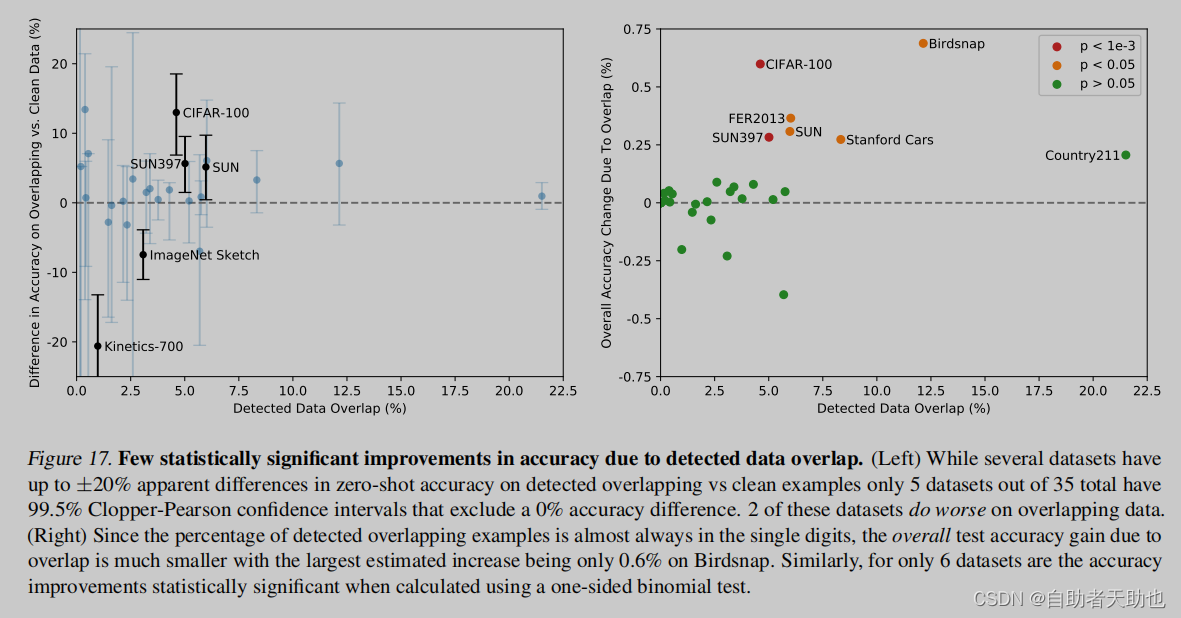
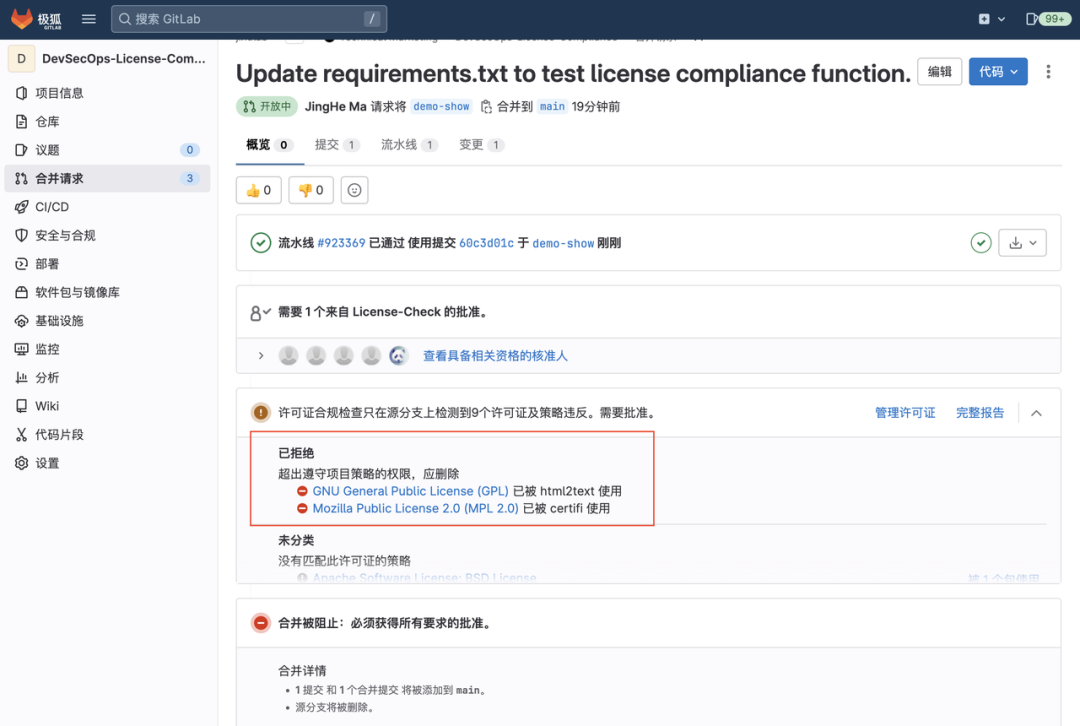
主要是记录学习mini3d代码时,查的资料;
从github下载的代码:
GitHub - skywind3000/mini3d: 3D Software Renderer in 700 Lines !!3D Software Renderer in 700 Lines !! Contribute to skywind3000/mini3d development by creating an account on GitHub.![]() https://github.com/skywind3000/mini3d
https://github.com/skywind3000/mini3d
1. 数学运算
1.1 类型定义以及结构体
typedef unsigned int IUINT32;
//=====================================================================
// 数学库:此部分应该不用详解,熟悉 D3D 矩阵变换即可
//=====================================================================
typedef struct { float m[4][4]; } matrix_t;
typedef struct { float x, y, z, w; } vector_t;
typedef vector_t point_t;定义了向量类型(vector_t)、矩阵类型(matrix_t)、点类型(point_t);
1.2 基础判断方法
int CMID(int x, int min, int max) { return (x < min)? min : ((x > max)? max : x); }
// 计算插值:t 为 [0, 1] 之间的数值
float interp(float x1, float x2, float t) { return x1 + (x2 - x1) * t; }
CMID使用用来将x的值约束在min和max之间的有效值;如果小于min,则返回min;如果大于max,则返回max;
interp用来计算两个数值之间的线性插值,在x1到x2范围内的值,分割x1-x2为两部分,即0-t和t-1两部分,可以计算得到t点对应的数值。范围在[x1,x2]内;
1.3 向量(点)运算
向量的运算主要有,对向量取模、归一化处理求得单位向量、加、减、点积、叉积;
坐标点的运算,则只有加、减、插值;
这里有困惑的地方是,按照GAMES101中的说法,点的w都是1,向量的w都是0,这里在加减、叉积、插值等运算中都将w设置为了1;不过也可能是代码比较简洁,省略了这个地方;
// | v |
float vector_length(const vector_t *v) {
float sq = v->x * v->x + v->y * v->y + v->z * v->z;
return (float)sqrt(sq);
}
// z = x + y
void vector_add(vector_t *z, const vector_t *x, const vector_t *y) {
z->x = x->x + y->x;
z->y = x->y + y->y;
z->z = x->z + y->z;
z->w = 1.0;
}
// z = x - y
void vector_sub(vector_t *z, const vector_t *x, const vector_t *y) {
z->x = x->x - y->x;
z->y = x->y - y->y;
z->z = x->z - y->z;
z->w = 1.0;
}
// 矢量点乘
float vector_dotproduct(const vector_t *x, const vector_t *y) {
return x->x * y->x + x->y * y->y + x->z * y->z;
}
// 矢量叉乘
void vector_crossproduct(vector_t *z, const vector_t *x, const vector_t *y) {
float m1, m2, m3;
m1 = x->y * y->z - x->z * y->y;
m2 = x->z * y->x - x->x * y->z;
m3 = x->x * y->y - x->y * y->x;
z->x = m1;
z->y = m2;
z->z = m3;
z->w = 1.0f;
}
// 矢量插值,t取值 [0, 1]
void vector_interp(vector_t *z, const vector_t *x1, const vector_t *x2, float t) {
z->x = interp(x1->x, x2->x, t);
z->y = interp(x1->y, x2->y, t);
z->z = interp(x1->z, x2->z, t);
z->w = 1.0f;
}
// 矢量归一化
void vector_normalize(vector_t *v) {
float length = vector_length(v);
if (length != 0.0f) {
float inv = 1.0f / length;
v->x *= inv;
v->y *= inv;
v->z *= inv;
}
}1.4 矩阵运算
1.4.1 矩阵间运算
包括了矩阵之间的加法、减法以及矩阵乘法;
// c = a + b
void matrix_add(matrix_t *c, const matrix_t *a, const matrix_t *b) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
c->m[i][j] = a->m[i][j] + b->m[i][j];
}
}
// c = a - b
void matrix_sub(matrix_t *c, const matrix_t *a, const matrix_t *b) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
c->m[i][j] = a->m[i][j] - b->m[i][j];
}
}
// c = a * b
void matrix_mul(matrix_t *c, const matrix_t *a, const matrix_t *b) {
matrix_t z;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
z.m[j][i] = (a->m[j][0] * b->m[0][i]) +
(a->m[j][1] * b->m[1][i]) +
(a->m[j][2] * b->m[2][i]) +
(a->m[j][3] * b->m[3][i]);
}
}
c[0] = z;
}1.4.2 矩阵与常数
// c = a * f
void matrix_scale(matrix_t *c, const matrix_t *a, float f) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
c->m[i][j] = a->m[i][j] * f;
}
}1.4.3 矩阵与向量
在该代码中,将向量设置为行向量,则与矩阵的乘法为向量右乘矩阵;
// y = x * m
void matrix_apply(vector_t *y, const vector_t *x, const matrix_t *m) {
float X = x->x, Y = x->y, Z = x->z, W = x->w;
y->x = X * m->m[0][0] + Y * m->m[1][0] + Z * m->m[2][0] + W * m->m[3][0];
y->y = X * m->m[0][1] + Y * m->m[1][1] + Z * m->m[2][1] + W * m->m[3][1];
y->z = X * m->m[0][2] + Y * m->m[1][2] + Z * m->m[2][2] + W * m->m[3][2];
y->w = X * m->m[0][3] + Y * m->m[1][3] + Z * m->m[2][3] + W * m->m[3][3];
}1.4.4 初始化矩阵
// 设置为单位矩阵
void matrix_set_identity(matrix_t *m) {
m->m[0][0] = m->m[1][1] = m->m[2][2] = m->m[3][3] = 1.0f;
m->m[0][1] = m->m[0][2] = m->m[0][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[1][0] = m->m[1][2] = m->m[1][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[2][0] = m->m[2][1] = m->m[2][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[3][0] = m->m[3][1] = m->m[3][2] = 0.0f;
}
// 设置为全0矩阵
void matrix_set_zero(matrix_t *m) {
m->m[0][0] = m->m[0][1] = m->m[0][2] = m->m[0][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[1][0] = m->m[1][1] = m->m[1][2] = m->m[1][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[2][0] = m->m[2][1] = m->m[2][2] = m->m[2][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[3][0] = m->m[3][1] = m->m[3][2] = m->m[3][3] = 0.0f;
}1.5 缩放、平移、旋转
齐次矩阵被用于图形学中对图像的缩放、平移以及旋转的操作;
2D图像使用三维齐次矩阵,3D图像使用四维齐次矩阵;多出来的一个维度是w和平移值;一般情况下w为0表示该行向量或者列向量为向量,w为1表示该行或者该列为一个点;
关于缩放、平移以及旋转的原理,请查图形学相关章节;
平移
// 平移变换
void matrix_set_translate(matrix_t *m, float x, float y, float z) {
matrix_set_identity(m);
m->m[3][0] = x;
m->m[3][1] = y;
m->m[3][2] = z;
}缩放
// 缩放变换
void matrix_set_scale(matrix_t *m, float x, float y, float z) {
matrix_set_identity(m);
m->m[0][0] = x;
m->m[1][1] = y;
m->m[2][2] = z;
}旋转
实现绕(x,y,z)向量旋转theta度的变换矩阵,一般情况下,使用四元数的旋转计算公式即可;
// 旋转矩阵
void matrix_set_rotate(matrix_t *m, float x, float y, float z, float theta) {
float qsin = (float)sin(theta * 0.5f);
float qcos = (float)cos(theta * 0.5f);
vector_t vec = { x, y, z, 1.0f };
float w = qcos;
vector_normalize(&vec);
x = vec.x * qsin;
y = vec.y * qsin;
z = vec.z * qsin;
m->m[0][0] = 1 - 2 * y * y - 2 * z * z;
m->m[1][0] = 2 * x * y - 2 * w * z;
m->m[2][0] = 2 * x * z + 2 * w * y;
m->m[0][1] = 2 * x * y + 2 * w * z;
m->m[1][1] = 1 - 2 * x * x - 2 * z * z;
m->m[2][1] = 2 * y * z - 2 * w * x;
m->m[0][2] = 2 * x * z - 2 * w * y;
m->m[1][2] = 2 * y * z + 2 * w * x;
m->m[2][2] = 1 - 2 * x * x - 2 * y * y;
m->m[0][3] = m->m[1][3] = m->m[2][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[3][0] = m->m[3][1] = m->m[3][2] = 0.0f;
m->m[3][3] = 1.0f;
}
详细内容请参见四元数的旋转:
四元数和旋转(Quaternion & rotation)![]() https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78987582
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78987582
也可以看之前的笔记,关于绕任意轴旋转的笔记: VTK笔记-几何变换-绕任意轴旋转![]() https://blog.csdn.net/liushao1031177/article/details/119829226
https://blog.csdn.net/liushao1031177/article/details/119829226
2. MVP变换
2.1 模型视图变换
在计算投影图像之前,需要将相机平移到世界原点位置,将相机的朝向-z方向,将相机的向上方向与+y平行;
在移动和旋转相机的同时,将物体也一并移动和缩放;通过这一变换,就形成了标准的投影变换前的坐标系,后面只要通过投影变换、View变换就可以得到渲染2D图像;
详细的计算步骤,查看博客:
3、计算机图形学——模型视图变换、投影变换与视口变换![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Master_Cui/article/details/119219663
https://blog.csdn.net/Master_Cui/article/details/119219663
matrix_set_lookat函数是一并计算了平移和旋转后的变换矩阵;
// 设置摄像机
void matrix_set_lookat(matrix_t *m, const vector_t *eye, const vector_t *at, const vector_t *up) {
vector_t xaxis, yaxis, zaxis;
vector_sub(&zaxis, at, eye);
vector_normalize(&zaxis);
vector_crossproduct(&xaxis, up, &zaxis);
vector_normalize(&xaxis);
vector_crossproduct(&yaxis, &zaxis, &xaxis);
m->m[0][0] = xaxis.x;
m->m[1][0] = xaxis.y;
m->m[2][0] = xaxis.z;
m->m[3][0] = -vector_dotproduct(&xaxis, eye);
m->m[0][1] = yaxis.x;
m->m[1][1] = yaxis.y;
m->m[2][1] = yaxis.z;
m->m[3][1] = -vector_dotproduct(&yaxis, eye);
m->m[0][2] = zaxis.x;
m->m[1][2] = zaxis.y;
m->m[2][2] = zaxis.z;
m->m[3][2] = -vector_dotproduct(&zaxis, eye);
m->m[0][3] = m->m[1][3] = m->m[2][3] = 0.0f;
m->m[3][3] = 1.0f;
}程序使用投影变换是采用D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH的方法,z轴的映射范围为[0,1],x和y的范围为[-1,1],其计算方法和GAMES101中的方法有所不同:
按照GAMES101的投影变换的博客,可以参照上面那篇博客;
这是解析同样这个代码的笔记:
光栅化渲染器 学习笔记 - 知乎![]() https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74510058
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74510058
其中fovy是fov的角度,aspect是屏幕的宽高比,zn为前裁剪平面z坐标;zf为后裁剪平面z坐标;
// D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH
void matrix_set_perspective(matrix_t *m, float fovy, float aspect, float zn, float zf) {
float fax = 1.0f / (float)tan(fovy * 0.5f);
matrix_set_zero(m);
m->m[0][0] = (float)(fax / aspect);
m->m[1][1] = (float)(fax);
m->m[2][2] = zf / (zf - zn);
m->m[3][2] = - zn * zf / (zf - zn);
m->m[2][3] = 1;
}计算后的点坐标满足下面的等式:
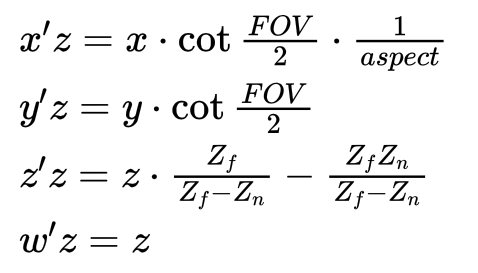
因为变换后的w的值是z;
定义一个记录变换信息的结构体transform_t,内部有三个变换矩阵,和一个由三个变换矩阵右乘后的结果变换矩阵,以及平面的宽w和高h;
//=====================================================================
// 坐标变换
//=====================================================================
typedef struct {
matrix_t world; // 世界坐标变换
matrix_t view; // 摄影机坐标变换
matrix_t projection; // 投影变换
matrix_t transform; // transform = world * view * projection
float w, h; // 屏幕大小
} transform_t;调用方法transform_update可以更新ts对象内的transform最终变换矩阵;
// 矩阵更新,计算 transform = world * view * projection
void transform_update(transform_t *ts) {
matrix_t m;
matrix_mul(&m, &ts->world, &ts->view);
matrix_mul(&ts->transform, &m, &ts->projection);
}在初始时,由初设的宽度和高度,计算出初始的变换矩阵,这里将world和view设置为单位矩阵,FOV为45度,相机在原点,前裁剪平面位于(0,0,1)处,后裁剪平面位于(0,0,500)处;
// 初始化,设置屏幕长宽
void transform_init(transform_t *ts, int width, int height) {
float aspect = (float)width / ((float)height);
matrix_set_identity(&ts->world);
matrix_set_identity(&ts->view);
matrix_set_perspective(&ts->projection, 3.1415926f * 0.5f, aspect, 1.0f, 500.0f);
ts->w = (float)width;
ts->h = (float)height;
transform_update(ts);
}计算x坐标投影变换到视平面上的坐标:
// 将矢量 x 进行 project
void transform_apply(const transform_t *ts, vector_t *y, const vector_t *x) {
matrix_apply(y, x, &ts->transform);
}// 检查齐次坐标同 cvv 的边界用于视锥裁剪
int transform_check_cvv(const vector_t *v) {
float w = v->w;
int check = 0;
if (v->z < 0.0f) check |= 1;
if (v->z > w) check |= 2;
if (v->x < -w) check |= 4;
if (v->x > w) check |= 8;
if (v->y < -w) check |= 16;
if (v->y > w) check |= 32;
return check;
}还不清楚这的x是什么坐标,这里的w值会是什么样子??
w是计算后的投影变换的结果,从结果上看值是等于z的;
这里加日志或者断点,看看-------------------
// 归一化,得到屏幕坐标
void transform_homogenize(const transform_t *ts, vector_t *y, const vector_t *x) {
float rhw = 1.0f / x->w;
y->x = (x->x * rhw + 1.0f) * ts->w * 0.5f;
y->y = (1.0f - x->y * rhw) * ts->h * 0.5f;
y->z = x->z * rhw;
y->w = 1.0f;
}和顶点相关的结构体:
//=====================================================================
// 几何计算:顶点、扫描线、边缘、矩形、步长计算
//=====================================================================
// 颜色
typedef struct { float r, g, b; } color_t;
// 纹理uv坐标
typedef struct { float u, v; } texcoord_t;
// 顶点信息
typedef struct {
point_t pos; // 三维坐标点
texcoord_t tc; // 纹理坐标
color_t color; // RGB颜色
float rhw; // W的倒数
} vertex_t;
typedef struct {
vertex_t v; // 边上的某一个点,用作输出或者标识;
vertex_t v1; //
vertex_t v2; // 边的两个端点
} edge_t;
typedef struct {
float top; // 梯形上边的y值
float bottom; // 梯形底边的y值
edge_t left; // 梯形左腰边信息
edge_t right; // 梯形右腰边信息
} trapezoid_t;
typedef struct { vertex_t v, step; int x, y, w; } scanline_t;Reciprocal of Homogeneous W的缩写是rhw,是齐次矩阵中的w的倒数;
void vertex_rhw_init(vertex_t *v) {
float rhw = 1.0f / v->pos.w;
v->rhw = rhw;
v->tc.u *= rhw;
v->tc.v *= rhw;
v->color.r *= rhw;
v->color.g *= rhw;
v->color.b *= rhw;
}这里没有看懂,记录下,后面看看这个博客:
深入探索透视纹理映射(下)![]() https://blog.csdn.net/popy007/article/details/5570803
https://blog.csdn.net/popy007/article/details/5570803
顶点间的运算
// 齐次坐标中所有元素的插值;
void vertex_interp(vertex_t *y, const vertex_t *x1, const vertex_t *x2, float t) {
vector_interp(&y->pos, &x1->pos, &x2->pos, t);
y->tc.u = interp(x1->tc.u, x2->tc.u, t);
y->tc.v = interp(x1->tc.v, x2->tc.v, t);
y->color.r = interp(x1->color.r, x2->color.r, t);
y->color.g = interp(x1->color.g, x2->color.g, t);
y->color.b = interp(x1->color.b, x2->color.b, t);
y->rhw = interp(x1->rhw, x2->rhw, t);
}
// 顶点之间的除法,可以看做是做了一个变相的插值;
void vertex_division(vertex_t *y, const vertex_t *x1, const vertex_t *x2, float w) {
float inv = 1.0f / w;
y->pos.x = (x2->pos.x - x1->pos.x) * inv;
y->pos.y = (x2->pos.y - x1->pos.y) * inv;
y->pos.z = (x2->pos.z - x1->pos.z) * inv;
y->pos.w = (x2->pos.w - x1->pos.w) * inv;
y->tc.u = (x2->tc.u - x1->tc.u) * inv;
y->tc.v = (x2->tc.v - x1->tc.v) * inv;
y->color.r = (x2->color.r - x1->color.r) * inv;
y->color.g = (x2->color.g - x1->color.g) * inv;
y->color.b = (x2->color.b - x1->color.b) * inv;
y->rhw = (x2->rhw - x1->rhw) * inv;
}
// 两个顶点的加法,即使齐次坐标的各个元素的加法;
void vertex_add(vertex_t *y, const vertex_t *x) {
y->pos.x += x->pos.x;
y->pos.y += x->pos.y;
y->pos.z += x->pos.z;
y->pos.w += x->pos.w;
y->rhw += x->rhw;
y->tc.u += x->tc.u;
y->tc.v += x->tc.v;
y->color.r += x->color.r;
y->color.g += x->color.g;
y->color.b += x->color.b;
}计算三角形,可以计算到待绘制三角形的信息,使用与x平行的线扫描方式,因此将三角形按照y方向的直线分割最为简单;
trapezoid_init_triangle方法分别根据三种不同的情况,生成0个、1个或2个梯形信息;包括了top的y最大值、y最小值,梯形的左腰边两端的顶点,梯形右腰边两端的顶点;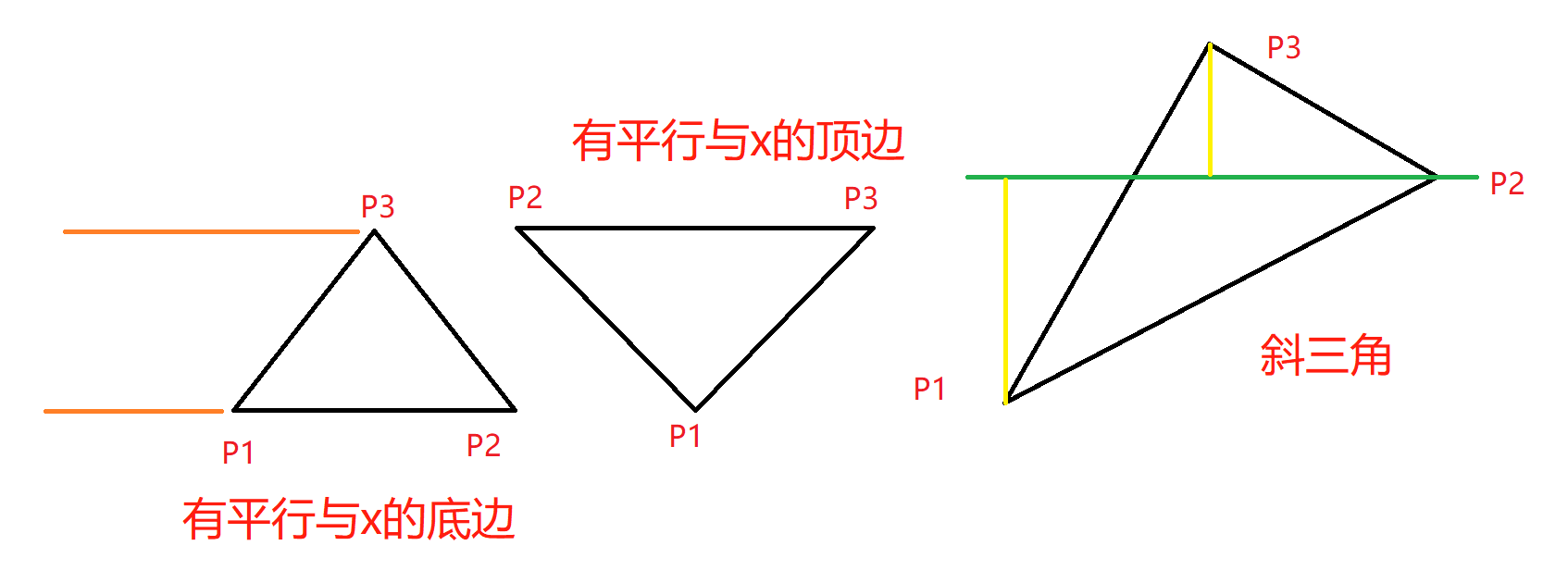
在之前学习TinyRenderer的时,填充三角网格的方法即是分别填充上三角形和下三角形;学习TinyRenderer![]() https://blog.csdn.net/liushao1031177/article/details/128733314
https://blog.csdn.net/liushao1031177/article/details/128733314
具体代码如下:
// 根据三角形生成 0-2 个梯形,并且返回合法梯形的数量
int trapezoid_init_triangle(trapezoid_t *trap, const vertex_t *p1,
const vertex_t *p2, const vertex_t *p3) {
const vertex_t *p;
float k, x;
// 三个点按照y,从小到大排列;
if (p1->pos.y > p2->pos.y) p = p1, p1 = p2, p2 = p;
if (p1->pos.y > p3->pos.y) p = p1, p1 = p3, p3 = p;
if (p2->pos.y > p3->pos.y) p = p2, p2 = p3, p3 = p;
// 如果三点在同一y方向上,或者在同一个x方向上,即共线,返回个数为0;
if (p1->pos.y == p2->pos.y && p1->pos.y == p3->pos.y) return 0;
if (p1->pos.x == p2->pos.x && p1->pos.x == p3->pos.x) return 0;
// 如果前面两个点y相等,就以这两个点为三角形的底边;
if (p1->pos.y == p2->pos.y) { // triangle down
// 底边上的两个点根据x坐标排序
if (p1->pos.x > p2->pos.x) p = p1, p1 = p2, p2 = p;
// 梯形的上下两个y值
trap[0].top = p1->pos.y;
trap[0].bottom = p3->pos.y;
// 左侧腰,边上两个顶点;
trap[0].left.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].left.v2 = *p3;
// 右侧腰,边上两个顶点;
trap[0].right.v1 = *p2;
trap[0].right.v2 = *p3;
// 应该是用来判别方向的,感觉和梯形数据没啥关系;
// 不对,由于已经根据Y排序了,这里不应该出现top小于bottom的情况;
// 因此是用来验证结果的合法性;
return (trap[0].top < trap[0].bottom)? 1 : 0;
}
// 如果后面两个点相等,则可以用这两个点作为倒三角的上边;
if (p2->pos.y == p3->pos.y) { // triangle up
// 上边上的两个点根据x坐标排序
if (p2->pos.x > p3->pos.x) p = p2, p2 = p3, p3 = p;
trap[0].top = p1->pos.y;
trap[0].bottom = p3->pos.y;
trap[0].left.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].left.v2 = *p2;
trap[0].right.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].right.v2 = *p3;
// 同上
return (trap[0].top < trap[0].bottom)? 1 : 0;
}
// 如果没有两个点在一个水平方向上,则三角形为斜着的;
// 根据中间的点的Y坐标分割三角形;
// 分为上三角和下三角
trap[0].top = p1->pos.y;
trap[0].bottom = p2->pos.y;
trap[1].top = p2->pos.y;
trap[1].bottom = p3->pos.y;
k = (p3->pos.y - p1->pos.y) / (p2->pos.y - p1->pos.y);
x = p1->pos.x + (p2->pos.x - p1->pos.x) * k;
if (x <= p3->pos.x) { // triangle left
trap[0].left.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].left.v2 = *p2;
trap[0].right.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].right.v2 = *p3;
trap[1].left.v1 = *p2;
trap[1].left.v2 = *p3;
trap[1].right.v1 = *p1;
trap[1].right.v2 = *p3;
} else { // triangle right
trap[0].left.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].left.v2 = *p3;
trap[0].right.v1 = *p1;
trap[0].right.v2 = *p2;
trap[1].left.v1 = *p1;
trap[1].left.v2 = *p3;
trap[1].right.v1 = *p2;
trap[1].right.v2 = *p3;
}
// 会有两个三角形
return 2;
}使用 trapezoid_edge_interp方法可以计算到y=y的直线与梯形的左腰和右腰边的交点,这里是分别计算了用y分割两个边的比例,然后插值得到目标点的坐标;
这里应该没有必要必要分别计算t1和t2,感觉t1和t2在数值上应该是相等的;
需要验证一下。。。。。。。
// 按照 Y 坐标计算出左右两条边纵坐标等于 Y 的顶点
void trapezoid_edge_interp(trapezoid_t *trap, float y) {
float s1 = trap->left.v2.pos.y - trap->left.v1.pos.y;
float s2 = trap->right.v2.pos.y - trap->right.v1.pos.y;
float t1 = (y - trap->left.v1.pos.y) / s1;
float t2 = (y - trap->right.v1.pos.y) / s2;
vertex_interp(&trap->left.v, &trap->left.v1, &trap->left.v2, t1);
vertex_interp(&trap->right.v, &trap->right.v1, &trap->right.v2, t2);
}vertex_division可以计算出每个扫描点之前的差值,用于做线绘制时使用;
// 根据左右两边的端点,初始化计算出扫描线的起点和步长
void trapezoid_init_scan_line(const trapezoid_t *trap, scanline_t *scanline, int y) {
float width = trap->right.v.pos.x - trap->left.v.pos.x;
scanline->x = (int)(trap->left.v.pos.x + 0.5f);
scanline->w = (int)(trap->right.v.pos.x + 0.5f) - scanline->x;
scanline->y = y;
scanline->v = trap->left.v;
if (trap->left.v.pos.x >= trap->right.v.pos.x) scanline->w = 0;
vertex_division(&scanline->step, &trap->left.v, &trap->right.v, width);
}画布-绘制设备
设备信息结构体:
//=====================================================================
// 渲染设备
//=====================================================================
typedef struct {
transform_t transform; // 坐标变换器
int width; // 窗口宽度
int height; // 窗口高度
IUINT32 **framebuffer; // 像素缓存:framebuffer[y] 代表第 y行
float **zbuffer; // 深度缓存:zbuffer[y] 为第 y行指针
IUINT32 **texture; // 纹理:同样是每行索引
int tex_width; // 纹理宽度
int tex_height; // 纹理高度
float max_u; // 纹理最大宽度:tex_width - 1
float max_v; // 纹理最大高度:tex_height - 1
int render_state; // 渲染状态
IUINT32 background; // 背景颜色
IUINT32 foreground; // 线框颜色
} device_t;
#define RENDER_STATE_WIREFRAME 1 // 渲染线框
#define RENDER_STATE_TEXTURE 2 // 渲染纹理
#define RENDER_STATE_COLOR 4 // 渲染颜色初始化设备,清理设备;
// 设备初始化,fb为外部帧缓存,非 NULL 将引用外部帧缓存(每行 4字节对齐)
void device_init(device_t *device, int width, int height, void *fb) {
int need = sizeof(void*) * (height * 2 + 1024) + width * height * 8;
char *ptr = (char*)malloc(need + 64);
char *framebuf, *zbuf;
int j;
assert(ptr);
device->framebuffer = (IUINT32**)ptr;
device->zbuffer = (float**)(ptr + sizeof(void*) * height);
ptr += sizeof(void*) * height * 2;
device->texture = (IUINT32**)ptr;
ptr += sizeof(void*) * 1024;
framebuf = (char*)ptr;
zbuf = (char*)ptr + width * height * 4;
ptr += width * height * 8;
if (fb != NULL) framebuf = (char*)fb;
for (j = 0; j < height; j++) {
device->framebuffer[j] = (IUINT32*)(framebuf + width * 4 * j);
device->zbuffer[j] = (float*)(zbuf + width * 4 * j);
}
device->texture[0] = (IUINT32*)ptr;
device->texture[1] = (IUINT32*)(ptr + 16);
memset(device->texture[0], 0, 64);
device->tex_width = 2;
device->tex_height = 2;
device->max_u = 1.0f;
device->max_v = 1.0f;
device->width = width;
device->height = height;
device->background = 0xc0c0c0;
device->foreground = 0;
transform_init(&device->transform, width, height);
device->render_state = RENDER_STATE_WIREFRAME;
}
// 删除设备
void device_destroy(device_t *device) {
if (device->framebuffer)
free(device->framebuffer);
device->framebuffer = NULL;
device->zbuffer = NULL;
device->texture = NULL;
}设置当前纹理,将bits指针指向的纹理二维数组的行首指针赋值给texture;更新设备信息中纹理相关的数据;
// 设置当前纹理
void device_set_texture(device_t *device, void *bits, long pitch, int w, int h) {
char *ptr = (char*)bits;
int j;
assert(w <= 1024 && h <= 1024);
for (j = 0; j < h; ptr += pitch, j++) // 重新计算每行纹理的指针
device->texture[j] = (IUINT32*)ptr;
device->tex_width = w;
device->tex_height = h;
device->max_u = (float)(w - 1);
device->max_v = (float)(h - 1);
}根据坐标读取纹理
IUINT32 device_texture_read(const device_t *device, float u, float v) {
int x, y;
u = u * device->max_u;
v = v * device->max_v;
x = (int)(u + 0.5f);
y = (int)(v + 0.5f);
x = CMID(x, 0, device->tex_width - 1);
y = CMID(y, 0, device->tex_height - 1);
return device->texture[y][x];
}在设备上绘制点线面
// 画点
void device_pixel(device_t *device, int x, int y, IUINT32 color) {
if (((IUINT32)x) < (IUINT32)device->width && ((IUINT32)y) < (IUINT32)device->height) {
device->framebuffer[y][x] = color;
}
}
// 绘制线段
void device_draw_line(device_t *device, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, IUINT32 c) {
int x, y, rem = 0;
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
device_pixel(device, x1, y1, c);
} else if (x1 == x2) {
int inc = (y1 <= y2)? 1 : -1;
for (y = y1; y != y2; y += inc) device_pixel(device, x1, y, c);
device_pixel(device, x2, y2, c);
} else if (y1 == y2) {
int inc = (x1 <= x2)? 1 : -1;
for (x = x1; x != x2; x += inc) device_pixel(device, x, y1, c);
device_pixel(device, x2, y2, c);
} else {
int dx = (x1 < x2)? x2 - x1 : x1 - x2;
int dy = (y1 < y2)? y2 - y1 : y1 - y2;
if (dx >= dy) {
if (x2 < x1) x = x1, y = y1, x1 = x2, y1 = y2, x2 = x, y2 = y;
for (x = x1, y = y1; x <= x2; x++) {
device_pixel(device, x, y, c);
rem += dy;
if (rem >= dx) {
rem -= dx;
y += (y2 >= y1)? 1 : -1;
device_pixel(device, x, y, c);
}
}
device_pixel(device, x2, y2, c);
} else {
if (y2 < y1) x = x1, y = y1, x1 = x2, y1 = y2, x2 = x, y2 = y;
for (x = x1, y = y1; y <= y2; y++) {
device_pixel(device, x, y, c);
rem += dx;
if (rem >= dy) {
rem -= dy;
x += (x2 >= x1)? 1 : -1;
device_pixel(device, x, y, c);
}
}
device_pixel(device, x2, y2, c);
}
}
}
// 绘制扫描线
void device_draw_scanline(device_t *device, scanline_t *scanline) {
IUINT32 *framebuffer = device->framebuffer[scanline->y];
float *zbuffer = device->zbuffer[scanline->y];
int x = scanline->x;
int w = scanline->w;
int width = device->width;
int render_state = device->render_state;
for (; w > 0; x++, w--) {
if (x >= 0 && x < width) {
float rhw = scanline->v.rhw;
if (rhw >= zbuffer[x]) {
float w = 1.0f / rhw;
zbuffer[x] = rhw;
if (render_state & RENDER_STATE_COLOR) {
float r = scanline->v.color.r * w;
float g = scanline->v.color.g * w;
float b = scanline->v.color.b * w;
int R = (int)(r * 255.0f);
int G = (int)(g * 255.0f);
int B = (int)(b * 255.0f);
R = CMID(R, 0, 255);
G = CMID(G, 0, 255);
B = CMID(B, 0, 255);
framebuffer[x] = (R << 16) | (G << 8) | (B);
}
if (render_state & RENDER_STATE_TEXTURE) {
float u = scanline->v.tc.u * w;
float v = scanline->v.tc.v * w;
IUINT32 cc = device_texture_read(device, u, v);
framebuffer[x] = cc;
}
}
}
vertex_add(&scanline->v, &scanline->step);
if (x >= width) break;
}
}
// 清空 framebuffer 和 zbuffer
void device_clear(device_t *device, int mode) {
int y, x, height = device->height;
for (y = 0; y < device->height; y++) {
IUINT32 *dst = device->framebuffer[y];
IUINT32 cc = (height - 1 - y) * 230 / (height - 1);
cc = (cc << 16) | (cc << 8) | cc;
if (mode == 0) cc = device->background;
for (x = device->width; x > 0; dst++, x--) dst[0] = cc;
}
for (y = 0; y < device->height; y++) {
float *dst = device->zbuffer[y];
for (x = device->width; x > 0; dst++, x--) dst[0] = 0.0f;
}
}// 主渲染函数
void device_render_trap(device_t *device, trapezoid_t *trap) {
scanline_t scanline;
int j, top, bottom;
top = (int)(trap->top + 0.5f);
bottom = (int)(trap->bottom + 0.5f);
for (j = top; j < bottom; j++) {
if (j >= 0 && j < device->height) {
trapezoid_edge_interp(trap, (float)j + 0.5f);
trapezoid_init_scan_line(trap, &scanline, j);
device_draw_scanline(device, &scanline);
}
if (j >= device->height) break;
}
}
// 根据 render_state 绘制原始三角形
void device_draw_primitive(device_t *device, const vertex_t *v1,
const vertex_t *v2, const vertex_t *v3) {
point_t p1, p2, p3, c1, c2, c3;
int render_state = device->render_state;
// 按照 Transform 变化
transform_apply(&device->transform, &c1, &v1->pos);
transform_apply(&device->transform, &c2, &v2->pos);
transform_apply(&device->transform, &c3, &v3->pos);
// 裁剪,注意此处可以完善为具体判断几个点在 cvv内以及同cvv相交平面的坐标比例
// 进行进一步精细裁剪,将一个分解为几个完全处在 cvv内的三角形
if (transform_check_cvv(&c1) != 0) return;
if (transform_check_cvv(&c2) != 0) return;
if (transform_check_cvv(&c3) != 0) return;
// 归一化
transform_homogenize(&device->transform, &p1, &c1);
transform_homogenize(&device->transform, &p2, &c2);
transform_homogenize(&device->transform, &p3, &c3);
// 纹理或者色彩绘制
if (render_state & (RENDER_STATE_TEXTURE | RENDER_STATE_COLOR)) {
vertex_t t1 = *v1, t2 = *v2, t3 = *v3;
trapezoid_t traps[2];
int n;
t1.pos = p1;
t2.pos = p2;
t3.pos = p3;
t1.pos.w = c1.w;
t2.pos.w = c2.w;
t3.pos.w = c3.w;
vertex_rhw_init(&t1); // 初始化 w
vertex_rhw_init(&t2); // 初始化 w
vertex_rhw_init(&t3); // 初始化 w
// 拆分三角形为0-2个梯形,并且返回可用梯形数量
n = trapezoid_init_triangle(traps, &t1, &t2, &t3);
if (n >= 1) device_render_trap(device, &traps[0]);
if (n >= 2) device_render_trap(device, &traps[1]);
}
if (render_state & RENDER_STATE_WIREFRAME) { // 线框绘制
device_draw_line(device, (int)p1.x, (int)p1.y, (int)p2.x, (int)p2.y, device->foreground);
device_draw_line(device, (int)p1.x, (int)p1.y, (int)p3.x, (int)p3.y, device->foreground);
device_draw_line(device, (int)p3.x, (int)p3.y, (int)p2.x, (int)p2.y, device->foreground);
}
}
//=====================================================================
// Win32 窗口及图形绘制:为 device 提供一个 DibSection 的 FB
//=====================================================================
int screen_w, screen_h, screen_exit = 0;
int screen_mx = 0, screen_my = 0, screen_mb = 0;
int screen_keys[512]; // 当前键盘按下状态
static HWND screen_handle = NULL; // 主窗口 HWND
static HDC screen_dc = NULL; // 配套的 HDC
static HBITMAP screen_hb = NULL; // DIB
static HBITMAP screen_ob = NULL; // 老的 BITMAP
unsigned char *screen_fb = NULL; // frame buffer
long screen_pitch = 0;
int screen_init(int w, int h, const TCHAR *title); // 屏幕初始化
int screen_close(void); // 关闭屏幕
void screen_dispatch(void); // 处理消息
void screen_update(void); // 显示 FrameBuffer
// win32 event handler
static LRESULT screen_events(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#pragma comment(lib, "gdi32.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "user32.lib")
#endif
// 初始化窗口并设置标题
int screen_init(int w, int h, const TCHAR *title) {
WNDCLASS wc = { CS_BYTEALIGNCLIENT, (WNDPROC)screen_events, 0, 0, 0,
NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, _T("SCREEN3.1415926") };
BITMAPINFO bi = { { sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), w, -h, 1, 32, BI_RGB,
w * h * 4, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
RECT rect = { 0, 0, w, h };
int wx, wy, sx, sy;
LPVOID ptr;
HDC hDC;
screen_close();
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)GetStockObject(BLACK_BRUSH);
wc.hInstance = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
if (!RegisterClass(&wc)) return -1;
screen_handle = CreateWindow(_T("SCREEN3.1415926"), title,
WS_OVERLAPPED | WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU | WS_MINIMIZEBOX,
0, 0, 0, 0, NULL, NULL, wc.hInstance, NULL);
if (screen_handle == NULL) return -2;
screen_exit = 0;
hDC = GetDC(screen_handle);
screen_dc = CreateCompatibleDC(hDC);
ReleaseDC(screen_handle, hDC);
screen_hb = CreateDIBSection(screen_dc, &bi, DIB_RGB_COLORS, &ptr, 0, 0);
if (screen_hb == NULL) return -3;
screen_ob = (HBITMAP)SelectObject(screen_dc, screen_hb);
screen_fb = (unsigned char*)ptr;
screen_w = w;
screen_h = h;
screen_pitch = w * 4;
AdjustWindowRect(&rect, GetWindowLong(screen_handle, GWL_STYLE), 0);
wx = rect.right - rect.left;
wy = rect.bottom - rect.top;
sx = (GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXSCREEN) - wx) / 2;
sy = (GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYSCREEN) - wy) / 2;
if (sy < 0) sy = 0;
SetWindowPos(screen_handle, NULL, sx, sy, wx, wy, (SWP_NOCOPYBITS | SWP_NOZORDER | SWP_SHOWWINDOW));
SetForegroundWindow(screen_handle);
ShowWindow(screen_handle, SW_NORMAL);
screen_dispatch();
memset(screen_keys, 0, sizeof(int) * 512);
memset(screen_fb, 0, w * h * 4);
return 0;
}
int screen_close(void) {
if (screen_dc) {
if (screen_ob) {
SelectObject(screen_dc, screen_ob);
screen_ob = NULL;
}
DeleteDC(screen_dc);
screen_dc = NULL;
}
if (screen_hb) {
DeleteObject(screen_hb);
screen_hb = NULL;
}
if (screen_handle) {
CloseWindow(screen_handle);
screen_handle = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
static LRESULT screen_events(HWND hWnd, UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
switch (msg) {
case WM_CLOSE: screen_exit = 1; break;
case WM_KEYDOWN: screen_keys[wParam & 511] = 1; break;
case WM_KEYUP: screen_keys[wParam & 511] = 0; break;
default: return DefWindowProc(hWnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
void screen_dispatch(void) {
MSG msg;
while (1) {
if (!PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_NOREMOVE)) break;
if (!GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) break;
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
void screen_update(void) {
HDC hDC = GetDC(screen_handle);
BitBlt(hDC, 0, 0, screen_w, screen_h, screen_dc, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
ReleaseDC(screen_handle, hDC);
screen_dispatch();
}
//=====================================================================
// 主程序
//=====================================================================
vertex_t mesh[8] = {
{ { -1, -1, 1, 1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1.0f, 0.2f, 0.2f }, 1 },
{ { 1, -1, 1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 0.2f, 1.0f, 0.2f }, 1 },
{ { 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 1 }, { 0.2f, 0.2f, 1.0f }, 1 },
{ { -1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1.0f, 0.2f, 1.0f }, 1 },
{ { -1, -1, -1, 1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.2f }, 1 },
{ { 1, -1, -1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 0.2f, 1.0f, 1.0f }, 1 },
{ { 1, 1, -1, 1 }, { 1, 1 }, { 1.0f, 0.3f, 0.3f }, 1 },
{ { -1, 1, -1, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0.2f, 1.0f, 0.3f }, 1 },
};
void draw_plane(device_t *device, int a, int b, int c, int d) {
vertex_t p1 = mesh[a], p2 = mesh[b], p3 = mesh[c], p4 = mesh[d];
p1.tc.u = 0, p1.tc.v = 0, p2.tc.u = 0, p2.tc.v = 1;
p3.tc.u = 1, p3.tc.v = 1, p4.tc.u = 1, p4.tc.v = 0;
device_draw_primitive(device, &p1, &p2, &p3);
device_draw_primitive(device, &p3, &p4, &p1);
}
void draw_box(device_t *device, float theta) {
matrix_t m;
matrix_set_rotate(&m, -1, -0.5, 1, theta);
device->transform.world = m;
transform_update(&device->transform);
draw_plane(device, 0, 1, 2, 3);
draw_plane(device, 7, 6, 5, 4);
draw_plane(device, 0, 4, 5, 1);
draw_plane(device, 1, 5, 6, 2);
draw_plane(device, 2, 6, 7, 3);
draw_plane(device, 3, 7, 4, 0);
}
void camera_at_zero(device_t *device, float x, float y, float z) {
point_t eye = { x, y, z, 1 }, at = { 0, 0, 0, 1 }, up = { 0, 0, 1, 1 };
matrix_set_lookat(&device->transform.view, &eye, &at, &up);
transform_update(&device->transform);
}
void init_texture(device_t *device) {
static IUINT32 texture[256][256];
int i, j;
for (j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
int x = i / 32, y = j / 32;
texture[j][i] = ((x + y) & 1)? 0xffffff : 0x3fbcef;
}
}
device_set_texture(device, texture, 256 * 4, 256, 256);
}
int main(void)
{
device_t device;
int states[] = { RENDER_STATE_TEXTURE, RENDER_STATE_COLOR, RENDER_STATE_WIREFRAME };
int indicator = 0;
int kbhit = 0;
float alpha = 1;
float pos = 3.5;
TCHAR *title = _T("Mini3d (software render tutorial) - ")
_T("Left/Right: rotation, Up/Down: forward/backward, Space: switch state");
if (screen_init(800, 600, title))
return -1;
device_init(&device, 800, 600, screen_fb);
camera_at_zero(&device, 3, 0, 0);
init_texture(&device);
device.render_state = RENDER_STATE_TEXTURE;
while (screen_exit == 0 && screen_keys[VK_ESCAPE] == 0) {
screen_dispatch();
device_clear(&device, 1);
camera_at_zero(&device, pos, 0, 0);
if (screen_keys[VK_UP]) pos -= 0.01f;
if (screen_keys[VK_DOWN]) pos += 0.01f;
if (screen_keys[VK_LEFT]) alpha += 0.01f;
if (screen_keys[VK_RIGHT]) alpha -= 0.01f;
if (screen_keys[VK_SPACE]) {
if (kbhit == 0) {
kbhit = 1;
if (++indicator >= 3) indicator = 0;
device.render_state = states[indicator];
}
} else {
kbhit = 0;
}
draw_box(&device, alpha);
screen_update();
Sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}从0开始制作软渲染器(三)本文开始编写渲染器的代码。 本着色器很大程度上参考了韦易笑大神的RenderHelp渲染器。我的渲染器的理论是跟着Games101和《Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition》这本书来的,和韦大神渲染器中的方程不太一样(尤其是透视投影,深度测试的地方),所以如果要跟着我这系列博客学习,请务必从头看到尾,以避免公式和细节不一致的情况出现。 最 https://visualgmq.gitee.io/2022/03/08/%E4%BB%8E0%E5%BC%80%E5%A7%8B%E5%88%B6%E4%BD%9C%E8%BD%AF%E6%B8%B2%E6%9F%93%E5%99%A8%EF%BC%88%E4%B8%89%EF%BC%89/
https://visualgmq.gitee.io/2022/03/08/%E4%BB%8E0%E5%BC%80%E5%A7%8B%E5%88%B6%E4%BD%9C%E8%BD%AF%E6%B8%B2%E6%9F%93%E5%99%A8%EF%BC%88%E4%B8%89%EF%BC%89/
纹理UV坐标UV![]() https://baike.baidu.com/item/UV/2490475?fr=aladdin
https://baike.baidu.com/item/UV/2490475?fr=aladdin