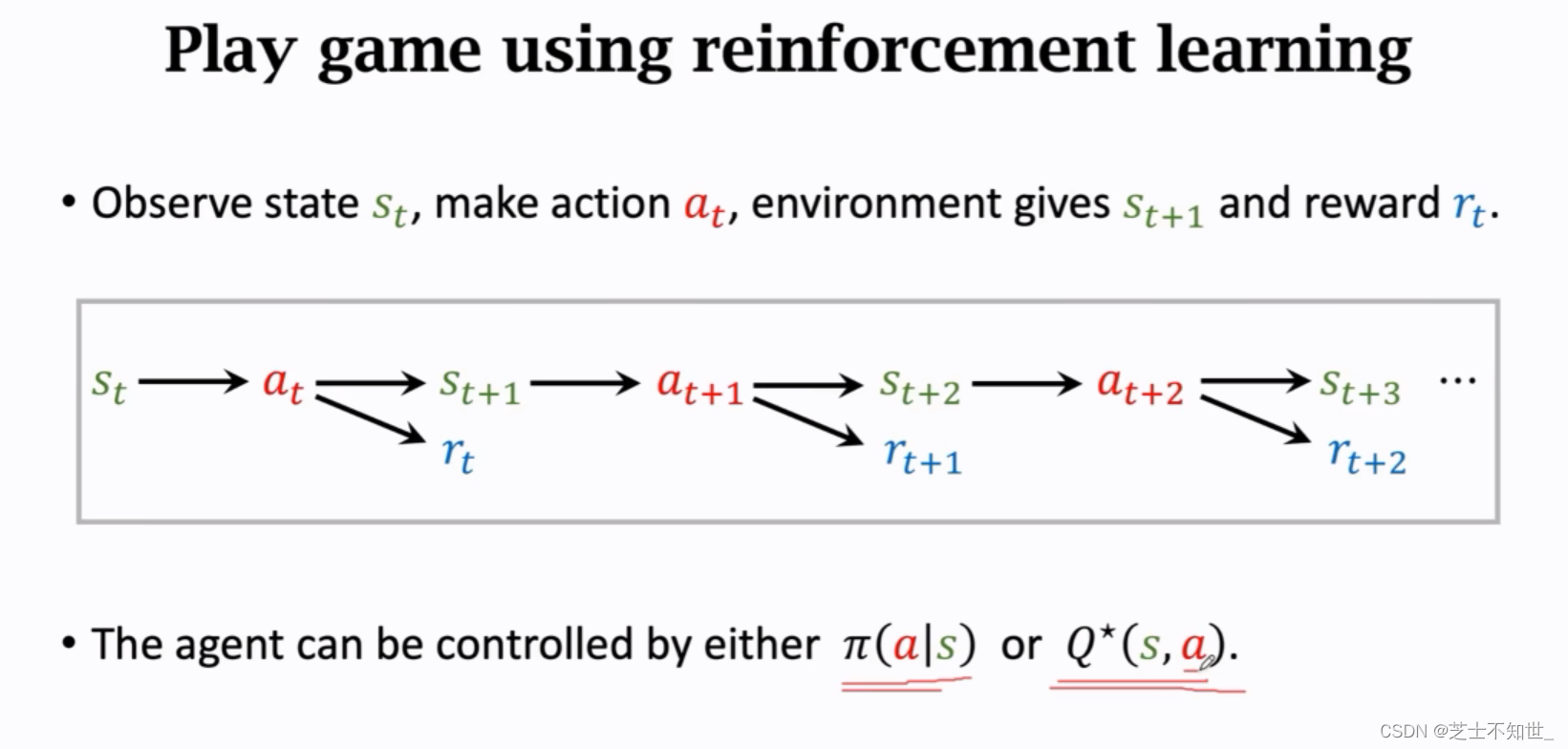
1 overView
1.1 图的构成
图由节点和边组成,其中VertexRDD[VD] 和EdgeRDD[ED] 继承和优化了 RDD[(VertexId, VD)] 和RDD[Edge[ED]] 。
class Graph[VD, ED] {
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
}
1.2 图使用示例
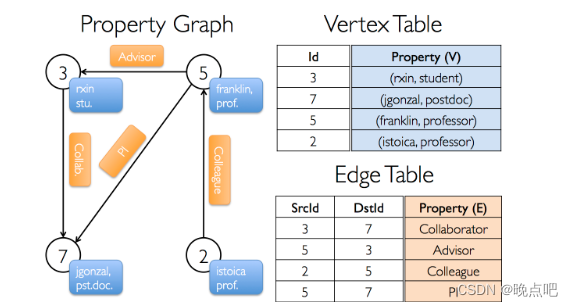
如下图所示,使用spark Graph表示为图 ,其中用户节点有两个属性。每条边有一个属性。
① 构建图
// Assume the SparkContext has already been constructed
val sc: SparkContext
// Create an RDD for the vertices
val users: RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] =
sc.parallelize(Array((3L, ("rxin", "student")), (7L, ("jgonzal", "postdoc")),
(5L, ("franklin", "prof")), (2L, ("istoica", "prof"))))
// Create an RDD for edges
val relationships: RDD[Edge[String]] =
sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(3L, 7L, "collab"), Edge(5L, 3L, "advisor"),
Edge(2L, 5L, "colleague"), Edge(5L, 7L, "pi")))
// Define a default user in case there are relationship with missing user
val defaultUser = ("John Doe", "Missing")
// Build the initial Graph
val graph = Graph(users, relationships, defaultUser)
② 获取节点和边
graph.vertices 返回 VertexRDD[(String, String)] 其中 VertexRDD[(String, String)]继承于 RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] 。
graph.edges 返回 EdgeRDD ,EdgeRDD 包含 Edge[String] 对象。
val graph: Graph[(String, String), String] // Constructed from above
// Count all users which are postdocs
graph.vertices.filter { case (id, (name, pos)) => pos == "postdoc" }.count
// Count all the edges where src > dst
graph.edges.filter(e => e.srcId > e.dstId).count
graph.edges.filter { case Edge(src, dst, prop) => src > dst }.count
③ EdgeTriplet
EdgeTriplet 包含 srcAttr 和 dstAttr属性 ,继承于Edge,
val graph: Graph[(String, String), String] // Constructed from above
// Use the triplets view to create an RDD of facts.
val facts: RDD[String] =
graph.triplets.map(triplet =>
triplet.srcAttr._1 + " is the " + triplet.attr + " of " + triplet.dstAttr._1)
facts.collect.foreach(println(_))
2 图的基本操作
2.1 常用图操作算子
/** Summary of the functionality in the property graph */
class Graph[VD, ED] {
// Information about the Graph ===================================================================
val numEdges: Long
val numVertices: Long
val inDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
val outDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
val degrees: VertexRDD[Int]
// Views of the graph as collections =============================================================
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
val triplets: RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]
// Functions for caching graphs ==================================================================
def persist(newLevel: StorageLevel = StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY): Graph[VD, ED]
def cache(): Graph[VD, ED]
def unpersistVertices(blocking: Boolean = true): Graph[VD, ED]
// Change the partitioning heuristic ============================================================
def partitionBy(partitionStrategy: PartitionStrategy): Graph[VD, ED]
// Transform vertex and edge attributes ==========================================================
def mapVertices[VD2](map: (VertexId, VD) => VD2): Graph[VD2, ED]
def mapEdges[ED2](map: Edge[ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapEdges[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[Edge[ED]]) => Iterator[ED2]): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapTriplets[ED2](map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapTriplets[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]) => Iterator[ED2])
: Graph[VD, ED2]
// Modify the graph structure ====================================================================
def reverse: Graph[VD, ED]
def subgraph(
epred: EdgeTriplet[VD,ED] => Boolean = (x => true),
vpred: (VertexId, VD) => Boolean = ((v, d) => true))
: Graph[VD, ED]
def mask[VD2, ED2](other: Graph[VD2, ED2]): Graph[VD, ED]
def groupEdges(merge: (ED, ED) => ED): Graph[VD, ED]
// Join RDDs with the graph ======================================================================
def joinVertices[U](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(mapFunc: (VertexId, VD, U) => VD): Graph[VD, ED]
def outerJoinVertices[U, VD2](other: RDD[(VertexId, U)])
(mapFunc: (VertexId, VD, Option[U]) => VD2)
: Graph[VD2, ED]
// Aggregate information about adjacent triplets =================================================
def collectNeighborIds(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[VertexId]]
def collectNeighbors(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[(VertexId, VD)]]
def aggregateMessages[Msg: ClassTag](
sendMsg: EdgeContext[VD, ED, Msg] => Unit,
mergeMsg: (Msg, Msg) => Msg,
tripletFields: TripletFields = TripletFields.All)
: VertexRDD[A]
// Iterative graph-parallel computation ==========================================================
def pregel[A](initialMsg: A, maxIterations: Int, activeDirection: EdgeDirection)(
vprog: (VertexId, VD, A) => VD,
sendMsg: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => Iterator[(VertexId,A)],
mergeMsg: (A, A) => A)
: Graph[VD, ED]
// Basic graph algorithms ========================================================================
def pageRank(tol: Double, resetProb: Double = 0.15): Graph[Double, Double]
def connectedComponents(): Graph[VertexId, ED]
def triangleCount(): Graph[Int, ED]
def stronglyConnectedComponents(numIter: Int): Graph[VertexId, ED]
}
2.2 属性操作
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def mapVertices[VD2](map: (VertexId, VD) => VD2): Graph[VD2, ED]
def mapEdges[ED2](map: Edge[ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
def mapTriplets[ED2](map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
}
2.3 图结构操作
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def reverse: Graph[VD, ED]
def subgraph(epred: EdgeTriplet[VD,ED] => Boolean,
vpred: (VertexId, VD) => Boolean): Graph[VD, ED]
def mask[VD2, ED2](other: Graph[VD2, ED2]): Graph[VD, ED]
def groupEdges(merge: (ED, ED) => ED): Graph[VD,ED]
}
子图操作
// Create an RDD for the vertices
val users: RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] =
sc.parallelize(Array((3L, ("rxin", "student")), (7L, ("jgonzal", "postdoc")),
(5L, ("franklin", "prof")), (2L, ("istoica", "prof")),
(4L, ("peter", "student"))))
// Create an RDD for edges
val relationships: RDD[Edge[String]] =
sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(3L, 7L, "collab"), Edge(5L, 3L, "advisor"),
Edge(2L, 5L, "colleague"), Edge(5L, 7L, "pi"),
Edge(4L, 0L, "student"), Edge(5L, 0L, "colleague")))
// Define a default user in case there are relationship with missing user
val defaultUser = ("John Doe", "Missing")
// Build the initial Graph
val graph = Graph(users, relationships, defaultUser)
// Notice that there is a user 0 (for which we have no information) connected to users
// 4 (peter) and 5 (franklin).
graph.triplets.map(
triplet => triplet.srcAttr._1 + " is the " + triplet.attr + " of " + triplet.dstAttr._1
).collect.foreach(println(_))
// Remove missing vertices as well as the edges to connected to them
val validGraph = graph.subgraph(vpred = (id, attr) => attr._2 != "Missing")
// The valid subgraph will disconnect users 4 and 5 by removing user 0
validGraph.vertices.collect.foreach(println(_))
validGraph.triplets.map(
triplet => triplet.srcAttr._1 + " is the " + triplet.attr + " of " + triplet.dstAttr._1
).collect.foreach(println(_))
2.4 join 操作
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def joinVertices[U](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(map: (VertexId, VD, U) => VD)
: Graph[VD, ED]
def outerJoinVertices[U, VD2](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(map: (VertexId, VD, Option[U]) => VD2)
: Graph[VD2, ED]
}
2.5 Neighborhood Aggregation
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def aggregateMessages[Msg: ClassTag](
sendMsg: EdgeContext[VD, ED, Msg] => Unit,
mergeMsg: (Msg, Msg) => Msg,
tripletFields: TripletFields = TripletFields.All)
: VertexRDD[Msg]
}
the aggregateMessages operator to compute the average age of the more senior followers of each user.
import org.apache.spark.graphx.{Graph, VertexRDD}
import org.apache.spark.graphx.util.GraphGenerators
// Create a graph with "age" as the vertex property.
// Here we use a random graph for simplicity.
val graph: Graph[Double, Int] =
GraphGenerators.logNormalGraph(sc, numVertices = 100).mapVertices( (id, _) => id.toDouble )
// Compute the number of older followers and their total age
val olderFollowers: VertexRDD[(Int, Double)] = graph.aggregateMessages[(Int, Double)](
triplet => { // Map Function
if (triplet.srcAttr > triplet.dstAttr) {
// Send message to destination vertex containing counter and age
triplet.sendToDst(1, triplet.srcAttr)
}
},
// Add counter and age
(a, b) => (a._1 + b._1, a._2 + b._2) // Reduce Function
)
// Divide total age by number of older followers to get average age of older followers
val avgAgeOfOlderFollowers: VertexRDD[Double] =
olderFollowers.mapValues( (id, value) =>
value match { case (count, totalAge) => totalAge / count } )
// Display the results
avgAgeOfOlderFollowers.collect.foreach(println(_))
2.6Map Reduce Triplets Transition Guide
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def mapReduceTriplets[Msg](
map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => Iterator[(VertexId, Msg)],
reduce: (Msg, Msg) => Msg)
: VertexRDD[Msg]
}
The following code block using mapReduceTriplets:
val graph: Graph[Int, Float] = ...
def msgFun(triplet: Triplet[Int, Float]): Iterator[(Int, String)] = {
Iterator((triplet.dstId, "Hi"))
}
def reduceFun(a: String, b: String): String = a + " " + b
val result = graph.mapReduceTriplets[String](msgFun, reduceFun)
can be rewritten using aggregateMessages as:
val graph: Graph[Int, Float] = ...
def msgFun(triplet: EdgeContext[Int, Float, String]) {
triplet.sendToDst("Hi")
}
def reduceFun(a: String, b: String): String = a + " " + b
val result = graph.aggregateMessages[String](msgFun, reduceFun)
2.7 Computing Degree Information
// Define a reduce operation to compute the highest degree vertex
def max(a: (VertexId, Int), b: (VertexId, Int)): (VertexId, Int) = {
if (a._2 > b._2) a else b
}
// Compute the max degrees
val maxInDegree: (VertexId, Int) = graph.inDegrees.reduce(max)
val maxOutDegree: (VertexId, Int) = graph.outDegrees.reduce(max)
val maxDegrees: (VertexId, Int) = graph.degrees.reduce(max)
2.8 Collecting Neighbors
class GraphOps[VD, ED] {
def collectNeighborIds(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[VertexId]]
def collectNeighbors(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[ Array[(VertexId, VD)] ]
}
These operators can be quite costly as they duplicate information and require substantial communication. If possible try expressing the same computation using the aggregateMessages operator directly.



![[MatLab]图像绘制](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d30b150ee89c4a688855859af1e386cd.png)

![错误:PermissionError: [WinError 32] 另一个程序正在使用此文件,进程无法访问。“+文件路径“的解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/608254e378738a9f10a46f56eaf2f7d9.png)