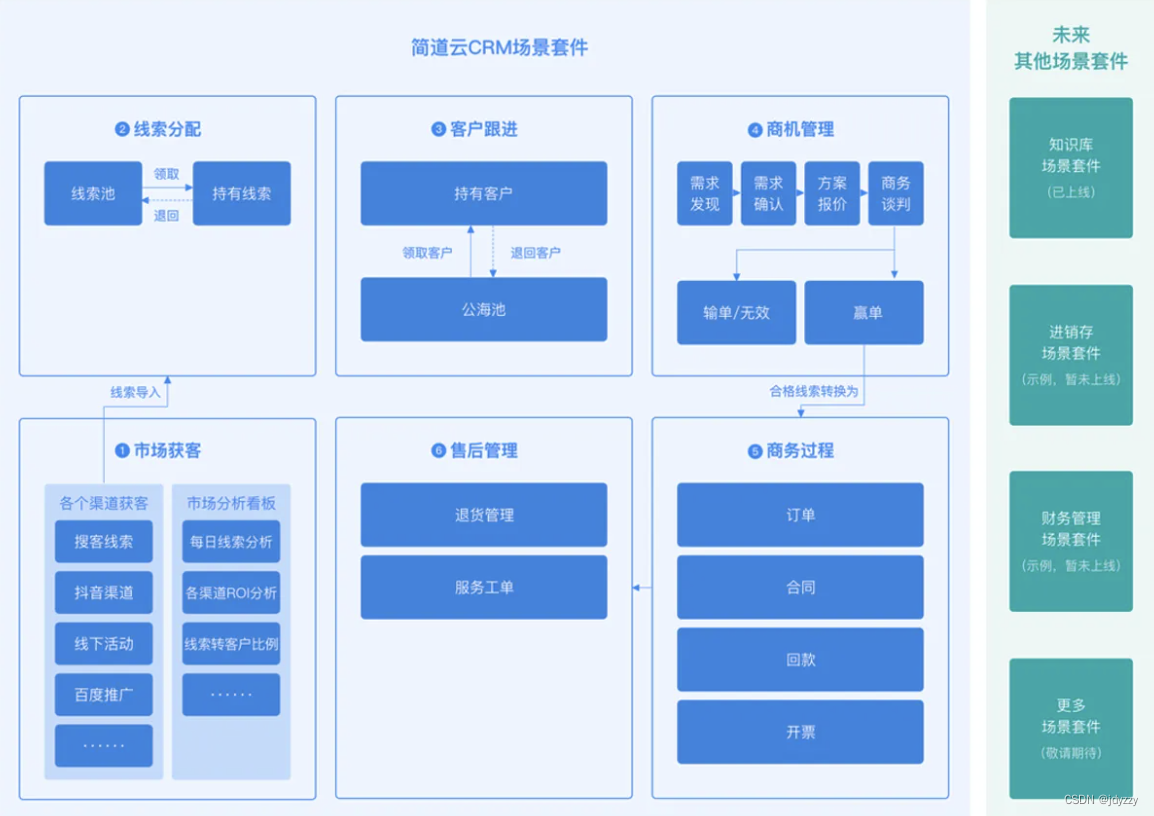
项目要点
-
torch 版本: torch.__version__ # '1.13.1+cpu'
-
设置GPU: device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
-
train_ds = datasets.MNIST('./', train = True, transform=transformation, download= True) # 数据导入 transformation = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
-
train_d1 = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True) # 转换为dataloader
-
通过iter转换为迭代器: images, labels = next(iter(train_d1))
-
数据转换为numpy: img = img.numpy()
-
显示图片: plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
-
创建卷积模型:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3) # 3表示3*3卷积
# in 64 , 1, 28, 28 -> 64, 32, 26, 26
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2)) # 池化 , # in : 64, 32, 13, 13
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3) # in: 64, 32, 13, 13 -> out: 64,64,11,11
# 再加一层池化, input: 64, 64, 11, 11 -> out: 64, 64, 5, 5
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(64* 5* 5, 256) # 计算
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(256, 10) # 10个数字的one_hot编码
def forward(self, input):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(input))
# 再加池化
x = self.pool(x)
# 卷积
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x= self.pool(x)
# flatten
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 5 * 5)
# 卷积
x = F.relu(self.linear_1(x))
x = self.linear_2(x)
return x- 定义损失函数: loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- optimizer 优化器: optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # 防止过拟合
- 数据位置调整: x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
- 梯度清零: optimizer.zero_grad()
- backward 反向传播: loss.backward()
一 手写数字识别
1.1 导包
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt- 查看torch版本
# torch 版本
torch.__version__ # '1.13.1+cpu'1.2 定义GPU设置
- 使用GPU进行训练
- 把模型转移到GPU上
- 将每一批次的训练数据转移到GPU上
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
device # device(type='cpu')1.3 导入数据
transforms.ToTensor:
- 1.把数据转化为tensor
- 2.数据的值转化为0到1之间
- 3.会把channel放到第一个维度上
# torchvision 内置了常用的数据集和常见的模型.
import torchvision
# transforms 用来做数据增强, 数据预处理的功能
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
transformation = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), ])
# 训练数据
train_ds = datasets.MNIST('./',train = True,transform=transformation,download= True)
# 测试数据
test_ds = datasets.MNIST('./',train = False,transform=transformation,download= True)- 转换成dataloader
# 转换成dataloader
train_d1 = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_d1 = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=256)- 通过 iter 转换为迭代器
# 通过iter转换为迭代器
images, labels = next(iter(train_d1))
# pytorch中图片的表现形式[batch, channel, highet, width]
images.shape # torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
labels
img = images[0]
img.shape # torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
img = img.numpy()
img.shape # (1, 28, 28)
img = np.squeeze(img) # 去掉1所在的维度
img.shape # (28, 28)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')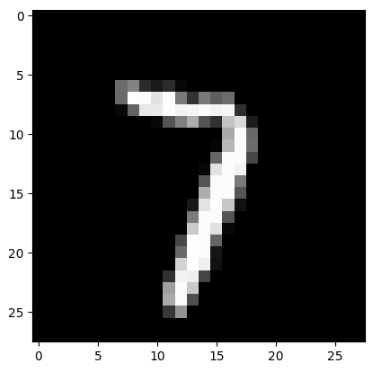
1.4 创建模型
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3) # 3表示3*3卷积
# in 64 , 1, 28, 28 -> 64, 32, 26, 26
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2)) # 池化 , # in : 64, 32, 13, 13
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3) # in: 64, 32, 13, 13 -> out: 64,64,11,11
# 再加一层池化, input: 64, 64, 11, 11 -> out: 64, 64, 5, 5
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(64* 5* 5, 256) # 计算
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(256, 10) # 10个数字的one_hot编码
def forward(self, input):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(input))
# 再加池化
x = self.pool(x)
# 卷积
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x= self.pool(x)
# flatten
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 5 * 5)
# 卷积
x = F.relu(self.linear_1(x))
x = self.linear_2(x)
return x
model = Model()
# 把model拷贝到GPU
model.to(device)
1.5 定义训练过程
# 定义损失函数
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# optimizer 优化器, 防止过拟合
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)# 训练过程
def fit(epoch, model, train_loader, test_loader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
for x, y in train_loader:
# 把数据放到GPU上
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
# 梯度清零
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward() # backward 反向传播
optimizer.step()
# 计算损失过程
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
# 循环完一次后, 计算损失
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader.dataset)
epoch_acc = correct / total
# 测试数据的代码
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_loader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
# 计算损失
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
# 计算平均损失
test_epoch_loss = test_running_loss /len(test_loader.dataset)
test_epoch_acc = test_correct / test_total
# 打印输出
print('epoch:', epoch,
'loss:', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss:', round(test_epoch_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(test_epoch_acc, 3))
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, test_epoch_loss, test_epoch_acc# 执行操作 # 可以打包一个history
epochs = 20
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, test_epoch_loss, test_epoch_acc = fit(epoch, model,
train_d1, test_d1)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(test_epoch_loss)
test_acc.append(test_epoch_acc)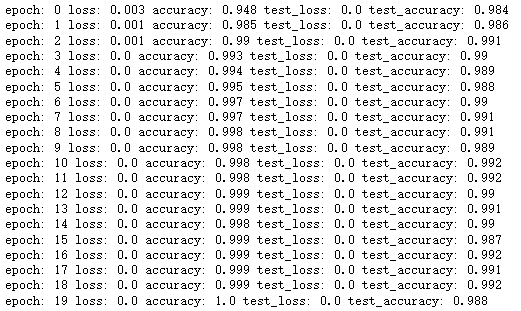
1.6 添加dropout 和 BN层
# 定义模型
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3) # 16 * 94 * 94
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) # 16 * 47 * 47
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3) # 32 * 45 * 45 -> pooling -> 32 * 22 * 22
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3) # 64 * 20 * 20 -> pooling -> 64 * 10 * 10
self.dropout = nn.Dropout()
# batch , channel, height, width, 64,
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64 * 10 * 10, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
# x.view(-1, 64 * 10 * 10)
x = nn.Flatten()(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x# 添加BN层. # 定义模型
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3) # 16 * 94 * 94
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) # 16 * 47 * 47
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3) # 32 * 45 * 45 -> pooling -> 32 * 22 * 22
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3) # 64 * 20 * 20 -> pooling -> 64 * 10 * 10
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout()
# batch , channel, height, width, 64,
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64 * 10 * 10, 1024)
self.bn_fc1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 256)
self.bn_fc2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
x = self.bn3(x)
# x.view(-1, 64 * 10 * 10)
x = nn.Flatten()(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.bn_fc1(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.bn_fc2(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x