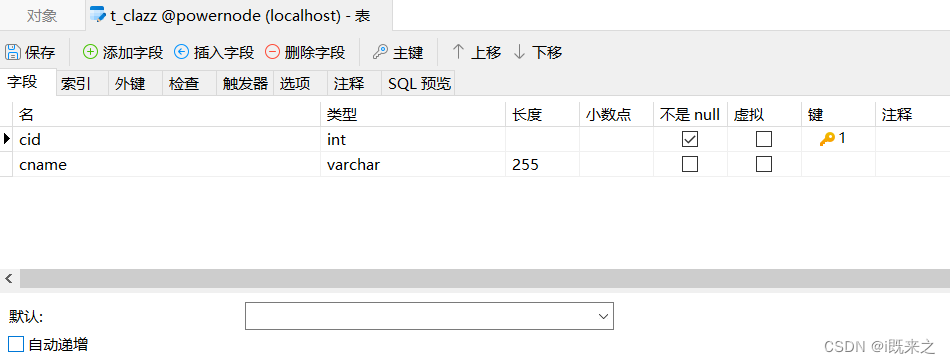
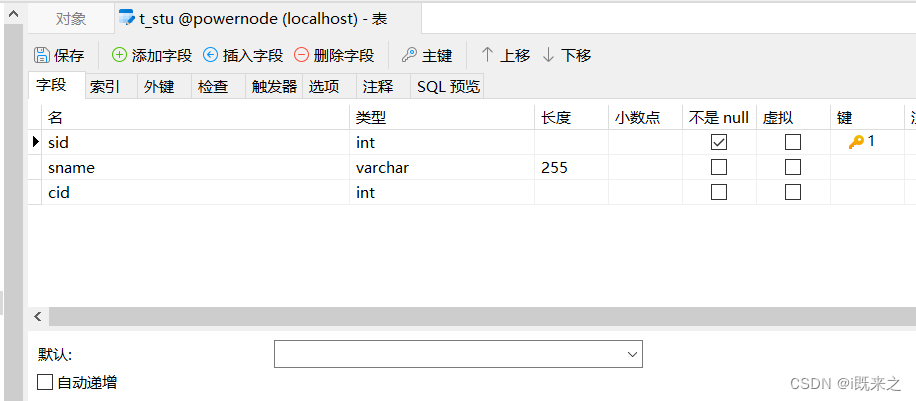
1 数据库表的准备
准备数据库表:一个班级对应多个学生。班级表:t_clazz。学生表:t_stu
2 环境搭建
创建模块
打包方式:jar
引入依赖:mybatis依赖、mysql驱动依赖、junit依赖、logback依赖
配置文件:mybatis-config.xml、logback.xml、jdbc.properties
创建工具类:SqlSessionUtil
创建pojo类:Student、Clazz
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo;
/**
* 学生信息
*/
public class Student {
private Integer sid;
private String sname;
private Clazz clazz;
......
//此处省略构造方法、getting setting toString方法
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo;
/**
* 班级信息
*/
public class Clazz {
private Integer cid;
private String cname;
private List<Student> stus;
......
//此处省略构造方法、getting setting toString方法
创建mapper接口:StudentMapper、ClazzMapper
创建mapper映射文件:StudentMapper.xml、ClazzMapper.xml
3 多对一
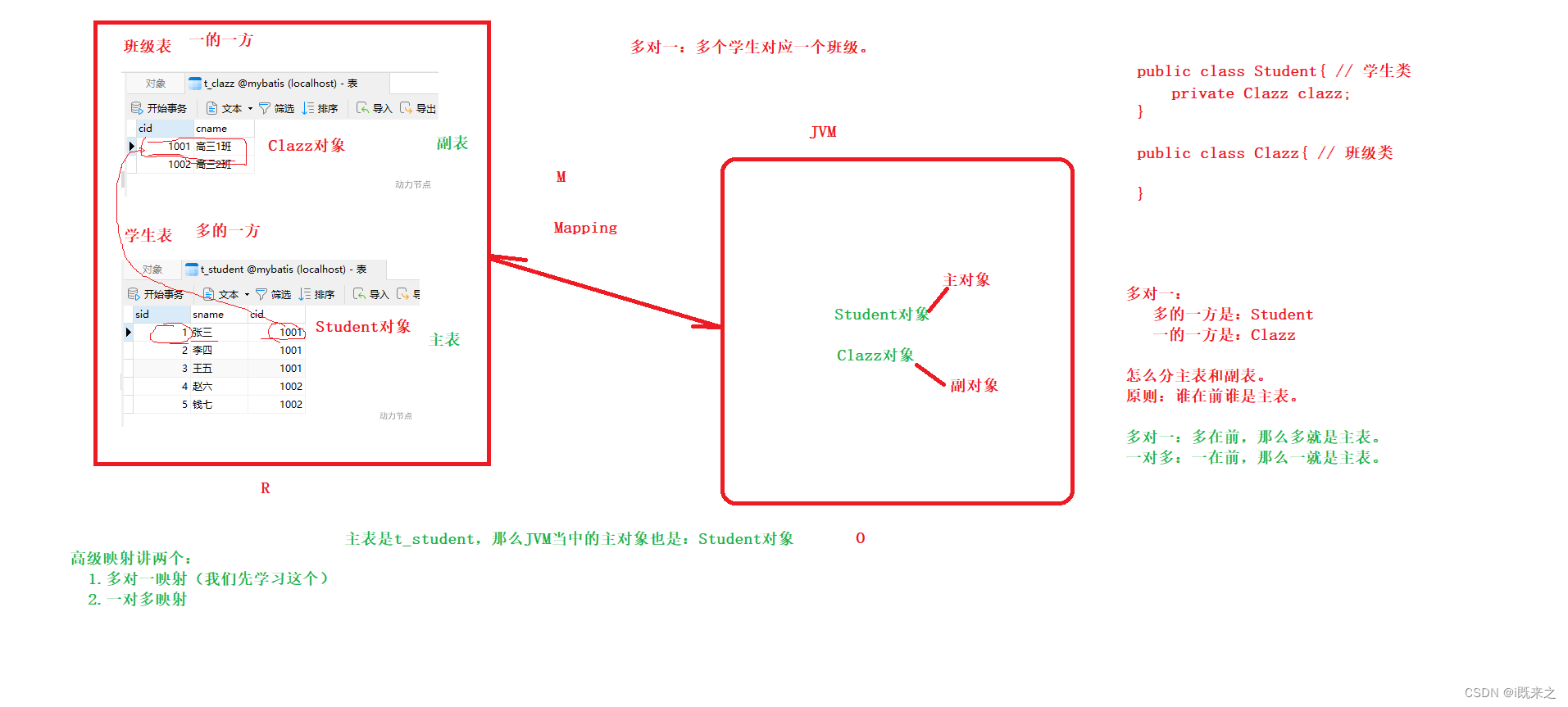
多种方式,常见的包括三种:
- 第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射。
- 第二种方式:一条SQL语句,association。
- 第三种方式:两条SQL语句,分步查询。(这种方式常用:优点一是可复用。优点二是支持懒加载。)
第一种方式:级联属性映射
StudentMapper接口
package com.powernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Student;
public interface StudentMapper {
/**
* 根据id获取学生信息,同时获取学生关联的班级信息
* @param id 学生的id
* @return 学生对象,但是学生对象里面含有班级对象
*/
Student selectById(Integer id);
}
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!--多对一映射的第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射-->
<resultMap id="studentResulMap" type="Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result property="sname" column="sname"/>
<result property="clazz.cid" column="cid"/>
<result property="clazz.cname" column="cname"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="studentResulMap">
select
s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname
from
t_stu s left join t_clazz c on s.cid = c.cid
where
s.sid = #{sid}
</select>
</mapper>
StudentMapperTest
package com.powernode.mybatis.test;
import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Student;
import com.powernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StudentMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
第二种方式:association
association:关联。一个Student对象关联一个Clazz对象
property:提供要映射的POJO类的属性名
javaType:用来指定要映射的java类型
修改resultMap中的配置
<!--一条SQL语句,association。-->
<resultMap id="studentResulMap" type="Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result property="sname" column="sname"/>
<association property="clazz" javaType="Clazz">
<id property="cid" column="cid"/>
<result property="cname" column="cname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
第三种方式:分步查询
StudentMapper
/**
* 分布查询第一步:先根据学生的sid查询学生的信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Student selectByIdStep1(Integer id);
StudentMapper.xml
property:pojo类中的属性名称
select:执行的sql语句的id
column:给select传参
<!--第一步:根据学生的id查询学生的所有信息,信息中含有班级的id-->
<resultMap id="studentResulMapByStep" type="Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result property="sname" column="sname"/>
<association property="clazz"
select="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.ClazzMapper.selectByIdStep2"
column="cid">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByIdStep1" resultMap="studentResulMapByStep">
select sid,sname,cid from t_stu where sid = #{sid}
</select>
ClazzMapper
/**
* 分步查询第二步:根据cid获取班级信息
* @param cid
* @return
*/
Clazz selectByIdStep2(Integer cid);
ClazzMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.ClazzMapper">
<!--分步查询第二步-->
<select id="selectByIdStep2" resultType="Clazz">
select cid,cname from t_clazz where cid = #{cid}
</select>
</mapper>
StudentMapperTest
@Test
public void testSelectByIdStep1() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.selectByIdStep1(1);
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.close();
}
分步查询的优点:
第一:复用性增强。可以重复利用。(大步拆成N多个小碎步。每一个小碎步更加可以重复利用。)
第二:采用这种分步查询,可以充分利用他们的延迟加载/懒加载机制。
4 延迟加载
什么是延迟加载(懒加载),有什么用
- 延迟加载的核心原理是:用的时候再执行查询语句。不用的时候不查询。
作用:提高性能。尽可能的不查,或者说尽可能的少查。来提高效率。
在mybatis当中怎么开启延迟加载
-
局部设置
<!--在association中设置的仅是局部设置--> <association fetchType="lazy">注意:默认情况下是没有开启延迟加载的。需要设置:fetchType=“lazy”
在association标签中配置fetchType=“lazy”,是局部的设置,只对当前的association关联的sql语句起作用。 -
全局配置
在mybatis-config.xml核心配置文件中添加全局配置:lazyLoadingEnabled=true<settings> <!--延迟加载的全局开关,默认值false不开启--> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> </settings>全局的延迟加载打开。
如果某一步不需要使用延迟加载, 在association标签中配置fetchType=“eager”<association fetchType="eager">
5 一对多
一对多:一个班级对应多个学生(班级是主表,学生是副表)

一对多的实现通常包括两种实现方式:
- 第一种方式:collection
- 第二种方式:分步查询
第一种方式:collection
<resultMap id="clazzResultMap" type="Clazz">
<id property="cid" column="cid"/>
<result property="cname" column="cname"/>
<!--一对多 collection 集合-->
<!--ofType 属性用来指定集合中的元素类型-->
<collection property="stus" ofType="Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result property="sname" column="sname"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByIdCollection" resultMap="clazzResultMap">
select c.cid,c.cname,s.sid,s.sname from t_clazz c left join t_stu s on c.cid = s.cid where c.cid = #{cid}
</select>
第二种方式:分步查询
Clazz selectByStep1(Integer cid);
<!--分步查询,据班级cid查询班级信息-->
<resultMap id="selectResultMapStep" type="Clazz">
<id property="cid" column="cid"/>
<result property="cname" column="cname"/>
<collection property="stus"
select="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByCidStep2"
column="cid"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByStep1" resultMap="selectResultMapStep">
select cid,cname from t_clazz where cid = #{cid}
</select>
List<Student> selectByCidStep2(Integer cid);
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="selectByCidStep2" resultType="Student">
select * from t_stu where cid = #{cid}
</select>
</mapper>
@Test
public void testSelectByStep1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
ClazzMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ClazzMapper.class);
Clazz clazz = mapper.selectByStep1(1000);
System.out.println(clazz);
sqlSession.close();
}