目录
- 首页(Cluster)
- 节点信息
- Scheduler Metrics:集群调度信息
- 节点信息详解(Nodes)
- 应用列表信息(applications)
- 队列详情页(Scheduler)
- 指标详细说明(非常重要)
首页(Cluster)

集群监控信息指标详解
- Apps Submitted:已提交的应用
- Apps Completed:已完成的应用
- Apps Running:正在运行的应用
- Containers Running:正在运行的容器
- Memory Total:集群总内存,大小等于所有的NodeManager管理的内存之和
<property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name> <value>8192</value> <description>表示这个NodeManager管理的内存大小</description> </property> - Memory Used:已使用内存
- VCores Total:集群 CPU 总核数, 等于所有的NodeManager管理的虚拟核心之和
<property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores</name> <value>8</value> <description>表示这个NodeManager管理的虚拟核心个数</description> </property> - VCores Used:已使用的 CPU 核数
- Memory Reserved:预留的内存
- VCores Reserved:预留的 CPU 核数
VCores Reserved 和 Memory Reserved的存在逻辑
资源预留发生在应用向Yarn进行资源申请的时候。yarn的资源预留机制是一种资源保证机制,它发生在应用程序申请的资源无法得到满足的时候。即,当应用程序申请的资源此刻无法满足但是未来只要有一定的资源释放就可以得到满足的情况下,yarn会面临两种选择:
-
优先为这个应用程序预留一个节点上的资源,直到累计释放的空闲资源满足了应用的需求。这种资源的分配方式叫做增量资源分配,即Incremental placement;
-
暂时放弃当前节点资源,直到某个节点的资源一次性满足应用程序的需求。这种分配方式叫做一次性资源分配,即all-or-nothing;
两种分配方式各有优缺点,对于增量资源分配而言,资源预留机制会导致资源浪费,集群资源利用率低,而一次性资源分配虽然在发现资源无法满足某个应用需求的时候及时放弃,但是,这个应用有可能永远得不到自己请求的资源因而永远无法运行,即饿死现象;
因此,yarn最终还是采用了增量资源分配机制,尽管会造成一定的资源浪费,但是不会出现饿死现象,大小应用都有平等的运行机会;
Yarn的一次资源预留,精确来讲,是将 某一个container 在 某个服务器节点上 做资源预留;它发生在服务器节点的可用资源无法满足container所需要的资源的情况下。
YARN 实际的总内存为:Memory Total + Memory Reserved = 所有节点的(Mem Used + Mem Avail)之和
节点信息
- Active Nodes:当前集群存活的节点个数,(其实就是NodeManager的个数)
- Decommissioned Nodes:集群退役的节点个数
- Lost Nodes:集群丢失的节点个数
- Unhealthy Nodes:集群运行状况不良的节点个数
- Rebooted Nodes:集群重启的节点个数
Scheduler Metrics:集群调度信息
- Scheduler Type:集群使用的调度器类型(Apache默认Capacity CDH默认是Fair)
- Scheduling Resource Type:调度器资源类型内存
- Minimum Allocation:一个作业的最小内存为1G和1cpu核
- Maximum Allocation:一个作业的最大内存为8G和4cpu核
节点信息详解(Nodes)
Yarn 的集群节点的情况,从 Active Nodes 下面的数字点击进去,可以看到具体的节点列表信息。里面包含了所在机架、运行状态、节点地址、最后健康上报上报时间、运行的容器个数、使用内存CPU 等信息,还有版本号。如下图。

- Node Lables:节点标签,通过对节点打标签,可以控制任务运行在特定类型的标签节点上
- Rack:机架,可以通过机架感知机制与配置
- Node State:节点状态信息,Running表示运行正常
- Node Address: NodeManager的ip地址和访问端口
- Node HTTP Address:NodeManager的web应用HTTP访问地址
- Last health-update:节点健康汇报时间
- Health-report:心跳报告的存储路径
- Containers:节点内正在运行的Containers个数
- Mem Used:节点已用内存
- Mem Avail:节点可用的总内存(默认是8G yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb配置)
- Vcore Used:节点正在运行作业所占用的CPU核数
- Vcores Avail:节点可用的总虚拟CPU核数(yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores配置)
应用列表信息(applications)

包括以下内容:
- 任务的ID
- 任务的名字
- 应用的类型和所在队列
- 任务的开始、启动时间和结束时间
- 任务当前的状态和最终状态。
- 任务占用的相关资源。
- 任务的应用类型主页。如果是 spark 任务的话,显示的是 spark 的 ui 页面

Aggregate Resource Allocation是在org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.SchedulerApplicationAttempt类中进行计算的,主要逻辑如下:
// 资源信息更新间隔:3秒
private static final long MEM_AGGREGATE_ALLOCATION_CACHE_MSECS = 3000;
// 最后更新时间、最后更新时的每秒的内存和CPU使用量
protected long lastMemoryAggregateAllocationUpdateTime = 0;
private long lastMemorySeconds = 0;
private long lastVcoreSeconds = 0;
/**
* 返回任务拥有的所有container每秒所消耗的资源(内存、CPU)总和
* @return
*/
synchronized AggregateAppResourceUsage getRunningAggregateAppResourceUsage() {
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Don't walk the whole container list if the resources were computed
// recently.
// 判断是否达到更新条件:当前时间 - 最后更新时间 > 最大更新间隔(3秒)
if ((currentTimeMillis - lastMemoryAggregateAllocationUpdateTime)
> MEM_AGGREGATE_ALLOCATION_CACHE_MSECS) {
long memorySeconds = 0;
long vcoreSeconds = 0;
// 迭代所有的container,计算每个container每秒所消耗的资源(内存、CPU)
for (RMContainer rmContainer : this.liveContainers.values()) {
// 获取container的运行时间
long usedMillis = currentTimeMillis - rmContainer.getCreationTime();
// 计算container每秒所消耗的资源(内存、CPU)
Resource resource = rmContainer.getContainer().getResource();
// 汇总内存和CPU使用量
memorySeconds += resource.getMemory() * usedMillis /
DateUtils.MILLIS_PER_SECOND;
vcoreSeconds += resource.getVirtualCores() * usedMillis
/ DateUtils.MILLIS_PER_SECOND;
}
// 记录最后更新任务资源使用情况的时间、任务最后每秒使用的内存和CPU数量
lastMemoryAggregateAllocationUpdateTime = currentTimeMillis;
lastMemorySeconds = memorySeconds;
lastVcoreSeconds = vcoreSeconds;
}
return new AggregateAppResourceUsage(lastMemorySeconds, lastVcoreSeconds);
}
/**
* 返回任务使用的资源情况
* @return
*/
public synchronized ApplicationResourceUsageReport getResourceUsageReport() {
AggregateAppResourceUsage resUsage = getRunningAggregateAppResourceUsage();
// 返回任务所使用的资源情况:所使用的container数量、预留的container数量、当前消耗的资源、当前预留的资源、所需的总资源(当前消耗的资源+当前预留的资源)、每秒的内存和CPU使用量
return ApplicationResourceUsageReport.newInstance(liveContainers.size(),
reservedContainers.size(), Resources.clone(currentConsumption),
Resources.clone(currentReservation),
Resources.add(currentConsumption, currentReservation),
resUsage.getMemorySeconds(), resUsage.getVcoreSeconds());
}
点击到 appattempt_xxx 详情页,能看到任务申请的所有container,一般01_0000001 是代表ApplicationMaster的容器,还可以看到详细的日志信息。
队列详情页(Scheduler)
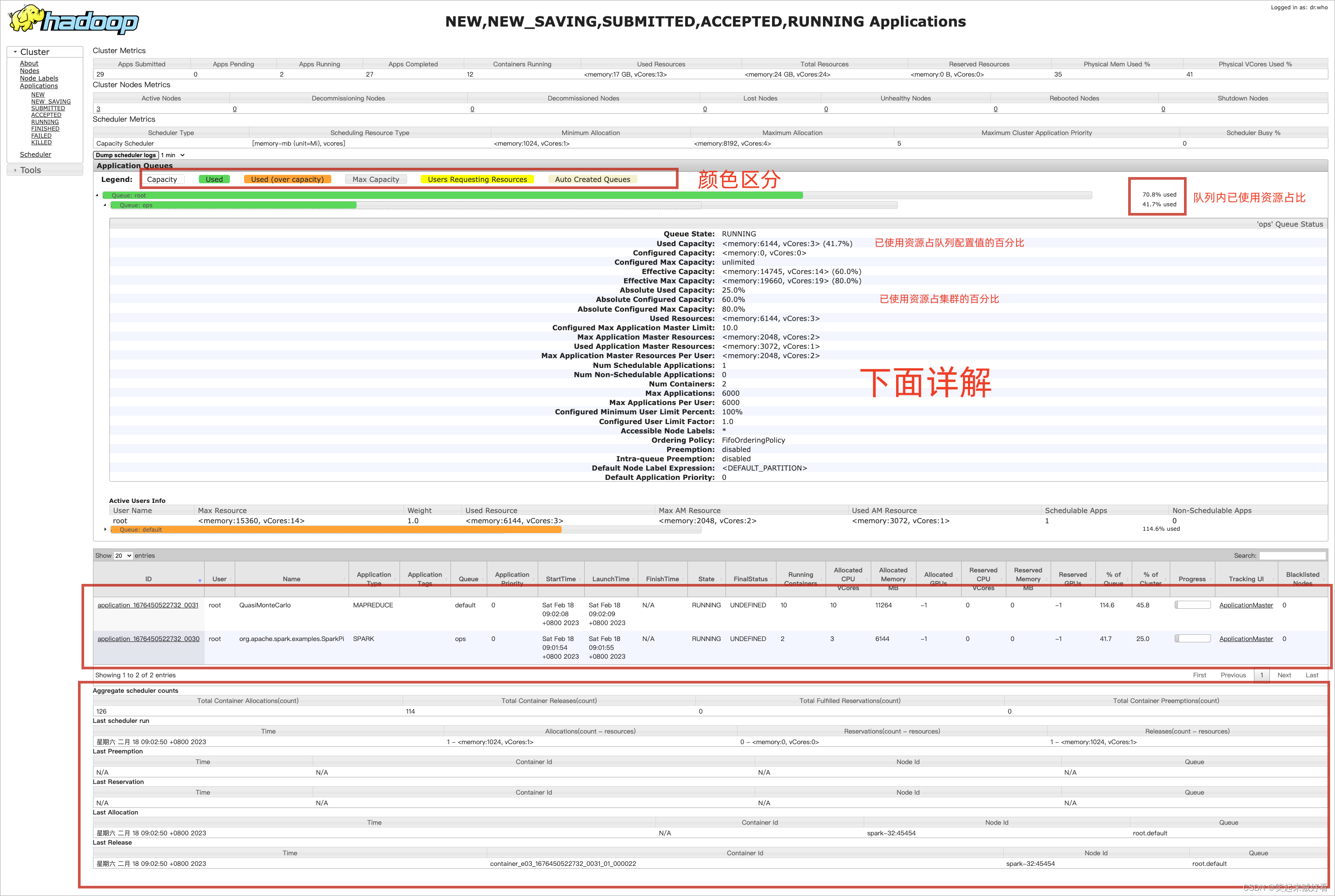
指标详细说明(非常重要)
可 参考 另外一篇 队列资源配置详解 YARN容量调度器多队列配置详解实战
- Queue State:队列运行状态,Running表示正常运行
- Used Capacity:已使用资源占队列配置值的百分比
- Configured Capacity:配置该队列容量(绝对资源容量)yarn.scheduler.capacity..capacity
- Configured Max Capacity:配置该队列最大可使用容量(绝对资源容量)yarn.scheduler.capacity..maximum-capacity
- Effective Capacity:配置该队列有效容量,通过(yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.{queue}.capacity)配置
- Effective Max Capacity:有效最大容量,通过(yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.{queue}.maximum-capacity)配置
- Absolute Used Capacity:已使用资源占集群的百分比
- Absolute Configured Capacity:队列资源容量的百分比
- Absolute Configured Max Capacity:队列资源容量的最大百分比
- Used Resources:已使用的memory和CPU
- Configured Max Application Master Limit:对用户使用队列的最大资源比例进行限制
- Max Application Master Resources:该queue能使用的最大的内存和core
- Used Application Master Resources:该queue已经被使用的内存和core
- Max Application Master Resources Per User:每个user最多可以使用该queue的最大内存和core
- Num Schedulable Applications:正在被调度的app应用个数
- Num Non-Schedulable Applications:没有被调度的app应用个数
- Num Containers:已启用的container容器数量
- Max Applications:最多可以运行的任务数量,配置项:yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-applications
- Max Applications Per User:每个user最多可以运行的任务数量
- Configured Minimum User Limit Percent:每个user最多可以使用队列资源的百分比
- Configured User Limit Factor:队列中的用户允许占用队列值的多少,默认值是0.0~1,如果将值设置为1,它代表:最大可以占用整个队列资源,如果将值设置为2,它代表:允许队列所占资源增长到最多为队列容量的两倍,配置项:yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.ops.user-limit-factor
- Accessible Node Labels:
- Ordering Policy:
- Preemption:
- Intra-queue Preemption:
- Default Node Label Expression:
- Default Application Priority:
希望对正在查看文章的您有所帮助,记得关注、评论、收藏,谢谢您








![[架构之路-110]-《软考-系统架构设计师》-软件架构设计-3-架构描述语言ADL与UML](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b201118048b68b678cecb7f56f530af0.png)