本篇文章主要讲述LinkedList链表中从初识到深入相关总结,常见OJ题秒AC,望各位大佬喜欢
一、单链表
1.1链表的概念及结构
1.2无头单向非循环链表模拟实现
1.3测试模拟代码
1.4链表相关面试OJ题
1.4.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
1.4.2 反转一个单链表
1.4.3 给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点
1.4.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
1.4.5 合并俩个有序链表
二、双链表
2.1双向链表模拟实现
2.2LinkedList其他常用方法介绍
2.3ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
1.1链表的概念及结构
由于顺序表ArrayList不适合从任意位置插入或者删除元素,因此引入了LinkedList链表,链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,也称链式存储,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的。
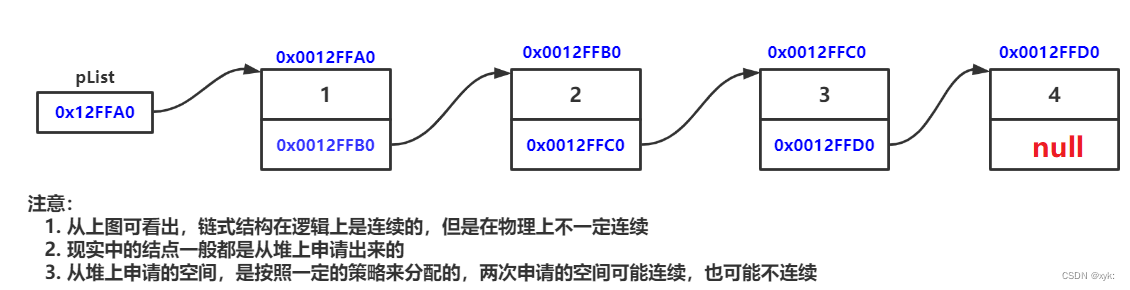
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
1. 单向或者双向
2. 带头或者不带头
3. 循环或者非循环

4.无头单向非循环链表或者无头双向链表
在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
1.2无头单向非循环链表模拟实现
public class MySingleList {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public void createLink() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(13);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(14);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(16);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
head = node1;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://遍历链表
*/
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
*/
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://得到单链表的长度 O(N)
*/
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://头插法 O(1)
*/
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://尾插法 O(N) 找尾巴的过程
*/
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description: //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
*/
public void addIndex(int index, int data) throws ListIndexOutofException {
checkIndex(index);
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndexSubOne(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description:找到 index-1位置的节点的地址
*/
private ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index - 1) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
private void checkIndex(int index) throws ListIndexOutofException {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new ListIndexOutofException("index位置不合法!");
}
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 O(N)
*/
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPrev(key);
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description:找到关键字key的前一个节点
*/
private ListNode searchPrev(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description://删除所有值为key的节点
*/
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
}
/**
* @author 徐延焜xyk
* @Description:保证链表当中 所有的节点 都可以被回收
*/
public void clear() {
head = null;
}
}1.3测试模拟代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();
//LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
//Queue<MySingleList.ListNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
mySingleList.display();
System.out.println("=======");
System.out.println(mySingleList.contains(90));
System.out.println(mySingleList.size());
System.out.println("====测试插入===");
mySingleList.addLast(1);
mySingleList.addLast(2);
mySingleList.addLast(3);
mySingleList.addLast(4);
try {
mySingleList.addIndex(0,1);
}catch (ListIndexOutofException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySingleList.display();
System.out.println("=============");
mySingleList.removeAllKey(1);
mySingleList.display();
}

1.4链表相关面试OJ题
1.4.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == val){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}1.4.2 反转一个单链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}
}1.4.3 给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点
给你单链表的头结点
head,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}1.4.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
仅仅用一个指针进行遍历注定是没有办法很优美地实现此问题解答的,所以要用两个指针,这两个指针的位置相差k-1个距离,当快指针走到最后一个节点的时候,慢指针指向的位置就是我们要的倒数第k个节点了。思想就是这么简单了,很多链表类的题目都是活用指针就可以解决的,一个指针不可以的时候就两个指针来完成。
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
if (k <= 0 || head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (k - 1 != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
k--;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
1.4.5 合并俩个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null){
if (head1.val < head2.val){
tmp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}else {
tmp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if (head1 != null){
tmp.next = head1;
}
if (head2 != null){
tmp.next = head2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}上述这些oj题都是最基本的题目,请关注后续播客会有难度题上线!!
二、双链表
2.1双向链表模拟实现
public class MyLinkedList {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;//前驱
public ListNode next;//后继
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
//头插法O(1)
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
} else {
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
//尾插法O(1)
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new ListIndexOutOfException();
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
//1. 删除的是头节点
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
//只有一个节点
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
} else {
//中间 尾巴
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//不是尾巴节点
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
} else {
//是尾巴节点
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
//1. 删除的是头节点
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
//只有一个节点
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
} else {
//中间 尾巴
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//不是尾巴节点
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
} else {
//是尾巴节点
last = last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public int size() {
int len = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != head) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
last = null;
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList(); linkedList.addLast(1); linkedList.display(); }
1. LinkedList实现了List接口
2. LinkedList的底层使用了双向链表
3. LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持随机访问
4. LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为O(1)
5. LinkedList比较适合任意位置插入的场景
2.2LinkedList其他常用方法介绍
| 方法 | 解释 |
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
// 在起始位置插入0
list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
System.out.println(list);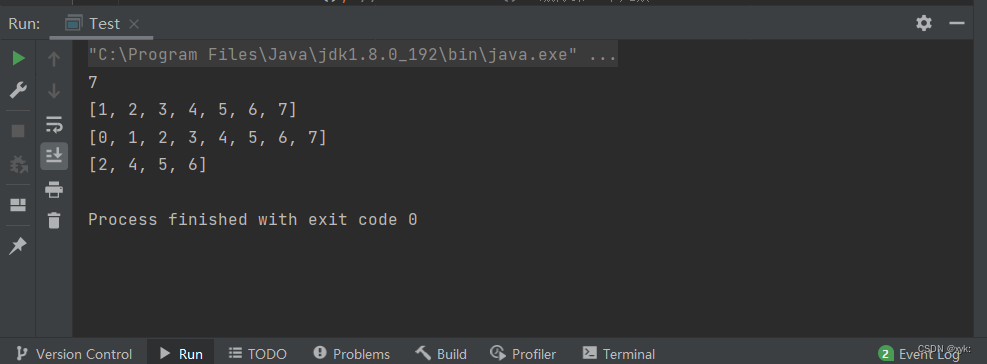
2.3ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
| 不同点 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持:O(N) |
| 头插 | 需要搬移元素,效率低O(N) | 只需修改引用的指向,时间复杂度为O(1) |
| 插入 | 空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |