目录
- 题目分析
- 递归法
题目来源
111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目分析
这道题目容易联想到104题的最大深度,把代码搬过来
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
public static int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
return Math.min(left,right)+1;
}
}
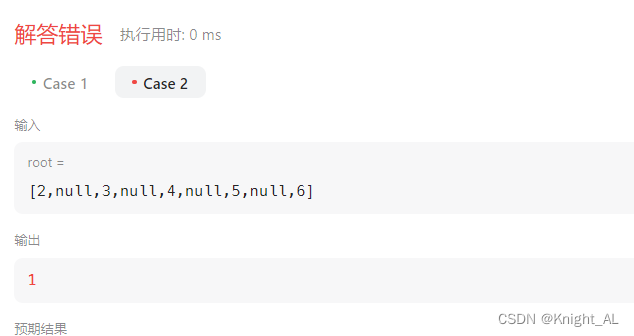
然后仔细读题
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。

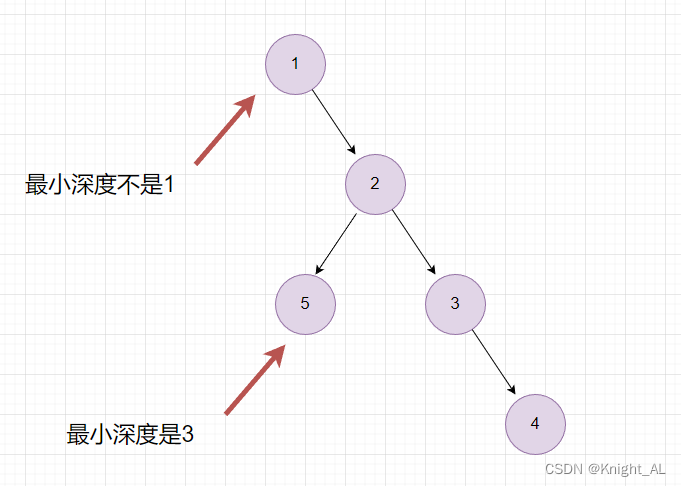
为了满足题目需求, 需要额外加上一个条件
if(root.left == null && root.right != null)
if(root.left != null && root.right == null)
递归法
递归三部曲
- 1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
代码如下:
int dfs(TreeNode root)
- 2.确定终止条件
终止条件也是遇到空节点返回0,表示当前节点的高度为0。
代码如下:
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
- 3.确定单层递归的逻辑
这块和求最大深度可就不一样了
如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
int leftDepth = dfs(root.left); // 左
int rightDepth = dfs(root.right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
return rightDepth + 1;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if(root.left != null && root.right == null){
return leftDepth + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
遍历的顺序为后序(左右中),可以看出:求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
整体递归代码
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return dfs(root);
}
public static int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = dfs(root.left); // 左
int rightDepth = dfs(root.right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
return rightDepth + 1;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if(root.left != null && root.right == null){
return leftDepth + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}
}
![[SSD固态硬盘技术 15] FTL映射表的神秘面纱](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/c1213fdcabb34ef2af8cb706aa6ae2b7.png)