有序列表和有序字典
有序列表和有序字典都是是一个键值对容器,像字典一样。
从习惯和描述推测,
- 列表控制一个数组
- 有序列表使用比有序字典更少的内存
- 如果一次性添加一堆数据,且这堆数据有序。那么有序列表比有序字典更快
有序列表大概长这样
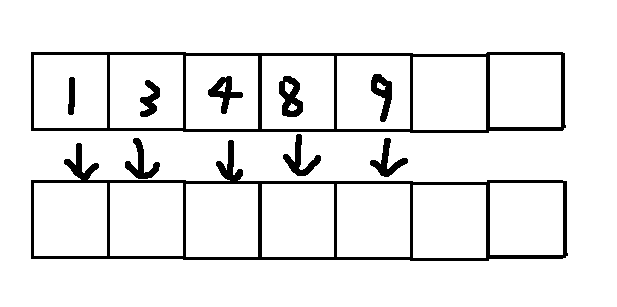
而有序字典长这样
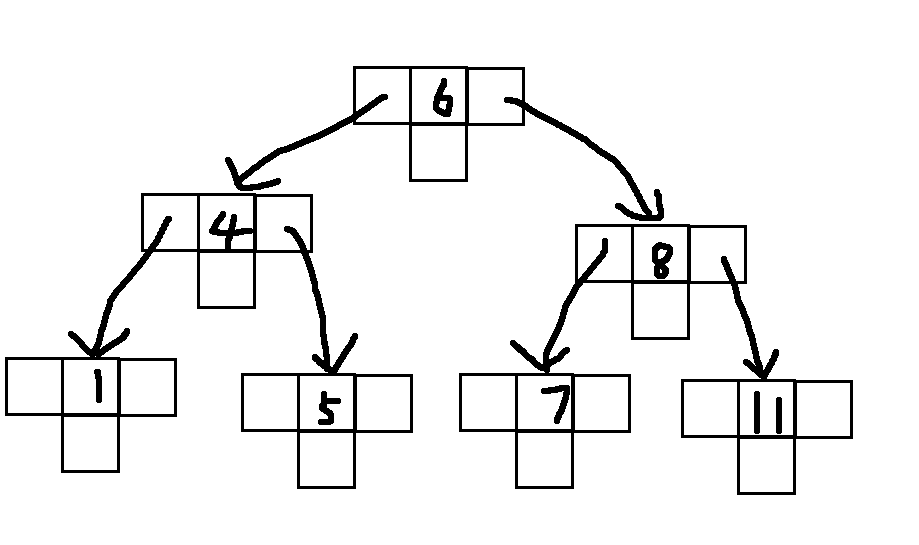
所以如果更多的倾向于只读,那么有序列表会更合适。
实现排序
作为键的类型,必须实现排序接口。
在插入到列表中的时候会使用排序接口的方法来决定放哪。
但是之后不会时刻保证他在正确的位置。如果你修改他的内容让他应在的位置有变化,列表是不知道的。
创建
可以啥也不填,也可以填入一个字典接口来初始化元素。排序列表使用数组,依然可以填入数字来初始化数组大小。
Dictionary<string, int> dic = new Dictionary<string, int>() { ["https"] = 5 };
SortedDictionary<string, int> sortDic1 = new SortedDictionary<string, int>();
SortedDictionary<string, int> sortDic2 = new SortedDictionary<string, int>(dic);
SortedList<string, int> sortList1 = new SortedList<string, int>();
SortedList<string, int> sortList2 = new SortedList<string, int>(10);
SortedList<string, int> sortList3 = new SortedList<string, int>(dic);
访问
索引器可以用于添加 / 覆盖元素,和用来访问元素。
sortList["hello"] = 5;
sortList["apple"] = 5;
sortList["carch"] = 3;
sortList["carch"] = 3;
int p = sortList["carch"];
仅限有序列表,可以通过索引来访问和修改值。
var key = sortList.GetKeyAtIndex(3);
var value = sortList.GetValueAtIndex(3);
sortList.SetValueAtIndex(2, 80);
遍历
如果没有因为修改键元素内容导致顺序发生变化,那么他的内容是根据键有序的。
foreach (string item in sortList.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("========");
foreach (int item in sortList.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("========");
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, int> item in sortList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
查找元素
ContainsKey和ContainsValue可以确定当前集合是否有指定的 键 / 值
sortList.ContainsKey("carch");
sortList.ContainsValue(3);
仅限于有序列表,他是用数组存储的,可以找索引
int indexKey = sortList.IndexOfKey("carch");//没找到返回-1
int indexValue = sortList.IndexOfValue(3);//没找到返回-1
删除元素
使用Remove删除指定键对应的元素。
进行有序列表,可以删除指定索引下的元素。
sortList.Remove("carch");
sortList.RemoveAt(1);
有序列表的数组容量
有序列表依然可以用属性和方法控制他背后数组的大小。
Console.WriteLine(sortList.Capacity);//获取数组大小
sortList.Capacity = 50;//设置数组大小,不能低于已占用元素数量
sortList.TrimExcess();//如果元素数量低于90%总容量,裁切数组到元素数量。