Linux环境中实现并发TCP/IP服务器。多线程在解决方案中提供了并发性。由于并发性,它允许多个客户端同时连接到服务器并与服务器交互。
Linux多线程编程概述
许多应用程序同时处理多项杂务。服务器应用程序处理并发客户端;交互式应用程序通常在处理后台计算时处理用户输入;计算密集型应用程序利用多个处理器的功能。共同的主题是使用多个控制线程来提供处理并发活动的上下文,无论是在一个处理器上多路复用、在多个处理器上并行执行,还是利用具有“超线程技术”的处理器以及AMD和Intel的新双核处理器的设施。
协调这些线程的执行涉及同步对共享数据结构的访问,确保程序行为良好且具有确定性,而不管其组件线程的相对执行速度如何。多线程程序和单线程程序一样,必须处理异常和与外界的交互。尽管在这样的程序中可能有许多并发活动,但程序作为一个整体应该对这样的外部输入做出清晰的响应。
线程的实现方式有很多种,包括用户级库、内核和各种组合。大多数Linux实现目前将每个线程视为使用克隆系统调用创建的单独进程(尽管每个线程都与其队列共享其地址空间)。
C/C++ 多线程并发服务器知识点
- 多线程并发服务器思路
1. socket(),创建监听套接字
2. bind(),绑定监听套接字
3. setsockopt(),设置端口复用
4. listen(),监听状态,用来被动接受来自其他主动套接字的连接请求,并设置监听上限
5. pthread_attr_init()、pthread_attr_setdetachstate()、pthread_create(),在创建时指定属性
6. pthread_rwlock_wrlock()、pthread_rwlock_unlock(),并发程序引起的共享内存问题
...
Linux C/C++ 多线程TCP/UDP服务器 (监控系统状态)
目的:使用TCP/IP实现多线程客户端服务器。它允许多个客户端同时连接到服务器并与服务器交互。处理多线程TCP/UDP服务器监控系统状态:监控CPU负载、RAM使用情况、磁盘空间使用情况和可用网络接口。
服务器:
启动服务器并接受来自客户端的连接。在接受客户机连接后,它分派一个线程与客户机交互。
...
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 4)
{
printf ("Usage: %s <TCP/UDP> <port> <max_connections>\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if (strncmp ("TCP", argv[1], 3) == 0)
{
printf ("Using TCP");
protocol = TCP;
}
else if (strncmp ("UDP", argv[1], 3) == 0)
{
printf ("Using UDP");
protocol = UDP;
}
else
{
printf ("Unknown protocol: %s\n", argv[1]);
printf ("Usage: %s <TCP/UDP> <port> <max_connections>\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
const int port = atoi (argv[2]);
if (!port)
{
printf ("Wrong port number: %s\n", argv[2]);
printf ("Usage: %s <TCP/UDP> <port> <max_connections>\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
const int max_connections = atoi (argv[3]);
if (!max_connections)
{
printf ("Wrong max_connections number: %s\n", argv[3]);
printf ("Usage: %s <TCP/UDP> <port> <max_connections>\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
printf (" on port %i with no more than %i clients\n", port, max_connections);
/* Assign signal handlers to signals. */
if (signal (SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN) == SIG_ERR)
{
perror ("signal");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (signal (SIGTERM, signal_handler) == SIG_ERR)
{
perror ("signal");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (signal (SIGINT, signal_handler) == SIG_ERR)
{
perror ("signal");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pthread_attr_t pthread_attr;
pthread_arg_t *pthread_arg;
pthread_t pthread;
//为属性对象分配了动态内存空间
if (pthread_attr_init (&pthread_attr) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_attr_init");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//设置线程分离状态
if (pthread_attr_setdetachstate (&pthread_attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_attr_setdetachstate");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 开始观测
//指定已初始化的读写锁
pthread_rwlock_init (&rwlock, NULL);
if (pthread_create (&pthread, &pthread_attr, pthread_sysinfo, NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct addrinfo hints;
struct addrinfo *result, *rp;
int socket_fd;
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_family = AF_UNSPEC;
hints.ai_socktype = (protocol == TCP) ? SOCK_STREAM : SOCK_DGRAM;
hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE;
hints.ai_protocol = 0;
hints.ai_canonname = NULL;
hints.ai_addr = NULL;
hints.ai_next = NULL;
int s = getaddrinfo(NULL, argv[2], &hints, &result);
if (s != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo: %s\n", gai_strerror(s));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (rp = result; rp != NULL; rp = rp->ai_next)
{
socket_fd = socket(rp->ai_family, rp->ai_socktype,
rp->ai_protocol);
if (socket_fd == -1)
continue;
if (bind(socket_fd, rp->ai_addr, rp->ai_addrlen) == 0)
break; /* Success */
close (socket_fd);
}
if (rp == NULL) /* No address succeeded */
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not bind\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
freeaddrinfo (result);
if (protocol == UDP)
{
struct timeval timeout = {5, 0};
//设置端口复用
setsockopt (socket_fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVTIMEO, (char*)&timeout, sizeof(struct timeval));
for (;; udp_reply (socket_fd));
}
if (listen (socket_fd, BACKLOG) == -1)
{
perror ("listen");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while (protocol == TCP)
{
pthread_arg = (pthread_arg_t *) malloc (sizeof *pthread_arg);
if (!pthread_arg)
{
perror ("malloc");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
socklen_t client_address_len = sizeof pthread_arg->client_address;
int tcp_socket_fd = accept (socket_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&pthread_arg->client_address,
&client_address_len);
connections++;
if (tcp_socket_fd == -1)
{
perror ("accept");
free (pthread_arg);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (connections > max_connections)
{
close (tcp_socket_fd);
connections--;
free (pthread_arg);
continue;
}
printf ("New TCP connection accepted: now there are %i clients\n", connections);
pthread_arg->new_socket_fd = tcp_socket_fd;
if (pthread_create (&pthread, &pthread_attr, pthread_routine_tcp, (void *)pthread_arg) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
free (pthread_arg);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
return 0;
}
...
void *pthread_sysinfo ()
{
char *s = system_state_report ();
strcpy (system_state, s);
free (s);
for (;;)
{
if (connections > 0 || protocol == UDP)
{
s = system_state_report ();
pthread_rwlock_wrlock (&rwlock);
strcpy (system_state, s);
pthread_rwlock_unlock (&rwlock);
free (s);
}
}
return NULL;
}
void signal_handler (int signal_number)
{
/* Exit cleanup code here. */
// close (socket_fd);
exit (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
...
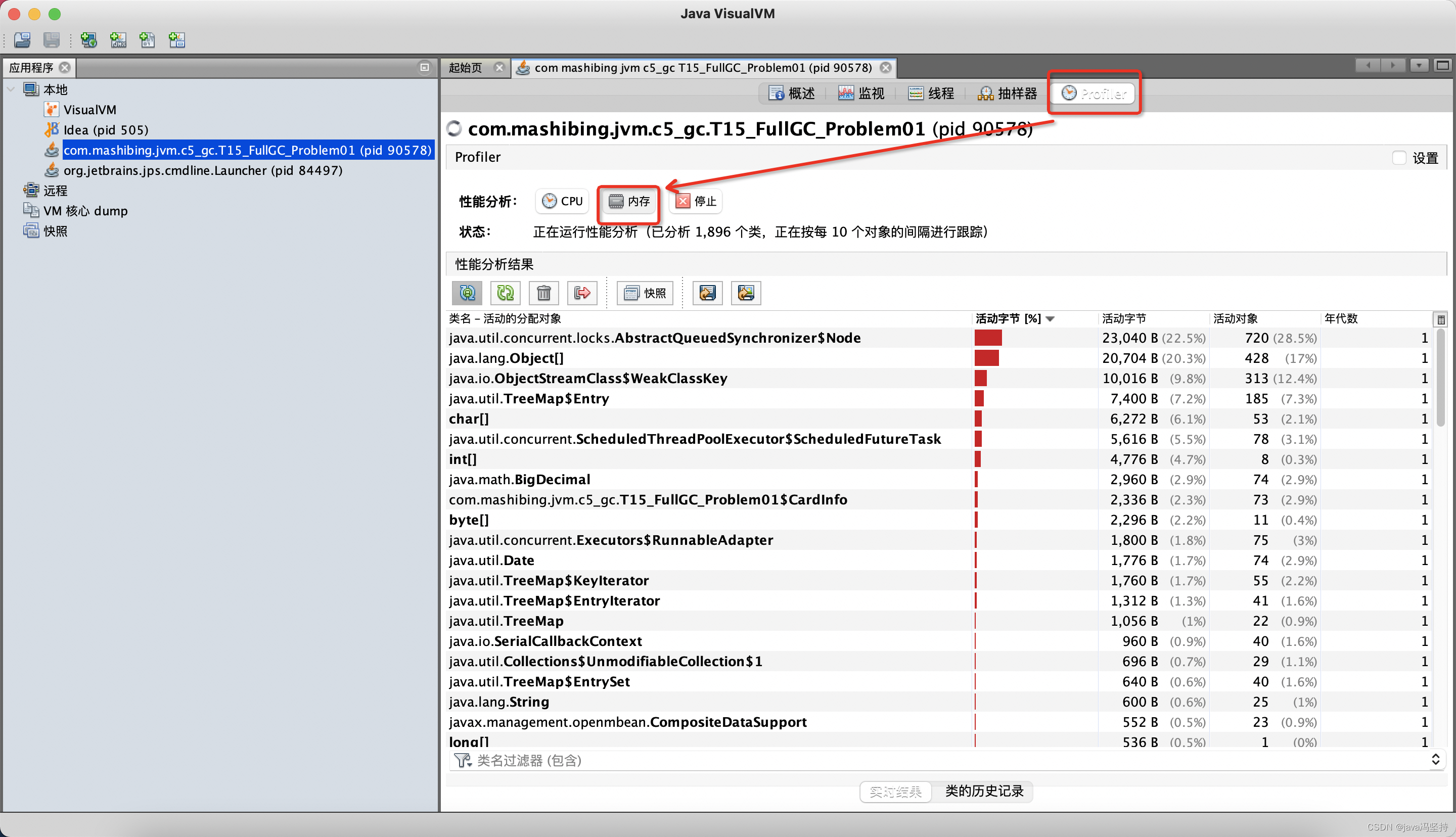
char *system_state_report ()
{
json_t *root = json_loads (BLANC_JSON_REPORT, 0, NULL);
cpu_usage (json_object_get(root, "CPU, %"));
ram_usage (json_object_get(root, "RAM"));
storage_usage (json_object_get(root, "Storage"));
net_usage (json_object_get(root, "Network"));
time_stamp (root);
char *s = json_dumps (root, 0);
json_decref (root);
return s;
}
int cpu_usage (json_t *cpu_state)
{
char buff[TXT_BUFFER_SIZE][TXT_BUFFER_SIZE];
int ncpu = get_nprocs ();
FILE* fp = fopen(STAT_PATH,"r");
for (int i = 0; i < ncpu + 1; i++)
{
fgets(buff[i], TXT_BUFFER_SIZE, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
sleep(TIME_LAG);
fp = fopen(STAT_PATH,"r");
for (int i = 0; i < ncpu + 1; i++)
{
fgets(buff[i + ncpu + 1], TXT_BUFFER_SIZE, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
for (int i = 0; i < ncpu + 1; i++)
{
long long sum = 0, lastSum = 0;
long long idle, lastIdle;
char* token = strtok(buff[i], " ");
for (int col = 0; token != NULL;)
{
token = strtok (NULL, " ");
if (token != NULL)
{
lastSum += atoll (token);
if (col == 3)
lastIdle = atoll (token);
col++;
}
}
...
int cpu_usage_pct = (1000 *((sum - lastSum) - (idle - lastIdle)) / (sum - lastSum) + 5) / 10;
json_t *json_cpu_pct;
json_cpu_pct = json_integer(cpu_usage_pct);
json_array_append (cpu_state, json_cpu_pct);
json_decref (json_cpu_pct);
}
return 0;
}
...
客户端:
与服务器交互。通常,会使用write将消息中的消息发送到服务器,并使用read从服务器接收消息并将其存储在消息中。
...
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
if (argc < 4)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Usage: %s <host> <port> <update_time (seconds)>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
const int time_lag = atoi (argv[3]);
if (!time_lag)
{
fprintf( stderr, "Impossible time lag: %s\n", argv[3]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_family = AF_UNSPEC; /* Allow IPv4 or IPv6 */
hints.ai_socktype = 0; /* Any type: TCP/UDP */
hints.ai_flags = 0;
hints.ai_protocol = 0; /* Any protocol */
s = getaddrinfo(argv[1], argv[2], &hints, &result);
if (s != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "getaddrinfo: %s\n", gai_strerror(s));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (rp = result; rp != NULL; rp = rp->ai_next)
{
sfd = socket(rp->ai_family, rp->ai_socktype,
rp->ai_protocol);
if (sfd == -1)
continue;
if (connect(sfd, rp->ai_addr, rp->ai_addrlen) != -1)
break;
close(sfd);
}
if (rp == NULL)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Could not connect to server %s at port: %s\n", argv[1], argv[2]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
freeaddrinfo(result);
// Server interaction.
for (;; sleep (time_lag))
{
char msg[BUF_SIZE];
char s[BUF_SIZE];
bzero (msg, BUF_SIZE);
write (sfd, "report", 6);
int server_response = read (sfd, msg, BUF_SIZE);
if (server_response <= 0)
{
printf ("Connection is closed by server\n");
break;
}
status (msg, s);
printf ("%s\n", s);
}
...
}
int status (const char *src, char *report)
{
...
int ncpu = json_array_size (cpu_status);
int tot_cpu_usage = json_integer_value (tot_cpu_load);
char buff[BUF_SIZE];
sprintf (report, "Total usage of %2i CPUs: %3i%%, ", ncpu - 1, tot_cpu_usage);
int mem_tot = json_integer_value (json_object_get (ram_status, "Total" ));
int mem_free = json_integer_value (json_object_get (ram_status, "Free" ));
int mem_buff = json_integer_value (json_object_get (ram_status, "Buffers"));
int mem_cach = json_integer_value (json_object_get (ram_status, "Cached" ));
int mem_not_used = mem_free + mem_buff + mem_cach;
int mem_used = mem_tot - mem_not_used;
sprintf(buff, "Memory: %.1f MB used, %.1f MB free", mem_used/1024.0, mem_not_used/1024.0);
...
}
If you need the complete source code, please add the WeChat number (c17865354792)
运行结果:
打开两个客户端连接服务器,最后再同时断开连接服务器。


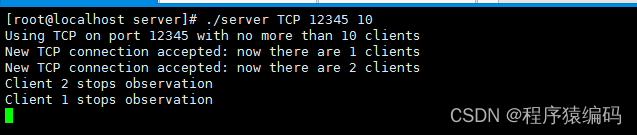
在客户端的请求消息报告中,作为响应,服务器给出系统当前状态的描述。
总结
多线程在解决方案中提供了并发性。由于并发性,客户端不必等待轮到他们,可以立即得到服务。当服务器有一个线程来处理新连接。接受这样的连接后,将创建一个新线程,负责与给定客户端的所有通信。最后要讲的是,熟悉多线程编程是一项重要的个人技能,只有掌握了多线程编程,才能更合理地选择使用或不使用多线程。
Welcome to follow WeChat official account【程序猿编码】