本文介绍了Spring Security 以及Shiro 在Spring Boot中的使用,对于Spring Security 有基于传统认证方式的Session认证,也有使用OAuth 协议的认证。一般来说,传统的Web架构中,使用Session 认证更加快速,但是,若结合微服务,前后端分离等架构时,则使用OAuth 认证更加方便。
在Spring Boot项目中,Spring Security 整合相对更加容易,可以首选,Shiro 虽不及其强大,但也能胜任绝大部分的项目了。
本文没有细谈密码学,关于这部分的加密内容,可以参见我之前密码学的文章,安全管理中对于密码还是相当看重的。不过在安全管理中,除了密码学认证同时还有权限角色的认证等,值得学习。
目录
- 引言
- Spring Security 基本配置
- 基本用法
- 基于内存的认证
- HttpSecurity
- 登陆表单详细配置
- 注销登录配置
- 方法安全
- 基于数据库的认证
- OAuth 2
- OAuth 2授权模式
- 实践
- Spring Boot 整合 Shiro
引言
在Java 开发领域常见的安全框架有Shiro 和Spring Security。Shiro 是一个轻量级的安全管理框架,提供了认证、授权、会话管理、密码管理、缓存管理等功能。Spring Security是一个相对复杂的安全管理框架,对OAuth 2的支持也更友好,可以和Spring 框架无缝整合。
Spring Security 基本配置
基本用法
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
项目中的资源就会被保护起来。
下面添加一个接口:
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
启动后,访问80/hello接口,会自动跳转到这个登陆页面,这个页面就是由Spring Security提供的。
用户名就是user,密码如下图得到:默认的密码随项目随机生成的,查看项目启动日志就行。
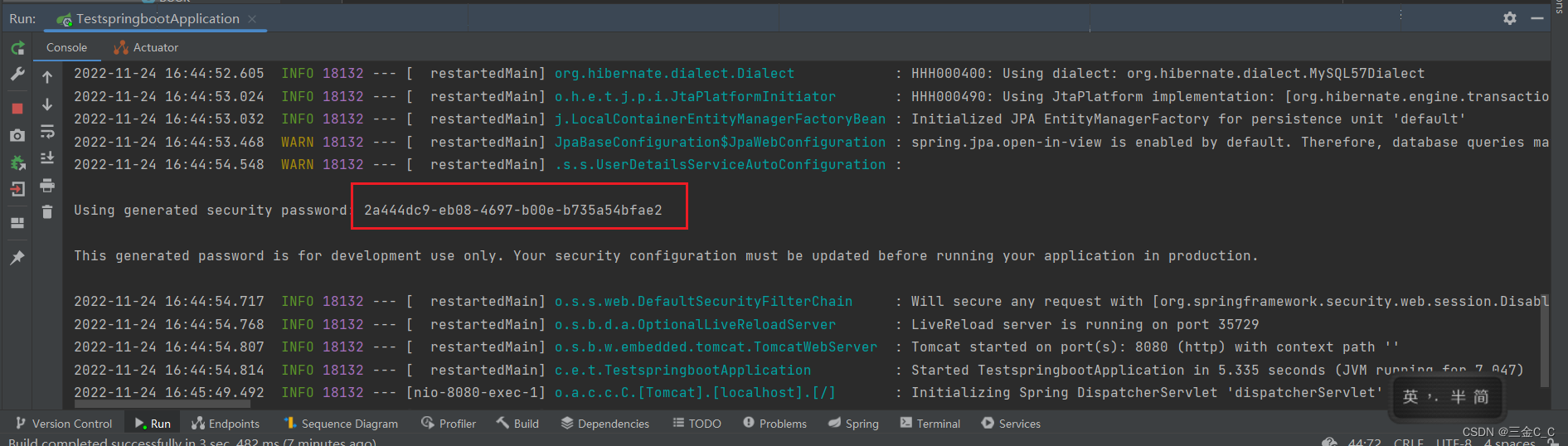
当然了,可以自定义配置用户名和密码:
在配置文件:
具有的角色是admin
spring.security.user.name=jacin
spring.security.user.password=123
spring.security.user.roles=admin
基于内存的认证
开发者可以自定义类继承自WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter ,进而实现对Spring Secuity进行更多的配置:
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN","USER")
.and()
.withUser("jacin").password("123").roles("ADMIN");
}
}
继承了 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 并重写了configure方法,在这里配置了两个用户,一个是admin 具有两个角色,另一个是jacin 角色是admin。
在Spring Security 5.x 引入了众多密码加密方式,本案例使用的是NoOpPasswordEncoder 不加密。
HttpSecurity
可以实现认证功能,但是受保护的资源是默认的,不能根据实际情况进行角色管理。如果要实现功能,就要重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的方法:
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("root").password("123").roles("ADMIN","DBA")
.and()
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN","USER")
.and()
.withUser("user").password("123").roles("USERS");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception{
//调用了authorizeRequests()方法开启HttpSecurity配置
http.authorizeRequests()
//其中/admin/**的URL必须具有admin的角色
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/users/**")
.access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN','USER')")
.antMatchers("/db/**")
.access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
//下两行表示除了前面定义的URL模式以外,用户访问其他的URL都必须认证后访问
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
// 开启表单登陆
.formLogin()
//配置此接口方便Ajax 或者 移动端调用登录接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
// 和登录相关的接口不需要认证即可访问
.permitAll()
.and()
// 关闭csrf
.csrf()
.disable();
}
}
这里设置了三个用户,分别具有不同的角色。
下面在controller进行测试:
// 此Controller层为RestController
@GetMapping("/admin/hello")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin!";
}
@GetMapping("/user/hello")
public String user() {
return "hello user";
}
@GetMapping("/db/hello")
public String dba() {
return "hello dba";
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
测试的时候,会发现登陆相应的页面。例如管理登陆后可以访问/admin/**,/user/ 界面。
登陆表单详细配置
到目前为止,登陆表单使用的是Spring Security 提供的页面,登陆成功后也是默认的页面跳转。但是前后端分离是开发的主流,在此开发模式下,前后端数据通过JSON进行,这是登陆后就不是页面跳转了,而是一段JSON提示。
和上文一样,这里给出部分代码,其余部分见上文:
.formLogin()
//登陆页面。这里的/login就是开发者自定义的登陆页面,也就是路径
.loginPage("/login")
// 配置了loginProcessingUrl,登陆请求处理接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
// 认证需要的参数
.usernameParameter("name")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
// 登陆成功的处理逻辑,本次是返回一段JSON,第三个参数是当前用户登陆信息
.successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
response.setStatus(200);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status",200);
map.put("msq",principal);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
out.write(om.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
.failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
response.setStatus(401);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status",401);
if(exception instanceof LockedException) {
map.put("msg","账户被锁定");
} else if (exception instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
map.put("msg","账户或者密码输入错误");
} else if (exception instanceof DisabledException) {
map.put("msg","账户被禁用");
} else if (exception instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
map.put("msg","账户过期");
}
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
out.write(om.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
.permitAll()
在templates下面建一个简单的提交表单:
<form method="post">
name <input name="name" type="text">
pass <input name="passwd" type="password">
<input type="submit">
</form>
然后在Controller写跳转页面:
这里返回的就是视图层而不是字符串。
@Controller
public class testController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "login_page";
}
}
当然我们也可以用postman来进行测试:
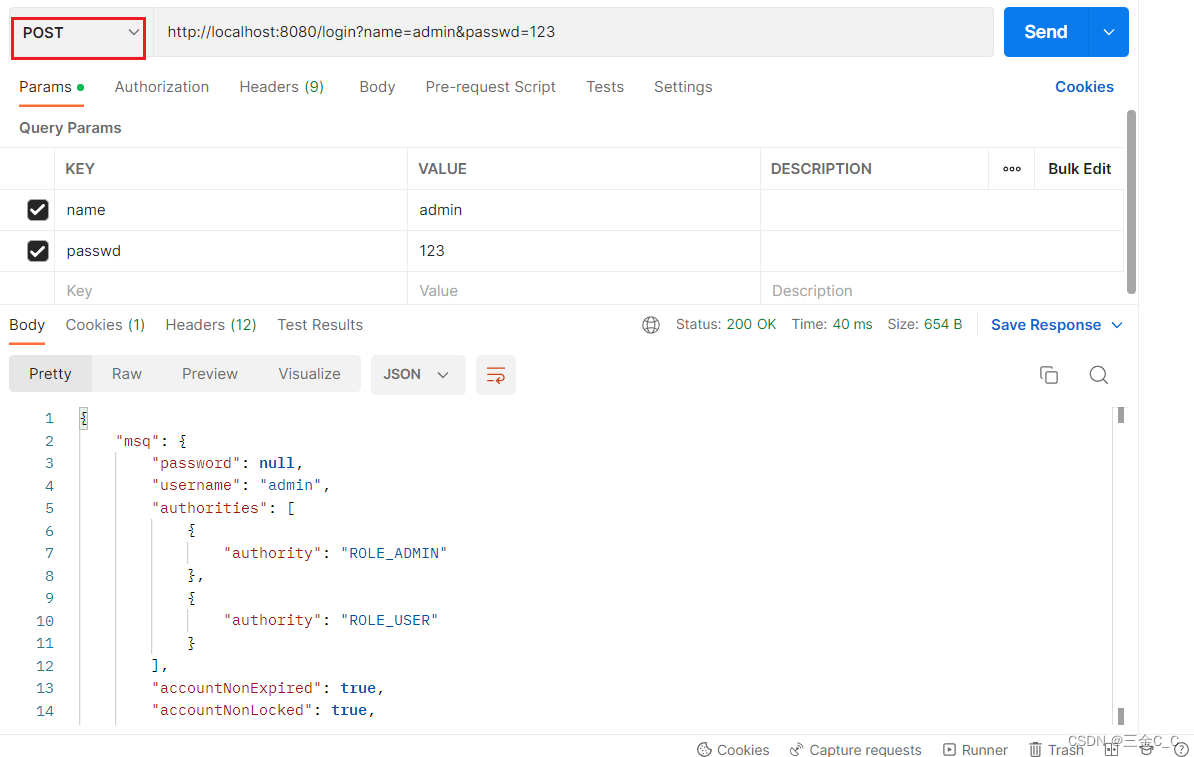
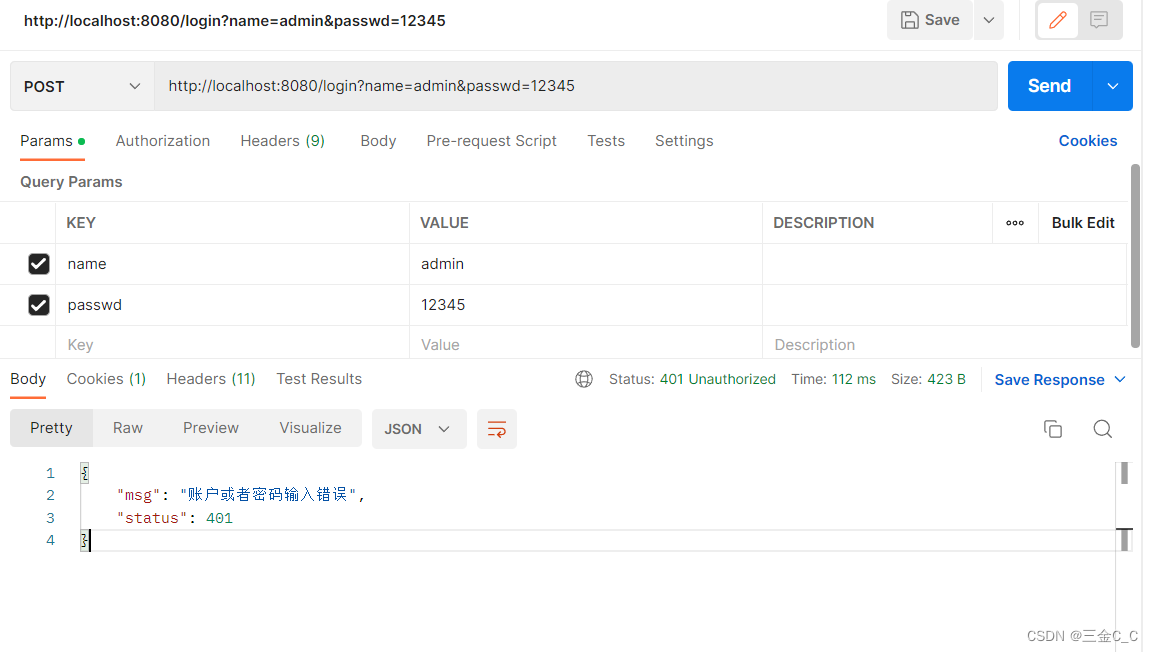
这里用到了Ajax技术。
注销登录配置
如果想注销登录也只需要提供简单的配置:
.and()
// 开启注销登陆的配置
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 清除身份认证信息
.clearAuthentication(true)
// 使session失效
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
//可以写一下数据清除工作
.addLogoutHandler(new LogoutHandler() {
@Override
public void logout(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) {
}
})
// 注销成功后的业务逻辑
.logoutSuccessHandler(new LogoutSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("/login");
}
})
.and()
方法安全
上述的认证和授权都是基于URL的,开发者也可以通过注解来灵活配置方法安全,要通过注解来开启基于注解的安全配置:
@Configuration
// 解锁两个注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true,securedEnabled = true)
public class SecutityCon {
}
开启安全配置后,可以创建一个Service来测试:
@Service
public class MethodService {
// 访问该方法需要admin角色,注意在角色面前需要加ROLE_
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin";
}
// 既需要ADMIN 又需要 DBA
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
public String dba() {
return "hello dba";
}
}
基于数据库的认证
上述的认证数据定义在内存中,真实项目中,用户的基本信息和角色存储在数据库中。
数据库建表:
create table user (
id int(11) primary key ,
username varchar(32),
password varchar(255),
enabled tinyint(1),
locked tinyint(1)
);
create table role(
id int(11) primary key ,
name varchar(32),
nameZh varchar(32)
);
create table user_role(
id int(11) primary key ,
uid int(11),
rid int(11)
);
默认插入一些数据:
use ay_user;show tables ;
insert into user (id, username, password, enabled, locked) values (1,'root','123','1','0');
insert into user (id, username, password, enabled, locked) values (2,'user','123','1','0');
insert into role (id, name, nameZh) values (1,'ROLE_dba','ADMINDBA');
insert into role (id, name, nameZh) values (2,'ROLE_user','user');
insert into user_role values (1,'1','1');
insert into user_role values (2,'1','2');
创建实体类:
public class Role {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String nameZh;
//省略getter/setter
}
创建用户表类:
public class User implements UserDetails {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Boolean enabled;
private Boolean locked;
private List<Role> roles;
// 获取当前用户的角色信息,角色都存储在roles,直接遍历roles 属性,然后构造集合并返回。
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
for (Role role : roles) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()));
}
return authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return !locked;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
//省略getter/setter
// public Boolean getEnabled() {
// return enabled;
// }
public void setEnabled(Boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public Boolean getLocked() {
return locked;
}
public void setLocked(Boolean locked) {
this.locked = locked;
}
public List<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(List<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}
用户类需要实现UserDetails 接口,并实现接口的方法:
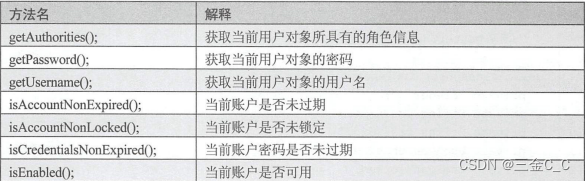
本案例中数据库只有enabled和locked 字段,故未过期和密码未过期都返回true.(不需要自己进行密码角色等匹配了)
创建UserService:
// 实现接口
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Resource
UserMapper userMapper;
// 用户登陆时的用户名,并通过用户名去数据库查找用户,如果没查到就抛出异常
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userMapper.loadUserByUsername(username);
if(user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("账户不存在");
}
user.setRoles(userMapper.getUserRolesByUid(user.getId()));
return user;
}
}
UserMapper.java:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
User loadUserByUsername(String username);
List<Role> getUserRolesByUid(Integer id);
}
其中UserMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.testspringboot.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="loadUserByUsername" resultType="com.example.testspringboot.model.User">
select * from user where username=#{username}
</select>
<select id="getUserRolesByUid" resultType="com.example.testspringboot.model.Role">
select * from role r,user_role ur where r.id=ur.rid and ur.uid=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
对Spring Security 配置:
@Configuration
public class SQLsecuity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Resource
UserService userService;
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userService);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin")
.antMatchers("/db/**").hasRole("dba")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("user")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login").permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}
这里同样没有使用加密方法,接着便可以像之前基于内存的方法在controller层进行测试了。
OAuth 2
OAuth 是一个开发标准,允许用户第三方应用访问在某一网站存储的私密资源,而这个过程中无须提供用户名和密码,实现这个功能是通过一个令牌(token)。例如,用户想通过QQ登录知乎,这是知乎就是第三方应用,知乎要访问用户的基本信息就需要得到授权,采取令牌的方式可以让用户灵活对第三方应用授权或者收回权限。传统Web开发基于Session,前后端分离的时候有不便,所以OAuth 2都可以解决。
OAuth 2授权模式
基本角色:资源所有者(用户)、客户端(上文提到的知乎)、授权服务器,资源服务器。
具体步骤:

一般来说授权模式有4种:
1.授权码模式 (基本都是使用这个) 2.简化模式 3.密码模式 4.客户端模式
实践
本次介绍的是在前后端分离应用提供的认证服务器如何搭建OAuth服务,主要是密码模式。
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
OAuth协议是在Spring Security 基础上完成的,因此要添加Spring Security 依赖,令牌可以存储在Redis缓存服务器上,同时Redis具有过期等功能,所以也加入Redis 依赖。
在application.properties配置Redis 连接信息:
# redis
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1ms
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
授权服务器和资源服务器可以是同一台服务器,通过不同的配置分别开启授权和资源服务器:
授权服务器:
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
// 继承,完成对授权服务器配置,通过上面注解开启
public class AuthorizationServerConfig
extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
// 支持password 模式
@Resource
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
// 用来完成Redis 缓存,将令牌信息存储到Redis 缓存中
@Resource
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;
// 刷新token 提供支持
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients)
throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient("password")
.authorizedGrantTypes("password", "refresh_token")
.accessTokenValiditySeconds(1800)
.resourceIds("rid")
.scopes("all")
// 明文是123
.secret("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq");
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints)
throws Exception {
endpoints.tokenStore(new RedisTokenStore(redisConnectionFactory))
.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security)
throws Exception {
security.allowFormAuthenticationForClients();
}
}
资源服务器:
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfig
extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources)
throws Exception {
// 配置资源id,和授权服务器资源id 一致,然后设置这些资源仅基于令牌认证
resources.resourceId("rid").stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("user")
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
配置Spring Security:
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
// 注入授权服务器配置类使用
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
@Override
protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return super.userDetailsService();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin")
.password("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq")
.roles("admin")
.and()
.withUser("sang")
.password("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq")
.roles("user");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/oauth/**").authorizeRequests()
// 遇到oauth 直接放行
.antMatchers("/oauth/**").permitAll()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
在controller层依旧是:
@GetMapping("/admin/hello")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin!";
}
@GetMapping("/user/hello")
public String user() {
return "hello user";
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
现在启动Redis 服务器,首先发送一个POST请求,地址如下:
http://localhost:8080/oauth/token?username=sang&password=123&grant_type=password&client_id=password&scope=all&client_secret=123
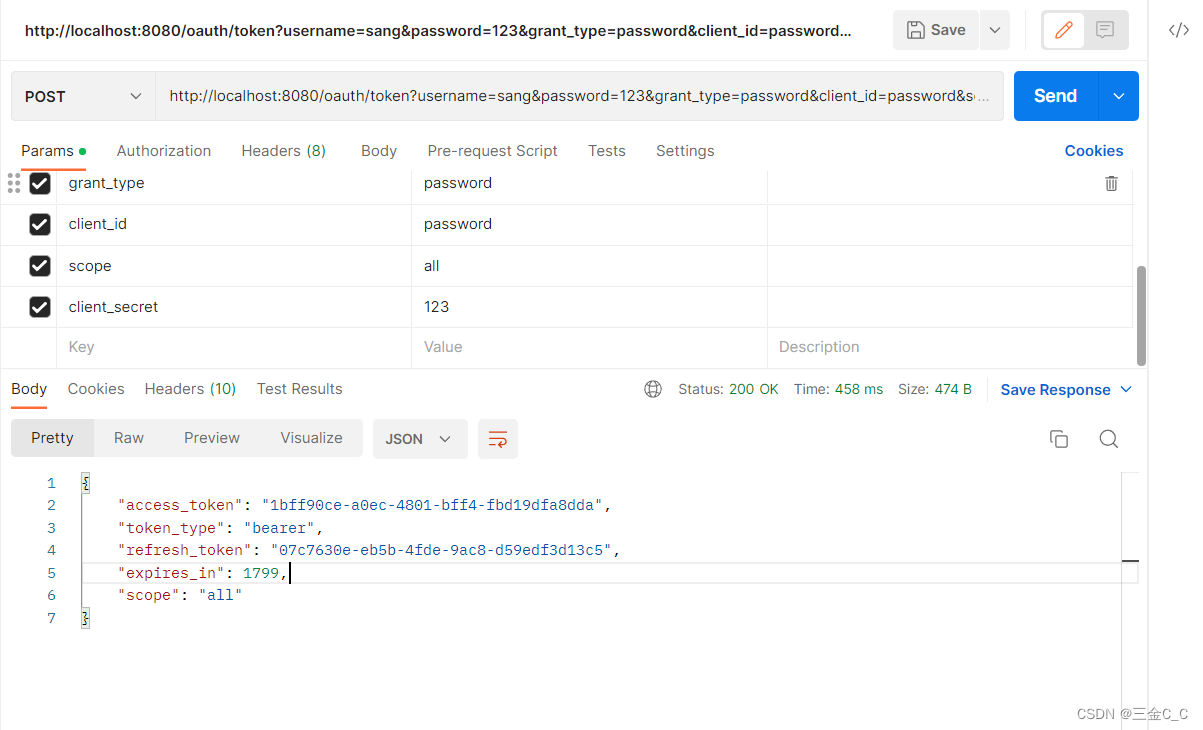
请求地址包括了用户名密码授权模式 客户端id scope 以及客户端密码。
返回结果如上,其中access_token 是获取其他资源要用的令牌,refresh_token 用来刷新令牌,expires_in 表示过期时间,当过期后,使用refresh_token 重新获取新的access_token 。
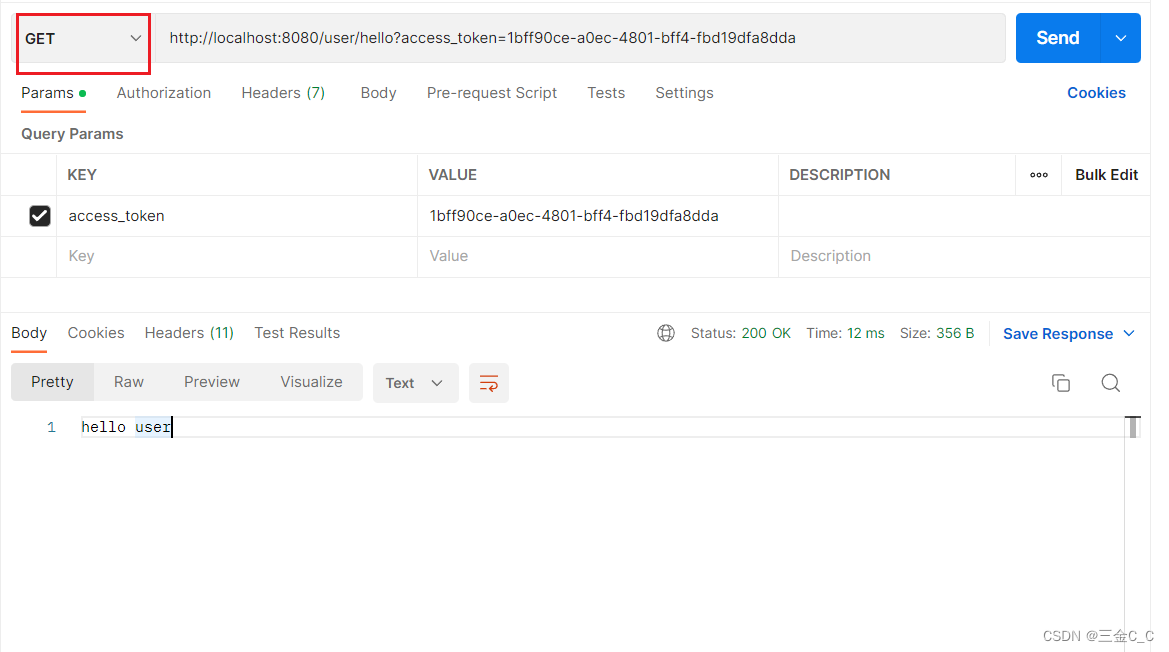
访问所有资源,携带access_token 参数接口:
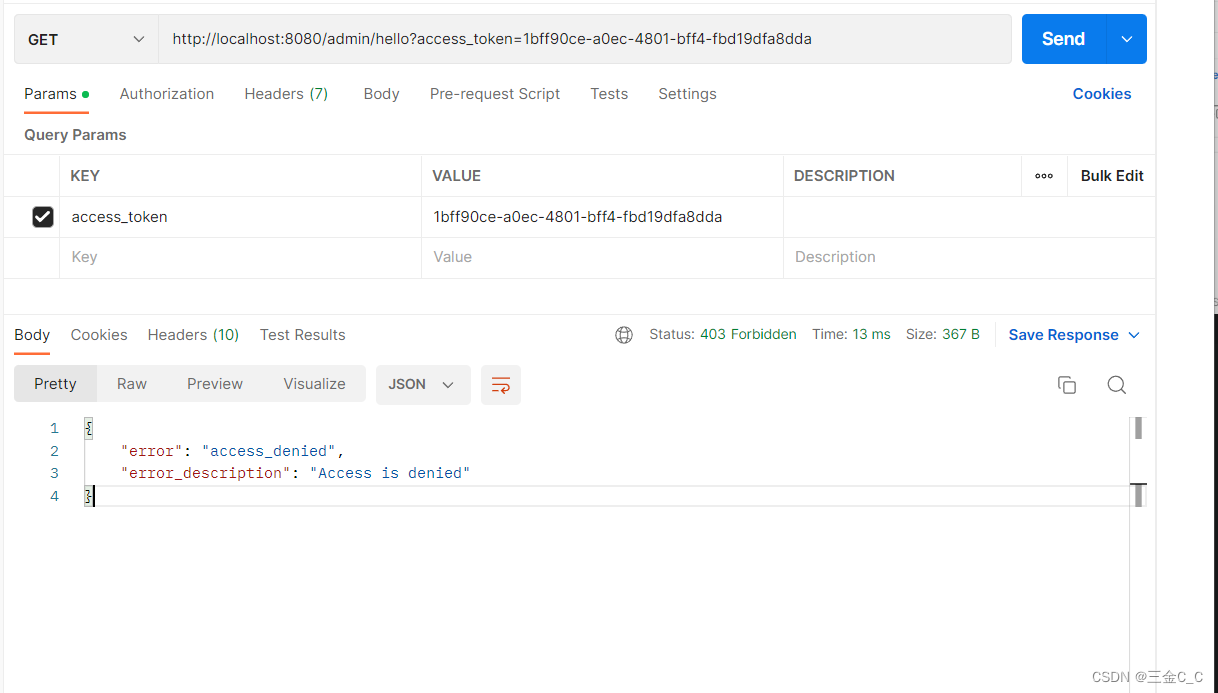
如果非法访问一个资源,访问/admin/hello:
接着来看Redis 数据:
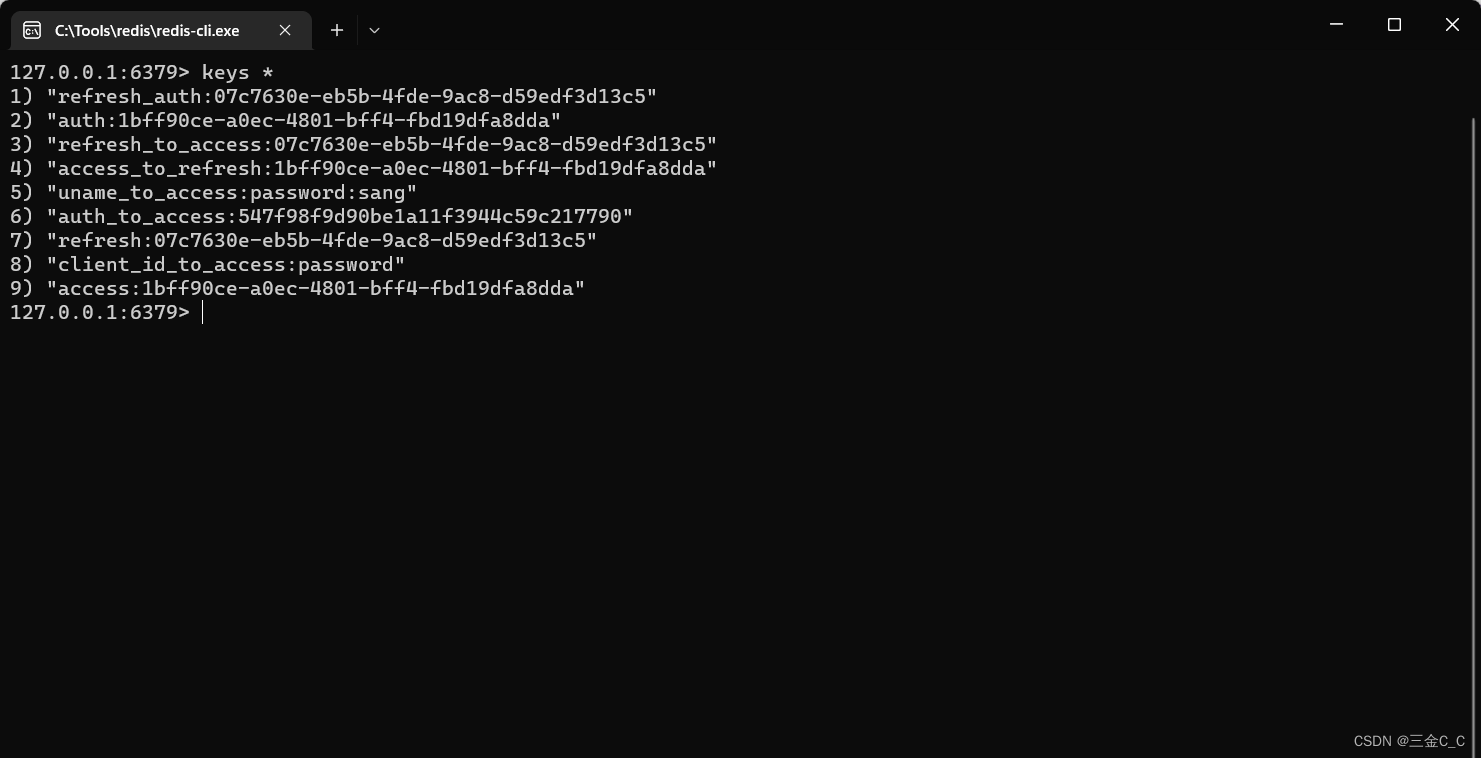
至此一个password 模式的OAuth 认证体系就搭建完成了。
整体来说,Spring Security OAuth 2的使用还是比较复杂,配置也相当繁琐,如果应用场景较简单,可以按照上文搭建。
Spring Boot 整合 Shiro
Apache Shiro 是一个开源轻量级Java 安全框架,提供身份验证,授权,密码管理以及会话管理,相对于Spring Security ,Shiro 更加直观易用,也提供健壮的安全性。在SSM框架中,手动整合Shiro 配置步骤还是比较多,针对Spring Boot ,Shiro 提供了shiro-spring-boot-web-starter 用来简化配置。
引入依赖:
// 这部分代码可以不要,因为在shiro-spring已经集成了
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.theborakompanioni</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
在application.properties 中配置Shiro 信息:
# 开启Shiro
shiro.enabled=true
# 开启Shiro Web
shiro.web.enabled=true
# 表示登录地址
shiro.loginUrl=/login
shiro.successUrl=/index
shiro.unauthorizedUrl=/unauthorized
# 表示允许通过URL 参数实现会话跟踪,如果网站支持Cook
shiro.sessionManager.sessionIdUrlRewritingEnabled=true
shiro.sessionManager.sessionIdCookieEnabled=true
配置Shiro ,提供两个最基本的Bean:
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
// 没有配置数据库连接,这里直接配置两个用户,分别对应不同的角色,同时角色也有不同的读写权限
@Bean
public Realm realm() {
TextConfigurationRealm realm = new TextConfigurationRealm();
realm.setUserDefinitions("sang=123,user\n admin=123,admin");
realm.setRoleDefinitions("admin=read,write\n user=read");
return realm;
}
@Bean
public ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition() {
DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition chainDefinition =
new DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition();
// 可以匿名访问
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/login", "anon");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/doLogin", "anon");
// 注销操作
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/logout", "logout");
chainDefinition.addPathDefinition("/**", "authc");
return chainDefinition;
}
// 如果不在Thymelead 使用Shiro,可以不写
@Bean
public ShiroDialect shiroDialect() {
return new ShiroDialect();
}
}
接下来配置登录接口以及页面访问接口:
@Controller
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/doLogin")
public String doLogin(String username, String password, Model model) {
System.out.println("123");
UsernamePasswordToken token =
new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
model.addAttribute("error", "用户名或密码输入错误!");
return "login";
}
return "redirect:/index";
}
@RequiresRoles("admin")
@GetMapping("/admin")
public String admin() {看,
return "admin";
}
@RequiresRoles(value = {"admin","user"},logical = Logical.OR)
@GetMapping("/user")
public String user() {
return "user";
}
}
在doLogin 中,构造了 UsernamePasswordToken实例,获取一个Subject对象并调用login 方法执行登录,当异常抛出的时候,说明登录失败,登录成功重新定向/index
对于其他不需要角色就能访问的接口,直接在WebMvc配置即可:
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/unauthorized").setViewName("unauthorized");
}
}
接下来创建全局异常处理器进行全局异常处理,本案例主要是处理授权异常:
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/unauthorized").setViewName("unauthorized");
}
}
然后分别建立5个html:
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:shiro="http://www.pollix.at/thymeleaf/shiro">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Hello, <shiro:principal/></h3>
<h3><a href="/logout">注销登录</a></h3>
<h3><a shiro:hasRole="admin" href="/admin">管理员页面</a></h3>
<h3><a shiro:hasAnyRoles="admin,user" href="/user">普通用户页面</a></h3>
</body>
</html>
注意这里导入的名称空间和jsp中导入的shiro 是不同的。
login.html:
<form action="/doLogin" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username"><br>
<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<div th:text="${error}"></div>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
user.html:
<h1>普通用户页面</h1>
admin.html:
<h1>管理员页面</h1>
unauthorized.html:
<div>
<h3>未获授权,非法访问</h3>
<h3 th:text="${error}"></h3>
</div>
下面开始测试,直接运行后,输入sang ,123 便可以登录:
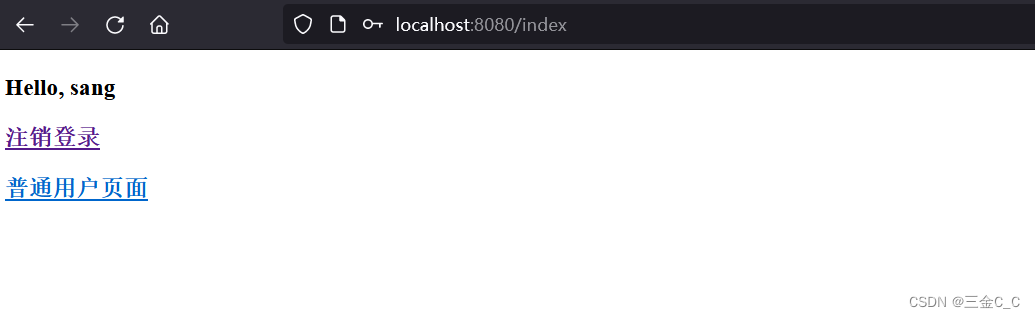
如果此时的路径是admin,将会提示非法访问。
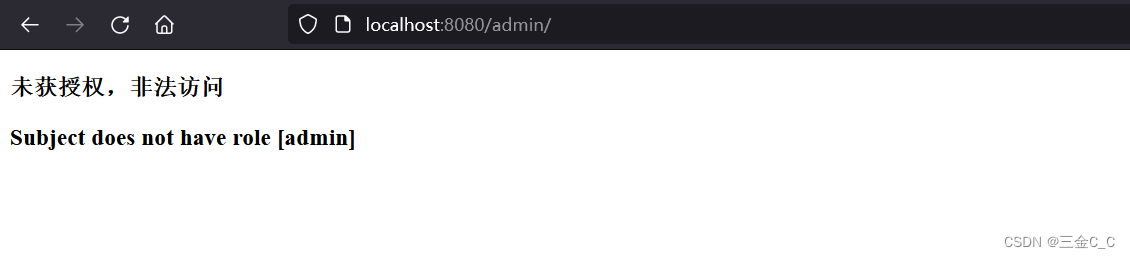
以上。


![[Flask]Flask零基础项目---登录demo](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7c054f28a5b343a7a091126b6288d278.png)