1、WebRTC版本
m74
2、GCC的概念
GCC全称Google Congest Control,所谓拥塞控制,就是控制数据发送的速率避免网络的拥塞。可以对比TCP的拥塞控制算法,由于WebRTC使用基于UDP的RTP来传输媒体数据,需要一个拥塞控制算法来保证基本的Qos。
*注:本文不涉及Transport CC,只是早期版本的GCC。
3、GCC的思想
GCC核心思想就是通过预测可用带宽来控制发送的速率,会结合发送端和接收端两端各自估测的带宽来综合计算,其中发送端的带宽估测主要依赖于丢包率(其实也有延迟),接收端的带宽估测依赖于延迟(的变化)。
换句话说,GCC主要是依靠丢包、延迟、抖动等网络参数来预估当前的可用带宽进而控制发送的速率从而避免网络拥塞引起的丢包、延迟、抖动等现象,是一个反馈的过程。
由于WebRTC还有NACK、FEC等策略来解决丢包问题,实际上发送端的带宽估测对较小程度的丢包来说并不太敏感,反而是接收端的带宽估测对延迟的抖动有较大的灵敏度。GCC的接收端通过一系列算法检测当前网络延迟是否有变化,延迟变大的话,在考虑并消除掉数据尺寸变化的影响后,可以认为是网络路由的拥塞,需要降低码率,否则在延迟变小的情况下,认为网络空闲,可以提高码率。所以在延迟抖动较大的情况下,即使没有丢包,GCC也会进行较大程度的带宽调整。
也就是说,延迟如果稳定的话,即使值较大,也并不影响带宽的估测,反过来如果平均延迟比较小,但是出现较多较大的抖动,则会迅速将估测带宽调低。
4、发送端
主要实现:SendSideBandwidthEstimation
4.1 基本流程
发送端核心的带宽估测逻辑是SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateEstimate这个函数,主要有两个地方会触发:
收到RR包,受限于RR包的频率,大概1秒1次,更新了丢包率、RTT之后调用;
定时器,25ms一次,kUpdateIntervalMs=25,这个应该是为了防止RR包丢失或者不及时,更迅速灵敏的进行调整;
SendSideBandwidthEstimation::SetSendBitrate设置初始的预估带宽为300kbps,SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateEstimate函数会根据丢包、RTT以及当前的估测带宽来调整下个时刻的估测带宽。
4.2 计算丢包率/RTT
通过SR(Sender Report)、RR(Receiver Report)包计算。
SR包结构:
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
header |V=2|P| RC | PT=SR=200 | length |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SSRC of sender |
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
sender | NTP timestamp, most significant word |
info +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| NTP timestamp, least significant word |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| RTP timestamp |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| sender's packet count |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| sender's octet count |
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
report | SSRC_1 (SSRC of first source) |
block +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1 | fraction lost | cumulative number of packets lost |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| extended highest sequence number received |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| interarrival jitter |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| last SR (LSR) |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| delay since last SR (DLSR) |
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
report | SSRC_2 (SSRC of second source) |
block +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
2 : ... :
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
| profile-specific extensions |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
RR包结构
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
header |V=2|P| RC | PT=RR=201 | length |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| SSRC of packet sender |
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
report | SSRC_1 (SSRC of first source) |
block +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1 | fraction lost | cumulative number of packets lost |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| extended highest sequence number received |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| interarrival jitter |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| last SR (LSR) |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| delay since last SR (DLSR) |
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
report | SSRC_2 (SSRC of second source) |
block +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
2 : ... :
+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+=+
| profile-specific extensions |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
4.2.1 丢包率
接收端构造RR包,发送端收到并解析RR包计算丢包率。主要通过以下3个字段:
fraction lost,丢包率,发送两次RR包这两次统计间隔之间的丢包率,以小数形式的丢包率*255,乘以255主要是为了降低精度到8位;
cumulative number of packets lost,目前时刻的累计丢包数,24位;
extended highest sequence number received,目前时刻收到的的最大序列号,32位,低16位为接收端收到的最大序列号,高16位为序列号循环的次数。
4.2.1.1 接收端统计
接收端通过函数
StreamStatisticianImpl::OnRtpPacket ->
StreamStatisticianImpl::UpdateCounters
处理每个RTP包,更新计数器等统计信息:
StreamDataCounters StreamStatisticianImpl::UpdateCounters(
const RtpPacketReceived& packet) {
rtc::CritScope cs(&stream_lock_);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(ssrc_, packet.Ssrc());
int64_t now_ms = clock_->TimeInMilliseconds();
incoming_bitrate_.Update(packet.size(), now_ms);
receive_counters_.transmitted.AddPacket(packet); // 更新接收到的包数,用于计算丢包
int64_t sequence_number =
seq_unwrapper_.UnwrapWithoutUpdate(packet.SequenceNumber());
if (!ReceivedRtpPacket()) { // 如果收到第一个RTP包
received_seq_first_ = sequence_number;
last_report_seq_max_ = sequence_number - 1;
receive_counters_.first_packet_time_ms = now_ms;
} else if (UpdateOutOfOrder(packet, sequence_number, now_ms)) {
// 判断包是否是乱序的包,如果是乱序的,可能重传的包,如果是重传的包
// 则更新receive_counters_.transmitted重传包计数器,用于计算丢包
return receive_counters_;
}
// 更新接收到的最大序列号
received_seq_max_ = sequence_number;
seq_unwrapper_.UpdateLast(sequence_number);
// 如果收到了一个更新的RTP包并且超过1个包有序,则更新抖动
if (packet.Timestamp() != last_received_timestamp_ &&
(receive_counters_.transmitted.packets -
receive_counters_.retransmitted.packets) > 1) {
UpdateJitter(packet, now_ms);
}
last_received_timestamp_ = packet.Timestamp();
last_receive_time_ms_ = now_ms;
return receive_counters_;
}
接收端通过函数
StreamStatisticianImpl::GetActiveStatisticsAndReset ->
StreamStatisticianImpl::CalculateRtcpStatistics
计算一次统计值,用于填充RR包:
RtcpStatistics StreamStatisticianImpl::CalculateRtcpStatistics() {
RtcpStatistics stats;
// 上个时刻到当前时刻期望接收到的包数 = 当前时刻接收到的最大序列号 - 上个时刻的接收到的最大序列号
int64_t exp_since_last = received_seq_max_ - last_report_seq_max_;
RTC_DCHECK_GE(exp_since_last, 0);
// 上个时刻到当前时刻实际接收到的包数
// 先计算上个时刻到当前时刻接收到的不包含重传包的包数 = 当前时刻接收到的不包含重传包的包数 - 上个时刻接收到的不包含重传包的包数
uint32_t rec_since_last = (receive_counters_.transmitted.packets -
receive_counters_.retransmitted.packets) -
last_report_inorder_packets_;
// 再计算上个时刻到当前时刻接收到的重传包的包数
uint32_t retransmitted_packets =
receive_counters_.retransmitted.packets - last_report_old_packets_;
// 上个时刻到当前时刻实际接收到的包数 = 上个时刻到当前时刻接收到的不包含重传包的包数 + 上个时刻到当前时刻接收到的重传包的包数
// 实际结果就是两个时刻的receive_counters_.transmitted.packets相减
rec_since_last += retransmitted_packets;
int32_t missing = 0;
if (exp_since_last > rec_since_last) {
// 上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包数 = 上个时刻到当前时刻期望接收到的包数 - 上个时刻到当前时刻实际接收到的包数
missing = (exp_since_last - rec_since_last);
}
uint8_t local_fraction_lost = 0;
if (exp_since_last) {
// 上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包率 = 上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包数 / 上个时刻到当前时刻期望接收到的包数
// *255是为了将值限制在(0,255)范围内,降低精度以8位存储
local_fraction_lost = static_cast<uint8_t>(255 * missing / exp_since_last);
}
stats.fraction_lost = local_fraction_lost;
// 更新并设置累计丢包数
cumulative_loss_ += missing;
stats.packets_lost = cumulative_loss_;
// 设置接收到的最大序列号
stats.extended_highest_sequence_number =
static_cast<uint32_t>(received_seq_max_);
// 设置抖动
stats.jitter = jitter_q4_ >> 4;
// Store this report.
last_reported_statistics_ = stats;
// 保存当前时刻收到的有序包的包数
last_report_inorder_packets_ = receive_counters_.transmitted.packets -
receive_counters_.retransmitted.packets;
// 保存当前时刻收到的重传包的包数
last_report_old_packets_ = receive_counters_.retransmitted.packets;
// 保存当前时刻收到的最大序列号
last_report_seq_max_ = received_seq_max_;
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT_WITH_SSRC(1, "cumulative_loss_pkts",
clock_->TimeInMilliseconds(),
cumulative_loss_, ssrc_);
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT_WITH_SSRC(
1, "received_seq_max_pkts", clock_->TimeInMilliseconds(),
(received_seq_max_ - received_seq_first_), ssrc_);
return stats;
}
上面代码中的3个值对应RR包中的3个字段:
stats.fraction_lost,发送两次RR包这两次统计间隔之间的丢包率;
stats.packets_lost,累计丢包数;
stats.extended_highest_sequence_number,目前时刻收到的的最大序列号。
总结:接收端的基本算法就是统计上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包率,总的丢包数,收到过的最大序列号,填入RR包发给发送端。
4.2.1.2 发送端计算
发送端通过函数
BitrateControllerImpl::OnReceivedRtcpReceiverReport ->
SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateReceiverBlock ->
SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdatePacketsLost
处理RR包中的Report Block,计算上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包率。
BitrateControllerImpl::OnReceivedRtcpReceiverReport:累计音视频等所有流的Report Block的总丢包,计算总的丢包率。
void BitrateControllerImpl::OnReceivedRtcpReceiverReport(
const ReportBlockList& report_blocks,
int64_t rtt,
int64_t now_ms) {
if (report_blocks.empty())
return;
{
rtc::CritScope cs(&critsect_);
int fraction_lost_aggregate = 0;
int total_number_of_packets = 0;
// 遍历所有的Report Block,可能有音频、视频等不同流的Report Block
for (const RTCPReportBlock& report_block : report_blocks) {
// 通过SSRC查找到Report Block对应的流
std::map<uint32_t, uint32_t>::iterator seq_num_it =
ssrc_to_last_received_extended_high_seq_num_.find(
report_block.source_ssrc);
int number_of_packets = 0;
if (seq_num_it != ssrc_to_last_received_extended_high_seq_num_.end()) {
// 跟接收端类似:这里计算的是单个流的,
// 上个时刻到当前时刻期望的包数 = 当前时刻接的最大序列号 - 上个时刻的到的最大序列号
number_of_packets =
report_block.extended_highest_sequence_number - seq_num_it->second;
}
// 上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包数 = 上个时刻到当前时刻期望的包数 * 上个时刻到当前时刻的丢包率
// 注意这里的丢包率还是(0, 255)范围,所有的流的丢包数累加
fraction_lost_aggregate += number_of_packets * report_block.fraction_lost;
// 更新上个时刻到当前时刻所有流的总包数
total_number_of_packets += number_of_packets;
// 保存当前流当前时刻的最大序列号
ssrc_to_last_received_extended_high_seq_num_[report_block.source_ssrc] =
report_block.extended_highest_sequence_number;
}
if (total_number_of_packets < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING)
<< "Received report block where extended high sequence "
"number goes backwards, ignoring.";
return;
}
if (total_number_of_packets == 0)
fraction_lost_aggregate = 0; // 容错,如果总包数为0,那么丢包也只能为0
else
// 计算所有流总的丢包率 = 所有流总的丢包数 / 所有流总的包数
// 注意这里的丢包率还是(0, 255)范围
// 加上total_number_of_packets / 2 是为了向上取整
fraction_lost_aggregate =
(fraction_lost_aggregate + total_number_of_packets / 2) /
total_number_of_packets;
if (fraction_lost_aggregate > 255)
return;
RTC_DCHECK_GE(total_number_of_packets, 0);
// 更新到带宽估计模块
bandwidth_estimation_.UpdateReceiverBlock(
fraction_lost_aggregate, TimeDelta::ms(rtt), total_number_of_packets,
Timestamp::ms(now_ms));
}
MaybeTriggerOnNetworkChanged();
}
SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateReceiverBlock:丢包率换算成总的丢包数。
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateReceiverBlock(uint8_t fraction_loss,
TimeDelta rtt,
int number_of_packets,
Timestamp at_time) {
const int kRoundingConstant = 128;
// 计算丢包数,向上取整
int packets_lost = (static_cast<int>(fraction_loss) * number_of_packets +
kRoundingConstant) >>
8;
UpdatePacketsLost(packets_lost, number_of_packets, at_time);
UpdateRtt(rtt, at_time);
}
SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdatePacketsLost:更新实际丢包率,需要保证包数累计到20个以上。
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdatePacketsLost(int packets_lost,
int number_of_packets,
Timestamp at_time) {
last_loss_feedback_ = at_time;
if (first_report_time_.IsInfinite())
first_report_time_ = at_time;
// Check sequence number diff and weight loss report
if (number_of_packets > 0) {
// 累计丢包数
lost_packets_since_last_loss_update_ += packets_lost;
// 累计发送端两次统计间隔的总包数,跟接收端的统计间隔可能不一致,接收端以RR包的间隔为统计周期,
// 发送端在此基础上还需要累计kLimitNumPackets个包,防止包数过少反应过于灵敏
expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_ += number_of_packets;
// 如果包数还没有达到20个.
if (expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_ < kLimitNumPackets)
return;
// 如果发送端两次统计间隔的包数已经超过20个,可以计算实际的丢包率
has_decreased_since_last_fraction_loss_ = false;
// 丢包数 * 256
int64_t lost_q8 = lost_packets_since_last_loss_update_ << 8;
// 发送端两次统计间隔的总包数
int64_t expected = expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_;
// 丢包率限制在(0,255)
last_fraction_loss_ = std::min<int>(lost_q8 / expected, 255);
// 重置发送端的统计计数器.
lost_packets_since_last_loss_update_ = 0;
expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_ = 0;
last_loss_packet_report_ = at_time;
// 启动发送端带宽估计.
UpdateEstimate(at_time);
}
UpdateUmaStatsPacketsLost(at_time, packets_lost);
}
综合以上步骤以后,发送端获得了最近一段时间的丢包率last_fraction_loss_,UpdateEstimate函数用丢包率、rtt等作为参数去调整预估带宽。
总结:
接收端通过两个时刻的最大序号之差得到两个时刻之间的期望包数,统计两个时刻之间的实际接收到的包数,计算得到单个流的两个时刻的丢包率(fraction lost),然后将丢包率(fraction lost)、累计丢包(cumulative packet lost)、最大序列号等字段填到RR包的Report Block中发送给发送端。发送端累计RR包中所有流的所有Report Block的丢包,计算总的丢包率。
4.2.2 RTT
发送端构造并发送携带发送时间戳t_sr的SR包,接收端构造并发送RR包,携带回SR包中携带的发送时间戳t_lsr(t_sr),以及接收端的处理时延t_dlrr,发送端收到RR包后获取收当前时间t_rr就可以计算出rtt:
rtt = t_rr - t_lsr - t_dlrr
SR携带的时间戳:
t_sr:SR包的发送时间;
RR包携带的时间戳:
t_lsr,也就是t_sr;
t_dlrr,接收端发送RR包的时间(t_rr_send) - 接收端接收到SR包的时间(t_sr_rcv) = 接收端处理时延;
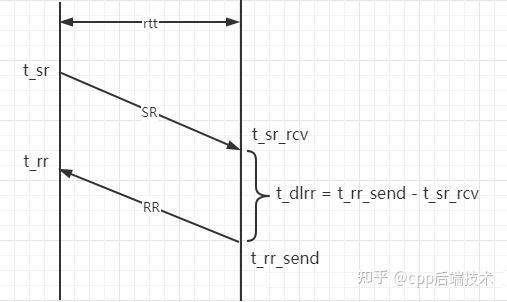
可以看到时间的运算中,t_sr、t_rr为发送端的绝对时间,t_sr_rcv、t_rr_send为接收端的绝对时间,拥有各自的时间基准,并不要求发送端、接收端NTP同步。
接收端RR包填充lsr、dlrr:
std::vector<rtcp::ReportBlock> RTCPSender::CreateReportBlocks(
const FeedbackState& feedback_state) {
std::vector<rtcp::ReportBlock> result;
if (!receive_statistics_)
return result;
// TODO(danilchap): Support sending more than |RTCP_MAX_REPORT_BLOCKS| per
// compound rtcp packet when single rtcp module is used for multiple media
// streams.
result = receive_statistics_->RtcpReportBlocks(RTCP_MAX_REPORT_BLOCKS);
if (!result.empty() && ((feedback_state.last_rr_ntp_secs != 0) ||
(feedback_state.last_rr_ntp_frac != 0))) {
// Get our NTP as late as possible to avoid a race.
uint32_t now = CompactNtp(TimeMicrosToNtp(clock_->TimeInMicroseconds()));
// last_rr_ntp_secs、last_rr_ntp_frac实际上是RTCPReceiver::HandleSenderReport在处理SR包
// 的时候获取的,也就是只有流的接收端有效,所以这里其实就是限定了只有RR包会携带有效的lsr、dlrr,
// TBD:P2P双向流??
uint32_t receive_time = feedback_state.last_rr_ntp_secs & 0x0000FFFF;
receive_time <<= 16;
receive_time += (feedback_state.last_rr_ntp_frac & 0xffff0000) >> 16;
// 计算dlrr
uint32_t delay_since_last_sr = now - receive_time;
// 填充Report Block的lsr、dlrr
for (auto& report_block : result) {
report_block.SetLastSr(feedback_state.remote_sr); // 设置lsr
report_block.SetDelayLastSr(delay_since_last_sr); // 设置dlrr
}
}
return result;
}
发送端处理RR包计算rtt:
void RTCPReceiver::HandleReportBlock(const ReportBlock& report_block,
PacketInformation* packet_information,
uint32_t remote_ssrc) {
……
int64_t rtt_ms = 0;
// 获取t_lsr
uint32_t send_time_ntp = report_block.last_sr();
// RFC3550, section 6.4.1, LSR field discription states:
// If no SR has been received yet, the field is set to zero.
// Receiver rtp_rtcp module is not expected to calculate rtt using
// Sender Reports even if it accidentally can.
// 上面这个注释说明了接收端不通过SR包计算rtt
if (send_time_ntp != 0) {
// 获取t_dlrr
uint32_t delay_ntp = report_block.delay_since_last_sr();
// 获取t_rr.
uint32_t receive_time_ntp =
CompactNtp(TimeMicrosToNtp(clock_->TimeInMicroseconds()));
// RTT in 1/(2^16) seconds.
// 公式:rtt = t_rr - t_dlrr - t_lsr
uint32_t rtt_ntp = receive_time_ntp - delay_ntp - send_time_ntp;
// Convert to 1/1000 seconds (milliseconds).
rtt_ms = CompactNtpRttToMs(rtt_ntp);
……
packet_information->rtt_ms = rtt_ms;
}
}
发送端计算出rtt后更新到SendSideBandwidthEstimation:
// 收到RR包计算出rtt后更新到SendSideBandwidthEstimation
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateRtt(TimeDelta rtt, Timestamp at_time) {
// Update RTT if we were able to compute an RTT based on this RTCP.
// FlexFEC doesn't send RTCP SR, which means we won't be able to compute RTT.
if (rtt > TimeDelta::Zero())
last_round_trip_time_ = rtt; // 保存最近的rtt
if (!IsInStartPhase(at_time) && uma_rtt_state_ == kNoUpdate) {
uma_rtt_state_ = kDone;
RTC_HISTOGRAM_COUNTS("WebRTC.BWE.InitialRtt", rtt.ms<int>(), 0, 2000, 50);
}
}
另外,上面展示的是发送端通过SR、RR包计算rtt的过程,接收端实际上也需要rtt,在接收端的带宽估计、NACK等模块都需要rtt,目前默认是写死的100ms或者200ms,并不能直接通过SR、RR包获取到rtt,如果有需要更新rtt的话,需要借助RFC3611的XR包的两个跟SR、RR包类似的Report Block来处理:
Receiver Reference Time Report Block
DLRR Report Block
处理过程跟通过SR、RR包计算rtt的过程基本相同,但是方向相反,也就是接收端发送带发送时间戳的XR(Receiver Reference Time Report Block),发送端回复带处理时延的XR(DLRR Report Block),接收端收到后可以使用相同的方法计算rtt。
4.3 带宽调整算法
实现于http://send_side_bandwidth_estimation.cc的SendSideBandwidthEstimation类。
4.4.1 初始化带宽 - SendSideBandwidthEstimation::SetBitrates
设置码率的最大值(默认没有限制)、最小值(默认5k),以及初始带宽(默认300k)。
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::SetBitrates(
absl::optional<DataRate> send_bitrate,
DataRate min_bitrate,
DataRate max_bitrate,
Timestamp at_time) {
// 设置码率上、下限
SetMinMaxBitrate(min_bitrate, max_bitrate);
if (send_bitrate) {
……
// 设置初始码率
SetSendBitrate(*send_bitrate, at_time);
}
}
4.4.2 接收端带宽REMB - SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateReceiverEstimate
保存接收端发过来的REMB包中的预估带宽值:
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateReceiverEstimate(Timestamp at_time,
DataRate bandwidth) {
// 保存接收端发过来的REMB包中的带宽值
bwe_incoming_ = bandwidth;
// 限制在阈值范围内,会更新当前的预估码率.
CapBitrateToThresholds(at_time, current_bitrate_);
}
4.4.3 核心调整逻辑 - SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateEstimate
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::UpdateEstimate(Timestamp at_time) {
DataRate new_bitrate = current_bitrate_; // 当前的预估带宽为基准
……
// 如果没有收到过RR包的丢包统计,并且在开始的2秒内,使用REMB包的接收端预估带宽
if (last_fraction_loss_ == 0 && IsInStartPhase(at_time)) {
// 先相信REMB包的预估带宽
new_bitrate = std::max(bwe_incoming_, new_bitrate);
// TCC,忽略
new_bitrate = std::max(delay_based_bitrate_, new_bitrate);
// 默认不使能
if (loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.Enabled()) {
loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.SetInitialBitrate(new_bitrate);
}
// 如果更新了预估码率
if (new_bitrate != current_bitrate_) {
// 清除历史最小码率表
min_bitrate_history_.clear();
if (loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.Enabled()) {
// 默认不使能
min_bitrate_history_.push_back(std::make_pair(at_time, new_bitrate));
} else {
// 保存当前的预估带宽到历史最小码率表,只有1个元素
min_bitrate_history_.push_back(
std::make_pair(at_time, current_bitrate_));
}
// 限制到阈值
CapBitrateToThresholds(at_time, new_bitrate);
return; // 开始的2秒就以REMB包为准,如果还没有REMB包、RR包,那还是初始带宽。
}
}
// 更新最小码率表,去掉过期的元素(超过1s),并删除掉所有比当前码率current_bitrate_大的元素,current_bitrate_保存在表尾.
// 所以历史最小码率表就是这样一张表:保存1s内的码率,有序,表尾最大值是最后一次预估的码率.
UpdateMinHistory(at_time);
// 如果还没有上报过一次丢包率(可能没有RR包,或者有RR包了,但是累计包数未满20),那么可以退出.
if (last_loss_packet_report_.IsInfinite()) {
// No feedback received.
CapBitrateToThresholds(at_time, current_bitrate_);
return;
}
// 默认不使能
if (loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.Enabled()) {
loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.Update(
at_time, min_bitrate_history_.front().second, last_round_trip_time_);
new_bitrate = MaybeRampupOrBackoff(new_bitrate, at_time);
CapBitrateToThresholds(at_time, new_bitrate);
return;
}
// time_since_loss_packet_report为当前距上次上报丢包率的时间
TimeDelta time_since_loss_packet_report = at_time - last_loss_packet_report_;
// time_since_loss_feedback为当前距收到上个RR包的时间,在不满20个包时不等于time_since_loss_packet_report
TimeDelta time_since_loss_feedback = at_time - last_loss_feedback_;
// 如果当前距上次上报丢包率的时间小于1.2 * 5 = 6s
if (time_since_loss_packet_report < 1.2 * kMaxRtcpFeedbackInterval) {
// 计算小数形式的丢包率
float loss = last_fraction_loss_ / 256.0f;
// 默认bitrate_threshold_为0, 所以这里就是只判断丢包率是否低于"低丢包阈值"low_loss_threshold_
if (current_bitrate_ < bitrate_threshold_ || loss <= low_loss_threshold_) {
// Loss < 2%: Increase rate by 8% of the min bitrate in the last
// kBweIncreaseInterval.
// Note that by remembering the bitrate over the last second one can
// rampup up one second faster than if only allowed to start ramping
// at 8% per second rate now. E.g.:
// If sending a constant 100kbps it can rampup immediately to 108kbps
// whenever a receiver report is received with lower packet loss.
// If instead one would do: current_bitrate_ *= 1.08^(delta time),
// it would take over one second since the lower packet loss to achieve
// 108kbps.
// 在丢包率低于2%的时候,认为网络很好,取到历史最小码率表的最小值并增加8%,
// 如果之前没有过调低的情况,则当前历史最小码率表的最小值就是上1秒的最大值,
// 也就是1秒前的码率,也就是说1秒增加8%的码率。
// 实际上这个增加速度并不快,预估带宽想要快速上升到实际水平需要接收端REMB
// 包的通知,可以直接更新预估码率.
new_bitrate =
DataRate::bps(min_bitrate_history_.front().second.bps() * 1.08 + 0.5);
// Add 1 kbps extra, just to make sure that we do not get stuck
// (gives a little extra increase at low rates, negligible at higher
// rates).
new_bitrate += DataRate::bps(1000);
} else if (current_bitrate_ > bitrate_threshold_) { // 默认bitrate_threshold_为0
if (loss <= high_loss_threshold_) {
// Loss between 2% - 10%: Do nothing.
// 丢包率在(2%, 10%)的区间内处于稳定状态,不进行调整.
} else {
// Loss > 10%: Limit the rate decreases to once a kBweDecreaseInterval
// + rtt.
// 丢包率超过10%
if (!has_decreased_since_last_fraction_loss_ && // 如果自上次上报丢包以来,没有降低过码率
(at_time - time_last_decrease_) >= // 如果距上次降低码率已经过去了rtt + 300ms的时间
(kBweDecreaseInterval + last_round_trip_time_)) {
time_last_decrease_ = at_time; // 记录降低码率的时间
// Reduce rate:
// newRate = rate * (1 - 0.5*lossRate);
// where packetLoss = 256*lossRate;
// 降低的幅度为50%的丢包率
new_bitrate =
DataRate::bps((current_bitrate_.bps() *
static_cast<double>(512 - last_fraction_loss_)) /
512.0);
// 置位这个标记,直到下次上报丢包的时候再次清除,
// 也就是两个限制,一个是需要上报丢包,这个需要两个RR的时间间隔,1个控制降速的时间间隔在rtt + 300ms,
// 在丢包比较严重的时候以这个策略为主降低码率,如果抖动比较厉害则以REMB为主降低码率.
has_decreased_since_last_fraction_loss_ = true;
}
}
}
} else if (time_since_loss_feedback > // 如果6秒没有上报丢包,并且15秒没有收到RR包
kFeedbackTimeoutIntervals * kMaxRtcpFeedbackInterval &&
(last_timeout_.IsInfinite() ||
at_time - last_timeout_ > kTimeoutInterval)) { // 控制调整频率为1秒
// 实际上这个逻辑默认情况下不会执行,主要是为了在长时间没有反馈包的情况下,
// 按照20%的幅度降低码率,但是in_timeout_experiment_默认是false.
if (in_timeout_experiment_) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Feedback timed out ("
<< ToString(time_since_loss_feedback)
<< "), reducing bitrate.";
new_bitrate = new_bitrate * 0.8;
// Reset accumulators since we've already acted on missing feedback and
// shouldn't to act again on these old lost packets.
lost_packets_since_last_loss_update_ = 0;
expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_ = 0;
last_timeout_ = at_time;
}
}
// 限制最终预估带宽在阈值之内
CapBitrateToThresholds(at_time, new_bitrate);
}
4.4.4 阈值限制 - SendSideBandwidthEstimation::CapBitrateToThresholds
void SendSideBandwidthEstimation::CapBitrateToThresholds(Timestamp at_time,
DataRate bitrate) {
if (bwe_incoming_ > DataRate::Zero() && bitrate > bwe_incoming_) {
// 如果输入预估带宽大于REMB包通知的接收端预估带宽,则以REMB包接收端预估带宽为准.
bitrate = bwe_incoming_;
}
// TCC,忽略
if (delay_based_bitrate_ > DataRate::Zero() &&
bitrate > delay_based_bitrate_) {
bitrate = delay_based_bitrate_;
}
// 默认不使能
if (loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.Enabled() &&
loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.GetEstimate() > DataRate::Zero()) {
bitrate = std::min(bitrate, loss_based_bandwidth_estimation_.GetEstimate());
}
// 限制最大值
if (bitrate > max_bitrate_configured_) {
bitrate = max_bitrate_configured_;
}
// 限制最小值
if (bitrate < min_bitrate_configured_) {
if (last_low_bitrate_log_.IsInfinite() ||
at_time - last_low_bitrate_log_ > kLowBitrateLogPeriod) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Estimated available bandwidth "
<< ToString(bitrate)
<< " is below configured min bitrate "
<< ToString(min_bitrate_configured_) << ".";
last_low_bitrate_log_ = at_time;
}
bitrate = min_bitrate_configured_;
}
// 日志
if (bitrate != current_bitrate_ ||
last_fraction_loss_ != last_logged_fraction_loss_ ||
at_time - last_rtc_event_log_ > kRtcEventLogPeriod) {
event_log_->Log(absl::make_unique<RtcEventBweUpdateLossBased>(
bitrate.bps(), last_fraction_loss_,
expected_packets_since_last_loss_update_));
last_logged_fraction_loss_ = last_fraction_loss_;
last_rtc_event_log_ = at_time;
}
// 更新当前预估码率
current_bitrate_ = bitrate;
//RTC_LOG(INFO) << "CapBitrateToThresholds: " << current_bitrate_.bps();
if (acknowledged_rate_) {
link_capacity_.OnRateUpdate(std::min(current_bitrate_, *acknowledged_rate_),
at_time);
}
}
4.4 发送端带宽调整算法总结
初始默认300k的带宽,并可以设置上下限;
如果收到REMB包,立刻以REMB包中的带宽为准更新预估带宽;
如果丢包率 < 2%,则以当前历史最小码率表的最小值也就是上一秒的码率为基准,增长8%;
如果丢包率在(2%, 10%)范围,则保持;
如果丢包率大于10%,则以rtt + 300ms为频率,每次降低丢包率 * 50%的带宽。
5、接收端
主要实现:
RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime:基于abs-send-time的接收端带宽估计,默认方式,本文只描述该方式;
RemoteBitrateEstimatorSingleStream:基于RTP时间戳的接收端带宽估计;
InterArrival:到达时间滤波器,计算包簇(帧)之间的时间差;
OveruseEstimator:卡尔曼滤波器,用于估算网络延迟变化(拥塞)的最优值;
OveruseDetector:过载检测器,检测链路是否过载;
RateStatistics:输入码率统计;
AimdRateControl:加增乘减码率控制器。
5.1 基本流程
接收端的带宽预测的基本原则是以输入码率为基准,根据链路的拥塞情况进行调整,而链路的拥塞情况用延迟的变化(到达时间间隔增量)来体现。
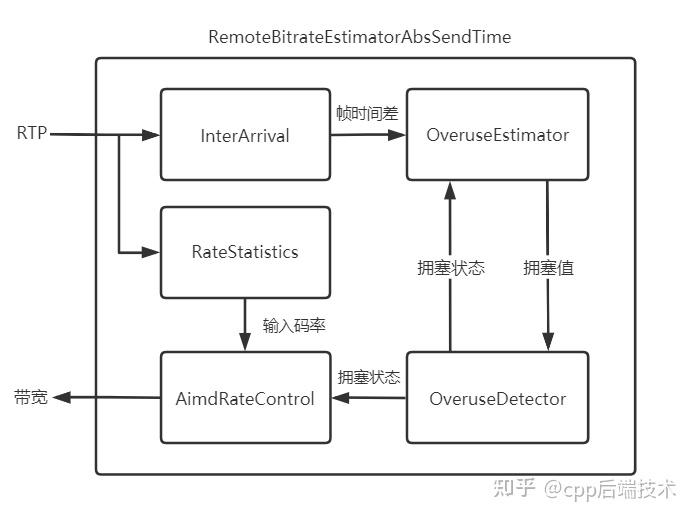
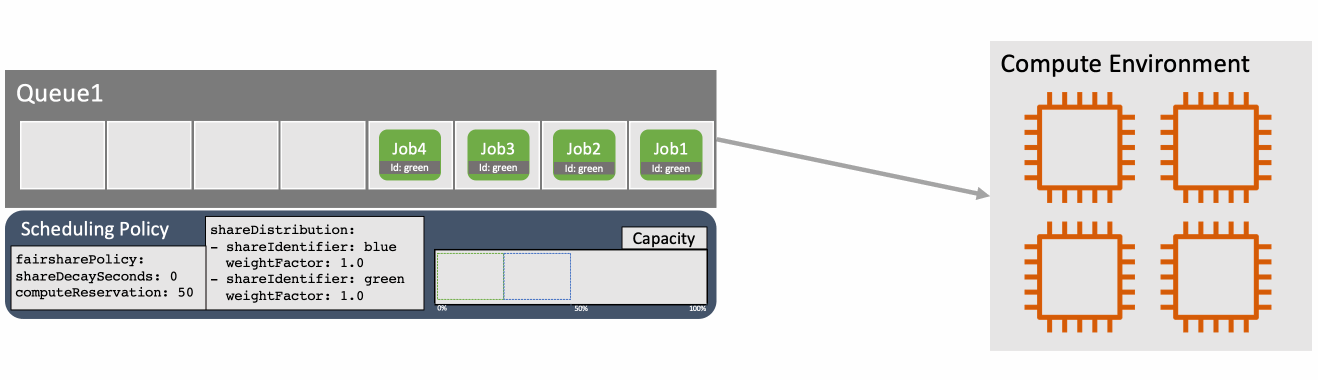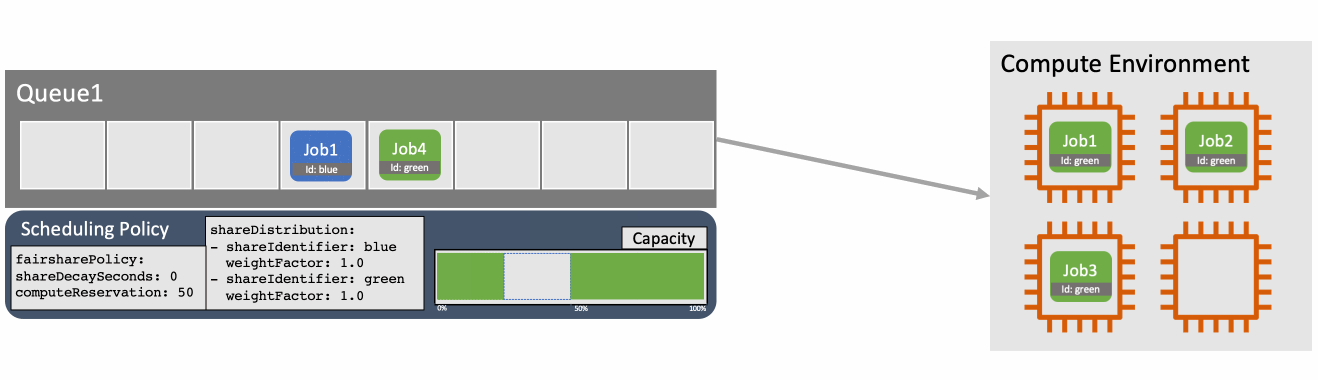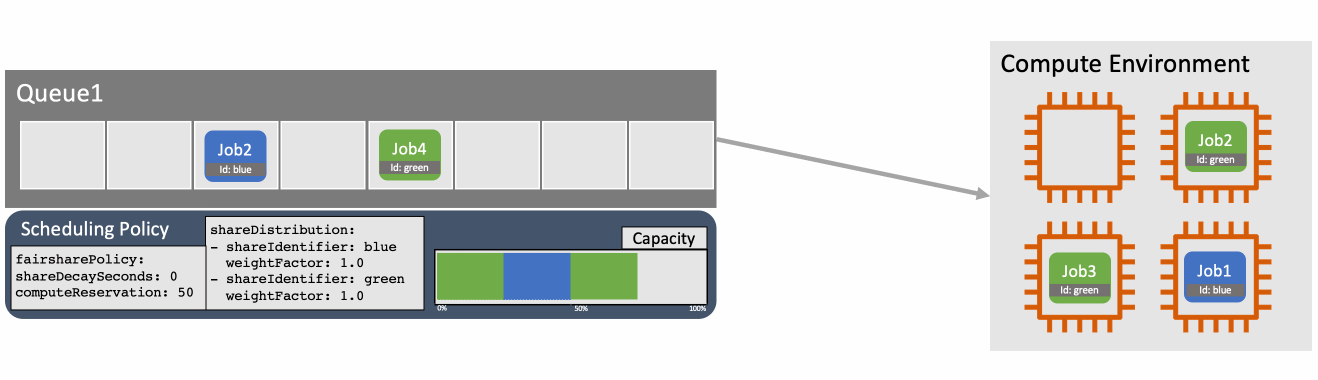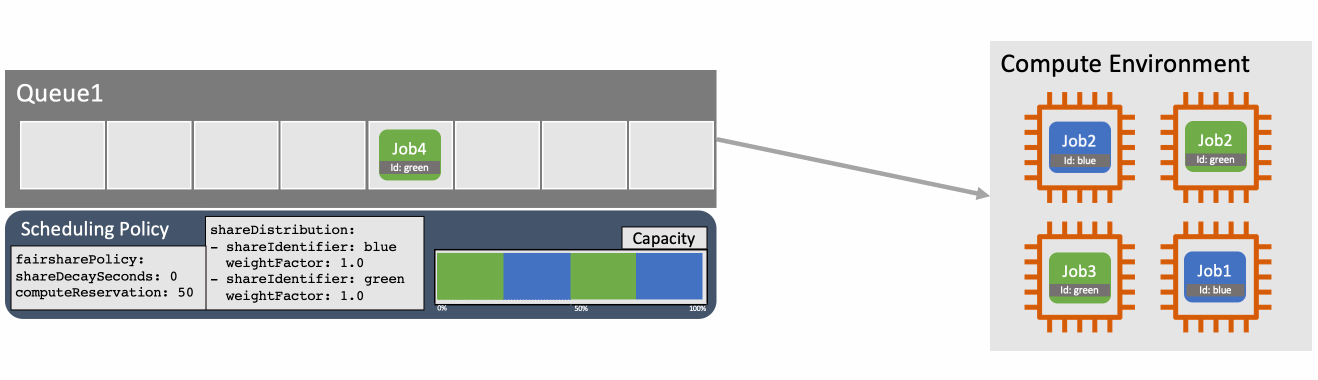
如上图所示,RTP包进入InterArrival(到达时间滤波器)后,InterArrival会缓存最近的两个5ms的包簇(TimestampGroup、或者叫帧),当缓存够两个包簇后,计算这两个包簇之间的发送时间差、到达时间差、尺寸差,输出给OveruseEstimator(卡尔曼滤波器),在没有网络拥塞的情况下,网络拥塞值 = 到达时间差 - 发送时间差 = 0,如果网络拥塞值 > 0,则可能是因为网络噪声造成了拥塞,或者数据尺寸变化造成了网络排队,如果网络拥塞值 < 0,则网络拥塞情况在好转,所以OveruseEstimator(卡尔曼滤波器)就以InterArrival的网络拥塞值、数据尺寸差为观测值,结合预测值进行拟合估算,计算出网络拥塞值的最优值,输出给OveruseDetector(过载检测器),OveruseDetector根据拥塞值(或者叫延迟变化值、抖动)来判断当前网络是否处于拥塞状态,将拥塞状态反馈到OveruseDetector并输出给AimdRateControl(加增乘减码率控制器),AimdRateControl使用输入码率和网络拥塞状态根据“加增乘减”原则来调整接收端当前的预估码率。
5.2 到达时间滤波器 - InterArrival
在不考虑NTP时间同步问题的情况下,一个数据在网络上的传输时间t = 数据到达时间tr - 数据发送时间ts,如果网络没有拥塞,同样的数据在相同的链路下的传输时间基本是不会变化的。如果传输时间变化,可能有以下两个原因:
网络波动、噪声;
数据大小变化,排队情况变化。
两个相同数据之间传输时间的差异(到达时间间隔增量)可以被定义为拥塞值:t_ts_delta = t2 - t1 = (tr2 - ts2) - (tr1 - ts1) = (tr2 - tr1) - (ts2 - ts1) = t_delta - ts_delta
也就是说拥塞值等于两个相同数据的到达时间差 - 发送时间差,经过这样的变换后NTP同步问题被解决。
接下来要考虑:
数据处理的频率;
突发数据的处理;
数据大小变化的影响。
为降低处理频率,InterArrival以5ms的数据为一组存储成一个包簇(TimestampGroup),缓存最近的两个包簇,计算这两个包簇之间的发送时间差、接收时间差(以计算传输时间差),并根据数据到达速度来判断数据突发,避免处理短时间到来的大量数据。为了消除数据大小变化的影响,InterArrival还输出两个包簇的尺寸差,将这些值作为输入参数传给卡尔曼滤波器来处理。
包簇结构:
struct TimestampGroup {
size_t size; // 总大小
uint32_t first_timestamp; // 第1个包的发送时间戳
uint32_t timestamp; // 最新包的发送时间戳作为包簇时间戳
int64_t first_arrival_ms; // 第1个包的接收时间
int64_t complete_time_ms; // 最新包的接收时间作为包簇接收时间
int64_t last_system_time_ms; // 最新包的当前处理时间
};
计算包簇发送时间差、接收时间差、尺寸差:
bool InterArrival::ComputeDeltas(uint32_t timestamp, // 输入,时间戳(abs-send-time或者RTP时间戳)
int64_t arrival_time_ms, // 输入,RTP包接收时间
int64_t system_time_ms, // 输入,RTP包当前处理时间
size_t packet_size, // 输入,RTP包大小
uint32_t* timestamp_delta, // 输出,发送时间差
int64_t* arrival_time_delta_ms, // 输出,接收时间差
int* packet_size_delta) { // 输出,尺寸差
assert(timestamp_delta != NULL);
assert(arrival_time_delta_ms != NULL);
assert(packet_size_delta != NULL);
bool calculated_deltas = false;
// 如果是第一个包
if (current_timestamp_group_.IsFirstPacket()) {
// We don't have enough data to update the filter, so we store it until we
// have two frames of data to process.
current_timestamp_group_.timestamp = timestamp; // 第一个包时间戳作为包簇时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.first_timestamp = timestamp; // 第一个包时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.first_arrival_ms = arrival_time_ms; // 第一个包到达时间
} else if (!PacketInOrder(timestamp)) { // 如果包乱序了,根据时间戳来大致估算
return false; // 本次计算失败
} else if (NewTimestampGroup(arrival_time_ms, timestamp)) { // 如果1个包簇满了,要创建新的包簇
// First packet of a later frame, the previous frame sample is ready.
// 如果有上个包簇
if (prev_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms >= 0) {
// 发送时间差 = 当前包簇发送时间戳 - 上个包簇发送时间戳
*timestamp_delta =
current_timestamp_group_.timestamp - prev_timestamp_group_.timestamp;
// 接收时间差 - 当前包簇接收时间 - 上个包簇接收时间
*arrival_time_delta_ms = current_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms -
prev_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms;
// Check system time differences to see if we have an unproportional jump
// in arrival time. In that case reset the inter-arrival computations.
// 检查接收时间和处理时间是否有过大偏差(3s),容错
int64_t system_time_delta_ms =
current_timestamp_group_.last_system_time_ms -
prev_timestamp_group_.last_system_time_ms;
if (*arrival_time_delta_ms - system_time_delta_ms >=
kArrivalTimeOffsetThresholdMs) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING)
<< "The arrival time clock offset has changed (diff = "
<< *arrival_time_delta_ms - system_time_delta_ms
<< " ms), resetting.";
Reset(); // 重置
return false;
}
// 从Socket上报的数据先发后至?乱序?
if (*arrival_time_delta_ms < 0) {
// The group of packets has been reordered since receiving its local
// arrival timestamp.
++num_consecutive_reordered_packets_;
if (num_consecutive_reordered_packets_ >= kReorderedResetThreshold) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING)
<< "Packets are being reordered on the path from the "
"socket to the bandwidth estimator. Ignoring this "
"packet for bandwidth estimation, resetting.";
Reset();
}
return false;
} else {
num_consecutive_reordered_packets_ = 0;
}
assert(*arrival_time_delta_ms >= 0);
// 尺寸差 = 当前包簇尺寸 - 上个包簇尺寸
*packet_size_delta = static_cast<int>(current_timestamp_group_.size) -
static_cast<int>(prev_timestamp_group_.size);
// 本次计算成功
calculated_deltas = true;
}
// 当前的包簇改为上个包簇
prev_timestamp_group_ = current_timestamp_group_;
// The new timestamp is now the current frame.
// 重置当前包簇,记录当前包簇的第一个包的时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.first_timestamp = timestamp; // 第一个包发送时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.timestamp = timestamp; // 当前包簇发送时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.first_arrival_ms = arrival_time_ms; // 第一个包到达时间
current_timestamp_group_.size = 0; // 当前包簇尺寸清零
} else {
// 如果不满1个包簇,设置当前包簇时间戳为较新的时间戳
current_timestamp_group_.timestamp =
LatestTimestamp(current_timestamp_group_.timestamp, timestamp);
}
// Accumulate the frame size.
// 累计当前包簇大小
current_timestamp_group_.size += packet_size;
// 更新当前包簇的接收时间为最新包接收时间
current_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms = arrival_time_ms;
// 更新当前包簇的最新包处理时间
current_timestamp_group_.last_system_time_ms = system_time_ms;
return calculated_deltas;
}
判断当前RTP包到达后当前包簇是否已满5ms并需创建新的包簇:
bool InterArrival::NewTimestampGroup(int64_t arrival_time_ms,
uint32_t timestamp) const {
if (current_timestamp_group_.IsFirstPacket()) { // 第一个包
return false; // 不创建新包簇
} else if (BelongsToBurst(arrival_time_ms, timestamp)) { // 突发,不创建新包簇
return false;
} else {
// 当前时间戳 - 当前包簇的第一个包时间戳 = 当前包簇总时长,是否大于kTimestampGroupLengthTicks个时间戳单位(90 * 5,也就是5ms)
uint32_t timestamp_diff =
timestamp - current_timestamp_group_.first_timestamp;
return timestamp_diff > kTimestampGroupLengthTicks;
}
}
判断当前RTP包是否属于突发:
bool InterArrival::BelongsToBurst(int64_t arrival_time_ms,
uint32_t timestamp) const {
// 默认使能
if (!burst_grouping_) {
return false;
}
assert(current_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms >= 0);
// 当前包距当前包簇最后1个包的接收时间差
int64_t arrival_time_delta_ms =
arrival_time_ms - current_timestamp_group_.complete_time_ms;
// 当前包距当前包簇最后1个包的发送时间差
uint32_t timestamp_diff = timestamp - current_timestamp_group_.timestamp;
// 发送时间差换算成ms
int64_t ts_delta_ms = timestamp_to_ms_coeff_ * timestamp_diff + 0.5;
// 时间戳几乎一致,是突发
if (ts_delta_ms == 0)
return true;
// 传输时延 = 接收时间差 - 发送时间差
int propagation_delta_ms = arrival_time_delta_ms - ts_delta_ms;
if (propagation_delta_ms < 0 && // 如果传输时延 < 0
arrival_time_delta_ms <= kBurstDeltaThresholdMs && // 如果接收时间差 < 5ms
arrival_time_ms - current_timestamp_group_.first_arrival_ms <
kMaxBurstDurationMs) // 如果当前包簇还不满100ms
return true; // 满足这些条件为突发
return false;
}
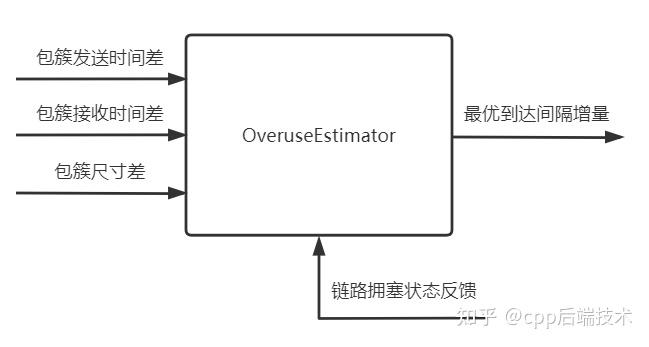
5.3 过载估计器 - OveruseEstimator
OveruseEstimator是一个卡尔曼滤波器,卡尔曼滤波器的具体原理、详细公式本文不准备列出,这里只简单描述其特性:建立一个线性系统,输入观测值,计算预测值,用观测值修正预测值,得到最优值。
具体到WebRTC,输入值为两个包簇的发送时间差、接收时间差之差(字面意思为到达间隔增量):t_ts_delta = t_delta - ts_delta,以及两个包簇的尺寸差、链路拥塞情况,输出为最优的到达间隔增量(或者称为拥塞值、延迟变化)。
5.4 过载检测器 - OveruseDetector
OveruseDetector(过载检测器)根据OveruseEstimator(过载估计器)输出的链路延迟变化情况,与特定的阈值比较,来检测链路是否处于过载状态,并反馈给OveruseEstimator。
BandwidthUsage OveruseDetector::Detect(double offset, // 链路延迟变化(到达时间间隔增量)
double ts_delta, // 两个包簇发送时间差
int num_of_deltas, // 估算使用的采样数
int64_t now_ms) { // 当前时间
if (num_of_deltas < 2) {
return BandwidthUsage::kBwNormal;
}
// 最多kMaxNumDeltas = 60个采样,计算总的网络拥塞值 = 采样数 * 单个采样的到达时间间隔增量
const double T = std::min(num_of_deltas, kMaxNumDeltas) * offset;
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "T", now_ms, T);
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "threshold", now_ms, threshold_);
// 如果网络拥塞值超过阈值,拥塞在加剧
if (T > threshold_) {
if (time_over_using_ == -1) {
// Initialize the timer. Assume that we've been
// over-using half of the time since the previous
// sample.
// 刚开始过载,过载时间设置为两个包簇的发送时间差/2
time_over_using_ = ts_delta / 2;
} else {
// Increment timer
// 持续过载,增加过载时间
time_over_using_ += ts_delta;
}
// 过载计数++
overuse_counter_++;
// 如果过载时间超过100ms,并且发生了持续的过载
if (time_over_using_ > overusing_time_threshold_ && overuse_counter_ > 1) {
// 如果到达间隔变大了,也就是数据来的越来越慢
if (offset >= prev_offset_) {
time_over_using_ = 0;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
// 设置为过载状态
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwOverusing;
}
}
} else if (T < -threshold_) { // 如果拥塞值 < 负的阈值,网络处于欠载状态,数据来的越来越快
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
// 设置为欠载状态
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwUnderusing;
} else {
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
// 设置为正常状态
hypothesis_ = BandwidthUsage::kBwNormal;
}
// 保存当前的到达间隔增量
prev_offset_ = offset;
// 更新阈值
UpdateThreshold(T, now_ms);
return hypothesis_;
}
根据链路拥塞情况与阈值的偏差来更新阈值:
void OveruseDetector::UpdateThreshold(double modified_offset, int64_t now_ms) {
if (!in_experiment_)
return;
if (last_update_ms_ == -1)
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
// 如果拥塞值超过阈值15ms,认为是波动了一个毛刺,不处理
if (fabs(modified_offset) > threshold_ + kMaxAdaptOffsetMs) {
// Avoid adapting the threshold to big latency spikes, caused e.g.,
// by a sudden capacity drop.
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
return;
}
// k_down_ = 0.039, k_up_ = 0.0087,这里是为了不拥塞时快速降低阈值,拥塞时缓慢增加阈值
const double k = fabs(modified_offset) < threshold_ ? k_down_ : k_up_;
const int64_t kMaxTimeDeltaMs = 100;
// 阈值变化量与时间成正比,最大100ms
int64_t time_delta_ms = std::min(now_ms - last_update_ms_, kMaxTimeDeltaMs);
// 根据当前拥塞变化的情况、时间差来调整阈值,也就是说如果拥塞情况modified_offset不变,那么阈值不变,
// 如果拥塞情况变大,间隔时间越长,阈值变得越大,如果拥塞情况变小,阈值会更迅速变小。
// 阈值变大,有利于保持住状态,避免迅速恶化,阈值变小,有利于更灵敏的感知链路状态的变化。
threshold_ += k * (fabs(modified_offset) - threshold_) * time_delta_ms;
// 阈值限制在(6,600)范围内
threshold_ = rtc::SafeClamp(threshold_, 6.f, 600.f);
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
}
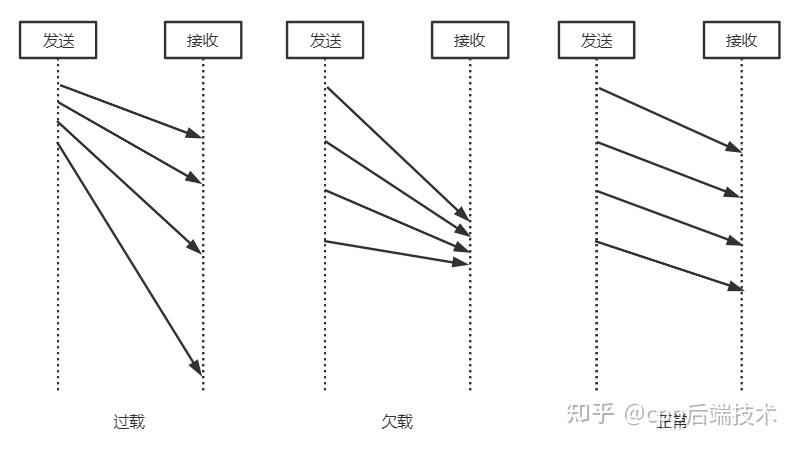
下图直观的描述这三种状态:
5.5 加增乘减码率控制 - AimdRateControl
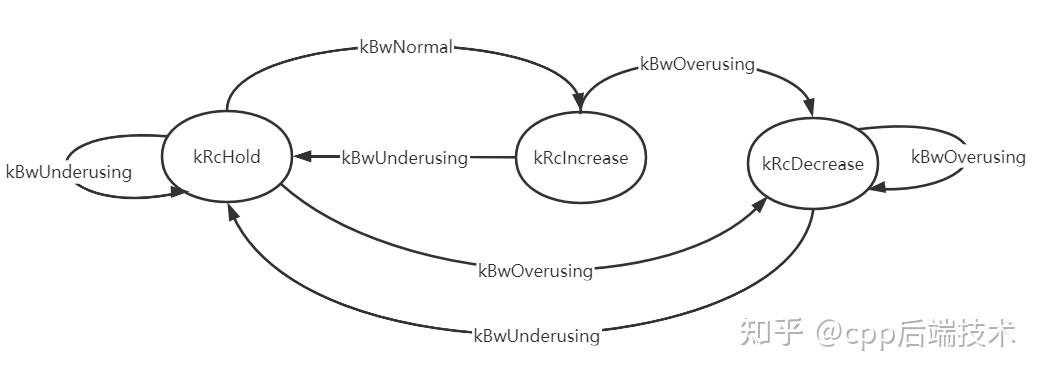
AimdRateControl根据当前预估带宽、输入码率、链路拥塞状态,来估算下一时刻的带宽,其内部维护一个码率控制状态,会根据当前的码率控制状态以及当前输入的链路拥塞状态(过载、欠载、正常),决定下一刻的码率控制状态。
码率控制状态:
kRcHold:保持码率不动;
kRcIncrease:增加码率,如果当前码率接近链路容积,则“加性”慢速增加码率,否则需要“乘性”快速增加码率;
kRcDecrease:降低码率,按照一定的比例"乘性"降低码率。
输入链路拥塞状态:
kBwNormal:正常;
kBwOverusing:过载;
kBwUnderusing:欠载。
状态转换:
最近的5ms包簇满了,获得一次链路的输入码率和拥塞状态,更新码率:
DataRate AimdRateControl::Update(const RateControlInput* input, // Input主要包含输入码率和链路拥塞状态
Timestamp at_time) {
RTC_CHECK(input);
// 初始带宽在RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime中使用Cluster、Probe等对象来探测,Probe是一个超过200字节的包,
// 包簇Cluster是5ms范围内Probe的集合,使用Cluster的集合来预估初始带宽(调用AimdRateControl::SetEstimate设置),
// 这里是为了保证如果5秒之后还没有通过包簇探测到初始带宽的情况下,使用输入的码率来设置初始带宽。
if (!bitrate_is_initialized_) { // 如果码率未初始化
const TimeDelta kInitializationTime = TimeDelta::seconds(5);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(kBitrateWindowMs, kInitializationTime.ms());
if (time_first_throughput_estimate_.IsInfinite()) { // 如果这个第一个数据
if (input->estimated_throughput) // 如果有输入码率
time_first_throughput_estimate_ = at_time; // 设置第一个数据时间
} else if (at_time - time_first_throughput_estimate_ >
kInitializationTime && // 如果距离第一个数据已经过去了5秒还初始化过带宽
input->estimated_throughput) {
current_bitrate_ = *input->estimated_throughput; // 使用5秒后的输入码率来初始化带宽
bitrate_is_initialized_ = true;
}
}
current_bitrate_ = ChangeBitrate(current_bitrate_, *input, at_time); // 修改码率
return current_bitrate_; // 返回修改后的码率
}
修改码率逻辑:
DataRate AimdRateControl::ChangeBitrate(DataRate new_bitrate, // 当前预估码率
const RateControlInput& input, // 输入码率
Timestamp at_time) { // 当前时间
DataRate estimated_throughput =
input.estimated_throughput.value_or(latest_estimated_throughput_); // 输入码率
if (input.estimated_throughput)
latest_estimated_throughput_ = *input.estimated_throughput; // 最后一个数据的时间
// An over-use should always trigger us to reduce the bitrate, even though
// we have not yet established our first estimate. By acting on the over-use,
// we will end up with a valid estimate.
// 如果码率没有初始化,并且未在过载状态,那么就返回当前默认的初始码率(30M).
if (!bitrate_is_initialized_ &&
input.bw_state != BandwidthUsage::kBwOverusing)
return current_bitrate_;
// 改变码率控制状态,参考上面的状态转换图.
ChangeState(input, at_time);
// 判断当前的码率控制状态
switch (rate_control_state_) {
case kRcHold: // 保持状态
break;
case kRcIncrease: // 增加码率
// 如果输入码率大大超过了链路容积,链路容积已经不准确,需要重新估计,
// 链路容积就是过载状态下的输入码率的平滑均值(历史值 * 95% + 采样值 * 5%)
if (estimated_throughput > link_capacity_.UpperBound())
link_capacity_.Reset();
// 如果链路容积没有被重置,说明目标码率跟链路容积接近,可以“加性”缓慢增加
if (link_capacity_.has_estimate()) {
// The link_capacity estimate is reset if the measured throughput
// is too far from the estimate. We can therefore assume that our target
// rate is reasonably close to link capacity and use additive increase.
// 计算"加性"增加的增量:按照目前码率每秒增加1个包产生的带宽
DataRate additive_increase =
AdditiveRateIncrease(at_time, time_last_bitrate_change_);
// "加性"增加预估码率
new_bitrate += additive_increase;
} else {
// If we don't have an estimate of the link capacity, use faster ramp up
// to discover the capacity.
// 如果没有获得链路容积,那么"乘性"快速增加,最大8%的增量
DataRate multiplicative_increase = MultiplicativeRateIncrease(
at_time, time_last_bitrate_change_, new_bitrate);
new_bitrate += multiplicative_increase;
}
time_last_bitrate_change_ = at_time;
break;
case kRcDecrease: // 降低码率
// Set bit rate to something slightly lower than the measured throughput
// to get rid of any self-induced delay.
// 输入码率的85%
new_bitrate = estimated_throughput * beta_;
// 如果输入码率的85%仍然大于当前预估码率
if (new_bitrate > current_bitrate_) {
// Avoid increasing the rate when over-using.
// 如果链路容积有效,则考虑一下链路容积
if (link_capacity_.has_estimate()) {
// 设置为链路容积的85%
new_bitrate = beta_ * link_capacity_.estimate();
}
// 计算当前预估码率和85%链路容积的最小值
new_bitrate = std::min(new_bitrate, current_bitrate_);
}
// 如果有初始码率,并且当前输入码率小于当前预估码率
if (bitrate_is_initialized_ && estimated_throughput < current_bitrate_) {
constexpr double kDegradationFactor = 0.9;
if (smoothing_experiment_ && // smoothing_experiment_默认false
new_bitrate < kDegradationFactor * beta_ * current_bitrate_) {
// If bitrate decreases more than a normal back off after overuse, it
// indicates a real network degradation. We do not let such a decrease
// to determine the bandwidth estimation period.
last_decrease_ = absl::nullopt;
} else {
last_decrease_ = current_bitrate_ - new_bitrate; // 保存最后一次降低的码率
}
}
// 如果输入码率远小于链路容积,重置链路容积,重新计算.
if (estimated_throughput < link_capacity_.LowerBound()) {
// The current throughput is far from the estimated link capacity. Clear
// the estimate to allow an immediate update in OnOveruseDetected.
link_capacity_.Reset();
}
// 这个时候码率肯定初始化了
bitrate_is_initialized_ = true;
// 给链路容积估算器1个采样:当前的输入码率
link_capacity_.OnOveruseDetected(estimated_throughput);
// Stay on hold until the pipes are cleared.
// 码率控制状态先进入保持
rate_control_state_ = kRcHold;
time_last_bitrate_change_ = at_time;
time_last_bitrate_decrease_ = at_time;
break;
default:
assert(false);
}
return ClampBitrate(new_bitrate, estimated_throughput); // 阈值限制
}
加性增加码率:
DataRate AimdRateControl::AdditiveRateIncrease(Timestamp at_time, // 当前时间
Timestamp last_time) const { // 上次修改的时间
double time_period_seconds = (at_time - last_time).seconds<double>(); // 距离上次修改的时间间隔
// 这段时间应该总共增加多少带宽 = 在当前码率下每秒增加1个包需要的带宽 * 距离上次修改的时间间隔
double data_rate_increase_bps =
GetNearMaxIncreaseRateBpsPerSecond() * time_period_seconds;
return DataRate::bps(data_rate_increase_bps);
}
计算在当前码率下每秒增加1个包需要的带宽,需要RTT了,但是GCC并没有更新它,默认200ms:
double AimdRateControl::GetNearMaxIncreaseRateBpsPerSecond() const {
RTC_DCHECK(!current_bitrate_.IsZero());
// 这一通操作实际上就是设置1个包的大小,最大设置为1200字节,如果帧大小小于1200字节,
// 则平均每个包大小就是帧的大小.
// 按照30帧计算帧间隔
const TimeDelta kFrameInterval = TimeDelta::seconds(1) / 30;
// 根据当前预估码率和帧间隔计算帧大小
DataSize frame_size = current_bitrate_ * kFrameInterval;
// 默认包大小
const DataSize kPacketSize = DataSize::bytes(1200);
// 每帧包数向上取整
double packets_per_frame = std::ceil(frame_size / kPacketSize);
// 实际的平均包大小,如果帧小于1200字节,则平均每个包大小就是帧的大小,否则包大小最大1200字节。
DataSize avg_packet_size = frame_size / packets_per_frame;
// Approximate the over-use estimator delay to 100 ms.
// 假设用response_time = f(rtt_)去传输一个avg_packet_size的包会产生多大的带宽呢?
TimeDelta response_time = rtt_ + TimeDelta::ms(100);
if (in_experiment_)
response_time = response_time * 2; // 控制下增量
// 带宽 = 尺寸 / 时间
double increase_rate_bps_per_second =
(avg_packet_size / response_time).bps<double>();
// 增量至少4K
double kMinIncreaseRateBpsPerSecond = 4000;
return std::max(kMinIncreaseRateBpsPerSecond, increase_rate_bps_per_second);
}
在没有链路容积(还未出现需要降低速率的情况)时的“乘性”快速增加:
DataRate AimdRateControl::MultiplicativeRateIncrease(
Timestamp at_time, // 当前时间
Timestamp last_time, // 上次修改码率时间
DataRate current_bitrate) const { // 当前预估码率
double alpha = 1.08;
if (last_time.IsFinite()) {
// 距离上次修改的时间
auto time_since_last_update = at_time - last_time;
// 线性增量随时间变化,距上次修改时间越大增量越大,控制在(1, 1.08)之间,
alpha = pow(alpha, std::min(time_since_last_update.seconds<double>(), 1.0));
}
// 计算线性增量
DataRate multiplicative_increase =
std::max(current_bitrate * (alpha - 1.0), DataRate::bps(1000));
return multiplicative_increase;
}
阈值限制:
DataRate AimdRateControl::ClampBitrate(DataRate new_bitrate,
DataRate estimated_throughput) const {
// Don't change the bit rate if the send side is too far off.
// We allow a bit more lag at very low rates to not too easily get stuck if
// the encoder produces uneven outputs.
// 最大码率设置为1.5倍的输入码率
const DataRate max_bitrate = 1.5 * estimated_throughput + DataRate::kbps(10);
// 如果最新预估的码率超过之前预估的码率并且超过1.5倍的输入码率
if (new_bitrate > current_bitrate_ && new_bitrate > max_bitrate) {
// 最新预估的码率将被设置成之前预估的码率、1.5倍的输入码率中的最大值
new_bitrate = std::max(current_bitrate_, max_bitrate);
}
// 限制最小值,可配置.
new_bitrate = std::max(new_bitrate, min_configured_bitrate_);
return new_bitrate;
}
总结:
AimdRateControl期望在前5秒通过外部的5ms包簇集来估算初始码率,之后根据当前链路拥塞状态、当前码率控制状态,来判断下一刻的码率控制状态,如果下一刻码率控制状态为增加,则根据当前是否已经探测到链路的容积来决定是“加性”缓慢增速,还是“乘性”快速增速,如果下一刻码率控制状态为减少,则“乘性”降低码率,否则保持码率不变。
5.6 码率预估 - RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime
RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime类是接收端的带宽估测类,整合了上述的所有模块实现接收端的带宽估测:
InterArrival:到达时间滤波器,计算包簇(帧)之间的时间差;
OveruseEstimator:卡尔曼滤波器,用于估算网络延迟变化(拥塞)的最优值;
OveruseDetector:过载检测器,检测链路是否过载;
RateStatistics:输入码率统计;
AimdRateControl:加增乘减码率控制器。
5.6.1 abs-send-time时间戳转换
abs-send-time为使用RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime时RTP使用的扩展头,携带了发送端的绝对时间戳的24位形式。
定义abs-send-time跟时间戳的转换精度:
enum {
kTimestampGroupLengthMs = 5, // 1个包簇的时间长度为5ms
kAbsSendTimeFraction = 18, // abs-send-time的小数部分用18位存放,单位(精度)为1/2^18秒,大约3.8us
kAbsSendTimeInterArrivalUpshift = 8, // abs-send-time的时间戳左移8位(凑满32位),
kInterArrivalShift = kAbsSendTimeFraction + kAbsSendTimeInterArrivalUpshift, // 1个时间戳的单位为1/2^26秒
kInitialProbingIntervalMs = 2000, // 使用包簇探测初始带宽的时间
kMinClusterSize = 4, // 一个有效包簇(Cluster)里包含的最小探测包(Probe)数
kMaxProbePackets = 15, // 总的最大探测包(Probe)数
kExpectedNumberOfProbes = 3
};
// 1个时间戳对应的ms,见下面分析
static const double kTimestampToMs =
1000.0 / static_cast<double>(1 << kInterArrivalShift);
abs-send-time是6.18固定24位浮点数,高6位单位为秒(最大26=64s),低18位单位为1/218秒(约3.8us),左移8位得到32位时间戳,也就是乘以256,那么原本1 / 218秒的精度换成时间戳后精度变成了1/218+8=1/226秒=1000/226毫秒,这个是到达时间滤波器需要的数据类型。
5.6.2 包处理核心逻辑 - RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::IncomingPacketInfo**
void RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::IncomingPacketInfo(
int64_t arrival_time_ms, // 到达时间
uint32_t send_time_24bits, // 发送时间戳,必须是abs-send-time
size_t payload_size, // 包大小
uint32_t ssrc) { // SSRC
RTC_CHECK(send_time_24bits < (1ul << 24));
if (!uma_recorded_) {
RTC_HISTOGRAM_ENUMERATION(kBweTypeHistogram, BweNames::kReceiverAbsSendTime,
BweNames::kBweNamesMax);
uma_recorded_ = true;
}
// Shift up send time to use the full 32 bits that inter_arrival works with,
// so wrapping works properly.
// abs-send-time转时间戳,左移8位成32位
uint32_t timestamp = send_time_24bits << kAbsSendTimeInterArrivalUpshift;
// 时间戳转为ms
int64_t send_time_ms = static_cast<int64_t>(timestamp) * kTimestampToMs;
// 当前时间
int64_t now_ms = clock_->TimeInMilliseconds();
// TODO(holmer): SSRCs are only needed for REMB, should be broken out from
// here.
// Check if incoming bitrate estimate is valid, and if it needs to be reset.
// 检查是否有输入码率
absl::optional<uint32_t> incoming_bitrate =
incoming_bitrate_.Rate(arrival_time_ms);
if (incoming_bitrate) {
// 如果有输入码率,设置incoming_bitrate_initialized_
incoming_bitrate_initialized_ = true;
} else if (incoming_bitrate_initialized_) {
// Incoming bitrate had a previous valid value, but now not enough data
// point are left within the current window. Reset incoming bitrate
// estimator so that the window size will only contain new data points.
// 如果之前有过输入码率,但是这次又没了,重置一下
incoming_bitrate_.Reset();
incoming_bitrate_initialized_ = false;
}
// 添加当前包到输入码率统计器
incoming_bitrate_.Update(payload_size, arrival_time_ms);
// 记录第一个包的时间
if (first_packet_time_ms_ == -1)
first_packet_time_ms_ = now_ms;
uint32_t ts_delta = 0;
int64_t t_delta = 0;
int size_delta = 0;
bool update_estimate = false;
uint32_t target_bitrate_bps = 0;
std::vector<uint32_t> ssrcs;
{
rtc::CritScope lock(&crit_);
TimeoutStreams(now_ms);
RTC_DCHECK(inter_arrival_.get());
RTC_DCHECK(estimator_.get());
ssrcs_[ssrc] = now_ms;
// For now only try to detect probes while we don't have a valid estimate.
// We currently assume that only packets larger than 200 bytes are paced by
// the sender.
// 这个逻辑用来初始化码率,因为最初的几秒可能其他模块的数据量不够,还没法正常工作。
// 使用超过200字节的包作为1个探测包(Probe),保留最近的15个探测包,
// Probe的集合称为包簇(Cluster),每个包簇里的包里包簇的平均时间间隔不超过2.5ms,也就是包簇总大小为5ms.
const size_t kMinProbePacketSize = 200;
if (payload_size > kMinProbePacketSize && // 探测包大小必须至少200字节
(!remote_rate_.ValidEstimate() || // 如果还没有预估出码率
now_ms - first_packet_time_ms_ < kInitialProbingIntervalMs)) { // 或者是最初的2秒
// TODO(holmer): Use a map instead to get correct order?
if (total_probes_received_ < kMaxProbePackets) { // 打印下log
int send_delta_ms = -1;
int recv_delta_ms = -1;
if (!probes_.empty()) {
send_delta_ms = send_time_ms - probes_.back().send_time_ms;
recv_delta_ms = arrival_time_ms - probes_.back().recv_time_ms;
}
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Probe packet received: send time=" << send_time_ms
<< " ms, recv time=" << arrival_time_ms
<< " ms, send delta=" << send_delta_ms
<< " ms, recv delta=" << recv_delta_ms << " ms.";
}
// 保存探测包
probes_.push_back(Probe(send_time_ms, arrival_time_ms, payload_size));
// 累加探测包计数器
++total_probes_received_;
// Make sure that a probe which updated the bitrate immediately has an
// effect by calling the OnReceiveBitrateChanged callback.
// 处理探测包,检查是否可以计算出初始码率,如果可以的话,内部直接更新到AimdRateControl
if (ProcessClusters(now_ms) == ProbeResult::kBitrateUpdated)
update_estimate = true;
}
// 到达时间滤波器,输入包的发送时间、接收时间、尺寸,输出5ms包簇(跟探测包簇不是一个东西)
// 之间的发送时间间隔、接收时间间隔、尺寸差
if (inter_arrival_->ComputeDeltas(timestamp, arrival_time_ms, now_ms,
payload_size, &ts_delta, &t_delta,
&size_delta)) {
// 发送时间戳之差转换成ms
double ts_delta_ms = (1000.0 * ts_delta) / (1 << kInterArrivalShift);
// 卡尔曼滤波器处理到达时间滤波器的输出,得到到达间隔增量,也就是延迟变化量,或者称拥塞值
estimator_->Update(t_delta, ts_delta_ms, size_delta, detector_.State(),
arrival_time_ms);
// 过载检测器根据到达间隔增量检测链路过载状态
detector_.Detect(estimator_->offset(), ts_delta_ms,
estimator_->num_of_deltas(), arrival_time_ms);
}
// 检查是需要立刻更新预估码率
if (!update_estimate) {
// Check if it's time for a periodic update or if we should update because
// of an over-use.
// 周期性的判断:如果从来没有更新过预估码率,或者距离上次更新过去了一定时间(GetFeedbackInterval),
// 该时间为RTCP的发送间隔,大致在5%的预估带宽下,1个80字节的RTCP包的发送间隔,
// 并限制在(200ms, 1000ms)范围内.
if (last_update_ms_ == -1 ||
now_ms - last_update_ms_ > remote_rate_.GetFeedbackInterval().ms()) {
// 强制更新一次估算值
update_estimate = true;
} else if (detector_.State() == BandwidthUsage::kBwOverusing) {
// 时间不到但是已经在过载状态,则需要检查下是否需要提前更新,快速反应。
// TimeToReduceFurther函数判断有以下两个条件之一则成立:
// 1.距离上次更新过去了1个rtt的时间;
// 2.输入码率小于50%的当前预估带宽
absl::optional<uint32_t> incoming_rate =
incoming_bitrate_.Rate(arrival_time_ms);
if (incoming_rate &&
remote_rate_.TimeToReduceFurther(Timestamp::ms(now_ms),
DataRate::bps(*incoming_rate))) {
// 强制更新一次估算值
update_estimate = true;
}
}
}
// 如果需要更新预估带宽
if (update_estimate) {
// The first overuse should immediately trigger a new estimate.
// We also have to update the estimate immediately if we are overusing
// and the target bitrate is too high compared to what we are receiving.
// 输入为当前的输入码率、链路拥塞状态.
const RateControlInput input(
detector_.State(),
OptionalRateFromOptionalBps(incoming_bitrate_.Rate(arrival_time_ms)));
// 估算并返回当前的带宽
target_bitrate_bps =
remote_rate_.Update(&input, Timestamp::ms(now_ms)).bps<uint32_t>();
// 是否估算成功
update_estimate = remote_rate_.ValidEstimate();
ssrcs = Keys(ssrcs_);
}
}
// 如果估算成功
if (update_estimate) {
// 记录更新时间
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
// 通知订阅了这个预估码率的模块.
observer_->OnReceiveBitrateChanged(ssrcs, target_bitrate_bps);
}
}
5.6.3 处理包簇初始化码率 - RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::ProcessClusters
处理包簇:
RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::ProbeResult
RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::ProcessClusters(int64_t now_ms) {
std::list<Cluster> clusters;
// 通过探测包构建包簇集
ComputeClusters(&clusters);
// 如果构建包簇集失败
if (clusters.empty()) {
// If we reach the max number of probe packets and still have no clusters,
// we will remove the oldest one.
// 如果探测包溢出(15个),删除最旧的,直到正确构建包簇集.
if (probes_.size() >= kMaxProbePackets)
probes_.pop_front();
return ProbeResult::kNoUpdate;
}
// 计算所有包簇的最佳探测带宽(取最大值)
std::list<Cluster>::const_iterator best_it = FindBestProbe(clusters);
if (best_it != clusters.end()) {
// 获取通过发送时间、接收时间计算的码率的最小值作为当前包簇的探测带宽
int probe_bitrate_bps =
std::min(best_it->GetSendBitrateBps(), best_it->GetRecvBitrateBps());
// Make sure that a probe sent on a lower bitrate than our estimate can't
// reduce the estimate.
// 如果探测带宽优于当前带宽
if (IsBitrateImproving(probe_bitrate_bps)) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Probe successful, sent at "
<< best_it->GetSendBitrateBps() << " bps, received at "
<< best_it->GetRecvBitrateBps()
<< " bps. Mean send delta: " << best_it->send_mean_ms
<< " ms, mean recv delta: " << best_it->recv_mean_ms
<< " ms, num probes: " << best_it->count;
// 直接设置到AimdRateControl作为初始码率.
remote_rate_.SetEstimate(DataRate::bps(probe_bitrate_bps),
Timestamp::ms(now_ms));
return ProbeResult::kBitrateUpdated;
}
}
// Not probing and received non-probe packet, or finished with current set
// of probes.
if (clusters.size() >= kExpectedNumberOfProbes)
probes_.clear();
return ProbeResult::kNoUpdate;
}
遍历所有的探测包,聚集5ms范围的探测包,并检查个数是否到达4个,形成包簇(这个算法在丢包比较严重的情况下可能会失效,因为常常连续出现5ms包簇的探测包不足4个的情况,这种情况下,只能以输入码率来估算带宽,这可能获得一个很小且增长缓慢的值)。
void RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::ComputeClusters(
std::list<Cluster>* clusters) const {
Cluster current;
int64_t prev_send_time = -1;
int64_t prev_recv_time = -1;
// 遍历探测包
for (std::list<Probe>::const_iterator it = probes_.begin();
it != probes_.end(); ++it) {
if (prev_send_time >= 0) {
// 计算两个探测包的时间间隔
int send_delta_ms = it->send_time_ms - prev_send_time;
int recv_delta_ms = it->recv_time_ms - prev_recv_time;
if (send_delta_ms >= 1 && recv_delta_ms >= 1) {
// 累加当前包簇有有效时间的包数
++current.num_above_min_delta;
}
// 如果探测包不在包簇平均时间的5ms范围之内
if (!IsWithinClusterBounds(send_delta_ms, current)) {
// 如果聚集了超过4个有效探测包
if (current.count >= kMinClusterSize && current.send_mean_ms > 0.0f &&
current.recv_mean_ms > 0.0f) {
// 添加1个新的包簇到包簇集合,会求得包簇尺寸、时间的平均值,以便计算码率
AddCluster(clusters, ¤t);
}
// 重置当前包簇
current = Cluster();
}
// 更新当前包簇的累计时间、尺寸
current.send_mean_ms += send_delta_ms;
current.recv_mean_ms += recv_delta_ms;
current.mean_size += it->payload_size;
++current.count;
}
prev_send_time = it->send_time_ms;
prev_recv_time = it->recv_time_ms;
}
// 剩余的不满5ms的探测包也判断下是否有必要添加成1个有效包簇
if (current.count >= kMinClusterSize && current.send_mean_ms > 0.0f &&
current.recv_mean_ms > 0.0f) {
AddCluster(clusters, ¤t);
}
}
计算包簇集合的最佳码率(取每个包簇探测带宽的最大值):
std::list<Cluster>::const_iterator
RemoteBitrateEstimatorAbsSendTime::FindBestProbe(
const std::list<Cluster>& clusters) const {
int highest_probe_bitrate_bps = 0;
// 遍历所有包簇
std::list<Cluster>::const_iterator best_it = clusters.end();
for (std::list<Cluster>::const_iterator it = clusters.begin();
it != clusters.end(); ++it) {
if (it->send_mean_ms == 0 || it->recv_mean_ms == 0)
continue;
if (it->num_above_min_delta > it->count / 2 && // 如果当前包簇有有效时间的探测包数超过1半
(it->recv_mean_ms - it->send_mean_ms <= 2.0f && // 并且接收时间差和发送时间差很接近
it->send_mean_ms - it->recv_mean_ms <= 5.0f)) {
// 获取通过发送时间、接收时间计算的码率的最小值作为当前包簇的探测带宽
int probe_bitrate_bps =
std::min(it->GetSendBitrateBps(), it->GetRecvBitrateBps());
// 记录所有包簇的探测带宽的最大值
if (probe_bitrate_bps > highest_probe_bitrate_bps) {
highest_probe_bitrate_bps = probe_bitrate_bps;
best_it = it;
}
} else {
// 如果发现无效的包簇,则本次探测失败.
int send_bitrate_bps = it->mean_size * 8 * 1000 / it->send_mean_ms;
int recv_bitrate_bps = it->mean_size * 8 * 1000 / it->recv_mean_ms;
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Probe failed, sent at " << send_bitrate_bps
<< " bps, received at " << recv_bitrate_bps
<< " bps. Mean send delta: " << it->send_mean_ms
<< " ms, mean recv delta: " << it->recv_mean_ms
<< " ms, num probes: " << it->count;
break;
}
}
// 返回最佳码率
return best_it;
}
5.7 接收端带宽调整算法总结
接收端处理每个RTP包,累计5ms的探测包簇计算初始带宽,然后通过到达时间滤波器、卡尔曼滤波器、过载检测器来计算链路的延迟变化,从而判断链路的拥塞状态,结合输入码率来估算接收端的带宽,然后通过REMB包反馈给发送端,该反馈的带宽将直接被发送端采用,并作为发送端后续带宽调整算法的基准。
原文https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/497444640
★文末名片可以免费领取音视频开发学习资料,内容包括(FFmpeg ,webRTC ,rtmp ,hls ,rtsp ,ffplay ,srs)以及音视频学习路线图等等。
见下方!↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓