汽车架构:车载HAL是汽车与车辆网络服务之间的接口定义(同时保护传入的数据):
车载HAL与Android Automotive架构:
- Car App:包括OEM和第三方开发的App
- Car API:内有包含CarSensorManager在内的API。位于/platform/packages/services/Car/car-lib
- CarService:系统中与车相关的服务,位于/platform/packages/services/Car/
- Vehicle HAL:汽车的硬件抽象层描述。位于hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/(接口属性:hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/impl/vhal_v2_0/)
Framework CarService
Android O/P为Automotive场景提供了一系列的服务,这些服务统被称为CarService。它们与HAL层的VehicleHAL通信,进而通过车载总线(例如CAN总线)与车身进行通讯,同时它们还为应用层的APP提供接口,从而让APP能够实现对车身的控制与状态的显示
- Car***Manager:packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/hardware
- Car***Service:packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/
CarService启动流程
和汽车相关的服务的启动主要依靠一个系统服务CarServiceHelperService开机时在SystemServer中启动:
CarServiceHelperService启动
private static final String CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.internal.car.CarServiceHelperService";
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
......
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
t.traceBegin("StartCarServiceHelperService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
}
......
}
CarServiceHelperService被定义在frameworks/opt/car/下,它和其他系统服务一样,属于SystemService的子类,通过SystemServiceManager.startService启动:
SystemServiceManager.startService
public SystemService startService(String className) {
final Class<SystemService> serviceClass = loadClassFromLoader(className,
this.getClass().getClassLoader());
return startService(serviceClass);
}
private static Class<SystemService> loadClassFromLoader(String className,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
return (Class<SystemService>) Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
...
}
}
loadClassFromLoader通过类加载器直接获取CarServiceHelperService的class对象,拿到class对象进而再调用startService重载方法:
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
...
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
...
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
...
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
...
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
接着通过反射构造CarServiceHelperService的实例对象,然后再调用startService重载方法:
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
这里先将CarServiceHelperService保存到mServices这个list中,然后调用CarServiceHelperService的onStart方法正式启动此服务。
CarServiceHelperService.onStart
@Override
public void onStart() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CAR_HELPER_START, mHalEnabled ? 1 : 0);
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_REBOOT);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SHUTDOWN);
mContext.registerReceiverForAllUsers(mShutdownEventReceiver, filter, null, null);
mCarWatchdogDaemonHelper.addOnConnectionChangeListener(mConnectionListener);
mCarWatchdogDaemonHelper.connect();
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setPackage("com.android.car");
intent.setAction(ICarConstants.CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE);
if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, mCarServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
UserHandle.SYSTEM)) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "cannot start car service");
}
loadNativeLibrary();
}
这里首先注册了开关机广播,CarWatchdogDaemonHelper用于监控此服务,接着会绑定一个包名为"com.android.car",Action为"android.car.ICar"的服务,这就是系统中和汽车相关的核心服务CarService,相关源代码在packages/services/Car/service目录下,然后我们先去看看CarService,等下再回头来看绑定此服务之后的mCarServiceConnection回调部分。
如下是CarService的AndroidManifest部分截图,可以看到CarService的sharedUserId是系统级别的,这是一个系统级服务,类似SystemUI,它编译出来同样是一个APK文件。 来具体看CarService,它的onStartCommand没什么东西,主要来看onBind:
CarService.onBind
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mICarImpl;
}
ICarImpl是一个Binder服务端,其顶级接口为ICar,在onCreate中初始化:
CarService.onCreate
@Override
public void onCreate() {
//通知用户有关 CAN 总线故障
mCanBusErrorNotifier = new CanBusErrorNotifier(this /* context */);
//获取Vehicle hal的client端
mVehicle = getVehicle();
if (mVehicle == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Vehicle HAL service is not available.");
}
try {
mVehicleInterfaceName = mVehicle.interfaceDescriptor();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
//实例化ICarImpl
mICarImpl = new ICarImpl(this,
mVehicle,
SystemInterface.Builder.defaultSystemInterface(this).build(),
mCanBusErrorNotifier,
mVehicleInterfaceName);
//初始化
mICarImpl.init();
//Vehicle hal对端死亡回调
linkToDeath(mVehicle, mVehicleDeathRecipient);
//将mICarImpl注册到ServiceManager
ServiceManager.addService("car_service", mICarImpl);
//修改boot.car_service_created属性为1
SystemProperties.set("boot.car_service_created", "1");
super.onCreate();
}
此方法中主要会对ICarImpl实例化,之后init进行初始化,最后将其注册到ServiceManager。
ICarImpl构造方法
ICarImpl(Context serviceContext, IVehicle vehicle, SystemInterface systemInterface,
CanBusErrorNotifier errorNotifier, String vehicleInterfaceName,
@Nullable CarUserService carUserService,
@Nullable CarWatchdogService carWatchdogService) {
......
mPerUserCarServiceHelper = new PerUserCarServiceHelper(serviceContext, mCarUserService);
mCarBluetoothService = new CarBluetoothService(serviceContext, mPerUserCarServiceHelper);
mCarInputService = new CarInputService(serviceContext, mHal.getInputHal(), mCarUserService);
mCarProjectionService = new CarProjectionService(
serviceContext, null /* handler */, mCarInputService, mCarBluetoothService);
mGarageModeService = new GarageModeService(mContext);
mAppFocusService = new AppFocusService(serviceContext, mSystemActivityMonitoringService);
mCarAudioService = new CarAudioService(serviceContext);
mCarNightService = new CarNightService(serviceContext, mCarPropertyService);
mFixedActivityService = new FixedActivityService(serviceContext);
mInstrumentClusterService = new InstrumentClusterService(serviceContext,
mAppFocusService, mCarInputService);
mSystemStateControllerService = new SystemStateControllerService(
serviceContext, mCarAudioService, this);
mCarStatsService = new CarStatsService(serviceContext);
mCarStatsService.init();
if (mFeatureController.isFeatureEnabled(Car.VEHICLE_MAP_SERVICE)) {
mVmsBrokerService = new VmsBrokerService(mContext, mCarStatsService);
} else {
mVmsBrokerService = null;
}
if (mFeatureController.isFeatureEnabled(Car.DIAGNOSTIC_SERVICE)) {
mCarDiagnosticService = new CarDiagnosticService(serviceContext,
mHal.getDiagnosticHal());
} else {
mCarDiagnosticService = null;
}
if (mFeatureController.isFeatureEnabled(Car.STORAGE_MONITORING_SERVICE)) {
mCarStorageMonitoringService = new CarStorageMonitoringService(serviceContext,
systemInterface);
} else {
mCarStorageMonitoringService = null;
}
mCarConfigurationService =
new CarConfigurationService(serviceContext, new JsonReaderImpl());
mCarLocationService = new CarLocationService(serviceContext);
mCarTrustedDeviceService = new CarTrustedDeviceService(serviceContext);
mCarMediaService = new CarMediaService(serviceContext, mCarUserService);
mCarBugreportManagerService = new CarBugreportManagerService(serviceContext);
......
CarLocalServices.addService(CarPowerManagementService.class, mCarPowerManagementService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarPropertyService.class, mCarPropertyService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarUserService.class, mCarUserService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarTrustedDeviceService.class, mCarTrustedDeviceService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarUserNoticeService.class, mCarUserNoticeService);
CarLocalServices.addService(SystemInterface.class, mSystemInterface);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarDrivingStateService.class, mCarDrivingStateService);
CarLocalServices.addService(PerUserCarServiceHelper.class, mPerUserCarServiceHelper);
CarLocalServices.addService(FixedActivityService.class, mFixedActivityService);
CarLocalServices.addService(VmsBrokerService.class, mVmsBrokerService);
.....
List<CarServiceBase> allServices = new ArrayList<>();
allServices.add(mFeatureController);
allServices.add(mCarUserService);
allServices.add(mSystemActivityMonitoringService);
allServices.add(mCarPowerManagementService);
allServices.add(mCarPropertyService);
allServices.add(mCarDrivingStateService);
...
mAllServices = allServices.toArray(new CarServiceBase[allServices.size()]);
}
这里省略了和Vehicle hal有关的初始化和分析,后续文章再看。
ICarImpl构造方法中创建了一系列CarService模块下的服务,这些服务有部分被添加到了CarLocalServices内部,其提供了getService静态方法用于直接获取这些服务,所有服务都被保存在ICarImpl内部的CarServiceBase类型数组mAllServices中(所有服务都是CarServiceBase的子类)。
ICarImpl构造方法完了之后会接着调用其init方法:
ICarImpl.init
@MainThread
void init() {
mBootTiming = new TimingsTraceLog(VHAL_TIMING_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_HAL);
traceBegin("VehicleHal.init");
//hal初始化
//...省略
traceEnd();
traceBegin("CarService.initAllServices");
for (CarServiceBase service : mAllServices) {
service.init();
}
traceEnd();
}
此方法很简单,遍历mAllServices,分别执行所有服务的init,各自初始化,有兴趣的可以自己去研究各个服务。
到此ICarImpl初始化完毕,最后会作为binder返回给绑定此服务的mCarServiceConnection:
private final ServiceConnection mCarServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
if (DBG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected:" + iBinder);
}
handleCarServiceConnection(iBinder);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
handleCarServiceCrash();
}
};
CarServiceHelperService.handleCarServiceConnection
void handleCarServiceConnection(IBinder iBinder) {
...
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mCarService == iBinder) {
return; // already connected.
}
mCarService = iBinder;
...
sendSetCarServiceHelperBinderCall();
......
}
}
这个方法我们主要关注上面部分,返回的ICarImpl被保存在了CarServiceHelperService的mCarService,后续可通过mCarService跨进程通信。
CarServiceHelperService.sendSetCarServiceHelperBinderCall
private void sendSetCarServiceHelperBinderCall() {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(ICarConstants.CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE);
data.writeStrongBinder(mHelper.asBinder());
// void setCarServiceHelper(in IBinder helper)
sendBinderCallToCarService(data, ICarConstants.ICAR_CALL_SET_CAR_SERVICE_HELPER);
}
这里将会进行跨进程通信,首先构造传输数据,ICarConstants是定义在ExternalConstants的静态内部类:
static final class ICarConstants {
....
static final String CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE = "android.car.ICar";
static final int ICAR_CALL_SET_CAR_SERVICE_HELPER = 0;
....
}
CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE用来标识远程服务接口,其具体传输数据是一个Binder对象,我们来看看mHelper是什么?
private final ICarServiceHelperImpl mHelper = new ICarServiceHelperImpl();
mHelper是定义在CarServiceHelperService的内部类,是一个Binder对象:
private class ICarServiceHelperImpl extends ICarServiceHelper.Stub {
......
.....
}
CarServiceHelperService.sendBinderCallToCarService 再回到前面看sendBinderCallToCarService方法:
private void sendBinderCallToCarService(Parcel data, int callNumber) {
// Cannot depend on ICar which is defined in CarService, so handle binder call directly
// instead.
IBinder carService;
synchronized (mLock) {
carService = mCarService;
}
if (carService == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Not calling txn " + callNumber + " because service is not bound yet",
new Exception());
return;
}
int code = IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + callNumber;
try {
carService.transact(code, data, null, Binder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
handleCarServiceCrash();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} finally {
data.recycle();
}
}
这个方法很明显就是跨进程传输的具体实现了,对端是mCarService即ICarImpl,调用binder的transact进行跨进程通信,其code代表需要调用的对端方法,data为携带的传输数据,ICAR_CALL_SET_CAR_SERVICE_HELPER等于0,这里调用的是对端的0号方法。
于是我们来看看ICar.aidl中定义的0号方法:
interface ICar {
.....
oneway void setCarServiceHelper(in IBinder helper) = 0;
......
}
ICarImpl.setCarServiceHelper
接着来看setCarServiceHelper具体实现:
@Override
public void setCarServiceHelper(IBinder helper) {
//权限检查
assertCallingFromSystemProcess();
ICarServiceHelper carServiceHelper = ICarServiceHelper.Stub.asInterface(helper);
synchronized (mLock) {
mICarServiceHelper = carServiceHelper;
}
mSystemInterface.setCarServiceHelper(carServiceHelper);
mCarOccupantZoneService.setCarServiceHelper(carServiceHelper);
}
这里将ICarServiceHelper的代理端保存在ICarImpl内部mICarServiceHelper,同时也传给了SystemInterface和CarOccupantZoneService,我们暂时不需要知道这三个类拿到ICarServiceHelper的代理端的具体用处,只需要知道他们有能力跨进程访问CarServiceHelperService就行了。
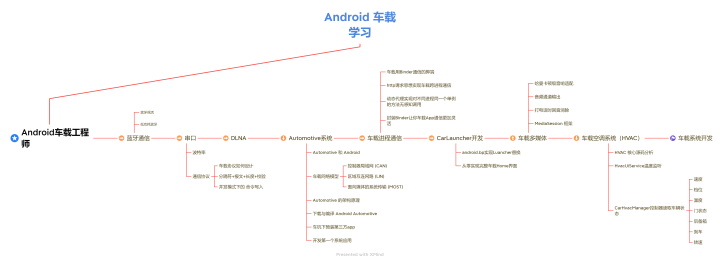
全文解析了车机开发中CarFramework框架的CarService启动流程;车机开发的知识点非常的多;总结如上图资料文档参考《车载技术手册》,里面内容包含以上进阶技术。
CarService启动流程总结
- 首先CarService是一个系统级别的服务APK,类似SystemUI,其在开机时由SystemServer通过CarServiceHelperService启动。
- CarServiceHelperService通过绑定服务的方式启动CarService,启动之后创建了一个Binder对象ICarImpl,并通过onBind返回给system_server进程。
- ICarImpl构造方法中创建了一系列和汽车相关的核心服务,并依次启动这些服务即调用各自init方法。
- ICarImpl返回给CarServiceHelperService之后,CarServiceHelperService也将其内部的一个Binder对象(ICarServiceHelperImpl)传递到了CarService进程,自此CarService和system_server两个进程建立了双向Binder通信。