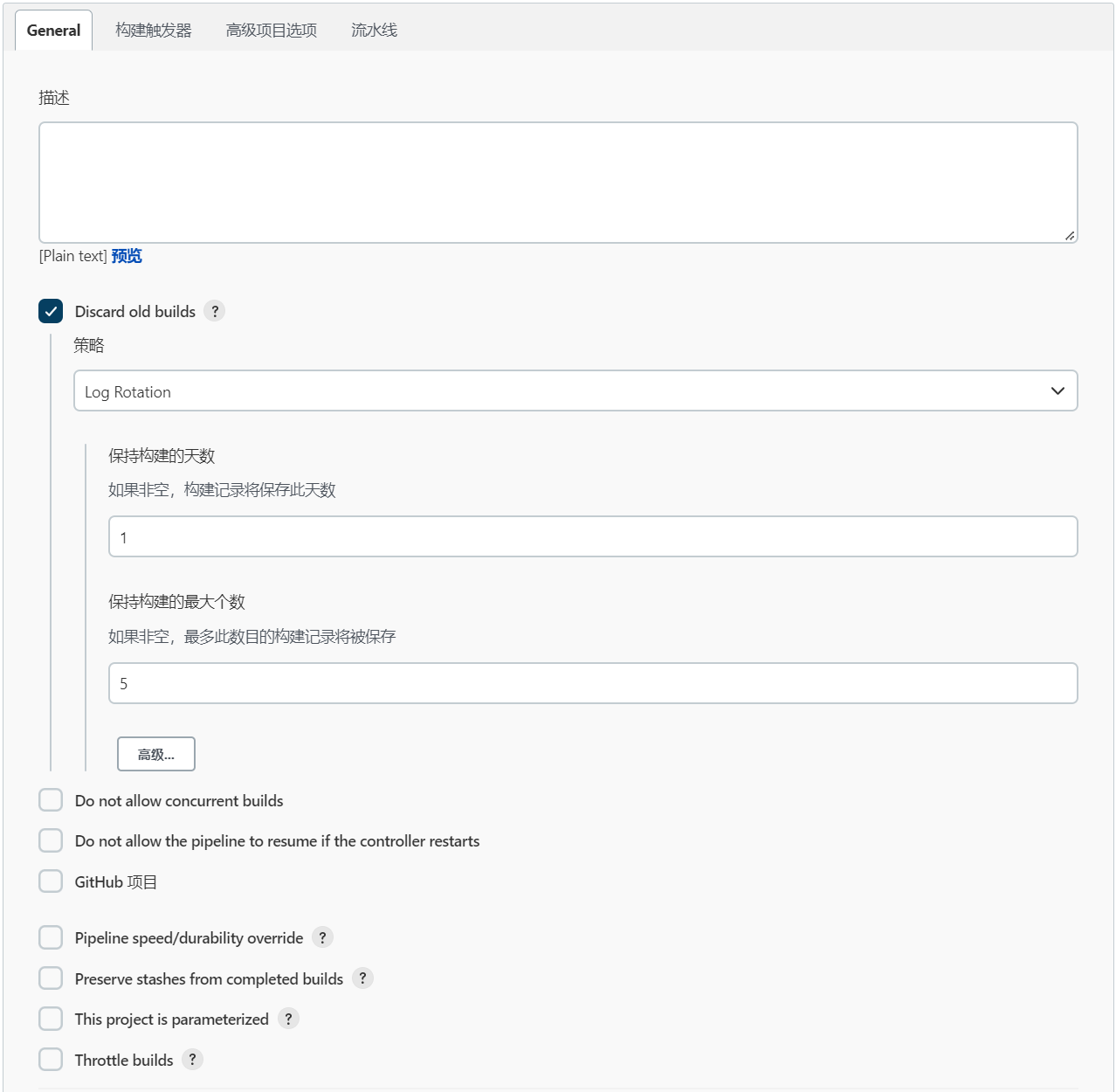
在“General”选项卡下勾选“丢弃旧的构建”,填写需要保留的构建天数和构建的最大个数。若不及时清理旧的构建,则会消耗服务器的磁盘空间。“保持构建天数” 和"保持构建的最大个数"是可以自定义的,需要根据实际情况确定一个合理的值。
7.3 流水线
流水线用特殊的语句或者元素定义章节,这遵循 Groovy 语法。
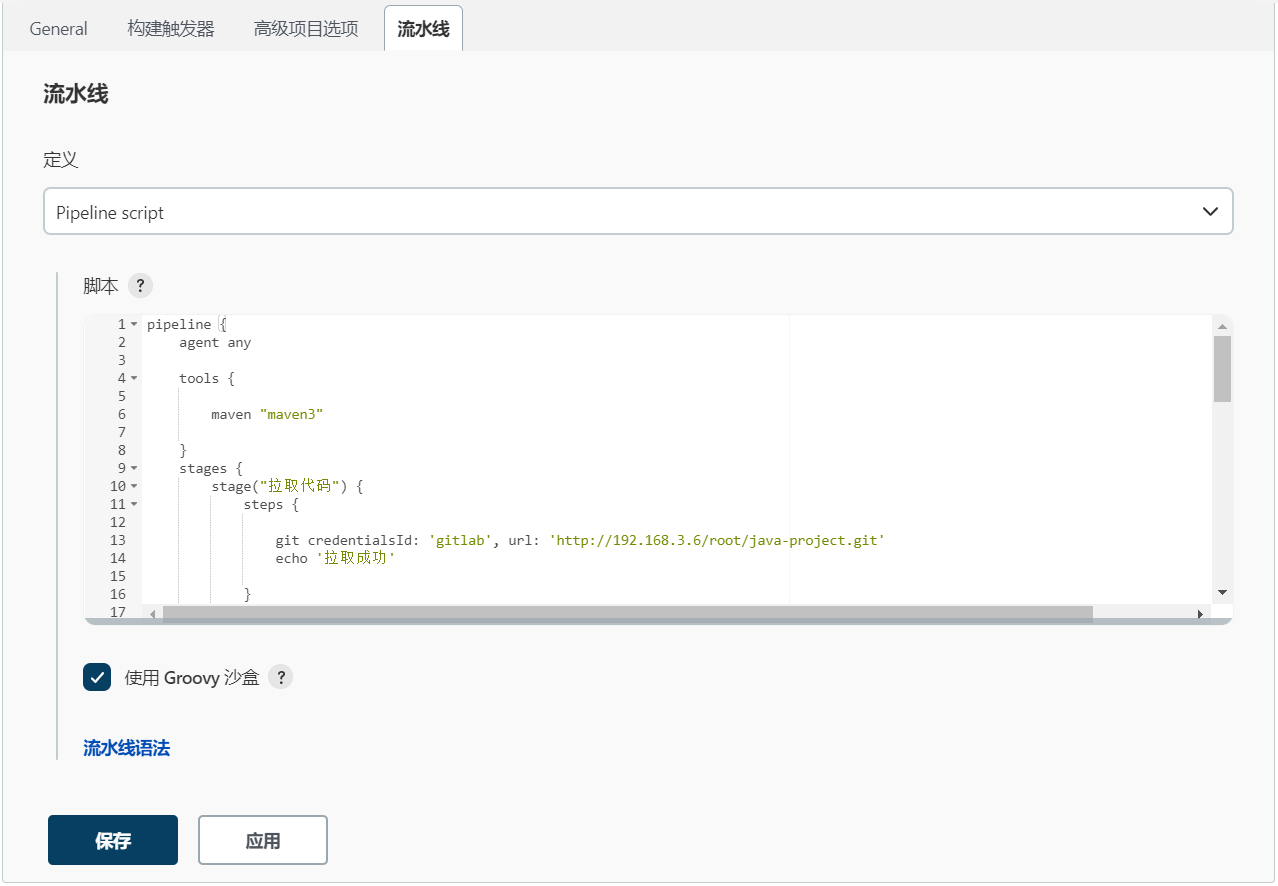
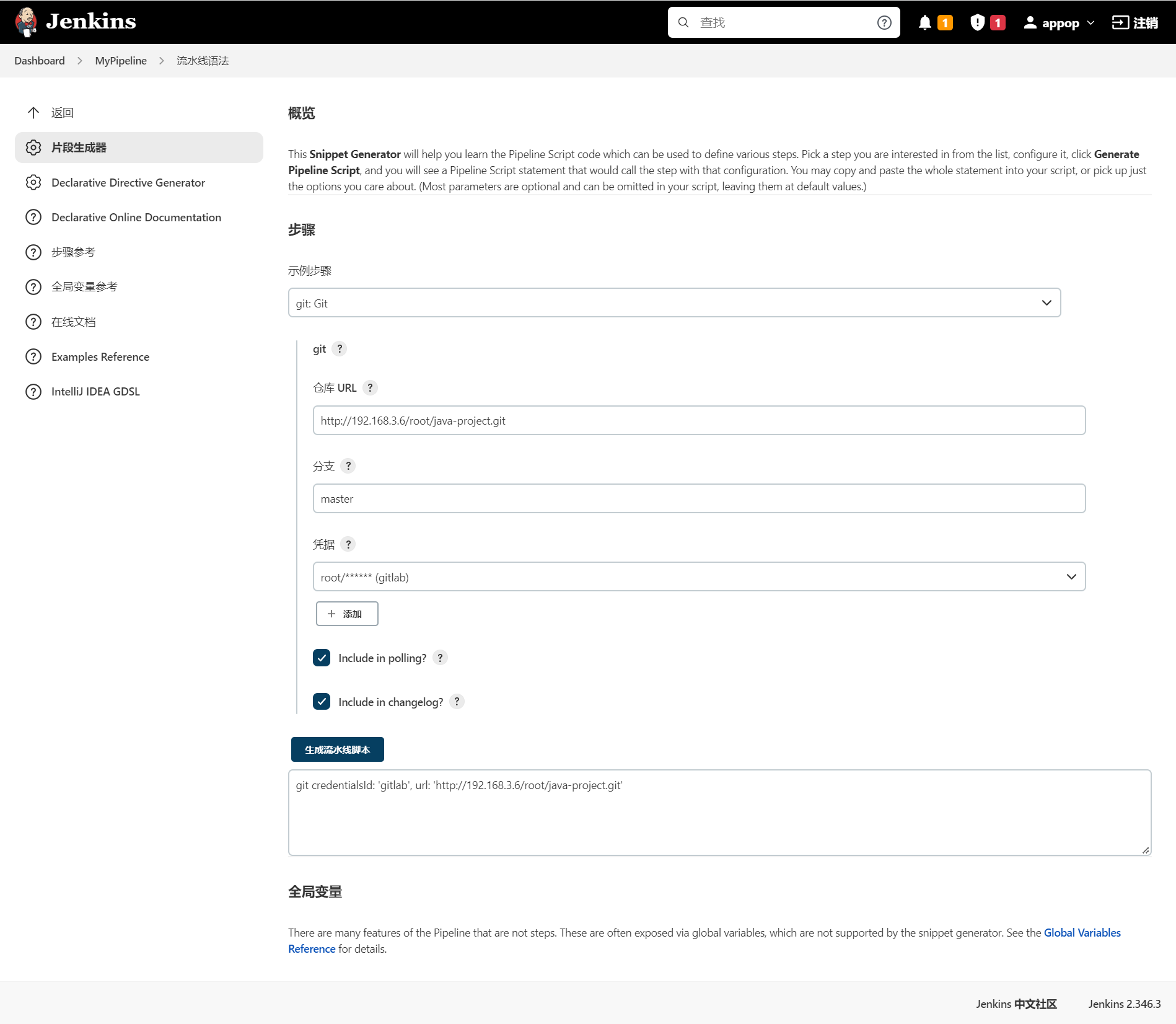
Pipeline脚本功能非常强大,默认支持数十个指令!你可能担心指令学习的成本,但这种担心其实是多余的——只需点击“流水线语法”按钮,就可以傻瓜化地使用Pipeline语法啦!
Pipeline脚本:
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven "maven"
}
stages {
stage("拉取代码") {
steps {
git credentialsId: 'gitlab', url: 'http://192.168.3.6/root/java-project.git'
echo '拉取成功'
}
}
stage("执行构建") {
steps {
sh """
mvn clean package
"""
echo '构建完成'
}
}
stage("运行前清理"){
steps{
sshPublisher(publishers: [sshPublisherDesc(configName: 'Tomcat', transfers: [sshTransfer(cleanRemote: false, excludes: '', execCommand: '''rm -rf *
docker stop demo
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)''', execTimeout: 120000, flatten: false, makeEmptyDirs: false, noDefaultExcludes: false, patternSeparator: '[, ]+', remoteDirectory: '/home/appop', remoteDirectorySDF: false, removePrefix: '', sourceFiles: '')], usePromotionTimestamp: false, useWorkspaceInPromotion: false, verbose: false)])
echo 'clean test server over!'
}
}
stage("发送jar包到测试服务器") {
steps {
sshPublisher(publishers: [sshPublisherDesc(configName: 'Tomcat', transfers: [sshTransfer(cleanRemote: false, excludes: '', execCommand: '', execTimeout: 120000, flatten: false, makeEmptyDirs: false, noDefaultExcludes: false, patternSeparator: '[, ]+', remoteDirectory: '/xxoo', remoteDirectorySDF: false, removePrefix: 'target', sourceFiles: '**/demo*.jar'), sshTransfer(cleanRemote: false, excludes: '', execCommand: '''docker build -t demo .
docker run -d --name demo -p 8080:8080 demo''', execTimeout: 120000, flatten: false, makeEmptyDirs: false, noDefaultExcludes: false, patternSeparator: '[, ]+', remoteDirectory: '/', remoteDirectorySDF: false, removePrefix: '', sourceFiles: 'Dockerfile')], usePromotionTimestamp: false, useWorkspaceInPromotion: false, verbose: false)])
echo 'jar send over!'
}
}
}
}
- environment:用于定义流水线执行过程中的环境变量。
- triggers:用于定义流水线的触发机制。pollSCM 定义了每分钟判断一次代码是否有变化,如果有变化则自动执行流水线。
- agent:用于定义整条流水线的执行环境,可以指定执行节点。
label 指定运行job的节点标签;any 不指定,由Jenkins分配。eg:
agent {
node {
label "jenkins-02"
}
}
- stages:流水线的所有阶段,都被定义在这部分。
- stage:某一阶段,可有多个。
- steps:阶段内的每一步,可执行命令。
7.4 构建计划
- 配置完成后,点击构建项目,执行构建。
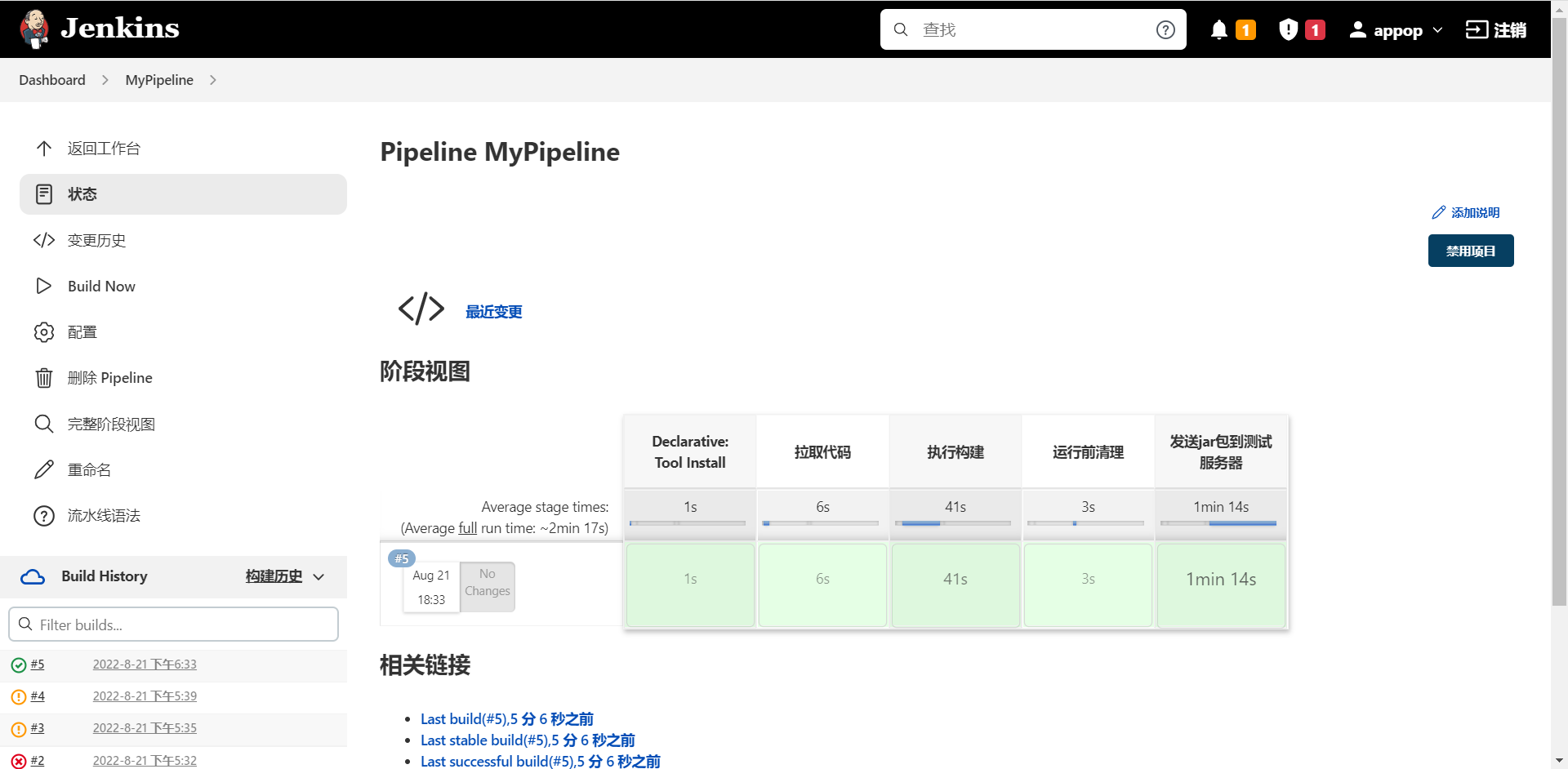
- 构建成功后,可通过界面视图查看每阶段的执行情况。
- 构建成功后,浏览器上访问,看是否能正常访问。

7.5 打开Blue Ocean
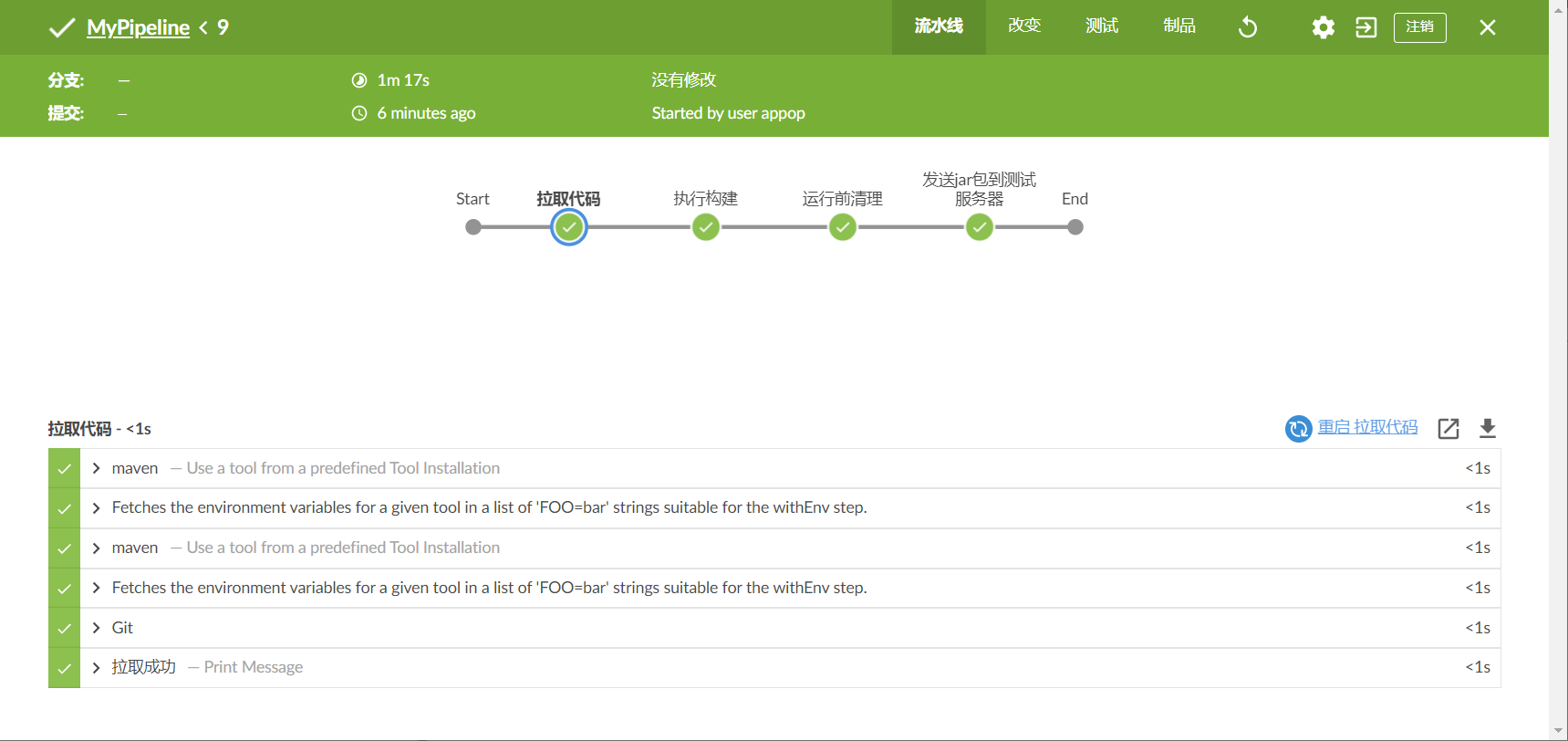
Blue Ocean插件安装好后,进入Jenkins主界面,在面板左侧的导航栏中点击“打开Blue Ocean”,进入“Blue Ocean可视化界面”,可进行流水线创建和流水线管理。
Blue Ocean 的主要特点包括:
- 持续交付 (CD) 管道的复杂可视化,允许快速直观地了解管道的状态
- 管道编辑器- 通过引导用户通过直观和可视化的过程来创建管道,使管道的创建变得平易近人
- 个性化以适应团队每个成员基于角色的需求
- 在需要干预和/或出现问题时精确定位。Blue Ocean 显示了管道中需要注意的地方,促进异常处理并提高生产力
- 分支和拉取请求的本机集成,在与 Git 服务中的其他人协作编写代码时,可最大限度地提高开发人员的生产力
post:流水线完成后可执行的任务
- always 无论流水线或者阶段的完成状态。
- changed 只有当流水线或者阶段完成状态与之前不同时。
- failure 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为"failure"运行。
- success 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为"success"运行。
- unstable 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为"unstable"运行。例如:测试失败。
- aborted 只有当流水线或者阶段状态为"aborted "运行。例如:手动取消。
7.6 总结
声明式流水线
优点:
- 更像是在Jenkins web ui中的操作
- 可读性比较高
- 可以使用blue ocean自动生成
- 支持语法检查
缺点:
- 代码逻辑能力比脚本式弱,不能完成特别复杂的任务
脚本式流水线
优点:
- 更少的代码和弱规范要求
- 更灵活的自定义代码操作
- 不受约束,可以构建特别复杂的工作流和流水线
缺点:
-
读写对编程要求比较高
-
比声明式流水线代码更复杂
8 学习资源
【尚硅谷】2022版Jenkins教程(从配置到实战)链接:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1bS4y1471A?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=98740c3a1a80e352dd48522ee3cfa51d