1.回文链表
编写一个函数,检查输入的链表是否是回文的。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
笔试的写法
重点是快速code,不考虑空间复杂度,怎么简单怎么来
思路:把链表的数据依次压入栈中,然后弹出比较
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val != stack.pop().val){
return false;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return true;
}
}
面试的写法
对于这种比较简单的题目,想要出彩,就要考虑优化的点,考虑空间复杂度,压缩空间。
思路:使用快慢指针,找到中间的节点,然后从中间节点反转链表,头尾同时遍历比较,最后再把反转的链表恢复过来。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// 进行一轮快慢指针
// fast!=null && fast.next!=null
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 从慢指针处反转链表
ListNode cur = slow;
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
while(next != null) {
ListNode nextnext = next.next;
next.next = cur;
cur = next;
next = nextnext;
}
//判断回文
ListNode l = head;
ListNode r = cur;
while(r != null) {
if(l.val!=r.val) {
next = cur.next;
while(next != null) {
ListNode nextnext = next.next;
next.next = cur;
cur = next;
next = nextnext;
}
return false;
}
l = l.next;
r = r.next;
}
//把反转链表恢复
next = cur.next;
while(next != null) {
ListNode nextnext = next.next;
next.next = cur;
cur = next;
next = nextnext;
}
return true;
}
}
2. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
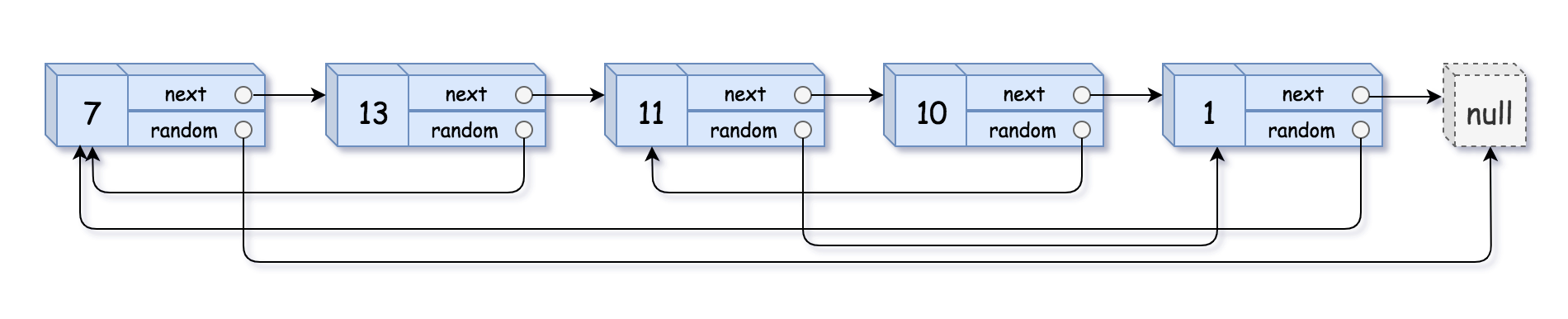
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
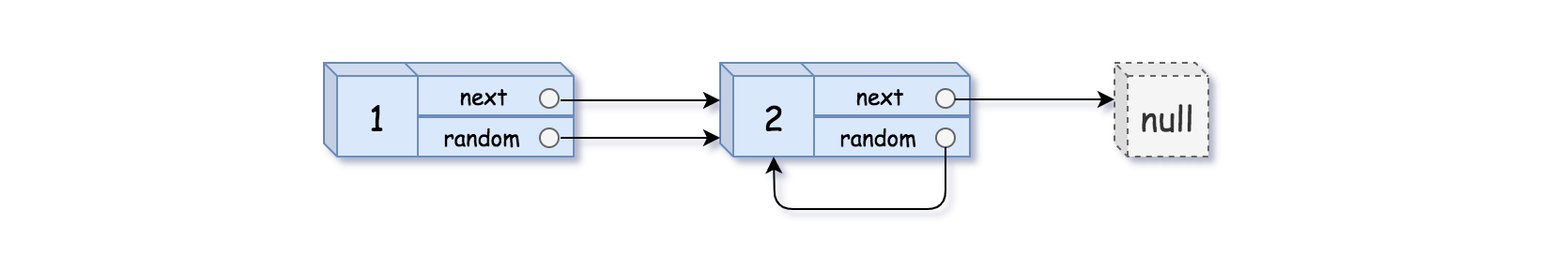
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
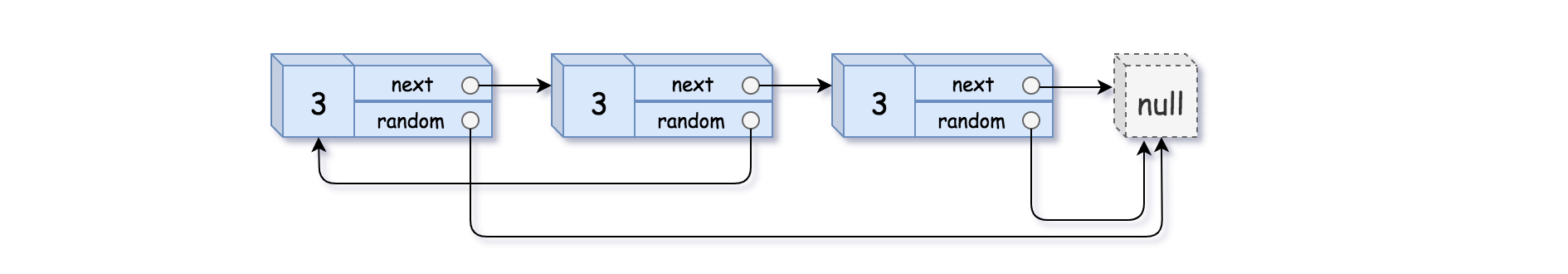
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
笔试的写法
重点是快速code,不考虑空间复杂度,怎么简单怎么来
思路:利用一个map,把原链表的Node当作key,新复制的Node当作value,然后利用Map的映射关系把原链表的Node的next和random复制到新复制的Node中
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
// 不考率空间复杂度的写法
HashMap<Node,Node> mapNode = new HashMap();
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
mapNode.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
mapNode.get(cur).next = mapNode.get(cur.next);
mapNode.get(cur).random = mapNode.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return mapNode.get(head);
}
}
面试的写法
对于这种比较简单的题目,想要出彩,就要考虑优化的点,考虑空间复杂度,压缩空间。
思路: 在Node后面串一个复制的Node,然后给复制的Node的random赋值,把复制的Node从老链表里拆出来
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
// 考率空间复杂度的写法 O(1)
Node cur = head;
// 在Node后面串一个复制的Node
while(cur != null) {
Node cp = new Node(cur.val);
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = cp;
cp.next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
// 给复制的Node的random赋值
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}else{
cur.next.random = null;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 把复制的Node从老链表里拆出来
cur = head;
Node newHead = cur.next;
while(cur != null) {
Node next = cur.next.next;
Node cp = cur.next;
cur.next = next;
cp.next = next != null?next.next:null;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
}