QT+OpenGL材质
本篇完整工程见gitee:QtOpenGL 对应点的tag,由turbolove提供技术支持,您可以关注博主或者私信博主
材质
在现实世界中,每个物体会对光照产生不同的反应

在OpenGL中模拟多种类型的物体,必须为每种物体分别定义一个材质属性
struct Material
{
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
}
uniform Material material;
这个时候如果我们再去掉shader内写死的环境光的分量的话
#version 330 core
struct Material {
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 lightColor;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 fragPos;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = lightColor;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - fragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * lightColor;
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - fragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), 32);
vec3 specular = spec * lightColor;
vec3 result = (ambient * material.ambient +
diffuse * material.diffuse +
specular * material.specular);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
整体显示会非常亮

添加材质,并且改变颜色
shader_program_.setUniformValue("material.ambient", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
shader_program_.setUniformValue("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
shader_program_.setUniformValue("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
shader_program_.setUniformValue("material.shininess", 32.0f);
lightColor.setX(sin(time/100 *2.0f));
lightColor.setY(sin(time/100 *0.7f));
lightColor.setZ(sin(time/100 *1.3f));
QVector3D diffuseColor = lightColor * QVector3D(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
QVector3D ambientColor = lightColor * QVector3D(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
shader_program_.setUniformValue("light.ambient", ambientColor);
shader_program_.setUniformValue("light.diffuse", diffuseColor); // 将光照调暗了一些以搭配场景
shader_program_.setUniformValue("light.specular", lightColor);
光照贴图
现实世界中的物体通常不只有一种材质,而是由多种材质组成
- 所以我们需要拓展之前的系统,引入漫反射和镜面光贴图
漫反射贴图
移除了环境材质颜色向量,因为环境光颜色在几乎所有情况下都等于漫反射颜色
注意sampler2D是所谓的不透明类型(Opaque Type),也就是说我们不能将它实例化,只能通过uniform来定义它。如果我们使用除uniform以外的方法(比如函数的参数)实例化这个结构体,GLSL会抛出一些奇怪的错误。这同样也适用于任何封装了不透明类型的结构体。
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
镜面光贴图
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
平行光

现实世界中,我们有很多种类的光照,每种的表现都不同。当一个光源处于很远的地方时,来自光源的每条光线就会近似于相互平行
struct Light {
// vec3 position; // 使用定向光就不再需要了
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
...
void main()
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction);
...
}
点光源

点光源是处于世界中的某一个位置的光源,他会朝着所有方向发光,但是光线会随着距离逐渐衰减。想象作为投光物的火把或者灯泡,他们都是点光源。
衰减:
点光源会随着光线传播距离的增长逐渐削减光的强度。
衰减公式如下:
F
a
t
t
=
1.0
K
c
+
K
l
∗
d
+
K
q
∗
d
2
F_{att} = \frac{1.0}{K_c+K_l*d +K_q *d^2}
Fatt=Kc+Kl∗d+Kq∗d21.0
在这里d代表了片段距光源的距离。接下来为了计算衰减值,我们定义3个(可配置的)项:常数项Kc、一次项Kl和二次项Kq。
#version 330 core
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
};
uniform Light light;
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 fragPos;
in vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
vec3 diffuseColor = vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specularColor = vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance +
light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// ambient
vec3 ambient = diffuseColor * light.ambient;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * diffuseColor * light.diffuse;
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - fragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), 32);
vec3 specular = spec * light.specular * specularColor;
// mix
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
聚光

LightDir : 从片段指向光源的向量
SpotDir: 聚光所指方向
Phi ϕ \phi ϕ: 指定了聚光半径的切光角。落在这个角度之外的物体都不会被这个聚光所照亮
Theta θ \theta θ:LightDir向量和SpotDir向量之间的夹角。在聚光内部的话 θ \theta θ值应该比 ϕ \phi ϕ值小。
手电筒就是普通的聚光灯,但是他的位置和方向会随着人的运动而改变。
#version 330 core
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
float cutOff;
};
uniform Light light;
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 fragPos;
in vec2 TexCoords;
void main()
{
vec3 diffuseColor = vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specularColor = vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
vec3 lightDir = normalize(fragPos - light.position);
float theta = dot(lightDir, normalize(light.direction));
if(theta > light.cutOff)
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = diffuseColor * light.ambient;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * diffuseColor * light.diffuse;
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - fragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), 32);
vec3 specular = spec * light.specular * specularColor;
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// mix
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
else
{
FragColor = vec4(light.ambient * diffuseColor, 1.0);
}
}

聚光边缘太过生硬,因此需要对边缘进行平滑软化;公式如下
I
=
θ
−
γ
ϵ
\begin{equation} I = \frac{\theta - \gamma}{\epsilon} \end{equation}
I=ϵθ−γ
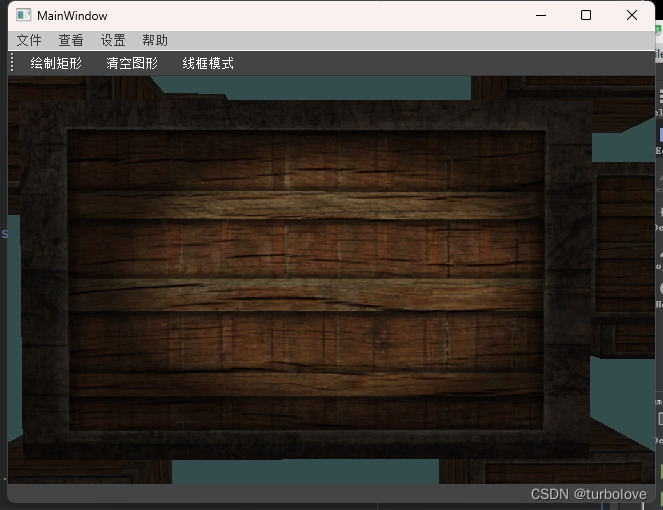
多光源
创建一个包含六个光源的场景,我们将模拟一个类似太阳的定向光源,四个分散在场景中的点光源和一个手电筒
#version 330 core
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
struct SpotLight {
vec3 position;
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
float cutOff;
float outerCutOff;
};
struct DirLight {
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
uniform DirLight dirLight;
uniform SpotLight spotLight;
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 fragPos;
in vec2 TexCoords;
vec3 CalcSpotLight(SpotLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir);
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir);
vec3 diffuseColor = vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specularColor = vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
void main()
{
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - fragPos);
vec3 result = vec3(0);
result += CalcSpotLight(spotLight, norm, viewDir);
result += CalcDirLight(dirLight, norm, viewDir);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
vec3 CalcSpotLight(SpotLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
// ambient
vec3 ambient = diffuseColor * light.ambient;
// diffuse
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * diffuseColor * light.diffuse;
// specular
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
vec3 specular = spec * light.specular * specularColor;
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
//ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
//smooth
float theta = dot(lightDir, normalize(-light.direction));
float epsilon = light.cutOff - light.outerCutOff;
float intensity = clamp((theta - light.outerCutOff) / epsilon, 0.0, 1.0);
diffuse *= intensity;
specular *= intensity;
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction);
// ambient
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// specular
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// attenuation
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * diffuseColor;
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * diffuseColor;
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * specularColor;
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
光照部分到此结束, 实现部分请参照gitee代码。如果您不能运行,可以联系私信博主咨询。