链表无小事,只要是涉及到链表的算法题,边界值的设定尤为重要,而且及其容易出错误。这就要求我们平时多加练习。但是,我们在面试和笔试的过程中往往会碰到链表相关的题目,所以我们在笔试的时候一般都会借助系统提供的工具类进行解答,但是在面试的过程中,面试官往往想听到的答案是和链表直接相关的解答。这就要求我们有2套不同的应答方案。
题目1:给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构
package code03.链表_01;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构
* https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
*
* 1)哈希表方法特别简单(笔试用)
* 2)改原链表的方法就需要注意边界了(面试用)
*/
public class Palindrome_01 {
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
//笔试用, 怎么简单怎么来,安全保险最重要
public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head)
{
//Letcode 默认仅有一个节点的链表也是回文
if (head == null /*|| head.next == null*/) {
return false;
}
//后进先出,正好和node是反着的
Stack stack = new Stack();
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.next;
}
boolean isPadinDrom = true;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val != ((ListNode) stack.pop()).val) {
isPadinDrom = false;
break;
}
head = head.next;
}
return isPadinDrom;
}
//面试用, 对链表进行操作,大体思路对即可,高端大气上档次
//这种写法节省了额外空间复杂度 Stack
public boolean isPalindrome2 (ListNode header)
{
//Letcode 默认仅有一个节点的链表也是回文
if (header == null /*|| header.next == null*/) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast = header;
ListNode slow = header;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { // fast.next.next != null 判断特别重要
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//奇数,slow正好是中间节点。 偶数,slow是2个中间节点靠后的一个
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode reverseNode = slow; //前一个逆转的node节点、
ListNode node2 = null;
//逆转回文后半部分链表节点
//假设原有链表是1->2->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> null结构
//假设原有链表是1->2->3->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> 3->null结构
while (next != null && reverseNode != null) {
node2 = next.next; //记录下一个节点
next.next = reverseNode; //当前节点指向之前被逆转的节点
reverseNode = next; //更新被逆转的节点
next = node2; //当前节点来到下一个节点处
}
//开始比较
//因为我们根据快慢指针进行切割并且第一个3作为中间节点,前一段链表是标准的结构;后一段链表存在以下2种情况
//1) 奇数,前后链表相同个数;偶数,厚一点链表多一个值。 因此以第一个链表为参考即可. 参考上一个while的备注
ListNode cur = header;
boolean isPadinDrom = true;
node2 = reverseNode;
while (cur!= null) {
if (cur.val != reverseNode.val) {
isPadinDrom = false;
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
reverseNode = reverseNode.next;
}
/**
* 如果我们不在意原有链表是否被破坏,那么以下while可以省略
* 如果我们还想要保持原有链表结构不被破坏,此处我们需要修复原有链表
* 假设原有链表是1->2->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> null结构
* 假设原有链表是1->2->3->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> 3->null结构
* 两个链表的最后一个节点在内存中是相同的,因此仅需要参考后一个链表进行修复即可(此处需要重点理解)
*/
reverseNode = null;
while (node2 != null) {
next = node2.next;
node2.next = reverseNode;
reverseNode = node2;
node2 = next;
}
return isPadinDrom;
}
public static void printNode (ListNode node) {
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("链表不存在");
}
System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.val);
//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点
if(node.next != null) {
printNode(node.next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Palindrome_01 test = new Palindrome_01();
ListNode node = new ListNode(1);
node.next = new ListNode(2);
node.next.next = new ListNode(3);
node.next.next.next = new ListNode(2);
node.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(1);
//node.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
boolean isPadinDrom = test.isPalindrome(node);
System.out.println(isPadinDrom);
boolean isPadinDrom2 = test.isPalindrome2(node);
System.out.println("测试原链表是否被修复");
printNode(node);
System.out.println(isPadinDrom2);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);
node2.next = new ListNode(2);
node2.next.next = new ListNode(3);
node2.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);
node2.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(2);
node2.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(1);
//node2.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
boolean isPadinDrom3 = test.isPalindrome(node2);
System.out.println(isPadinDrom3);
boolean isPadinDrom4 = test.isPalindrome2(node2);
System.out.println("测试原链表是否被修复");
printNode(node2);
System.out.println(isPadinDrom4);
}
}
题目2:将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
笔试用:
package code03.链表_01;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
* 笔试用,典型的快排
*/
public class SmallEqualBig_02 {
static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr, int a, int b) {
Node tmp = nodeArr[a];
nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b];
nodeArr[b] = tmp;
}
public void partition (Node[] nodes, int left, int right) {
//以最后一个值为参考值
Node pavoit = nodes[right];
int min = left;
int max = right;
int cur = left;
while (cur < max) {
if (nodes[cur].value < pavoit.value) {
swap(nodes, min++, cur++);
}
else if (nodes[cur].value > pavoit.value) {
swap(nodes, cur, --max);
}
else {
cur++;
}
}
swap(nodes, cur, right);
}
public Node sort(Node node)
{
if(node == null || node.next == null) {
return node;
}
int n = 0;
Node cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
n++;
}
Node[] arr = new Node[n];
cur = node;
for (int i =0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
partition(arr, 0, n-1);
cur = arr[0];
node = cur;
for (int i =1; i < arr.length; i++) {
cur.next = arr[i];
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
return node;
}
public static void printNode (Node node) {
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("链表不存在");
}
System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);
//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点
if(node.next != null) {
printNode(node.next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
SmallEqualBig_02 test = new SmallEqualBig_02();
System.out.println("排序前的节点");
printNode(head1);
System.out.println("=================");
Node n2 = test.sort(head1);
printNode(n2);
}
}
面试用:
package code03.链表_01;
//将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
public class SmallEqualBig_03 {
static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//笔试用, 不借助任何的新对象,纯粹借住现有的链表结构进行操作
public Node sort(Node node, int povit) {
Node maxStart = null;
Node maxEnd = null;
Node minStart = null;
Node minEnd = null;
Node equalStart = null;
Node equalEnd = null;
while (node != null) {
if(node.value < povit) {
if (minStart == null) {
minStart = node;
minEnd = node;
}
else {
minEnd.next = node;
minEnd = node;
}
}
else if(node.value > povit) {
if (maxStart == null) {
maxStart = node;
maxEnd = node;
}
else {
maxEnd.next = node;
maxEnd = node;
}
}
else {
if (equalStart == null) {
equalStart = node;
equalEnd = node;
}
else {
equalEnd.next = node;
equalEnd = node;
}
}
node = node.next;
}
if (minEnd != null) {
if (equalStart != null) {
minEnd.next = equalStart;
equalEnd.next = null;
}
else if (maxStart != null) {
minEnd.next = maxStart;
maxEnd.next = null;
}
}
if (equalEnd != null){
if (maxStart != null) {
equalEnd.next = maxStart;
maxEnd.next = null;
}
else
{
equalEnd.next = null;
}
}
return minStart != null ? minStart : equalStart != null ? equalStart : maxStart;
}
public static void printNode (Node node) {
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("链表不存在");
}
System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);
//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点
if(node.next != null) {
printNode(node.next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
SmallEqualBig_03 test = new SmallEqualBig_03();
System.out.println("排序前的节点");
printNode(head1);
System.out.println("=================");
Node n2 = test.sort(head1, 5);
printNode(n2);
}
}
题目3:
一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
Node(int val) { value = val; }
}
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。
给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点 head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
【要求】
时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
package code03.链表_01;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
* class Node {
* int value;
* Node next;
* Node rand;
* Node(int val) { value = val; }
* }
* rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。
* 给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点 head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
* 【要求】
* 时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
*
* 解题思路:
* 1. 借助系统容器,逐个深拷贝每个指针对象,然后将拷贝的指针串成新指针返回 (笔试用)
*
* 2.深拷贝每个指针对象,并且串联进当前的指针当中,然后将当前链表进行切割,生成新链表并返回(面试用)
*/
public class DeepCopyNode_04
{
static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
}
//借助系统容器,笔试用(快准稳)
public Node deepCopy1 (Node node)
{
//额外空间复杂度O(1), 此处只生成了一个map对象
//而深拷贝N个指针,是题目本身就要求的事情,因此可以忽略题目要求的O(N)空间复杂度
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
//深拷贝每个node
Node cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
Node n = new Node(cur.value);
map.put(cur, n);
cur = cur.next;
}
//构造新链表
cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);
cur = cur.next;
}
return (Node) map.get(node);
}
//纯链表实现,面试用
public Node deepCopy2 (Node node)
{
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
Node cur = node;
//假设链表为1-2-3 拷贝完以后就是 1-1-2-2-3-3
while (cur != null) {
//深拷贝
Node n = new Node(cur.value);
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = n;
n.next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = node;
Node copy = cur.next;
//rand有可能是后面指向前面,所以不能提前断开,否则找不到copy后后面的指针对象的rand
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) { //cur.next != null等价于copy != null
//假设 b 是copy a的节点,那么b的rand节点肯定就在a.rand节点后面
copy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;
cur = cur.next.next; //等价于cur = copy.next
copy = cur != null ? cur.next : null;
}
//最后分离
cur = node;
copy = cur.next;
Node ans = copy;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
Node curNext = cur.next.next;
Node copyNext = curNext != null ? curNext.next : null;
cur.next = curNext;
copy.next = copyNext;
cur = curNext;
copy = copyNext;
}
return ans;
}
public static void printNode (Node node) {
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("链表不存在");
}
System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);
System.out.println("当前链表的random值为: " + (node.rand == null ? null : node.rand.value));
//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点
if(node.next != null) {
printNode(node.next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.rand = head1.next.next.next.next;
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head1;
DeepCopyNode_04 test = new DeepCopyNode_04();
Node n = test.deepCopy1(head1);
printNode(n);
System.out.println("==================");
Node n2 = test.deepCopy2(head1);
printNode(n2);
}
}
题目4:给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
package code03.链表_01;
/**
* 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
*
* 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。
* 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。
* 注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
*
* 如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
* 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle
*/
public class LoopNode_05 {
static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode node)
{
//需要使用快慢指针
if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast = node.next.next;
ListNode slow = node.next;
//跳出当前循环
//1) fast == slow 循环链表
//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//无环链表
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
题目5:给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
package code03.链表_01;
/**
* 给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
*
* 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。
* 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。
* 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
* https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
*/
public class LoopNode_05_2
{
static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode node)
{
//需要使用快慢指针
if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = node.next.next;
ListNode slow = node.next;
//跳出当前循环
//1) fast == slow 循环链表
//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//无环链表
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
//有环链表
fast = node;
//备注1: 找出第一个相交节点,此处根据数据推导公式得出
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//返回fast 或 slow 都对
return fast;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(7);
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(9); head1.next = head2;
ListNode head3 = new ListNode(1); head2.next = head3;
ListNode head4 = new ListNode(8); head3.next = head4;
ListNode head5 = new ListNode(5); head4.next = head5;
ListNode head6 = new ListNode(6); head5.next = head6;
ListNode head7 = new ListNode(5); head6.next = head7;
LoopNode_05_2 loop = new LoopNode_05_2();
//测试无环
ListNode loopNode = loop.detectCycle(head1);
System.out.println((loopNode != null ? loopNode.value : "null"));
//测试有环
head7.next = head4; // head4作为环形链表的第一个值
ListNode loopNode2 = loop.detectCycle(head1);
System.out.println("第一个入环节点的值为: " + (loopNode2 != null ? loopNode2.value : "null"));
}
}
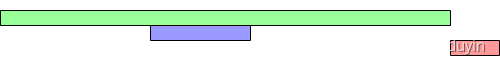
此处,需要对代码中的 “备注1” 进行解释一下,为什么fast = node; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next;} 当 fast = slow的时候,fast或slow就是相交的第一个节点? 不理解这一点,下面的题目无法继续进行下去

由此图,我们可知: 快指针从A点重新出现,跑了x距离。 那么慢指针就是跑 N圈额外加z一段距离,此时他们正好会在第一个相交的节点相遇。
题目6:给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
package code03.链表_01;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
* 题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
* https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
*
*/
public class DoubleLoopNodes_06
{
static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//借助java系统提供的容器
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
Map<ListNode, ListNode> map = new HashMap();
ListNode cur = headA;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur != null) {
if (map.containsKey(cur)) {
return map.get(cur);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//纯链表实现
public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = headA;
int n = 0;
while (cur != null) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur != null) {
n--;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表
ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n > 0) {
lNode = lNode.next;
n--;
}
//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同
while (lNode != sNode) {
lNode = lNode.next;
sNode = sNode.next;
if(lNode == null || sNode == null) {
return null;
}
}
return lNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//链表1
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);
//链表2
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(2);
//相交节点
ListNode node6 = new ListNode(8);
ListNode node7 = new ListNode(7);
ListNode node8 = new ListNode(3);
node1.next = node2; node2.next = node6; node6.next = node7; node7.next = node8;
node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5; node5.next = node6;
DoubleLoopNodes_06 test = new DoubleLoopNodes_06();
ListNode n1 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);
System.out.println("相交节点的值为 :" + (n1 != null ? n1.value : null));
ListNode n2 = test.getIntersectionNode2(node1, node3);
System.out.println("相交节点的值为 :" + (n2 != null ? n2.value : null));
}
}
说了这么多,终极大boss终于要登场了。
题目7:给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null
【要求】
如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度 请达到O(1)
解题思路:根据排除所得,要么两条链表无环相交,要么有环相交,只存在这两种情况
package code03.链表_01;
/**
* 给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null
* 【要求】
* 如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度 请达到O(1)。
*
* 解题思路:根据排除所得,要么两条链表无环相交,要么有环相交,只存在这两种情况
*/
public class DoubleLoopNodes_06_2
{
static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//获取单链表相交的第一个节点,不想交则返回null
public ListNode getLoopNode(ListNode node)
{
//需要使用快慢指针
if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = node.next.next;
ListNode slow = node.next;
//跳出当前循环
//1) fast == slow 循环链表
//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//无环链表
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
//有环链表
fast = node;
//备注1: 找出第一个相交节点,此处根据数据推导公式得出
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//返回fast 或 slow 都对
return fast;
}
//两个都没有循环链表的相交节点
public ListNode bothNoCycleNodes(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = headA;
int n = 0;
while (cur != null) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur != null) {
n--;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表
ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n > 0) {
lNode = lNode.next;
n--;
}
//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同
while (lNode != sNode) {
lNode = lNode.next;
sNode = sNode.next;
if(lNode == null || sNode == null) {
return null;
}
}
return lNode;
}
public ListNode bothCycleNodes(ListNode headA, ListNode loopA, ListNode headB, ListNode loopB)
{
//2种情况: 环外相交,正好第一个相交节点相交。 这种情况可以视为2个无环链表相交
if (loopA == loopB) {
int n = 0;
ListNode cur = headA;
while (cur != loopA) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = headB;
while (cur != loopB) {
n--;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表
ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n > 0) {
lNode = lNode.next;
n--;
}
//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同
while (lNode != sNode) {
lNode = lNode.next;
sNode = sNode.next;
}
return lNode;
}
else { //环内相交
ListNode cur1 = loopA.next;
while (cur1 != loopA) { //如果跑一圈都没找到相交节点,则无相交节点
if (cur1 == loopB) { //中途找到了相交节点
return loopB; //返回loopA 或 loopB 都行。 环内相交,说不清谁是第一个
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;
}
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode node1, ListNode node2)
{
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode loopNode1 = getLoopNode(node1);
ListNode loopNode2 = getLoopNode(node2);
ListNode ansNode = null;
if (loopNode1 == null && loopNode2 == null) { //两个都没有环的节点
ansNode = bothNoCycleNodes(node1, node2);
}
else if (loopNode1 != null && loopNode2 != null) { //两个环形链表相交
ansNode = bothCycleNodes(node1,loopNode1, node2,loopNode2);
}
return ansNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("================测试2个无环聊表相交===========================");
//链表1
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);
//链表2
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(2);
//相交节点
ListNode node6 = new ListNode(8);
ListNode node7 = new ListNode(7);
ListNode node8 = new ListNode(3);
node1.next = node2; node2.next = node6; node6.next = node7; node7.next = node8;
node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5;
DoubleLoopNodes_06_2 test = new DoubleLoopNodes_06_2();
//不相交
ListNode m1 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);
System.out.println("无环 不相交 :" + (m1 != null ? m1.value : null));
//相交
node5.next = node6;
ListNode m2 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);
System.out.println("无环 相交节点的值为 :" + (m2 != null ? m2.value : null));
System.out.println("================测试2个环形链表 环外 相交===========================");
//链表1
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(1);
//链表2
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(2);
//相交节点
ListNode n6 = new ListNode(8);
ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);
ListNode n8 = new ListNode(3);
n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n2;
n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n6;
ListNode m3 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n5);
System.out.println("有环 不相交 :" + (m3 != null ? m3.value : null)); //不相交
n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n3;
n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n3;
ListNode m4 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);
System.out.println("有环 第一个相交点相交 :" + (m4 != null ? m4.value : null)); //n3对应的值是5
n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n3;
n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n2;
ListNode m5 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);
System.out.println("有环 环外相交 :" + (m5 != null ? m5.value : null)); //n2对应的值是1
System.out.println("================测试2个环形链表 环内 相交===========================");
n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n4;
ListNode m6 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);
System.out.println("有环 环外相交 :" + (m6 != null ? m6.value : null)); //n2对应的值是1 n4对应6
}
}
![推荐系统[三]:粗排算法常用模型汇总(集合选择和精准预估),技术发展历史(向量內积,WideDeep等模型)以及前沿技术](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b935ff75e3e84d7f88de39613bb02bad.png)