参考信息
杭州市的个人所得税起征点是每月5000元。
个人所得税税率标准:
1、工资范围在1-5000元之间的,包括5000元,适用个人所得税税率为0%;
2、工资范围在5000-8000元之间的,包括8000元,适用个人所得税税率为3%;
3、工资范围在8000-17000元之间的,包括17000元,适用个人所得税税率为10%;
4、工资范围在17000-30000元之间的,包括30000元,适用个人所得税税率为20%;
5、工资范围在30000-40000元之间的,包括40000元,适用个人所得税税率为25%;
6、工资范围在40000-60000元之间的,包括60000元,适用个人所得税税率为30%;
7、工资范围在60000-85000元之间的,包括85000元,适用个人所得税税率为35%;
8、工资范围在85000元以上的,适用个人所得税税率为45%。
- 注意:这个月薪工资是扣除五险一金之后的个人所得金额,这部分需要缴纳个税。
思路
初级程序员
啊?这有什么难的,直接 判断做几十个if else不就OK了吗? 如果小于5000,直接扣税0,大于5000,再看是不是大于8000,是的话,先扣 3000 * 3%,一直往下走不就行了。
这样写确实实现了功能。不过如果这类问题标准有100项,岂不是需要写400行以上代码。
中级程序员
标准可以配置化,如果需求数值变更,只需要修改配置即可。
优化
多次计算的情况下,可以做预处理,减少重复加法。
代码
#define NDEBUG //禁用断言
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h> //引入所有的C++标准库头文件
using namespace std; //使用std命名空间
typedef struct ShuiCfg { //定义结构体类型ShuiCfg
ShuiCfg(int a, int b, int c){ //定义结构体初始化函数
min = a;
max = b;
rate = c;
}
int min = 0; //定义最小值
int max = INT32_MAX; //定义最大值
int rate = 0; //定义税率
} ShuiCfg;
GetAfterShui(vector<ShuiCfg> &vec, vector<int>& vec_rmb) { //定义函数GetAfterShui,参数为struct数组和int数组的引用
cout << "GetAfterShui" << endl; //输出字符串"GetAfterShui"
for (auto rmb : vec_rmb) { //使用范围for循环遍历vec_rmb
int shui = 0; //定义税为0
for (auto &it : vec) { //使用范围循环遍历vec数组
if (rmb > it.max) { //如果rmb大于it.max,即工资大于本档次最大值
shui += (it.max - it.min) * it.rate / 100; //税收增量=(最大值-最小值)×税率÷100
} else { //否则,即工资小于本档次最大值
shui += (rmb - it.min) * it.rate / 100; //税收增量=(工资-最小值)×税率÷100
break; //结束for循环
}
}
cout << rmb << " ,shui=" << shui << ", last=" << rmb - shui << endl; //输出工资、税收增量和取得实际收入后
}
}
GetAfterShui2(vector<ShuiCfg> &vec, vector<int>& vec_rmb) { //定义函数GetAfterShui2,参数为struct数组和int数组的引用
cout << "GetAfterShui2" << endl; //输出字符串"GetAfterShui2"
vector<int> vec_before; //定义存储之前税收的vector
int before = 0; //定义之前税收的累加值,初始值为0
for (auto &it : vec) { //使用范围循环遍历vec数组
vec_before.push_back(before); //将之前税收的累加值压入vec_before中
before += (it.max - it.min) * it.rate / 100; //之前税收累计值+=(最大值-最小值)×税率÷100
}
int shui = 0; //定义税为0
for (auto rmb : vec_rmb) { //使用范围for循环遍历vec_rmb
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); ++i) { //使用for循环遍历vec
auto it = vec[i]; //获取vec[i]元素
if (rmb < it.max && rmb >= it.min) { //如果工资值在该区间内
shui = (rmb - it.min) * it.rate / 100 + vec_before[i]; //税收增量=(工资-最小值)×税率÷100+累加值
break; //结束for循环
}
}
cout << rmb << " ,shui=" << shui << ", last=" << rmb - shui << endl; //输出工资、税收增量和取得实际收入后
}
}
int main() {
vector<ShuiCfg> vec{
{0,5000,0},
{5000,8000,3},
{8000,17000,10},
{17000,30000,20},
{30000,40000,25},
{40000,60000,30},
{60000,85000,35},
{85000,INT32_MAX,45},
}; //定义vector类型的数组vec
vector<int> vec_rmb{5000, 10000, 20000,50000, 100000}; //定义vector类型的数组vec_rmb
GetAfterShui(vec, vec_rmb); //调用函数GetAfterShui
GetAfterShui2(vec, vec_rmb); //调用函数GetAfterShui2
return 0; //返回0,代表程序正常结束
}
运行结果
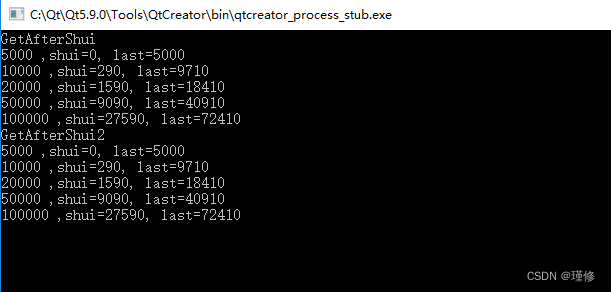
- 代码里写了两种计算方法
GetAfterShui,GetAfterShui2。计算的次数越多,配置越长,GetAfterShui2节省的时间越多。
有人可能会问了,“为什么你的注释写的这么多?这么详细?”
我会这么回答:“啊,这,这是chatGPT帮忙写的注释。”
朋友介绍的目前能用chatGPT。(这个网站不用科学 上网)
https://freegpt.one