什么是Shiro?
一个Java的安全(权限)框架,可以完成认证、授权、加密、会话管理、Web集成、缓存等
下载地址:Apache Shiro | Simple. Java. Security.

快速启动
先在官网找到入门案例:shiro/samples/quickstart at main · apache/shiro · GitHub
步骤:
1、新建一个 Maven 工程,删除其 src 目录,将其作为父工程
2、在父工程中新建一个 Maven 模块
3、在maven模块中,复制依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.24</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>4、复制 log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n
# General Apache libraries
log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN
# Spring
log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN
# Default Shiro logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO
# Disable verbose logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARN
5、复制 shiro.ini(要先在 IDEA中添加 ini 插件)
[users]
# user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role
root = secret, admin
# user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role
guest = guest, guest
# user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same combination on
# my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president'
presidentskroob = 12345, president
# user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz'
darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz
# user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz'
lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Roles with assigned permissions
#
# Each line conforms to the format defined in the
# org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[roles]
# 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*'
admin = *
# The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber:
schwartz = lightsaber:*
# The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with
# license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id)
goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5
6、复制 Quickstart
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.text.IniRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @ClassName Quickstart
* @Description TODO
* @Author GuoSheng
* @Date 2021/4/20 17:28
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class Quickstart {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The easiest way to create a Shiro SecurityManager with configured
// realms, users, roles and permissions is to use the simple INI config.
// We'll do that by using a factory that can ingest a .ini file and
// return a SecurityManager instance:
// Use the shiro.ini file at the root of the classpath
// (file: and url: prefixes load from files and urls respectively):
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager=new DefaultSecurityManager();
IniRealm iniRealm=new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini");
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(iniRealm);
// for this simple example quickstart, make the SecurityManager
// accessible as a JVM singleton. Most applications wouldn't do this
// and instead rely on their container configuration or web.xml for
// webapps. That is outside the scope of this simple quickstart, so
// we'll just do the bare minimum so you can continue to get a feel
// for things.
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
// Now that a simple Shiro environment is set up, let's see what you can do:
// get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//say who they are:
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
//test a role:
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
//test a typed permission (not instance-level)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
//all done - log out!
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
7、运行结果

Shiro的Subject分析
Quickstart 中的一些方法:
1、获取当前用户
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();2、通过当前用户拿到 Session
Session session = currentUser.getSession();3、用session存值取值
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");4、判断是否被认证
currentUser.isAuthenticated()5、执行登录操作
currentUser.login(token);6、打印其标识主体
currentUser.getPrincipal()7、判断当前用户是否有某个角色
currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")8、注销
currentUser.logout();SpringBoot整合Shiro环境搭建
步骤:
1、导入shiro的整合依赖
<!--shiro整合spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>2、在config包下,编写Shiro的配置类
①自定义 Realm 类
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的授权方法");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的认证方法");
return null;
}
}
②自定义 ShiroConfig
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Autowired DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
return bean;
}
//DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Autowired UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联 UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
//创建Realm对象,需要自定义类
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
}
Shiro实现登录拦截
功能:必须认证了才能访问add和update页面,没有认证直接跳到登录页面
步骤:
1、编写前端页面
①编写首页
<h1>首页</h1>②编写测试页
(登录首页的时候,通过controller跳到测试页,测试页包含可以跳到add和update页面的超链接)
<h1>测试页</h1>
<p th:text="${msg}"></p>
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a>
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a>③add页面
<h1>add</h1>
增加一个用户④update页面
<h1>update</h1>
修改一个用户⑤登录页
<h1>登录</h1>
<form action="toLogin">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码: <input type="password" name="password"> <br>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>2、编写Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index","/index.html"})
public String toIndex(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","hello,Shiro");
return "test";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
}
3、shiro配置登录拦截
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Autowired DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//添加shiro的内置过滤器
/*
anon:无需认证就可以访问
authc:必须认证了才能访问
user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能访问
perms:拥有某个权限才能访问
role:拥有某个角色才能访问
*/
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filterMap.put("/user/add", "authc");
filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
//设置登录的请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
return bean;
}
//DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Autowired UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联 UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
//创建Realm对象,需要自定义类
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
}

Shiro实现用户认证
步骤:
1、在 UserRealm中,编写认证方法
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的认证方法");
//用户名、密码(要从数据库中获取)
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token;
if(!userToken.getUsername().equals(name)){ //如果userToken中的username和数据库中取出来的name不一样
return null; //抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
//密码认证,shiro做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,"");
}2、在controller中封装用户数据
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password, Model model){
//获取当前用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//封装用户的登录数据
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
try{
subject.login(token); //执行登录方法,如果没有异常说明就ok了
return "index";
}catch (UnknownAccountException e){ //用户名不存在
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名错误");
return "login";
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){ //密码不存在
model.addAttribute("msg","密码错误");
return "login";
}
}步骤解析:




Shiro整合MyBatis
步骤:
1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
</dependency>2、编写application.yaml和application.properties配置文件
①application.yaml
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500②application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
3、编写实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
4、编写mapper层
①UserMapper接口
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
//根据用户名查用户信息
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
②UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserByName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
select * from mybatis.user where name = #{name};
</select>
</mapper>5、编写service层
①UserService接口
public interface UserService{
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
②UserServiceImpl
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User queryUserByName(String name) {
return userMapper.queryUserByName(name);
}
}
6、把之前在UserRealm中直接写的name和password,改成从数据库中查出来的
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
UserServiceImpl userService;
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的授权方法");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的认证方法");
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token;
//连接真实的数据库
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
//如果user为空,说明用户不存在
if(user == null){
return null; //抛异常 UnknownAccountException
}
//密码认证,shiro做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),"");
}
}
Shiro请求授权实现
1、在ShiroConfig中设置访问哪些路径,需要哪些权限,并配置未授权页面
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]"); //拥有 user:add 权限才能访问/user/add
filterMap.put("/user/update","perms[user:update]"); bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noauth");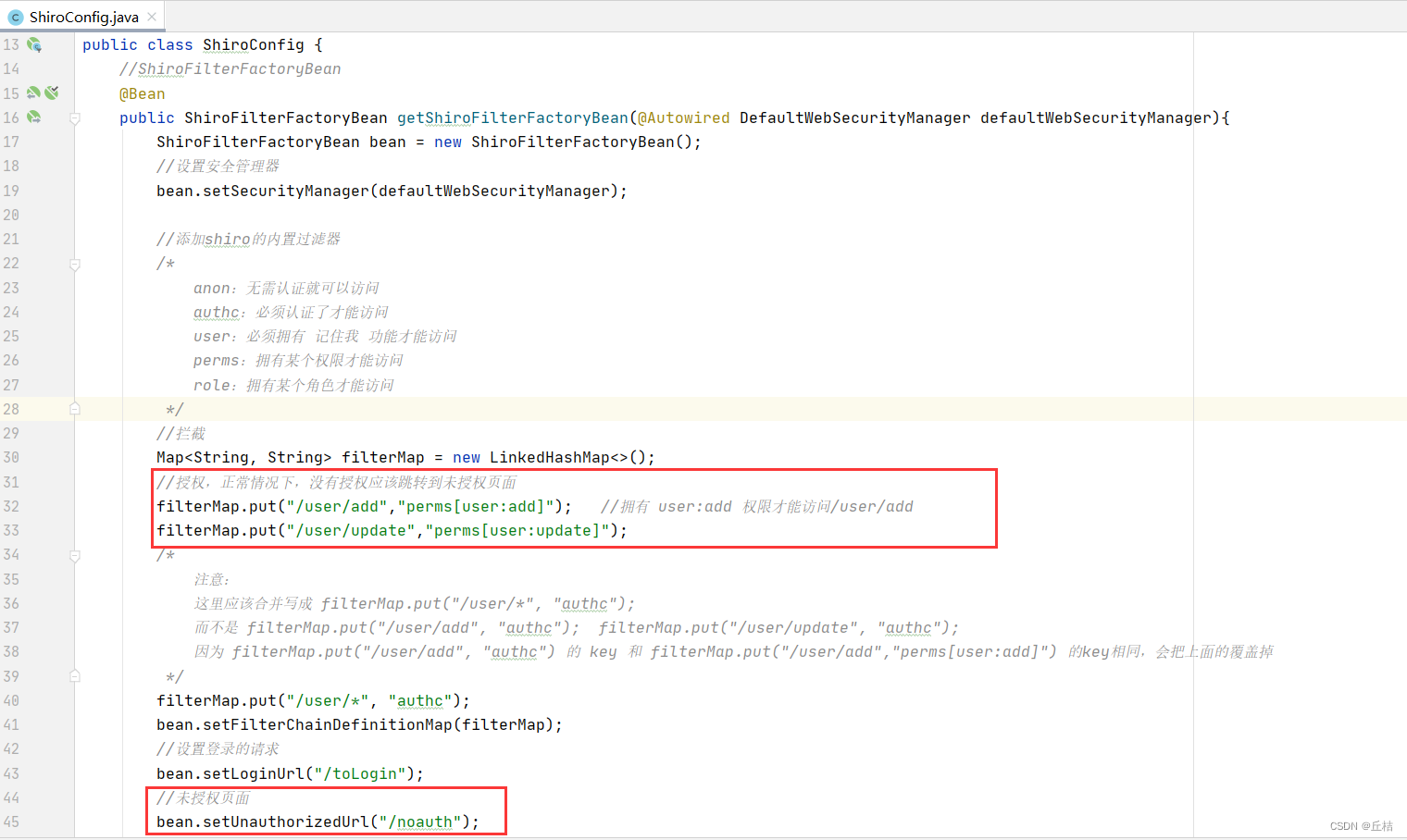
2、在UserRealm中给当前用户授权,其中权限是从数据库中查出来的
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了shiro的授权方法");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//拿到当前登录的这个对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
User currentUser = (User)subject.getPrincipal(); //拿到user对象
info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
3、在controller中设置未授权url处理
@RequestMapping("/noauth")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthorized(){
return "未经授权,无法访问此页面";
}Shiro整合Thymeleaf
1、导入依赖
<!--shiro-thymeleaf整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.theborakompanioni</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>2、在shiroConfig中整合thymeleaf
//ShiroDialect:用来整合 shiro thymeleaf
@Bean
public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){
return new ShiroDialect();
}3、更改前端页面
①在test页面编写一个登录连接
<p>
<a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登录</a>
</p>

②在首页设置add和update链接,拥有对应权限才可以访问
shiro命名空间:
xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro"链接:
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:add">
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a>
</div>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:update">
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a>
</div>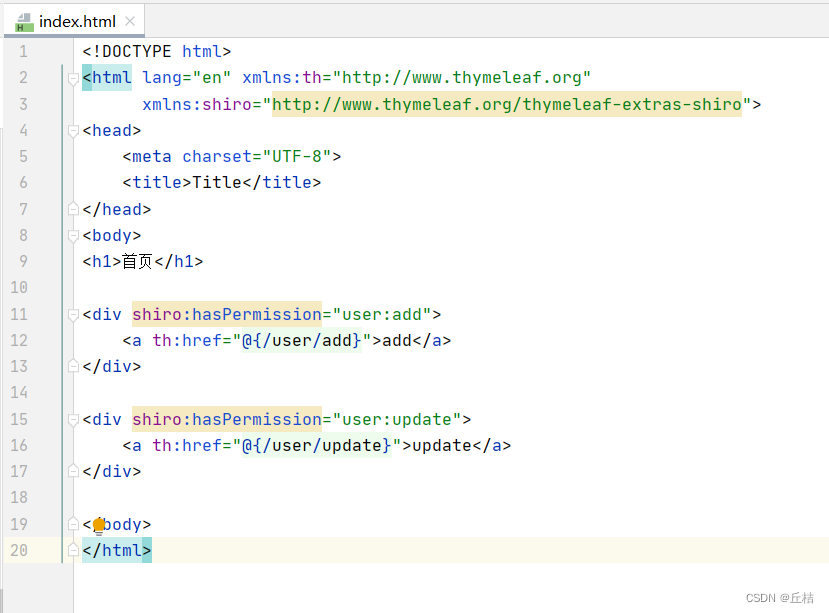






![编译DPDK出现[-Werror=implicit-fallthrough=]错误](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fcc9da954c4e4abf8e0a81af6f986161.png)