1 综述
一共是这些代码,我们主要看echo.py,segmentation.py,video.py,config.py。

2 配置文件config.py
基于配置文件设置路径。
"""Sets paths based on configuration files."""
import configparser
import os
import types
_FILENAME = None
_PARAM = {}
# 如果存在下面这些自定义的配置文件,则读取配置文件中的定义
for filename in ["echonet.cfg",
".echonet.cfg",
os.path.expanduser("~/echonet.cfg"),
os.path.expanduser("~/.echonet.cfg"),
]:
if os.path.isfile(filename):
_FILENAME = filename
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
with open(filename, "r") as f:
config.read_string("[config]\n" + f.read())
_PARAM = config["config"]
break
CONFIG = types.SimpleNamespace(
FILENAME=_FILENAME,
DATA_DIR=_PARAM.get("data_dir", "a4c-video-dir/")) # 默认的数据存放路径
3 数据集加载echo.py
4 左心室分割segmentation.py
Trains/tests segmentation model.
参数介绍:
data_dir(str,可选):包含数据集的目录。默认值为`echonet.config.DATA_DIR`。
output(str,可选):放置输出的目录。默认值为输出/分段/<模型名称>_<预训练/随机>/。
model_name(str,可选):分段模型的名称。“deeplabv3_resnet50”、``deeplabv3_resnet101“”、“fcn_resnet50”或“fcn_res net101”之一,(选项为torchvision.models.segmentation.<model_name>)默认值为“`deeplabv3_resnet50'”。
pretrained(bool,可选):是否对模型使用预训练权重,默认为False。
weights(str,可选):包含权重的检查点路径初始化模型。默认为“无”。
run_test(bool,可选):是否在测试中运行。默认为False。
save_video(bool,可选):是否保存带有分段的视频。默认为False。
num_epochs(int,可选):训练期间的纪元数。默认值为50。
lr(float,可选):SGD的学习率。默认值为1e-5。
weight_decay(浮动,可选):SGD的权重衰减。默认值为0。
lr_step_period(int或None,可选):学习率衰减的时间段。(学习率衰减0.1倍)。默认为math.inf(从不衰减学习率)。
num_train_patients(int或None,可选):培训患者的数量。用于消融。默认为所有患者。
num_workers(int,可选):用于数据的子进程数加载。如果为0,则数据将加载到主进程中。默认值为4。
device(str或None,可选):要运行的设备的名称。选项来自https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensor_attributes.html#torch.torch.device。如果可用,则默认为“cuda”,否则默认为“cpu”。
batch_size(int,可选):每个批次要加载的样本数。默认值为20。
seed(int,可选):随机数生成器的种子。默认值为0。
"""Functions for training and running segmentation."""
import math
import os
import time
import click
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.signal
import skimage.draw
import torch
import torchvision
import tqdm
import echonet
@click.command("segmentation")
@click.option("--data_dir", type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=False), default=None)
@click.option("--output", type=click.Path(file_okay=False), default=None)
@click.option("--model_name", type=click.Choice(
sorted(name for name in torchvision.models.segmentation.__dict__
if name.islower() and not name.startswith("__") and callable(torchvision.models.segmentation.__dict__[name]))),
default="deeplabv3_resnet50")
@click.option("--pretrained/--random", default=False)
@click.option("--weights", type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=False), default=None)
@click.option("--run_test/--skip_test", default=False)
@click.option("--save_video/--skip_video", default=False)
@click.option("--num_epochs", type=int, default=50)
@click.option("--lr", type=float, default=1e-5)
@click.option("--weight_decay", type=float, default=0)
@click.option("--lr_step_period", type=int, default=None)
@click.option("--num_train_patients", type=int, default=None)
@click.option("--num_workers", type=int, default=4)
@click.option("--batch_size", type=int, default=20)
@click.option("--device", type=str, default=None)
@click.option("--seed", type=int, default=0)
def run(
data_dir=None,
output=None,
model_name="deeplabv3_resnet50",
pretrained=False,
weights=None,
run_test=False,
save_video=False,
num_epochs=50,
lr=1e-5,
weight_decay=1e-5,
lr_step_period=None,
num_train_patients=None,
num_workers=4,
batch_size=20,
device=None,
seed=0,
):
# Seed RNGs
np.random.seed(seed) # 如果使用相同的seed()值,则每次生成的随机数都相同
torch.manual_seed(seed) #设置 CPU 生成随机数的 种子 ,方便下次复现实验结果。
# Set default output directory
if output is None:
output = os.path.join("output", "segmentation", "{}_{}".format(model_name, "pretrained" if pretrained else "random"))
os.makedirs(output, exist_ok=True)
# Set device for computations
if device is None:
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Set up model
# torchvision.models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet50
model = torchvision.models.segmentation.__dict__[model_name](pretrained=pretrained, aux_loss=False)#__dict__,会输出该由类中所有类属性组成的字典
# 设置分类器, 输出为1(即是心房是非心房,是01问题)
# model.classifier 为卷积核设置,修改卷积层,【-1】最后一层
model.classifier[-1] = torch.nn.Conv2d(model.classifier[-1].in_channels, 1, kernel_size=model.classifier[-1].kernel_size) # change number of outputs to 1
if device.type == "cuda":
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)# 用多个GPU来加速训练
model.to(device)
if weights is not None:
checkpoint = torch.load(weights)# ,map_location='cpu'
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
# Set up optimizer
optim = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=weight_decay)
if lr_step_period is None:
lr_step_period = math.inf
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optim, lr_step_period)
# Compute mean and std 由于医学数据集比较特殊, 需要计算一下自己的均值和标准差
mean, std = echonet.utils.get_mean_and_std(echonet.datasets.Echo(root=data_dir, split="train"))
tasks = ["LargeFrame", "SmallFrame", "LargeTrace", "SmallTrace"]
kwargs = {"target_type": tasks,
"mean": mean,
"std": std
}
# 获取训练集和验证集
# Set up datasets and dataloaders
dataset = {}
dataset["train"] = echonet.datasets.Echo(root=data_dir, split="train", **kwargs)
if num_train_patients is not None and len(dataset["train"]) > num_train_patients:
# Subsample patients (used for ablation experiment)
indices = np.random.choice(len(dataset["train"]), num_train_patients, replace=False)
dataset["train"] = torch.utils.data.Subset(dataset["train"], indices)
dataset["val"] = echonet.datasets.Echo(root=data_dir, split="val", **kwargs)
# Run training and testing loops 打开日志文件, 记录训练过程
with open(os.path.join(output, "log.csv"), "a") as f:
epoch_resume = 0 # 训练开始的周期位置
bestLoss = float("inf")
# Attempt to load checkpoint尝试加载检查点
try:
checkpoint = torch.load(os.path.join(output, "checkpoint.pt"))
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
optim.load_state_dict(checkpoint['opt_dict'])
scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['scheduler_dict'])
epoch_resume = checkpoint["epoch"] + 1
bestLoss = checkpoint["best_loss"]
f.write("Resuming from epoch {}\n".format(epoch_resume))
except FileNotFoundError:
f.write("Starting run from scratch\n") # 如果检查点文件不存在,则从头开始运行
# 开始训练
for epoch in range(epoch_resume, num_epochs):
print("Epoch #{}".format(epoch), flush=True)
for phase in ['train', 'val']:
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats(i)
ds = dataset[phase]
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
ds, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True, pin_memory=(device.type == "cuda"), drop_last=(phase == "train"))
#在循环中调用 run_epoch() 方法
loss, large_inter, large_union, small_inter, small_union = echonet.utils.segmentation.run_epoch(model, dataloader, phase == "train", optim, device)
overall_dice = 2 * (large_inter.sum() + small_inter.sum()) / (large_union.sum() + large_inter.sum() + small_union.sum() + small_inter.sum())
large_dice = 2 * large_inter.sum() / (large_union.sum() + large_inter.sum())
small_dice = 2 * small_inter.sum() / (small_union.sum() + small_inter.sum())
f.write("{},{},{},{},{},{},{},{},{},{},{}\n".format(epoch,
phase,
loss,
overall_dice,
large_dice,
small_dice,
time.time() - start_time,
large_inter.size,
sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())),
sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())),
batch_size))
f.flush()
scheduler.step()
# Save checkpoint
save = {
'epoch': epoch,
'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'best_loss': bestLoss,
'loss': loss,
'opt_dict': optim.state_dict(),
'scheduler_dict': scheduler.state_dict(),
}
torch.save(save, os.path.join(output, "checkpoint.pt"))
if loss < bestLoss:
torch.save(save, os.path.join(output, "best.pt"))
bestLoss = loss
# Load best weights
if num_epochs != 0:
checkpoint = torch.load(os.path.join(output, "best.pt"))
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
f.write("Best validation loss {} from epoch {}\n".format(checkpoint["loss"], checkpoint["epoch"]))
if run_test:
# Run on validation and test
for split in ["val", "test"]:
dataset = echonet.datasets.Echo(root=data_dir, split=split, **kwargs)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False, pin_memory=(device.type == "cuda"))
loss, large_inter, large_union, small_inter, small_union = echonet.utils.segmentation.run_epoch(model, dataloader, False, None, device)
overall_dice = 2 * (large_inter + small_inter) / (large_union + large_inter + small_union + small_inter)
large_dice = 2 * large_inter / (large_union + large_inter)
small_dice = 2 * small_inter / (small_union + small_inter)
with open(os.path.join(output, "{}_dice.csv".format(split)), "w") as g:
g.write("Filename, Overall, Large, Small\n")
for (filename, overall, large, small) in zip(dataset.fnames, overall_dice, large_dice, small_dice):
g.write("{},{},{},{}\n".format(filename, overall, large, small))
f.write("{} dice (overall): {:.4f} ({:.4f} - {:.4f})\n".format(split, *echonet.utils.bootstrap(np.concatenate((large_inter, small_inter)), np.concatenate((large_union, small_union)), echonet.utils.dice_similarity_coefficient)))
f.write("{} dice (large): {:.4f} ({:.4f} - {:.4f})\n".format(split, *echonet.utils.bootstrap(large_inter, large_union, echonet.utils.dice_similarity_coefficient)))
f.write("{} dice (small): {:.4f} ({:.4f} - {:.4f})\n".format(split, *echonet.utils.bootstrap(small_inter, small_union, echonet.utils.dice_similarity_coefficient)))
f.flush()
# 以下应该是加载测试集,分割,以及保存数据
# Saving videos with segmentations
dataset = echonet.datasets.Echo(root=data_dir, split="test",
target_type=["Filename", "LargeIndex", "SmallIndex"], # Need filename for saving, and human-selected frames to annotate需要用于保存的文件名和要注释的人工选定帧
mean=mean, std=std, # Normalization
length=None, max_length=None, period=1 # Take all frames
)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=10, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False, pin_memory=False, collate_fn=_video_collate_fn)
# Save videos with segmentation
if save_video and not all(os.path.isfile(os.path.join(output, "videos", f)) for f in dataloader.dataset.fnames):
# Only run if missing videos
model.eval()
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output, "videos"), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output, "size"), exist_ok=True)
echonet.utils.latexify()
with torch.no_grad():
with open(os.path.join(output, "size.csv"), "w") as g:
g.write("Filename,Frame,Size,HumanLarge,HumanSmall,ComputerSmall\n")
for (x, (filenames, large_index, small_index), length) in tqdm.tqdm(dataloader):
# Run segmentation model on blocks of frames one-by-one #逐个在帧块上运行分割模型
# The whole concatenated video may be too long to run together #整个串联视频可能太长,无法一起运行
y = np.concatenate([model(x[i:(i + batch_size), :, :, :].to(device))["out"].detach().cpu().numpy() for i in range(0, x.shape[0], batch_size)])
start = 0
x = x.numpy()
for (i, (filename, offset)) in enumerate(zip(filenames, length)):
# Extract one video and segmentation predictions
video = x[start:(start + offset), ...]
logit = y[start:(start + offset), 0, :, :]
# Un-normalize video
video *= std.reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
video += mean.reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
# Get frames, channels, height, and width
f, c, h, w = video.shape # pylint: disable=W0612
assert c == 3
# Put two copies of the video side by side # 并排存放两份视频
video = np.concatenate((video, video), 3)
# If a pixel is in the segmentation, saturate blue channel
# Leave alone otherwise
video[:, 0, :, w:] = np.maximum(255. * (logit > 0), video[:, 0, :, w:]) # pylint: disable=E1111
# Add blank canvas under pair of videos # 在视频对下添加空白画布
video = np.concatenate((video, np.zeros_like(video)), 2)
# Compute size of segmentation per frame # 计算每帧分割的大小
size = (logit > 0).sum((1, 2))
# Identify systole frames with peak detection
trim_min = sorted(size)[round(len(size) ** 0.05)]
trim_max = sorted(size)[round(len(size) ** 0.95)]
trim_range = trim_max - trim_min
systole = set(scipy.signal.find_peaks(-size, distance=20, prominence=(0.50 * trim_range))[0])
# Write sizes and frames to file
for (frame, s) in enumerate(size):
g.write("{},{},{},{},{},{}\n".format(filename, frame, s, 1 if frame == large_index[i] else 0, 1 if frame == small_index[i] else 0, 1 if frame in systole else 0))
# Plot sizes
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(size.shape[0] / 50 * 1.5, 3))
plt.scatter(np.arange(size.shape[0]) / 50, size, s=1)
ylim = plt.ylim()
for s in systole:
plt.plot(np.array([s, s]) / 50, ylim, linewidth=1)
plt.ylim(ylim)
plt.title(os.path.splitext(filename)[0])
plt.xlabel("Seconds")
plt.ylabel("Size (pixels)")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output, "size", os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + ".pdf"))
plt.close(fig)
# Normalize size to [0, 1]
size -= size.min()
size = size / size.max()
size = 1 - size
# Iterate the frames in this video
for (f, s) in enumerate(size):
# On all frames, mark a pixel for the size of the frame
video[:, :, int(round(115 + 100 * s)), int(round(f / len(size) * 200 + 10))] = 255.
if f in systole:
# If frame is computer-selected systole, mark with a line
video[:, :, 115:224, int(round(f / len(size) * 200 + 10))] = 255.
def dash(start, stop, on=10, off=10):
buf = []
x = start
while x < stop:
buf.extend(range(x, x + on))
x += on
x += off
buf = np.array(buf)
buf = buf[buf < stop]
return buf
d = dash(115, 224)
if f == large_index[i]:
# If frame is human-selected diastole, mark with green dashed line on all frames
# 如果帧是人类选择的舒张期,则在所有帧上用绿色虚线标记
video[:, :, d, int(round(f / len(size) * 200 + 10))] = np.array([0, 225, 0]).reshape((1, 3, 1))
if f == small_index[i]:
# If frame is human-selected systole, mark with red dashed line on all frames
# 如果帧是人为选择的收缩期,则在所有帧上用红色虚线标记
video[:, :, d, int(round(f / len(size) * 200 + 10))] = np.array([0, 0, 225]).reshape((1, 3, 1))
# Get pixels for a circle centered on the pixel
# 获取以像素为中心的圆的像素
r, c = skimage.draw.disk((int(round(115 + 100 * s)), int(round(f / len(size) * 200 + 10))), 4.1)
# On the frame that's being shown, put a circle over the pixel
# 在显示的帧上,在像素上画一个圆圈
video[f, :, r, c] = 255.
# Rearrange dimensions and save
video = video.transpose(1, 0, 2, 3)
video = video.astype(np.uint8)
echonet.utils.savevideo(os.path.join(output, "videos", filename), video, 50)
# Move to next video
start += offset
def run_epoch(model, dataloader, train, optim, device):
"""Run one epoch of training/evaluation for segmentation.
Args:
model (torch.nn.Module): Model to train/evaulate.
dataloder (torch.utils.data.DataLoader): Dataloader for dataset.
train (bool): Whether or not to train model.
optim (torch.optim.Optimizer): Optimizer
device (torch.device): Device to run on
"""
total = 0.
n = 0
pos = 0
neg = 0
pos_pix = 0
neg_pix = 0
model.train(train)
large_inter = 0
large_union = 0
small_inter = 0
small_union = 0
large_inter_list = []
large_union_list = []
small_inter_list = []
small_union_list = []
with torch.set_grad_enabled(train):
with tqdm.tqdm(total=len(dataloader)) as pbar:
# 遍历dataloader
for (_, (large_frame, small_frame, large_trace, small_trace)) in dataloader:
# 医学中的统计指标 Count number of pixels in/out of human segmentation
pos += (large_trace == 1).sum().item()
pos += (small_trace == 1).sum().item()
neg += (large_trace == 0).sum().item()
neg += (small_trace == 0).sum().item()
# Count number of pixels in/out of computer segmentation
pos_pix += (large_trace == 1).sum(0).to("cpu").detach().numpy()
pos_pix += (small_trace == 1).sum(0).to("cpu").detach().numpy()
neg_pix += (large_trace == 0).sum(0).to("cpu").detach().numpy()
neg_pix += (small_trace == 0).sum(0).to("cpu").detach().numpy()
# Run prediction for diastolic frames and compute loss
large_frame = large_frame.to(device)
large_trace = large_trace.to(device)
y_large = model(large_frame)["out"]
loss_large = torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(y_large[:, 0, :, :], large_trace, reduction="sum")
# Compute pixel intersection and union between human and computer segmentations
large_inter += np.logical_and(y_large[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., large_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum()
large_union += np.logical_or(y_large[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., large_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum()
large_inter_list.extend(np.logical_and(y_large[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., large_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum((1, 2)))
large_union_list.extend(np.logical_or(y_large[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., large_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum((1, 2)))
# Run prediction for systolic frames and compute loss
small_frame = small_frame.to(device)
small_trace = small_trace.to(device)
y_small = model(small_frame)["out"]
loss_small = torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(y_small[:, 0, :, :], small_trace, reduction="sum")
# Compute pixel intersection and union between human and computer segmentations
small_inter += np.logical_and(y_small[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., small_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum()
small_union += np.logical_or(y_small[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., small_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum()
small_inter_list.extend(np.logical_and(y_small[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., small_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum((1, 2)))
small_union_list.extend(np.logical_or(y_small[:, 0, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0., small_trace[:, :, :].detach().cpu().numpy() > 0.).sum((1, 2)))
# 计算loss然后反向传播,Take gradient step if training
loss = (loss_large + loss_small) / 2
if train:
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
# Accumulate losses and compute baselines
total += loss.item()
n += large_trace.size(0)
p = pos / (pos + neg)
p_pix = (pos_pix + 1) / (pos_pix + neg_pix + 2)
# Show info on process bar
pbar.set_postfix_str("{:.4f} ({:.4f}) / {:.4f} {:.4f}, {:.4f}, {:.4f}".format(total / n / 112 / 112, loss.item() / large_trace.size(0) / 112 / 112, -p * math.log(p) - (1 - p) * math.log(1 - p), (-p_pix * np.log(p_pix) - (1 - p_pix) * np.log(1 - p_pix)).mean(), 2 * large_inter / (large_union + large_inter), 2 * small_inter / (small_union + small_inter)))
pbar.update()
large_inter_list = np.array(large_inter_list)
large_union_list = np.array(large_union_list)
small_inter_list = np.array(small_inter_list)
small_union_list = np.array(small_union_list)
return (total / n / 112 / 112,
large_inter_list,
large_union_list,
small_inter_list,
small_union_list,
)
def _video_collate_fn(x):
……
训练和测试写到了一起,那我们如何测试自己的数据集呢?
重写代码?
由于检查点的存在,那么我们再次运行segmentation.py文件的时候,直接跳过训练进行预测。
生成文件介绍
log.csv
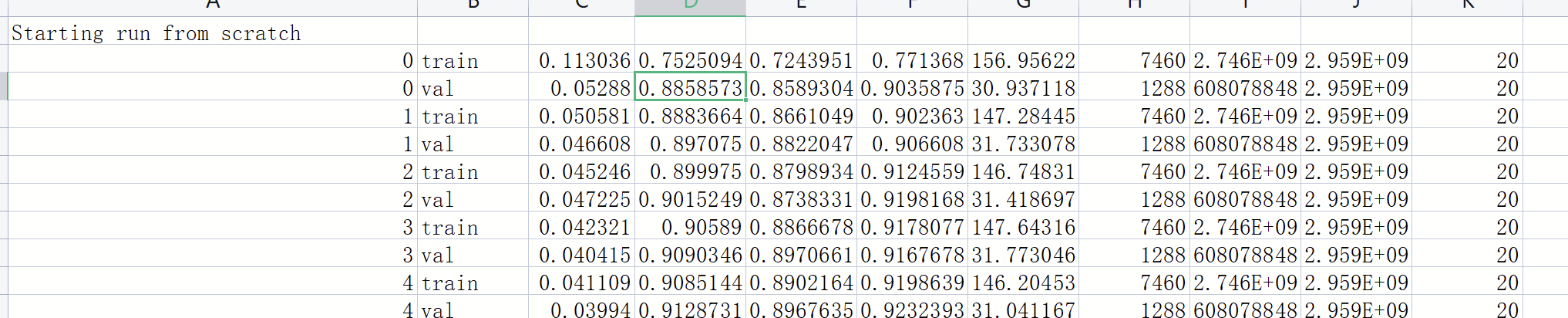 epoch, phase,loss,overall_dice, large_dice,small_dice,time.time() - start_time, large_inter.size,sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())), sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_cached() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())), batch_size
epoch, phase,loss,overall_dice, large_dice,small_dice,time.time() - start_time, large_inter.size,sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())), sum(torch.cuda.max_memory_cached() for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())), batch_size
5 射血分数预测vedio.py
“”“Functions for training and running EF prediction.”“”