2 反射
2.1 反射概述
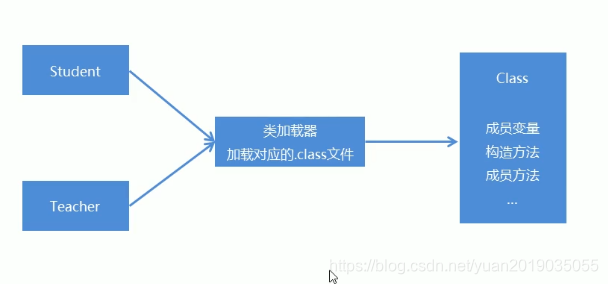
- Java反射机制:是指在运行时去获取一个类的变量和方法信息。然后通过获取到的信息来创建对象,调用方法的一种机制。由于这种动态性,可以极大的增强程序的灵活性,程序不用在编译期就完成确定,在运行期仍然可以扩展
2.2 反射获取Class类的对象
- 我们要想通过反射去使用一个类,首先我们要获取到该类的字节码文件对象,也就是类型为Class类型的对象这里我们提供三种方式获取Cass类型的对象
-
1、使用类的class属性来获取该类对应的Class对象。举例:
Student.class将会返回Student类对应的Class对象 -
2、调用对象的
getClass()方法, 返回该对象所属类对应的Class对象
该方法是Object类中的方法,所有的Java对象都可以调用该方法 -
3、使用Class类中的静态方法
forName(StringclassName), 该方法需要传入字符串参数,该字符串参数的值是某个类的全路径,也就是完整包名的路径
-
package test;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1、使用类的class属性来获取该类对应的Class对象
Class<Student> c1 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c1); //class test.Student
Class<Student> c2 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c1 == c2); //true;一个类只有一个字节码文件对象
//2、调用对象的getClass()方法, 返回该对象所属类对应的Class对象
Student s = new Student();
Class<? extends Student> c3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(c1 == c3); //true
//3、使用Class类中的静态方法forName(StringclassName)
Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("test.Student");
System.out.println(c1 == c4); //true
}
}
2.3 反射获取构造方法并使用
- Class类中用于获取构造方法的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() | 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组 |
Constructor<?> [] getDeclaredConstructors [dɪˈkleəd] | 返回所有构造方法对象的数组 |
Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>...parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共构造方法对象 |
Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?> ...parameterTypes) | 返回单个构造方法对象 |
- Constructor类中用来创建对象的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| T newInstance(Object…initargs) | 根据指定的构造方法创建对象 |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//1,Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组
Constructor<?>[] cons1 = c.getConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons1) {
System.out.println(con);
// public test.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
// public test.Student()
}
System.out.println("--------");
//2,Constructor<?> [] getDeclaredConstructors 返回所有构造方法对象的数组
Constructor<?>[] cons2 = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons2) {
System.out.println(con);
// public test.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
// test.Student(java.lang.String,int)
// private test.Student(java.lang.String)
// public test.Student()
}
System.out.println("--------");
/*
一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
二、c调用getConstructors()得到单个的构造方法对象con1
三、通过con1调用newInstance()创建一个对象,这就叫反射*/
//3,Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>...parameterTypes) 返回单个公共构造方法对象
//参数是:你要获得的构造方法的参数个数和数据类型对应字节码文件
Constructor<?> con1 = c.getConstructor();
//Constructor提供了一个类的单个构造方法信息和访问权限
//5,T newInstance(Object…initargs) 根据指定的构造方法创建对象
Object obj1 = con1.newInstance();
System.out.println(obj1); //Student{name='null', age=0, address='null'}
}
}
- 案例1:

package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给Class类的forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//public Student(String name, int age, String address)
// 二、c调用getConstructor()得到单个的构造方法对象con1
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class);//基本数据类型int也可以通过.class得到对应class类型
// 三、通过con调用newInstance()创建一个对象,这就叫反射
Object obj = con.newInstance("小白",10, "成都");
System.out.println(obj); //Student{name='小白', age=10, address='成都'}
}
}
- 案例2:

package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//private Student(String name)
//二、通过c调用getConstructor()创建无参构造方法对象
Constructor<?> con = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//三、通过con调用newInstance()创建一个对象
// Object obj = con.newInstance("小黑");
// System.out.println(obj); //IllegalAccessException:没法访问异常:private修饰的私有构造方法
//暴力反射:public void setAccessible(boolean flag):值为true,取消访问检查
con.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = con.newInstance("小黑");
System.out.println(obj); //Student{name='小黑', age=0, address='null'}
}
}
2.4 反射获取成员变量并使用
- Class类中用于获取成员变量的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Field[ ] getFields() | 返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组 |
| Field[ ] getDeclaredFields() | 返回所有成员变量对象的数组 |
| Field getField(String name) | 返回单个公共成员变量对象 |
| Field getDeclaredField(String name) | 返回单个成员变量对象 |
- Field类中用于给成员变量赋值的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void set(Object obj, Object value) | 给obj对象的成员变量赋值为value |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获取Class对象
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//1,Field[] getFields() 返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组
Field[] fields1 = c.getFields();
for(Field field:fields1) {
System.out.println(field);
//public java.lang.String test.Student.address
}
System.out.println("--------");
//2,Field[ ] getDeclaredFields() 返回所有成员变量对象的数组
Field[] fields2 = c.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:fields2) {
System.out.println(field);
// private java.lang.String test.Student.name
// int test.Student.age
// public java.lang.String test.Student.address
}
System.out.println("--------");
/*
一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
二、通过c调用getField()得到成员变量对象addressField
三、addressField调用set()方法给obj对象的address赋值*/
//3,Field getField(String name) 返回单个公共成员变量对象
Field addressField = c.getField("address");
System.out.println(addressField);
//public java.lang.String test.Student.address
//获取无参构造方法创建对象
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
//5,void set(Object obj, Object value) 给obj对象的成员变量赋值为value
addressField.set(obj,"成都"); //给obj的成员变量addressField》address赋值为成都
System.out.println(obj); //Student{name='null', age=0, address='成都'}
}
}
- 案例:

package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
//一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//二、通过c调用getConstructor()创建无参构造方法对象
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
//三、通过con调用newInstance()创建一个对象
Object obj = con.newInstance();
//四、通过c调用getDeclaredField()得到成员变量对象
Field nameField = c.getDeclaredField("name");
nameField.setAccessible(true); //取消私有变量的访问检查
//五、成员变量对象调用set()方法给obj对象的成员变量赋值
nameField.set(obj,"小黑");
Field ageField = c.getDeclaredField("age");
ageField.setAccessible(true);
ageField.set(obj,10);
Field addressField = c.getDeclaredField("address");
addressField.setAccessible(true);
addressField.set(obj,"成都");
System.out.println(obj); //Student{name='小黑', age=10, address='成都'}
}
}
2.5 反射获取成员方法并使用
- Class类中获取成员方法的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Method[ ] getMethods() | 返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的 |
| Method[ ] getDeclaredMethods() | 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的 |
| Method getMethod(String name, Class<?> … parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共成员方法对象 |
| Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?> … parameterTypes) | 返回单个成员方法对象 |
- Method类中用于调用成员方法的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Object invoke(Object obj, Objet… args) | 调用obj对象的成员方法,参数是args,返回值是Object类型 |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//1,Method[ ] getMethods() 返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的
Method[] methods1 = c.getMethods();
for(Method method:methods1) {
System.out.println(method);
// public java.lang.String test.Student.toString()
// public void test.Student.method1()
// public void test.Student.method3()
// public void test.Student.method2()
// public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
// public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
// ...
}
System.out.println("---------");
//2,Method[ ] getDeclaredMethods() 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的
Method[] methods2 = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method:methods2) {
System.out.println(method);
// public java.lang.String test.Student.toString()
// private void test.Student.function()
// public void test.Student.method1()
// public void test.Student.method3()
// public void test.Student.method2()
}
//3,Method getMethod(String name, Class<?> … parameterTypes) 返回单个公共成员方法对象
Method m = c.getMethod("method1");
//获取无参构造方法并创建对象
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
//5,Object invoke(Object obj, Objet… args) 调用obj对象的成员方法,参数是args,返回值是Object类型
//第一个Object:返回值类型;obj:对象;args:方法需要的参数
m.invoke(obj); //method1
}
}
-
案例:

-
Student类
package test;
public class Student {
//成员变量:一个私有、一个默认、一个公共
private String name;
int age;
public String address;
//构造方法:一个私有、一个默认、两个公共
public Student() {
}
private Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student(String name, int age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
//成员方法:一个私有,四个公共
private void function() {
System.out.println("function");
}
public void method1() {
System.out.println("method1");
}
public void method2(String s) {
System.out.println("method2:" + s);
}
public String method3(String s, int i) { return s + "," + i; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 测试类
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//一、首先把这个类的带包的字符串路径传给forName()方法得到字节码文件Class对象c
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
//二、通过c调用getConstructor()创建无参构造方法对象
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
//三、通过con调用newInstance()创建一个对象
Object obj = con.newInstance();
//四、通过字节码文件对象调用getMethod()方法得到method方法对象
Method m1 = c.getMethod("method1");
Method m2 = c.getMethod("method2", String.class);
Method m3 = c.getMethod("method3", String.class, int.class);
Method m4 = c.getDeclaredMethod("function");
//五、通过method方法对象调用invoke()方法
m1.invoke(obj); //method1
m2.invoke(obj,"小黑"); //method2:小黑
Object o = m3.invoke(obj, "小白", 10);
System.out.println(o); //小白,10
m4.setAccessible(true);
m4.invoke(obj); //function
}
}
2.6 案例
2.6.1案例1:通过反射往ArrayList<Integer>集合中,添加字符串数据
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<>();
// array.add("小黑"); 报错
Class<? extends ArrayList> c = array.getClass();
Method m = c.getMethod("add", Object.class); //因为Object是泛型没有指定数据类型
m.invoke(array, "小黑");
m.invoke(array, "小黑");
m.invoke(array, "小黑");
System.out.println(array); //[小黑, 小黑, 小黑]
}
}
2.6.2 案例2:通过配置文件运行类中的方法
- Student类
package test;
public class Student {
public void study() {
System.out.println("好好学习天天向上");
}
}
- class.txt配置文件
className=test.Student
methodName=study
- 测试类
package test;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//加载数据
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("E:\\test\\Demo\\class.txt");
prop.load(fr);
fr.close();
System.out.println(prop); //{methodName=study, className=test.Student}
String className = prop.getProperty("className");
String methodName = prop.getProperty("methodName");
//通过反射来使用
Class<?> c = Class.forName(className); //test.Student
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod(methodName);//study
m.invoke(obj); //好好学习天天向上
//class.txt中只需要改文件路径和方法名
}
}