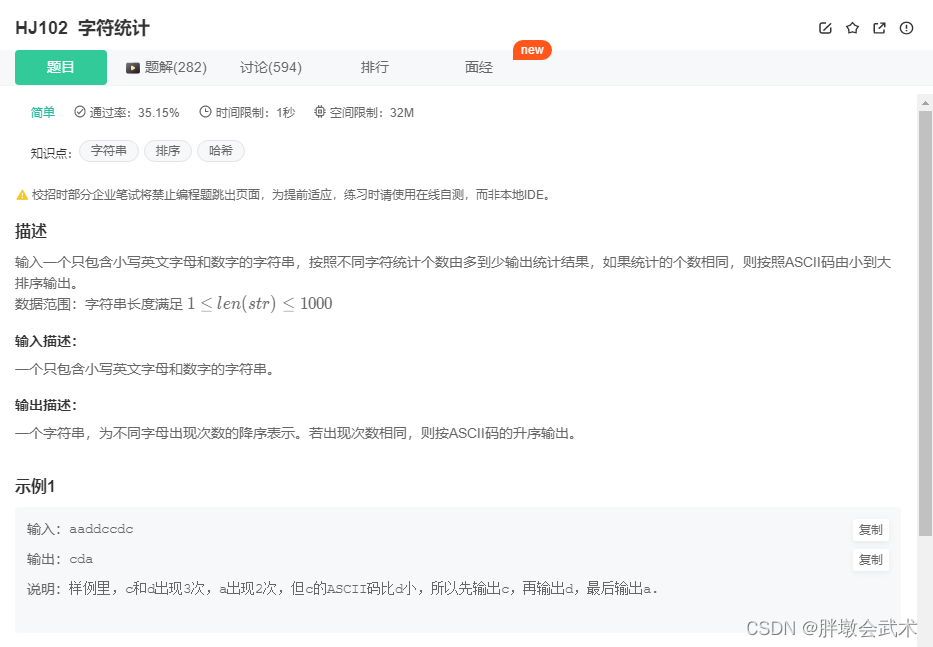
目录
string
1. string的成员函数
1.1 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1.1 构造函数
1.1.2 析构函数
1.1.3 赋值运算符重载
1.2 迭代器
1.3 容量
1.4 元素访问
1.4.1 遍历方法
1.5 修改器
1.6 字符串操作
2. string的成员常量
3. string的非成员函数
string
以下函数加粗为重点。
1. string的成员函数
1.1 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1.1 构造函数
| default 默认构造函数 | string(); | 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 |
| copy 拷贝构造函数 | string(const string& str); | 构造一个str的拷贝 |
| substring | string(const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); | 用str中从pos开始的len个字符的子串来构造 如果str太短或者len是string::npos,则复制到str的末尾 |
| from c-string | string(const char* s); | 用C格式字符串来构造 |
| from sequence | string(const char* s, size_t n); | 用从s指向的字符串中前n个字符来构造 |
| fill | string(size_t n, char c); | 用n个字符c来构造 |
| range | template <class InputIterator> string(InputIterator first, InputIterator last); | 用范围[first,last]中的字符序列来构造 |
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
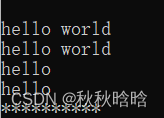
string s1;//default
cout << s1 << endl;//空字符串
string s2("hello world");//from c-string
cout << s2 << endl;//hello world
string s3(s2);//copy
cout << s3 << endl;//hello world
string s4(s3, 0, 5);//substring
cout << s4 << endl;//hello
string s5("hello world", 5);//from sequence
cout << s5 << endl;//hello
string s6(10, '*');//fill
cout << s6 << endl;//**********
return 0;
}
1.1.2 析构函数
| ~string(); | 销毁string类对象 |
1.1.3 赋值运算符重载
| string | string& operator=(const string& str); |
| c-string | string& operator=(const char* s); |
| character | string& operator=(char c); |
1.2 迭代器
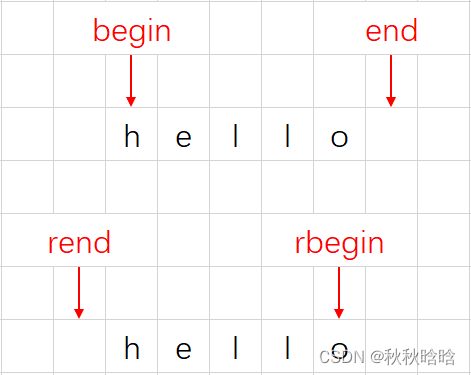
| begin & end | iterator begin(); iterator end(); | begin返回一个迭代器,指向字符串的第一个字符 end返回一个迭代器,指向字符串的最后一个字符的下一个位置 |
| rbegin & rend | reverse_iterator rbegin(); reverse_iterator rend(); | rbegin返回一个反向迭代器,指向字符串的最后一个字符 rend返回一个反向迭代器,指向字符串的第一个字符的上一个位置 |
| cbegin & cend | const_iterator cbegin() const; | cbegin返回一个const迭代器,指向字符串的第一个字符 cend返回一个const迭代器,指向字符串的最后一个字符的下一个位置 |
| crbegin & crend | const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const; | crbegin返回一个const反向迭代器,指向字符串的最后一个字符 crend返回一个const反向迭代器,指向字符串的第一个字符的上一个位置 |
begin&end和rbegin&rend返回的迭代器指向:
const_iterator是一个指向const内容的迭代器。迭代器本身可以修改,但是它不能被用来修改它所指向的内容。
begin&end/rbegin&rend和cbegin&cend/crbegin&crend的不同:
- begin&end/rbegin&rend的返回类型由对象是否是常量来决定。如果不是常量,返回iterator;如果是常量,返回const_iterator。
- cbegin&cend/crbegin&crend的返回类型是const_iterator,不管对象本身是否是常量。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//h e l l o w o r l d
auto rit = s.rbegin();
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
//d l r o w o l l e h
return 0;
}1.3 容量
| size | size_t size() const; | 返回字符串的长度 size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size() |
| length | size_t length() const; | 返回字符串的长度 |
| max_size | size_t max_size() const; | 返回字符串能够达到的最大长度 |
| resize | void resize(size_t n); void resize(size_t n, char c); | 调整字符串的长度为n(影响size) ·如果n<当前字符串的长度,多余的字符会被截掉 ·如果n>当前字符串的长度,则:1)如果没有指定填充字符,则多出的空间用空字符填充;2)如果指定了填充字符c,则多出的空间用c填充 |
| capacity | size_t capacity() const; | 返回分配的存储空间的大小 |
| reserve | void reserve(size_t n = 0); | 为字符串预留空间(影响capacity) ·如果n>当前的容量,容量增加到至少n个字符(空间大小满足16i-1) ·在所有其他情况下,它被视为缩小字符串容量的非约束性请求:容器实现可以自由地进行其他优化,并使字符串的容量大于n |
| clear | void clear(); | 清空字符串 |
| empty | bool empty() const; | 检测字符串是否为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| shrink_to_fit | void shrink_to_fit(); | 收缩容量以适应字符串的长度 这个请求没有约束力,容器实现可以自由地进行优化,使字符串的容量大于其大小 |
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << s.size() << endl;//11
cout << s.length() << endl;//11
cout << s.max_size() << endl;//2147483647
cout << s.capacity() << endl;//15
s.resize(15, '!');
cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!!
s.resize(13);
cout << s << endl;//hello world!!
s.reserve(30);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;//31
s.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s.capacity() << endl;//15
s.clear();
if (s.empty())
cout << "字符串为空" << endl;
else
cout << "字符串不为空" << endl;
//字符串为空
return 0;
}
1.4 元素访问
| operator[] | char& operator[] (size_t pos); const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const; | 返回字符串中pos位置的字符的引用 没有越界检查 |
| at | char& at(size_t pos); const char& at(size_t pos) const; | 返回字符串中pos位置的字符的引用 有越界检查,如果越界会抛异常 |
| back | char& back(); const char& back() const; | 返回字符串中最后一个字符的引用 |
| front | char& front(); const char& front() const; | 返回字符串中第一个字符的引用 |
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << s[0] << endl;//h
cout << s.at(1) << endl;//e
cout << s.back() << endl;//d
cout << s.front() << endl;//h
return 0;
}1.4.1 遍历方法
1.4.1.1 operator[](最常用)
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//h e l l o w o r l d
return 0;
}1.4.1.2 迭代器
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//h e l l o w o r l d
auto rit = s.rbegin();
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
//d l r o w o l l e h
return 0;
}1.4.1.3 范围for
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//h e l l o w o r l d
return 0;
}1.5 修改器
| operator+= | string& operator+=(const string& str); string& operator+=(const char* s); string& operator+=(char c); | 字符串追加 |
| append | string& append(const string& str); string& append(const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen); string& append(const char* s, size_t n); template <class InputIterator> string& append(InputIterator first, InputIterator last); | 字符串追加 |
| push_back | void push_back(char c); | 尾插(追加)一个字符 |
| assign | string& assign(const string& str); string& assign(const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen); string& assign(const char* s, size_t n); template <class InputIterator> string& assign(InputIterator first, InputIterator last); | 给字符串赋值,替换其当前内容 |
| insert | string& insert(size_t pos, const string& str); string& insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char c); void insert(iterator p, size_t n, char c); | 在字符串pos位置之前插入 |
| erase | string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos); iterator erase(iterator p); iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last); | 删除字符串的一部分 |
| replace | string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str); string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const string& str); string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen); string & replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s); string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s); string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s, size_t n); string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s, size_t n); string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c); string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, size_t n, char c); template <class InputIterator> string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, InputIterator first, InputIterator last); | 替换字符串的一部分 |
| swap | void swap(string& str); | 交换字符串的内容 |
| pop_back | void pop_back(); | 尾删 |
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
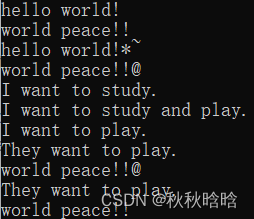
string s1("hello");
string s2("world");
s1 += " ";
s1 += s2;
s1 += '!';
cout << s1 << endl;//hello world!
s2.append(" peace");
s2.append(2, '!');
cout << s2 << endl;//world peace!!
//尾插一个字符的3种写法
s1 += '*';//operator+=最常用
s1.append(1, '~');
s2.push_back('@');
cout << s1 << endl;//hello world!*~
cout << s2 << endl;//world peace!!@
s1.assign("I want to study.");
cout << s1 << endl;//I want to study.
s1.insert(15, " and play");
cout << s1 << endl;//I want to study and play.
s1.erase(10, 10);
cout << s1 << endl;//I want to play.
s1.replace(0, 1, "They");
cout << s1 << endl;//They want to play.
s1.swap(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;//world peace!!@
cout << s2 << endl;//They want to play.
s1.pop_back();
cout << s1 << endl;//world peace!!
return 0;
}
把"hello world i love you"中的空格替换成"%20":
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world i love you");
/*//第1种方法
size_t num = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch == ' ')
++num;//计算有几个空格
}
//提前开空间,避免repalce时扩容
s.reserve(s.size() + 2 * num);
size_t pos = s.find(' ');//第一个空格的位置
while (pos != string::npos)//npos是长度参数,表示直到字符串结束
{
s.replace(pos, 1, "%20");
pos = s.find(' ', pos + 3);
}
cout << s << endl;//hello%20world%20i%20love%20you*/
//第2种方法
string newStr;
size_t num = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch == ' ')
++num;//计算有几个空格
}
//提前开空间,避免repalce时扩容
newStr.reserve(s.size() + 2 * num);
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch != ' ')
newStr += ch;
else
newStr += "%20";
}
s = newStr;
cout << newStr << endl;//hello%20world%20i%20love%20you
return 0;
}1.6 字符串操作
| c_str | const char* c_str() const; | 返回C格式字符串(以'\0'结尾) |
| data | const char* data() const; | 返回字符数组(不保证有‘\0’) |
| get_allocator | allocator_type get_allocator() const; | 返回配置器 |
| copy | size_t copy(char* s, size_t len, size_t pos = 0) const; | 将对象中从pos开始的len个字符的子串复制到s指向的数组中(不会在复制内容的末尾附加'\0') |
| find | size_t find(const string & str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往后匹配,返回第一次出现的位置 |
| rfind | size_t rfind(const string & str, size_t pos = npos) const; size_t rfind(const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const; size_t rfind(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; size_t rfind(char c, size_t pos = npos) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往前匹配,返回第一次出现的位置 |
| find_first_of | size_t find_first_of(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_first_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_first_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; size_t find_first_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往后匹配,返回第一个与参数中指定的任何字符相匹配的字符的位置 |
| find_last_of | size_t find_last_of(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; size_t find_last_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往前匹配,返回第一个与参数中指定的任何字符相匹配的字符的位置 |
| find_first_not_of | size_t find_first_not_of(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; size_t find_first_not_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往后匹配,返回第一个与参数中指定的任何字符不匹配的字符的位置 |
| find_last_not_of | size_t find_last_not_of(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_last_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; size_t find_last_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; size_t find_last_not_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; | 从对象中pos位置开始往前匹配,返回第一个与参数中指定的任何字符不匹配的字符的位置 |
| substr | string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const; | 返回一个从pos开始的len个字符的子串 |
| compare | int compare(const string& str) const; int compare(size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str) const; int compare(size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen) const; int compare(const char* s) const; int compare(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s) const; int compare(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s, size_t n) const; | 比较字符串 返回值=0,对象=比较字符串 返回值<0,对象<比较字符串 返回值>0,对象>比较字符串 |
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello");
cout << s.c_str() << endl;//hello
cout << (void*)s.c_str() << endl;//地址
cout << s.data() << endl;//hello
char buffer[10] = { '\0' };
s.copy(buffer, 3, 1);
for (auto ch : buffer)
{
cout << ch;
}
cout << endl;
//ell
size_t pos = s.find('l');
while (pos != string::npos)//npos是长度参数,表示直到字符串结束
{
s.replace(pos, 1, "L");
pos = s.find('l', pos + 1);
}
cout << s << endl;
//heLLo
pos = s.rfind('L');
while (pos != string::npos)
{
s.replace(pos, 1, "l");
pos = s.rfind('L', pos - 1);
}
cout << s << endl;
//hello
cout << s.find_first_of("jklmn") << endl;//2
cout << s.find_last_of("jklmn") << endl;//3
cout << s.find_first_not_of("heL") << endl;//2
cout << s.find_last_not_of("Lo") << endl;//3
cout << s.substr(1, 3) << endl;//ell
cout << s.compare("hello world") << endl;//-1
return 0;
}2. string的成员常量
npos为长度参数,表示直到字符串结束。
把"hello world i love you"中的空格替换成"%20":
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world i love you");
//第1种方法
size_t num = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch == ' ')
++num;//计算有几个空格
}
//提前开空间,避免repalce时扩容
s.reserve(s.size() + 2 * num);
size_t pos = s.find(' ');//第一个空格的位置
while (pos != string::npos)//npos是长度参数,表示直到字符串结束
{
s.replace(pos, 1, "%20");
pos = s.find(' ', pos + 3);
}
cout << s << endl;//hello%20world%20i%20love%20you
/*//第2种方法
string newStr;
size_t num = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch == ' ')
++num;//计算有几个空格
}
//提前开空间,避免repalce时扩容
newStr.reserve(s.size() + 2 * num);
for (auto ch : s)
{
if (ch != ' ')
newStr += ch;
else
newStr += "%20";
}
s = newStr;
cout << newStr << endl;//hello%20world%20i%20love%20you*/
return 0;
}3. string的非成员函数
| operatpr+ | string operator+ (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); string operator+ (const string & lhs, const char* rhs); string operator+ (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); string operator+ (const string& lhs, char rhs); string operator+ (char lhs, const string& rhs); | +运算符重载 (尽量少用,因为传值返回,导致深拷贝效率低) |
| relational operators | bool operator== (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator== (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator== (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator!= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); bool operator< (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator< (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator< (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator<= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); bool operator> (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator> (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator> (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator>= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs); bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs); | 关系运算符重载 |
| swap | void swap(string& x, string& y); | 交换两个字符串 |
| operator>> | istream& operator>>(istream& is, string& str); | >>运算符重载 |
| operator<< | ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const string& str); | <<运算符重载 |
| getline | istream& getline(istream& is, string& str, char delim); istream& getline(istream& is, string& str); | 从流中获取一行到字符串 |