Spring Boot启动流程目录
- 一、简述
- 二、注解
- @SpirngBootApplication注解
- 三、启动方法
- 1、创建SpringApplication实例
- 1.1、WebApplicationType
- 1.2、getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories
- 1.3、setInitializers && setListeners
- 1.4、deduceMainApplicationClass
- 2、run方法
- 2.1、configureHeadlessProperty
- 2.2、prepareEnvironment
- 2.3、printBanner
- 2.4、createApplicationContext
- 2.6、refresh
- 2.7、onRefresh
- 2.8、afterRefresh
- 2.9、停止计时并打印启动完毕相关日志
- 2.10、started
- 2.11、callRunners
- 2.12、running
- 四、总结
一、简述
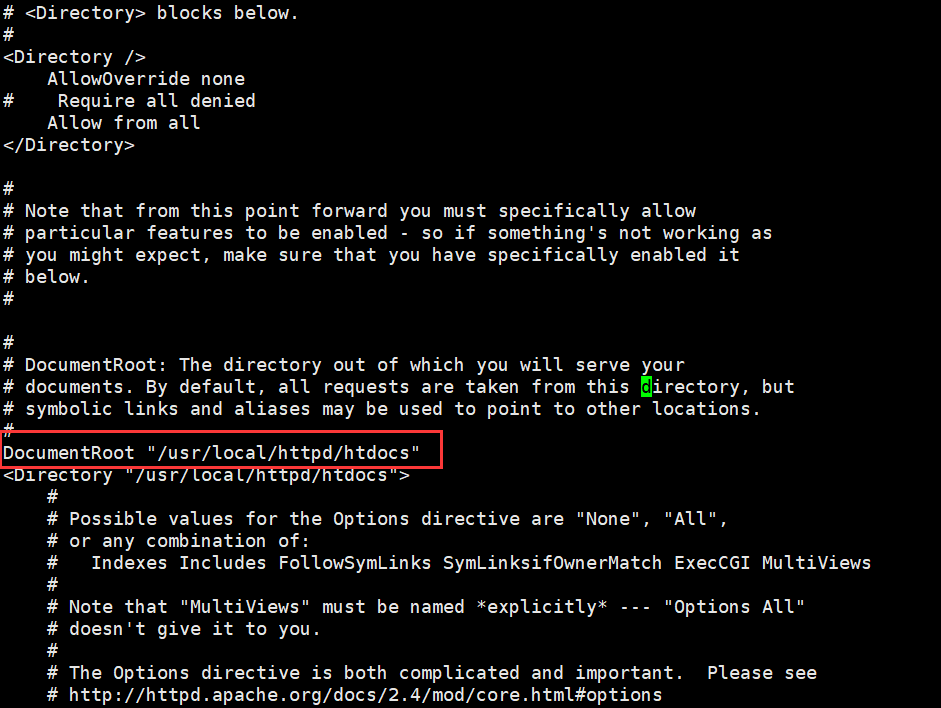
Spring Boot启动流程分析使用版本SpringBoot VERSION:版本 2.5.5-SNAPSHOT。
Spring Boot项目最简单的Application启动类。
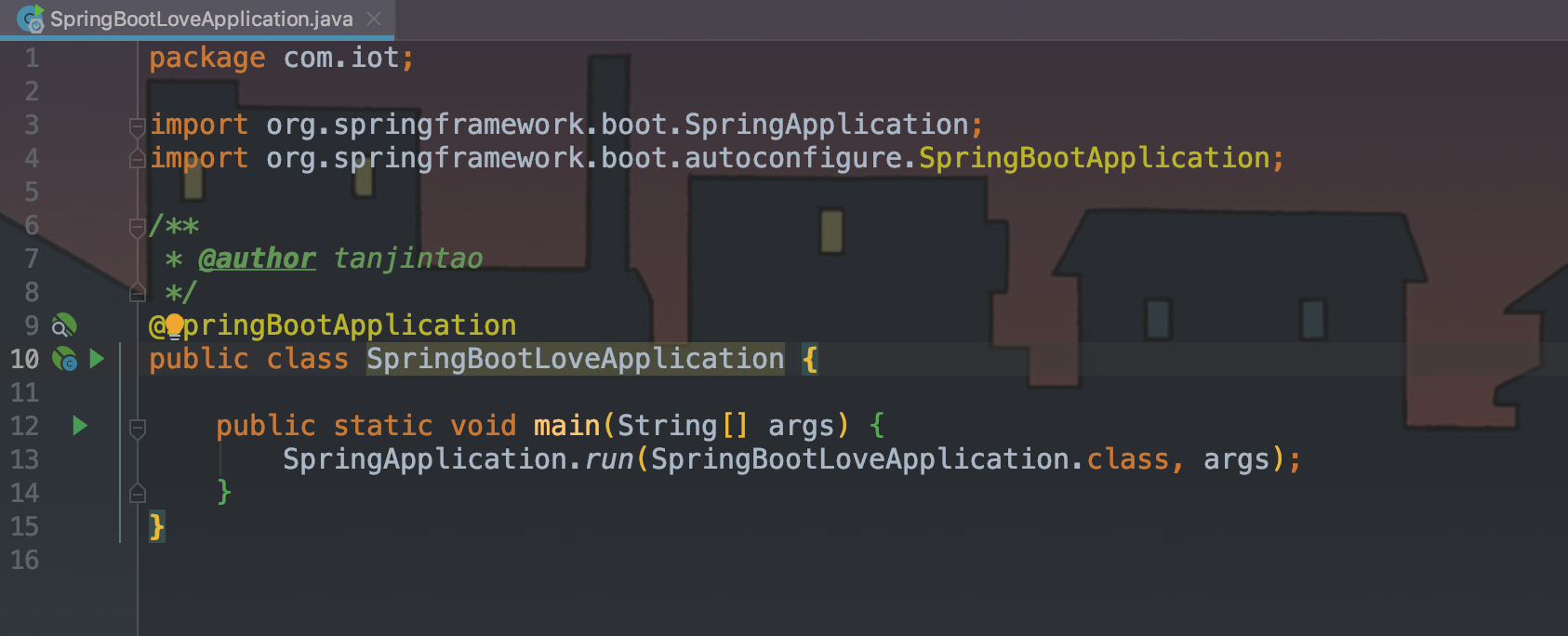
可以看出Application启动类中,包含了@SpringBootApplication 注解和 SpringApplication.run 启动方法,所以SpringBoot的启动可以分解为 注解 和 启动方法 两大过程,而仔细看启动类中还引入了一个【org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication】包,所以启动方法中又可以分为两个阶段即 创建SpringApplication 实例 和 执行run方法。
二、注解
注解暂且简单了解,暂不深入。
@SpirngBootApplication注解
进入@SpringBootApplication注解内。
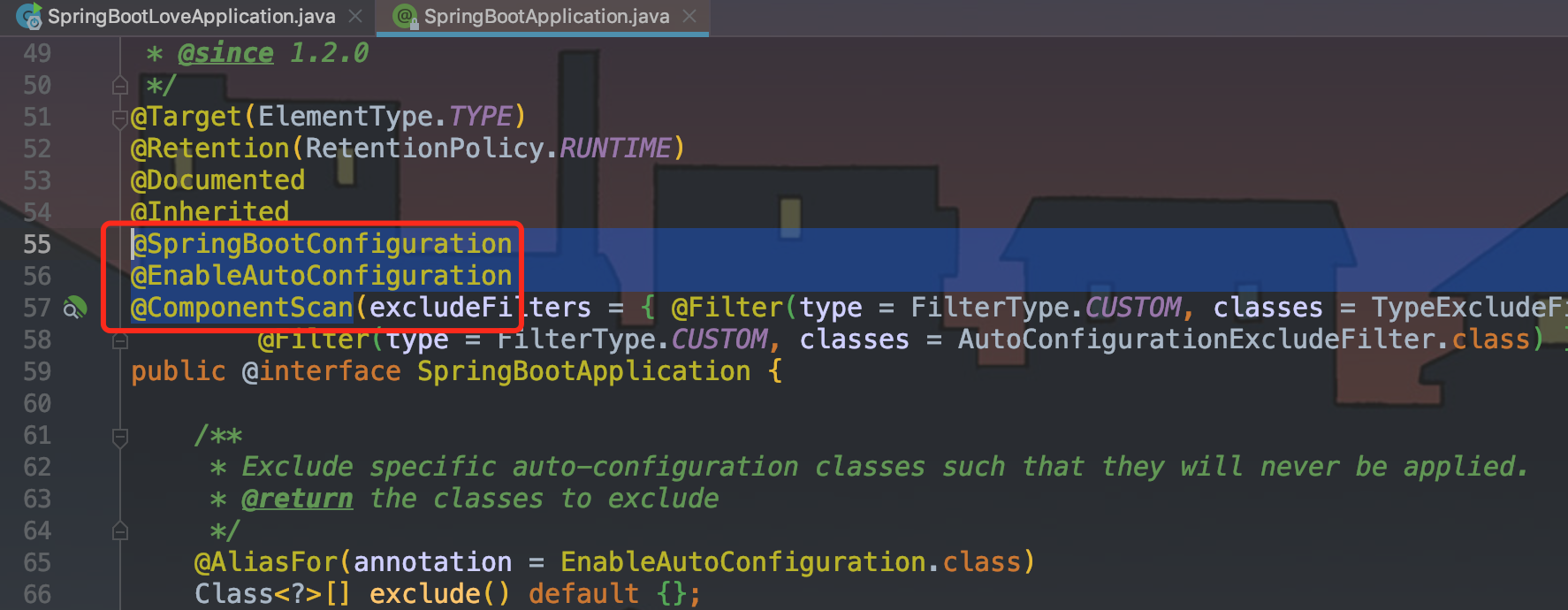
从@SpringBootApplication注解内部可以发现,它虽然定义使用了多个Annotation进行了原信息标注,但实际上重要的只有三个Annotation:
- @SpringBootConfiguration(@SpringBootConfiguration注解点开查看发现里面还是应用了@Configuration)->Spring IOC容器配置类。
- @EnableAutoConfiguration ->使用@Import将所有符合自动配置条件的bean定义加载到IOC容器。
- @ComponentScan ->自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean定义,默认扫描SpringApplication的run方法里的class
所在的包路径下文件,所以通常将该启动类放到根包路径下。
即 @SpringBootApplication = (默认属性)@Configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan。
三、启动方法
启动方法中分为两个阶段即 创建SpringApplication 实例 和 执行run方法。
1、创建SpringApplication实例
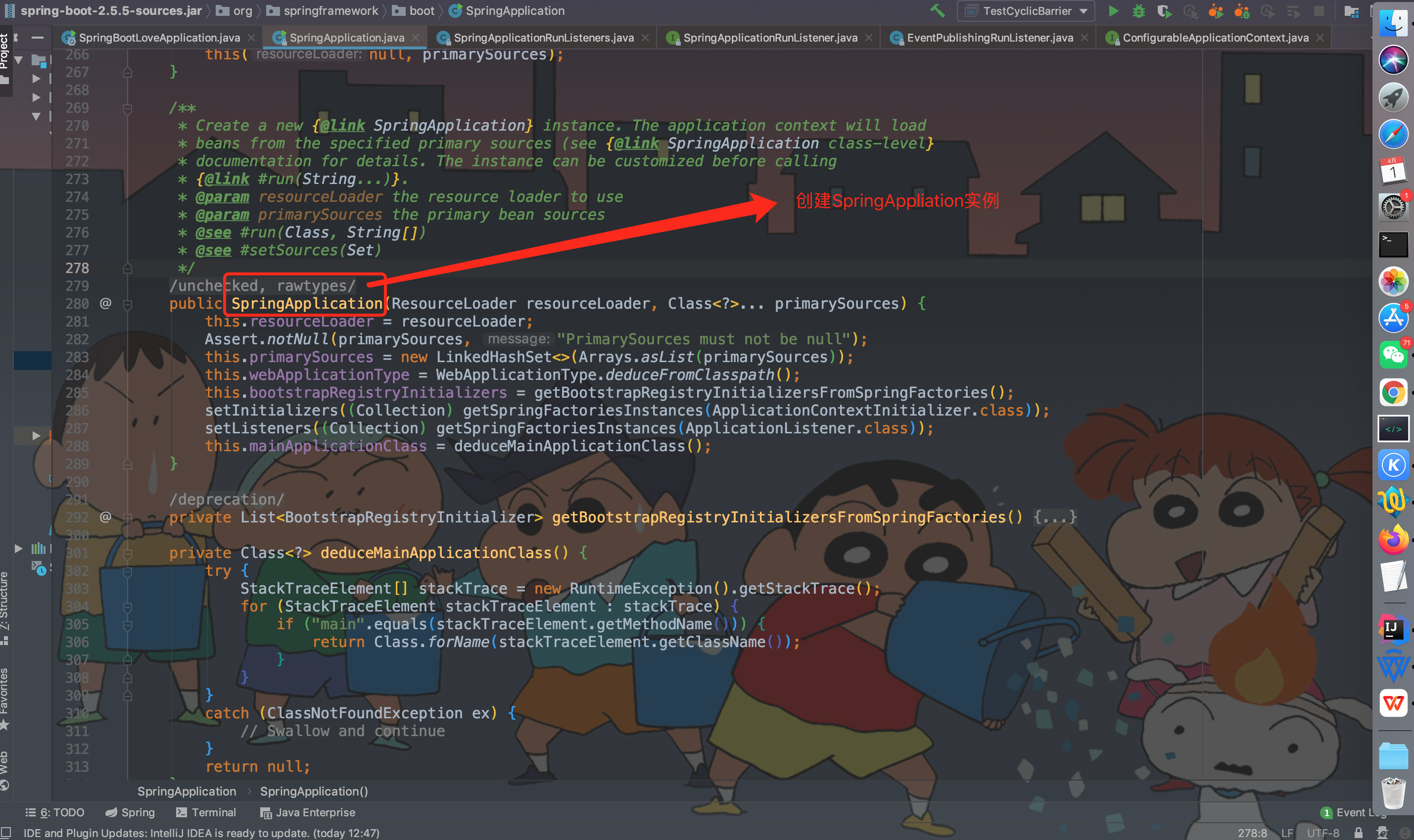
从启动类中的run方法跟进去,SpringApplication.run -> return run -> return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args) -> this(null, primarySources) -> SpringApplication。
其中:return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args) ,如果跟new SpringApplication(primarySources) 方法则是启动方法中的第一阶段即创建SpringApplication实例,跟run(args) 方法进去就是启动方法中的第二阶段。
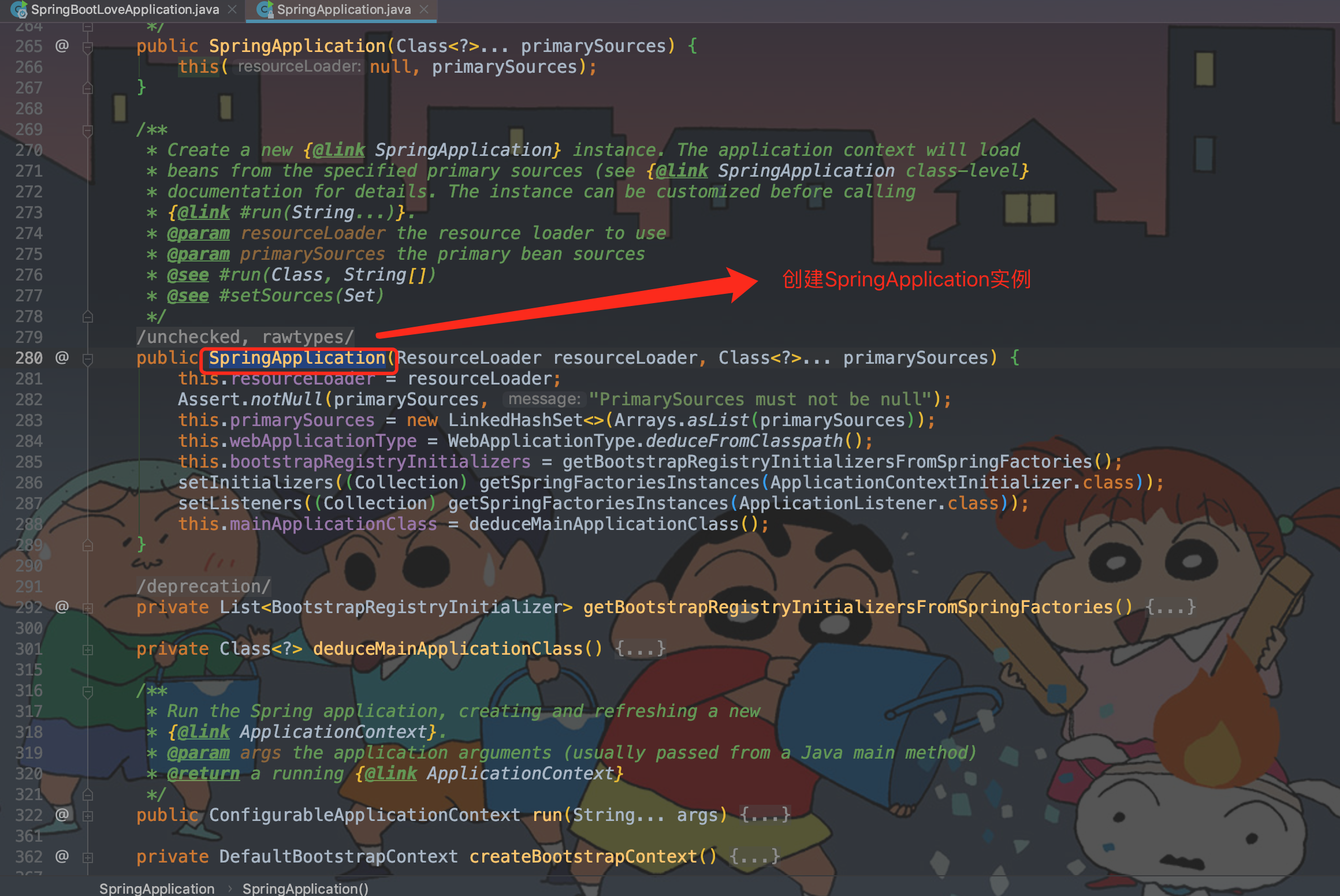
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>… primarySources)
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
*
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 初始化类加载器
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
// Assert 断言非空,若传入的class参数为null则打印异常并退出初始化
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 获取main方法中的args,初始化启动时配置的额外参数集合
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 判断项目启动类型:NONE/SERVLET/REACTIVE
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 从 Spring 工厂获取 Bootstrap Registry Initializers
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories();
// 获取 Spring 工厂实例 -> 容器上下文相关的初始化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 获取 Spring 工厂实例 -> 设置应用程序监听器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 推导出主应用程序类,即从当前的栈信息中寻找main所在主类:com.iot.SpringBootLoveApplication
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
1.1、WebApplicationType
WebApplicationType 判断项目类型。
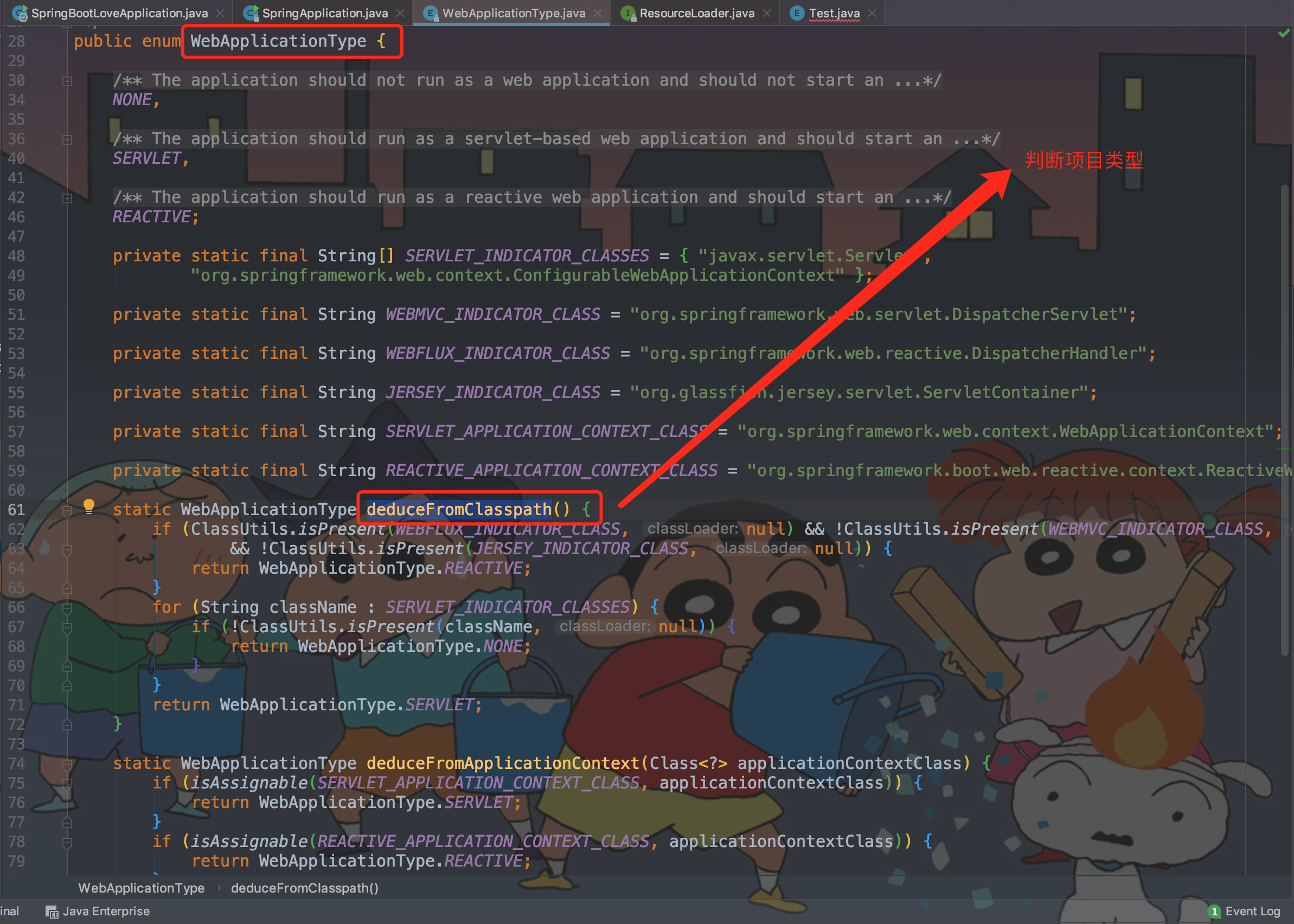
public enum WebApplicationType
/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
/**
* An enumeration of possible types of web application.
*
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Brian Clozel
* @since 2.0.0
*/
public enum WebApplicationType {
/**
* The application should not run as a web application and should not start an
* embedded web server.
*/
NONE,
/**
* The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an
* embedded servlet web server.
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an
* embedded reactive web server.
*/
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = {"javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"};
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext";
private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext";
/**
* deduceFromClasspath
* 依次循环遍历当前应用中是否存在相关的类来判断最终应用的启动类型
*
* @return
*/
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
/**
* REACTIVE:响应式WEB项目
* 若启动类型为REACTIVE,
* 则类路径下存在 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler 类
* 并且不存在 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 和 org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer
* 两者指的是SpringMVC/Tomcat和jersey容器
*/
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
/**
* NONE:非WEB项目,就是一个最简单的Springboot应用
* 若启动类型为NONE
* 则类路径下 javax.servlet.Servlet 和org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext都不存在
*/
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
/**
* SERVLET:SERVLET WEB 项目
* 若启动类型为Servlet,则必须有SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES中的javax.servlet.Servlet
* 和org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
static WebApplicationType deduceFromApplicationContext(Class<?> applicationContextClass) {
if (isAssignable(SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
if (isAssignable(REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
private static boolean isAssignable(String target, Class<?> type) {
try {
return ClassUtils.resolveClassName(target, null).isAssignableFrom(type);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
}
1.2、getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories
getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories方法从spring.factories 中获取 BootstrapRegistryInitializer。
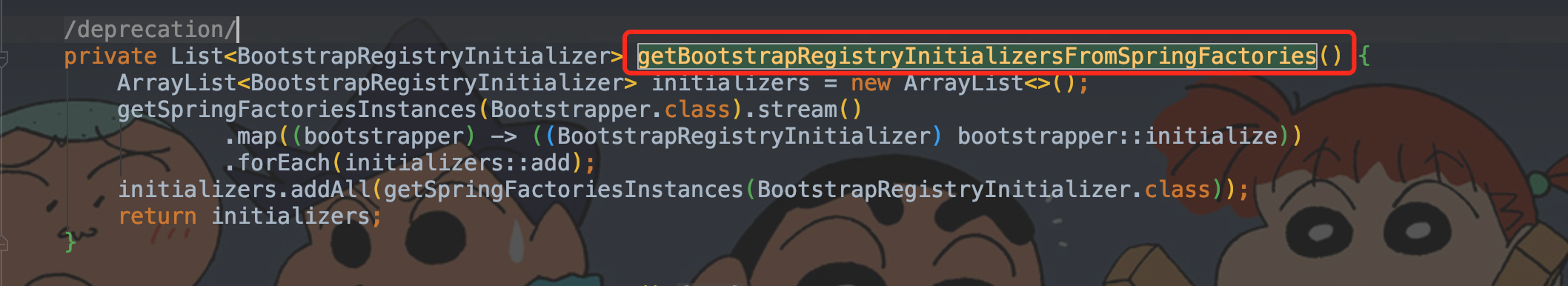
private List getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories()
private List<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories(){
ArrayList<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> initializers=new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 从spring.factories 中获取Bootstrapper集合,
* 然后遍历转化为BootstrapRegistryInitializer,再存入 initializers
*/
getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class).stream()
.map((bootstrapper)->((BootstrapRegistryInitializer)bootstrapper::initialize))
.forEach(initializers::add);
/**
* 从spring.factories 中获取BootstrapRegistryInitializer集合,再存入 initializers
* getSpringFactoriesInstances 该方法在整个启动流程中会频繁出现,下面集中介绍
*/
initializers.addAll(getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
return initializers;
}
1.3、setInitializers && setListeners
setInitializers && setListeners 分别是容器上下文初始化 & 监听器初始化。
容器上下文初始化setInitializers 和监听器初始化setListeners 都是调用了getSpringFactoriesInstances() 方法,从spring.factories中获取配置。不同的是传给它的type参数,主要有一下几种类型。
- ApplicationContextInitializer.class 上下文相关
- ApplicationListener.class 监听器相关
- SpringApplicationRunListener.class 运行时监听器
- SpringBootExceptionReporter.class 异常类相关
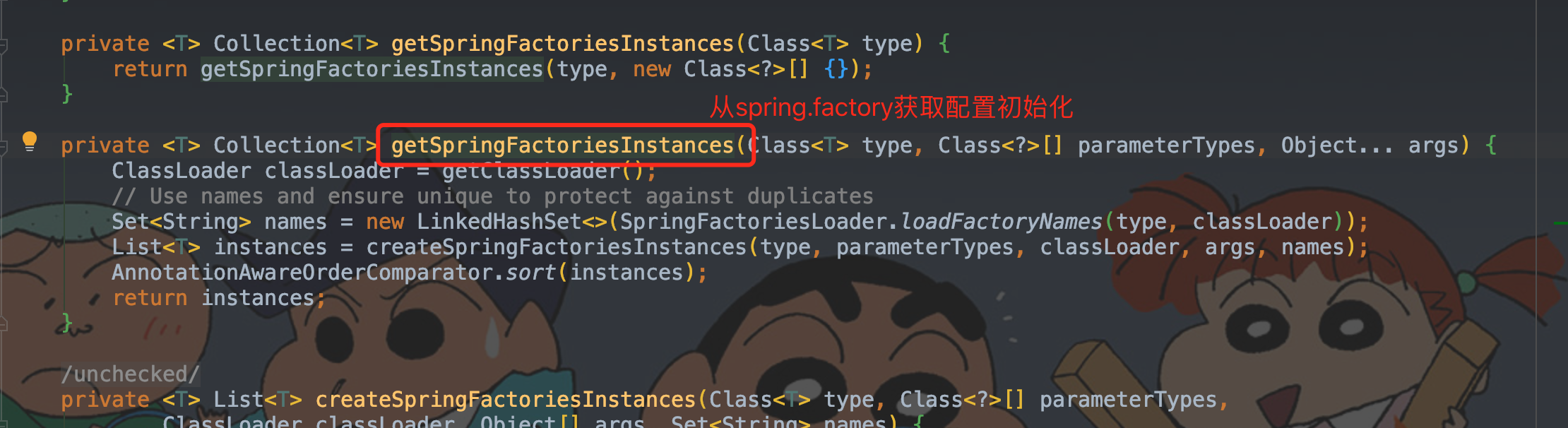
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object… args)
/**
* The location to look for factories.
* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*/
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
/**
* 从spring.factories中获取配置
*/
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
/**
* 加载各jar包中的"META-INF/spring.factories"配置
* 其中SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader) 方法
* 是获取spring.factories配置文件中已经配置的指定类型的的实现类集合
* 其中FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的值:META-INF/spring.factories
*/
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 通过反射创建这些类
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* <p>As of Spring Framework 5.3, if a particular implementation class name
* is discovered more than once for the given factory type, duplicates will
* be ignored.
*
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
* @see #loadFactories
*/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
/**
* Springboot自动配置的秘密
* Springboot在启动时读取了所有starter jar包里的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,实现了所谓的自动化配置
* 这里jar包里的都是默认配置,后续Springboot也会从xml、yaml文件中的用户配置去覆盖同名的配置。
* 另外,这里的缓存配置是保存在一个map类型的cache中,其中的key键对应上面提到的各种Type类型,value就是Type的各种初始jar包里的同类型Java类。
*/
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 获取相应类加载器中内容
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
// 存在则直接返回类加载器中内容
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// 不存在则初始化类加载器中内容
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
/**
* 获取资源 -> META-INF/spring.factories 列表
* 其中FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的值:META-INF/spring.factories
*/
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
// 可能存在多个META-INF/spring.factories 文件,循环加载
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
// 获取 META-INF/spring.factories 文件URL地址
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// 加载资源
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 加载资源配置
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
// key:value形式循环配置
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
// 逗号分隔列表到字符串数组
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
// 循环value中子项到列表中
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
// 列表去重
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
// 列表保存
cache.put(classLoader, result);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 反射创建实现类
*/
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
1.4、deduceMainApplicationClass
deduceMainApplicationClass 推导主应用程序类。
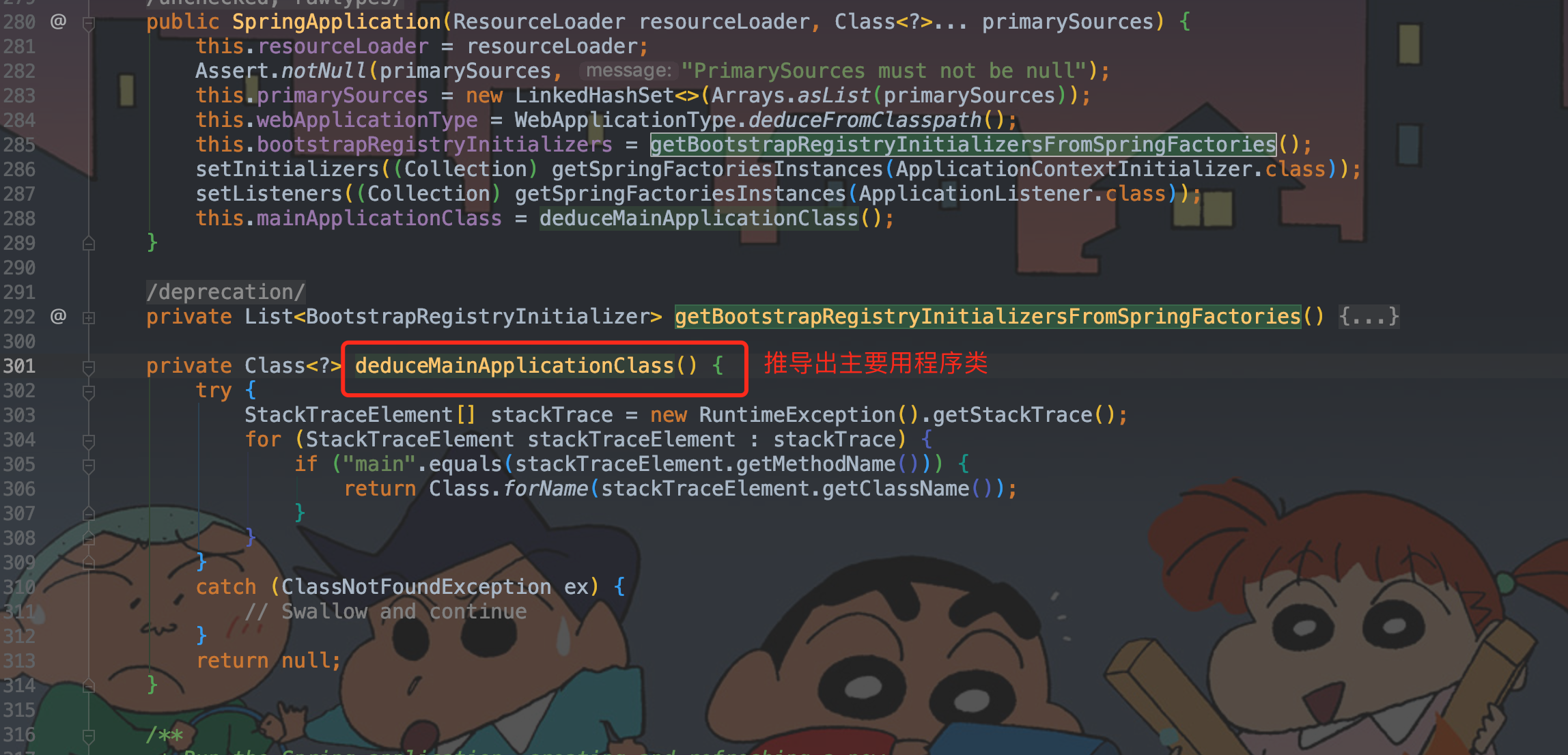
/**
* 推导主应用程序类
* @return
*/
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
// 获取当前的栈信息
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
// 获取main方法所在的类class,此处即com.iot.SpringBootLoveApplication
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass()
View Code
2、run方法
初始化完SpringApplication 就可以运行他的run方法了,也就是启动方法中的第二阶段。
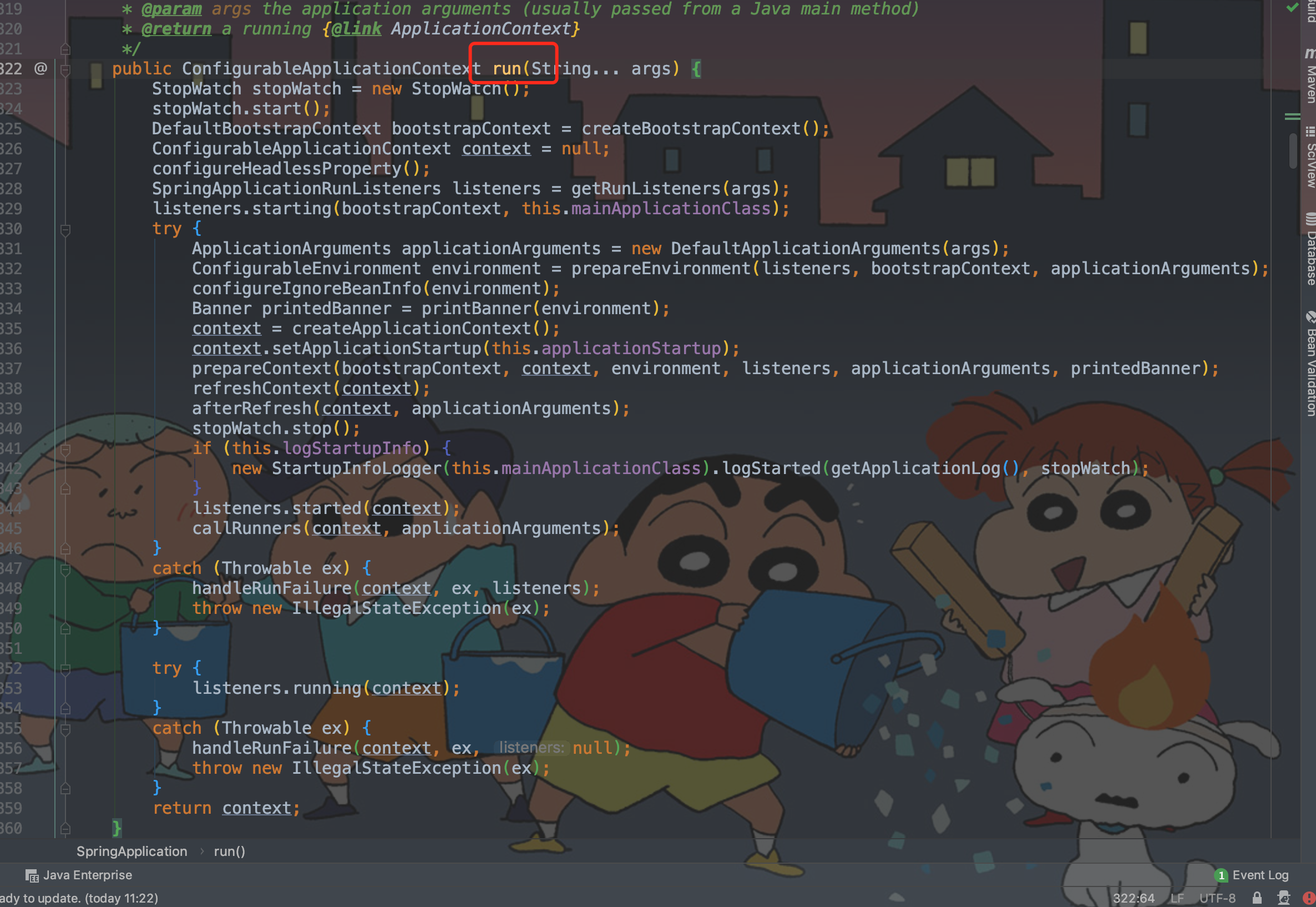
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String… args)
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
*
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
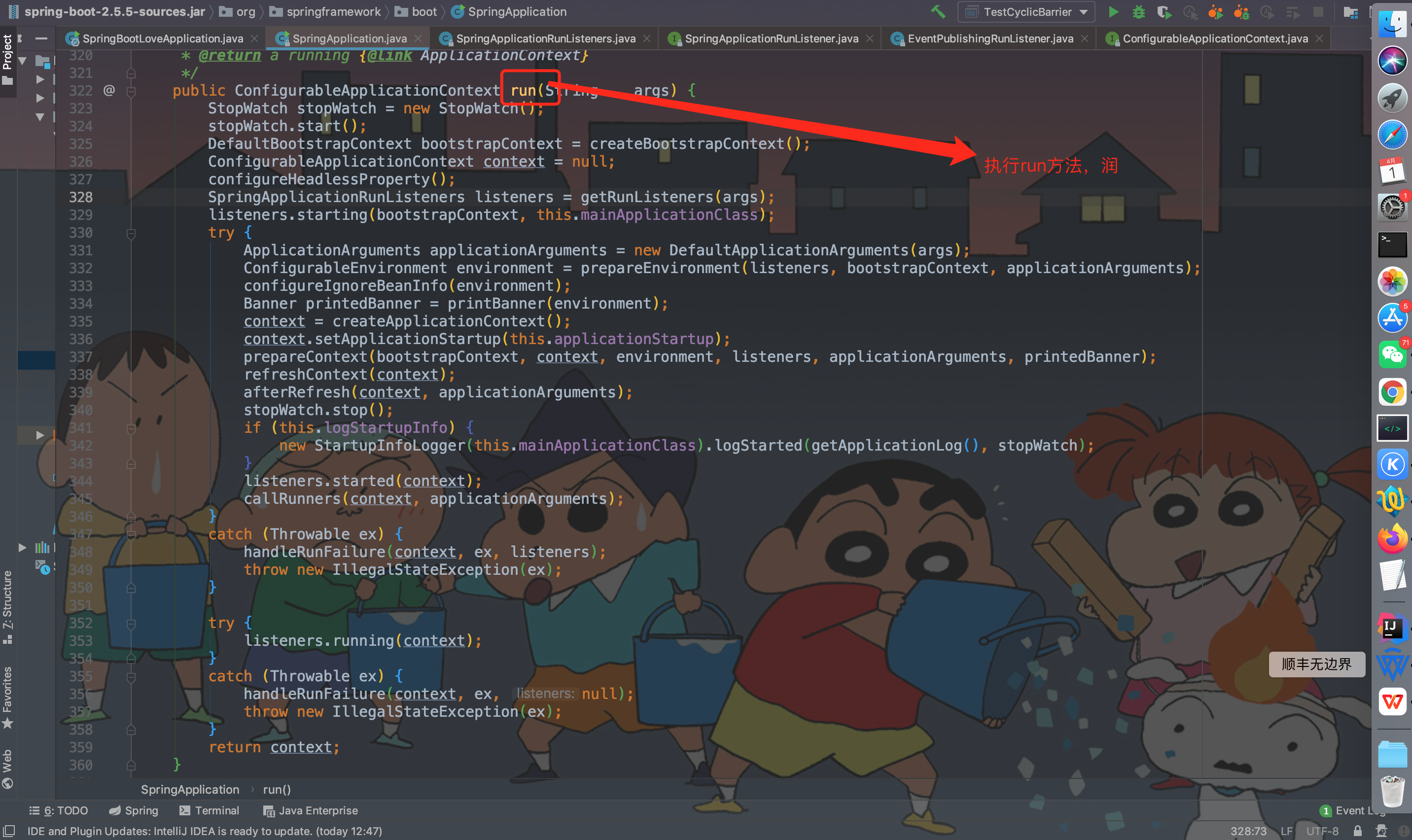
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 启动一个秒表计时器,用于统计项目启动时间
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 创建启动上下文对象即spring根容器
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
// 定义可配置的应用程序上下文变量
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
/**
* 设置jdk系统属性
* headless直译就是无头模式,
* headless模式的意思就是明确Springboot要在无鼠键支持的环境中运行,一般程序也都跑在Linux之类的服务器上,无鼠键支持,这里默认值是true;
*/
configureHeadlessProperty();
/**
* 获取运行监听器 getRunListeners, 其中也是调用了上面说到的getSpringFactoriesInstances 方法
* 从spring.factories中获取配置
*/
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 启动监听器
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 包装默认应用程序参数,也就是在命令行下启动应用带的参数,如--server.port=9000
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//
/**
* 准备环境 prepareEnvironment 是个硬茬,里面主要涉及到
* getOrCreateEnvironment、configureEnvironment、configurePropertySources、configureProfiles
* environmentPrepared、bindToSpringApplication、attach诸多方法可以在下面的例子中查看
*/
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
// 配置忽略的 bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印 SpringBoot 标志,即启动的时候在控制台的图案logo,可以在src/main/resources下放入名字是banner的自定义文件
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建 IOC 容器
context = createApplicationContext();
// 设置一个启动器,设置应用程序启动
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 配置 IOC 容器的基本信息 (spring容器前置处理)
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
/**
* 刷新IOC容器
* 这里会涉及Spring容器启动、自动装配、创建 WebServer启动Web服务即SpringBoot启动内嵌的 Tomcat
*/
refreshContext(context);
/**
* 留给用户自定义容器刷新完成后的处理逻辑
* 刷新容器后的扩展接口(spring容器后置处理)
*/
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
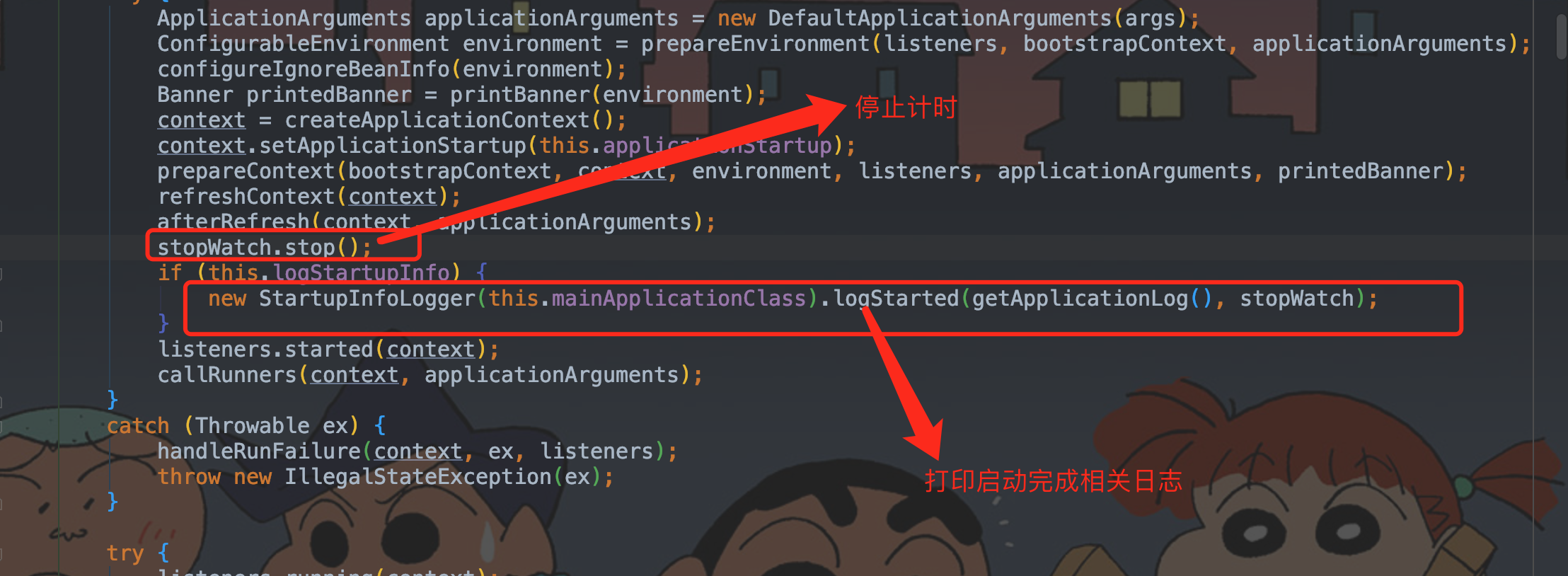
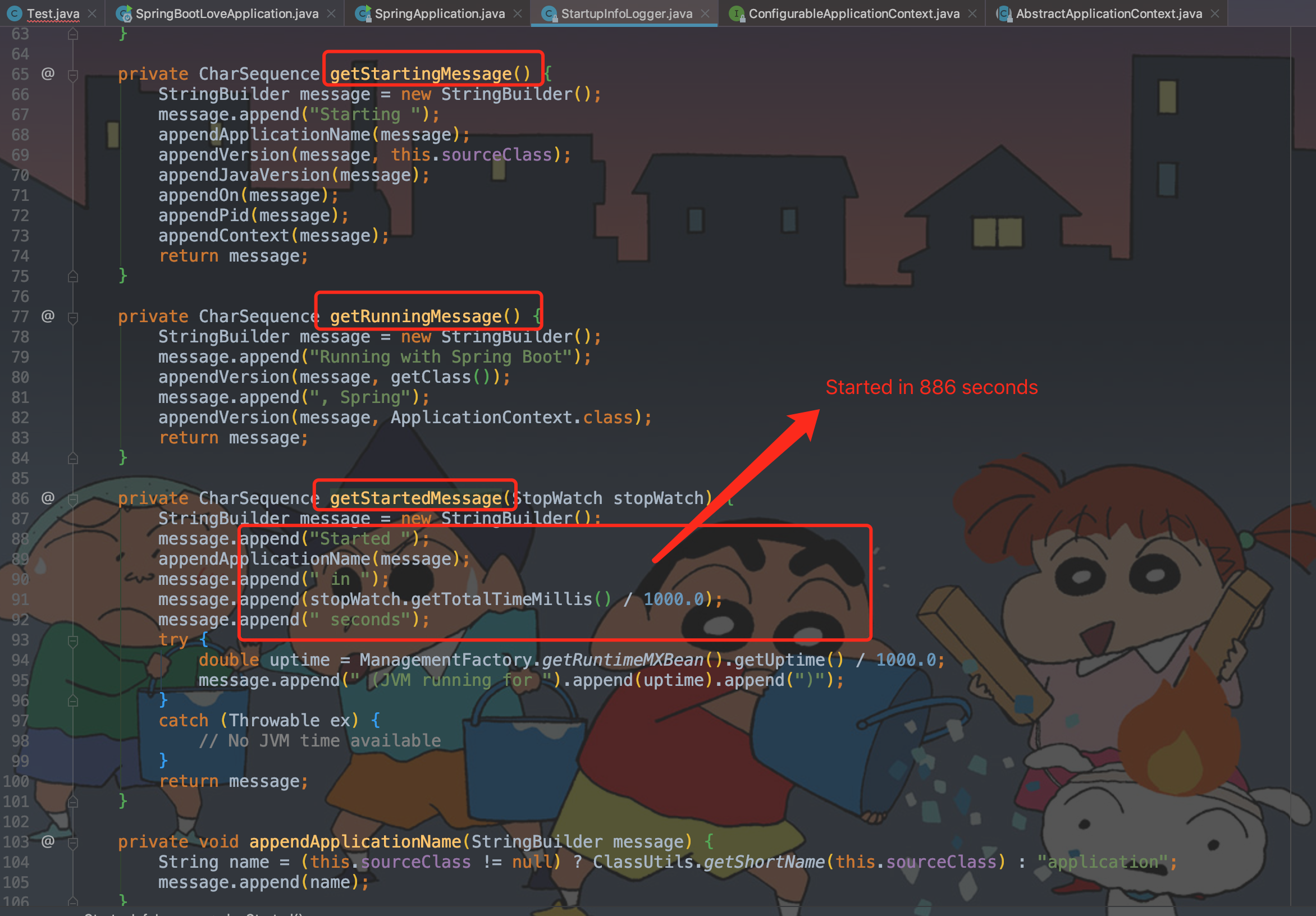
// 结束计时器并打印,这就是我们启动后console的显示的时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
// 打印启动完毕的那行日志
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发布监听应用上下文启动完成(发出启动结束事件),所有的运行监听器调用 started() 方法
listeners.started(context);
// 执行runner,遍历所有的 runner,调用 run 方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常处理,如果run过程发生异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 所有的运行监听器调用 running() 方法,监听应用上下文
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常处理
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回最终构建的容器对象
return context;
}
2.1、configureHeadlessProperty
configureHeadlessProperty 设置headless无头模式。

private void configureHeadlessProperty()
1 private static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS = "java.awt.headless";
2
3 /**
4 * headless直译就是无头模式,
5 * headless模式的意思就是明确Springboot要在无鼠键支持的环境中运行,一般程序也都跑在Linux之类的服务器上,无鼠键支持,这里默认值是true;
6 */
7 private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
8 // SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS = "java.awt.headless";
9 System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
10 System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
11 }
2.2、prepareEnvironment
prepareEnvironment 准备环境是个硬茬,里面主要涉及到getOrCreateEnvironment、configureEnvironment、configurePropertySources、configureProfilesenvironmentPrepared、bindToSpringApplication、attach诸多方法。
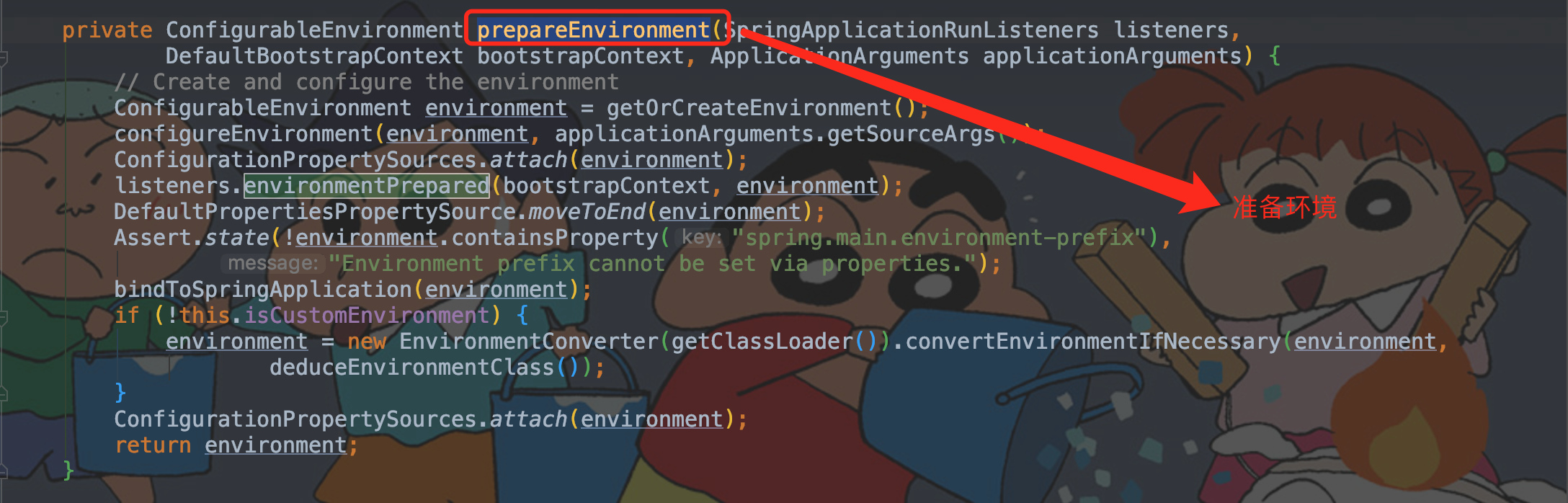
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments)
/**
* 准备环境
*
* @param listeners
* @param bootstrapContext
* @param applicationArguments
* @return
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment 创建和配置环境
// 根据项目类型建环境ConfigurableEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 从环境中获取并设置 PropertySources 和 activeProfiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 把 PropertySources 设置在自己PropertySources的第一个位置
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
/**
* 运行监听器调用
* 广播事件,listeners环境准备(就是广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件)
* 发布事件通知所有的监听器当前环境准备完成
*/
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 移动 defaultProperties 属性源到环境中的最后一个源
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// 断言 抛异常
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
// 与容器绑定当前环境
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 若非web环境,将环境转换成StandardEnvironment
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
/**
* 获取或创建环境Environment
*
* @return
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
// 存在则直接返回
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
/**
* 根据webApplicationType创建对应的Environment
*/
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
// SERVLET WEB 项目
case SERVLET:
return new ApplicationServletEnvironment();
// REACTIVE:响应式WEB项目
case REACTIVE:
return new ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment();
// 非WEB项目,就是一个最简单的Springboot应用
default:
return new ApplicationEnvironment();
}
}
/**
* 从环境中获取并设置 PropertySources 和 activeProfiles
* 将配置任务按顺序委托给configurePropertySources和configureProfiles
* Template method delegating to
* {@link #configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[])} and
* {@link #configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[])} in that order.
* Override this method for complete control over Environment customization, or one of
* the above for fine-grained control over property sources or profiles, respectively.
*
* @param environment this application's environment
* @param args arguments passed to the {@code run} method
* @see #configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[])
* @see #configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[])
*/
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());
}
// 配置PropertySources
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 配置Profiles
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
/**
* 配置PropertySources
* Add, remove or re-order any {@link PropertySource}s in this application's
* environment.
*
* @param environment this application's environment
* @param args arguments passed to the {@code run} method
* @see #configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[])
*/
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 初始化 defaultProperties
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) {
// 存在的话将其放到最后位置
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources);
}
/**
* 存在命令行参数,则解析它并封装进SimpleCommandLinePropertySource对象
* 同时将此对象放到sources的第一位置(优先级最高)
*/
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(
new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
} else {
// 放到首位
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
/**
* 配置Profiles
*
* @param environment
* @param args
*/
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
/**
* 保证environment的activeProfiles属性被初始化了。从PropertySources中查找spring.profiles.active属性
* 存在则将其值添加activeProfiles集合中。
* 配置应用环境中的哪些配置文件处于激活状态(或默认激活)
* 可以通过spring.profiles.active属性在配置文件处理期间激活其他配置文件
* 就是我们项目中通常配置的dev、sit、prod等环境配置信息设置哪些Profiles是激活的。
*/
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized
// But these ones should go first (last wins in a property key clash)
// 如果存在其他的Profiles,则将这些Profiles放到第一的位置
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
/**
* 运行监听器调用
*
* @param bootstrapContext
* @param environment
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.environment-prepared",
(listener) -> listener.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment));
}
/**
* 运行监听器调用
* Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the
* {@link ApplicationContext} has been created.
*
* @param environment the environment
* @deprecated since 2.4.0 for removal in 2.6.0 in favor of
* {@link #environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment)}
*/
@Deprecated
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
// 广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,后面再看
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
/**
* 与容器绑定当前环境
* Bind the environment to the {@link SpringApplication}.
*
* @param environment the environment to bind
*/
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
try {
// 将environment绑定到SpringApplication
Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}
/**
* 配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
* Attach a {@link ConfigurationPropertySource} support to the specified
* {@link Environment}. Adapts each {@link PropertySource} managed by the environment
* to a {@link ConfigurationPropertySource} and allows classic
* {@link PropertySourcesPropertyResolver} calls to resolve using
* {@link ConfigurationPropertyName configuration property names}.
* <p>
* The attached resolver will dynamically track any additions or removals from the
* underlying {@link Environment} property sources.
*
* @param environment the source environment (must be an instance of
* {@link ConfigurableEnvironment})
* @see #get(Environment)
*/
public static void attach(Environment environment) {
// 判断environment是否是ConfigurableEnvironment的实例
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
// 从environment获取PropertySources
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment)
.getPropertySources();
PropertySource<?> attached = sources.get(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
if (attached != null && attached.getSource() != sources) {
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
attached = null;
}
if (attached == null) {
// 将sources封装成ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource对象,并把这个对象放到sources的第一位置
sources.addFirst(new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(
ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources)));
}
}
2.3、printBanner
printBanner 打印SpringBoot标志。printBanner(environment)方法就是打印Banner,Banner就是项目启动时看到的那个logo。在工程项目src/main/resources路径下下放入名字是banner的文件,后缀后可以是SpringApplicationBannerPrinter.java类里的{ “gif”, “jpg”, “png” },或者是txt、图片也可以的,但是图片打印时会字符化,而不是打印图片本身。自定义banner链接
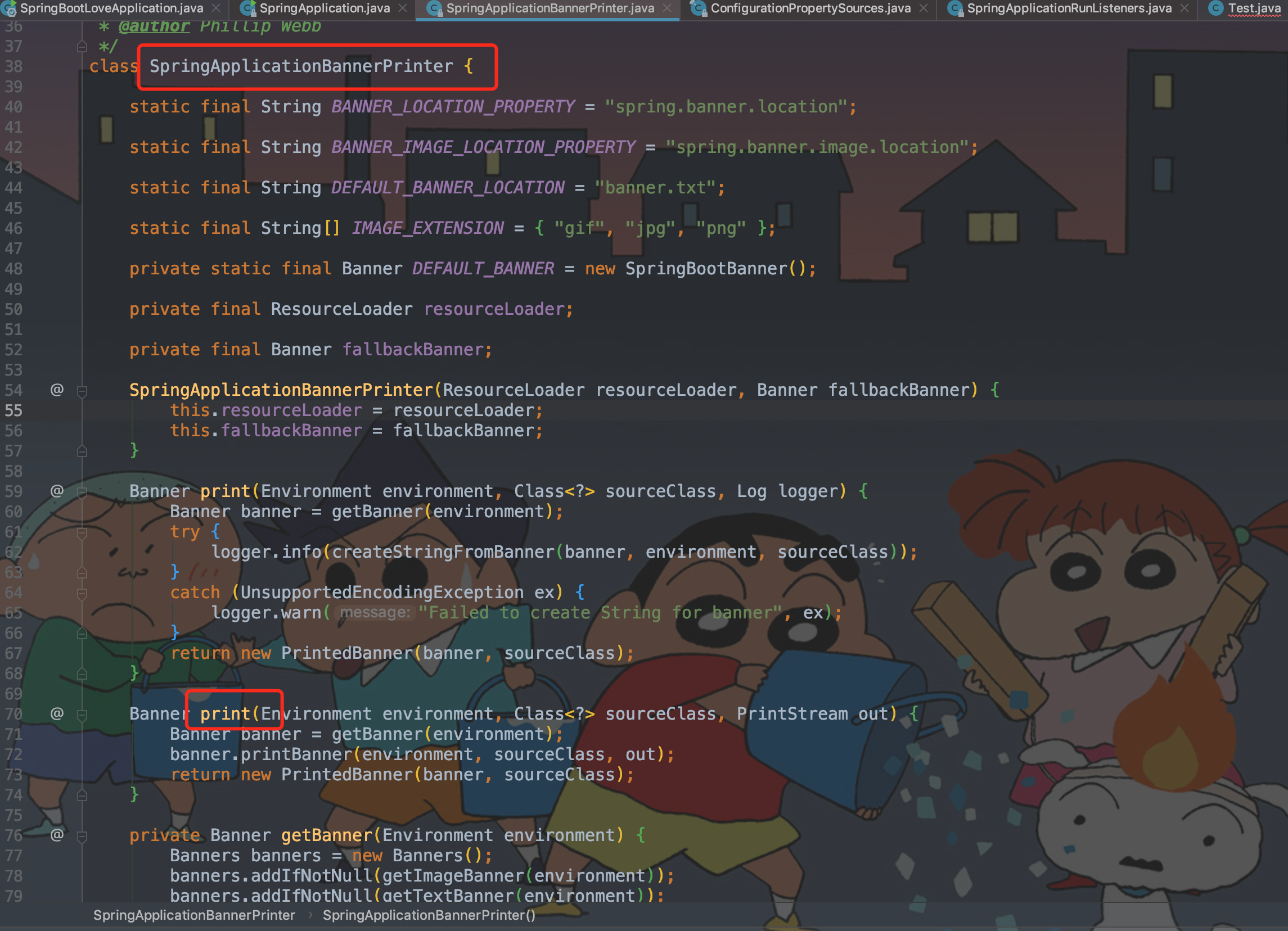
private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
/**
* 打印SpringBoot标志
* banner的输出默认有三种种模式,LOG、CONSOLE、OFF。
* 1. LOG:将banner信息输出到日志文件。
* 2. CONSOLE:将banner信息输出到控制台。
* 3. OFF:禁用banner的信息输出。
*
* @param environment
* @return
*/
private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
// 判断Banner的模式是否关闭,如果关闭直接返回。
if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) {
return null;
}
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader
: new DefaultResourceLoader(null);
// 创建SpringApplicationBannerPrinter 打印类
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(resourceLoader, this.banner);
// LOG:将banner信息输出到日志文件
if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) {
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger);
}
//banner没有关闭且没有指定是写到log文件中 将banner信息输出到控制台
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out);
}
/**
* 打印
*
* @param environment
* @param sourceClass
* @param logger
* @return
*/
Banner print(Environment environment, Class<?> sourceClass, Log logger) {
// 获取banner内容
Banner banner = getBanner(environment);
try {
logger.info(createStringFromBanner(banner, environment, sourceClass));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {
logger.warn("Failed to create String for banner", ex);
}
return new PrintedBanner(banner, sourceClass);
}
/**
* 获取banner内容
*
* @param environment
* @return
*/
private Banner getBanner(Environment environment) {
Banners banners = new Banners();
// 图片类型的banner内容
banners.addIfNotNull(getImageBanner(environment));
// 文本类型的banner内容
banners.addIfNotNull(getTextBanner(environment));
if (banners.hasAtLeastOneBanner()) {
return banners;
}
if (this.fallbackBanner != null) {
return this.fallbackBanner;
}
return DEFAULT_BANNER;
}
static final String BANNER_LOCATION_PROPERTY = "spring.banner.location";
static final String DEFAULT_BANNER_LOCATION = "banner.txt";
/**
* 文本类型的banner内容获取
*
* @param environment
* @return
*/
private Banner getTextBanner(Environment environment) {
/**
* 拿到自定义配置的banner文件地址
* BANNER_LOCATION_PROPERTY = "spring.banner.location"
* DEFAULT_BANNER_LOCATION = "banner.txt";
*/
String location = environment.getProperty(BANNER_LOCATION_PROPERTY, DEFAULT_BANNER_LOCATION);
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
try {
if (resource.exists() && !resource.getURL().toExternalForm().contains("liquibase-core")) {
return new ResourceBanner(resource);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
// Ignore
}
return null;
}
2.4、createApplicationContext
createApplicationContext创建IOC容器。
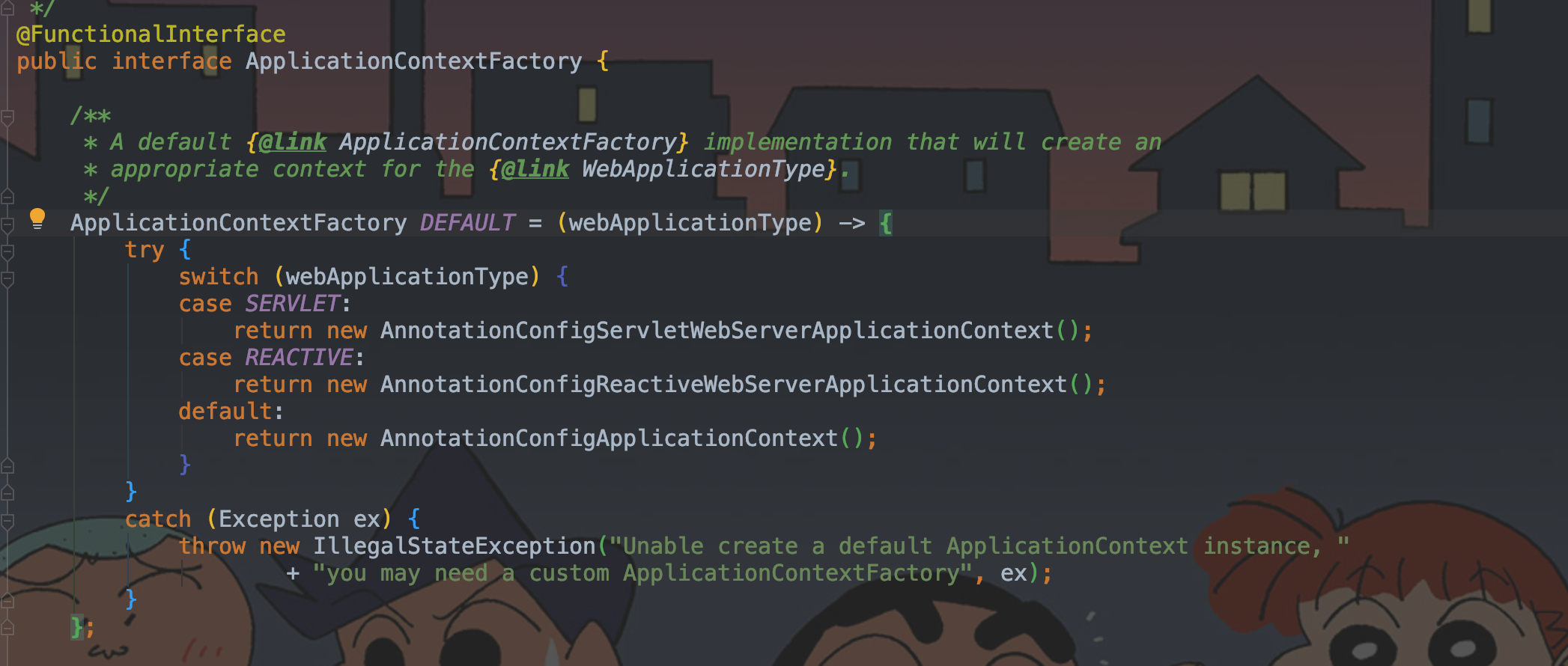
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext()
/**
* 创建 IOC 容器
* A default {@link ApplicationContextFactory} implementation that will create an
* appropriate context for the {@link WebApplicationType}.
*/
ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = (webApplicationType) -> {
try {
// 根据当前应用的类型创建 IOC 容器
switch (webApplicationType) {
// Web 应用环境对应 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
case SERVLET:
return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
// 响应式编程对应 AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext
case REACTIVE:
return new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
// 默认为 Spring 环境 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
default:
return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext instance, "
+ "you may need a custom ApplicationContextFactory", ex);
}
};
/**
* 设置一个启动器
* Set the {@link ApplicationStartup} for this application context.
* <p>This allows the application context to record metrics
* during startup.
* @param applicationStartup the new context event factory
* @since 5.3
*/
void setApplicationStartup(ApplicationStartup applicationStartup);
2.5、prepareContext
prepareContext 配置 IOC 容器的基本信息。
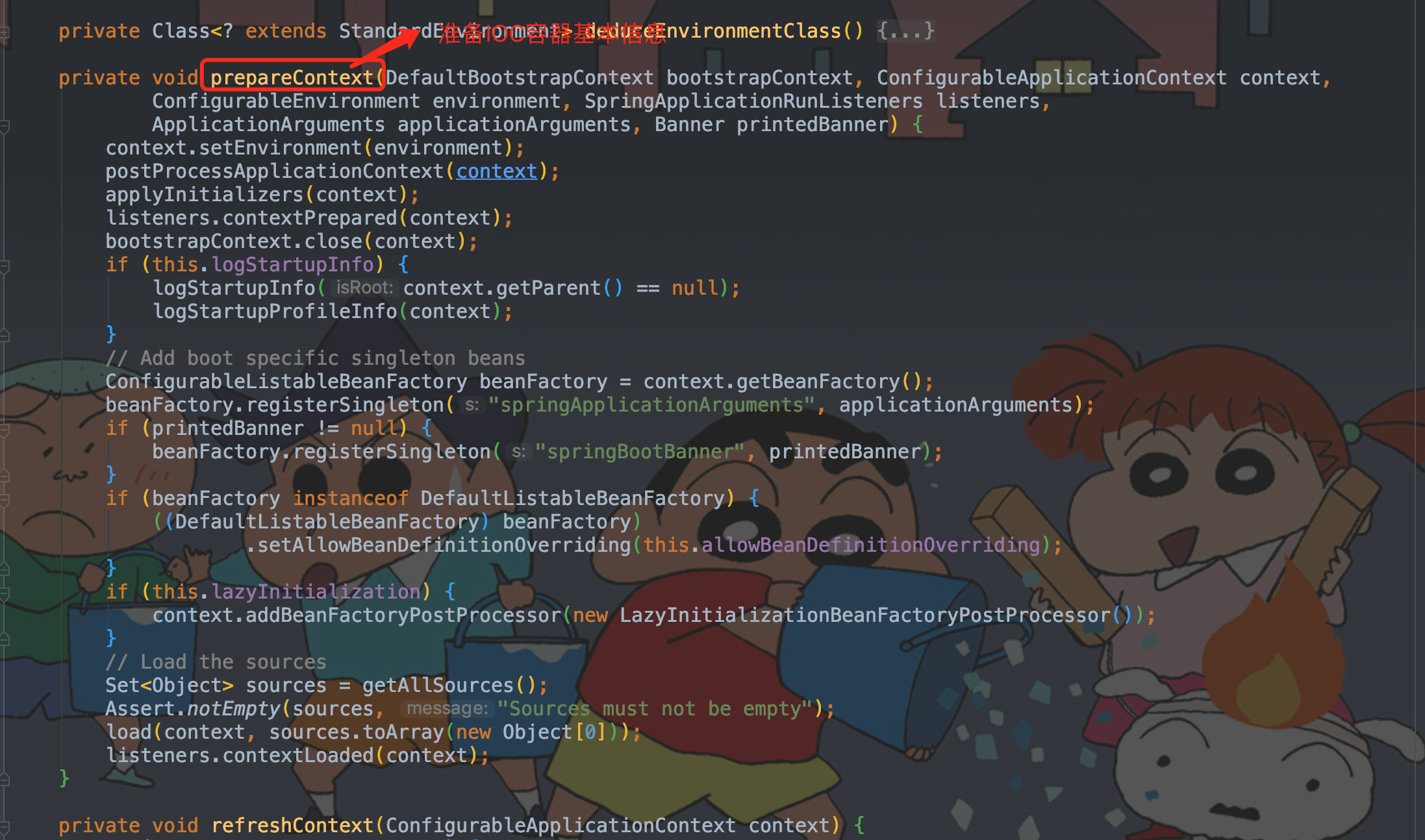
private void prepareContext(参数此处省略)
1 /**
2 * 准备IOC容器基本信息
3 * @param bootstrapContext
4 * @param context
5 * @param environment
6 * @param listeners
7 * @param applicationArguments
8 * @param printedBanner
9 */
10 private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
11 ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
12 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
13 // 设置容器环境,包括各种变量
14 context.setEnvironment(environment);
15 /**
16 * 后置处理流程
17 * 设置IOC容器的 bean 生成器和资源加载器
18 */
19 postProcessApplicationContext(context);
20 /**
21 * 获取所有的初始化器调用 initialize() 方法进行初始化
22 * 执行容器中的ApplicationContextInitializer(包括从 spring.factories和自定义的实例)初始化
23 */
24 applyInitializers(context);
25 /**
26 * 触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 contextPrepared 事件方法
27 * 所有的运行监听器调用 environmentPrepared() 方法,EventPublishingRunListener 发布事件通知 IOC 容器准备完成
28 */
29 listeners.contextPrepared(context);
30 bootstrapContext.close(context);
31 // 打印启动日志
32 if (this.logStartupInfo) {
33 logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
34 logStartupProfileInfo(context);
35 }
36 // Add boot specific singleton beans
37 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
38 // 注册添加特定的单例bean
39 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
40 if (printedBanner != null) {
41 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
42 }
43 if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
44 ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
45 .setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
46 }
47 if (this.lazyInitialization) {
48 context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
49 }
50 // Load the sources
51 // 加载所有资源
52 Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
53 // 断言资源费控
54 Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
55 // 创建BeanDefinitionLoader,加载启动类,将启动类注入容器
56 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
57 // 触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 contextLoaded 事件方法
58 listeners.contextLoaded(context);
59 }
2.6、refresh
refresh 刷新应用上下文,即刷新Spring上下文信息refreshContext。这里会涉及Spring容器启动、SpringBoot自动装配、创建 WebServer启动Web服务即SpringBoot启动内嵌的 Tomcat。
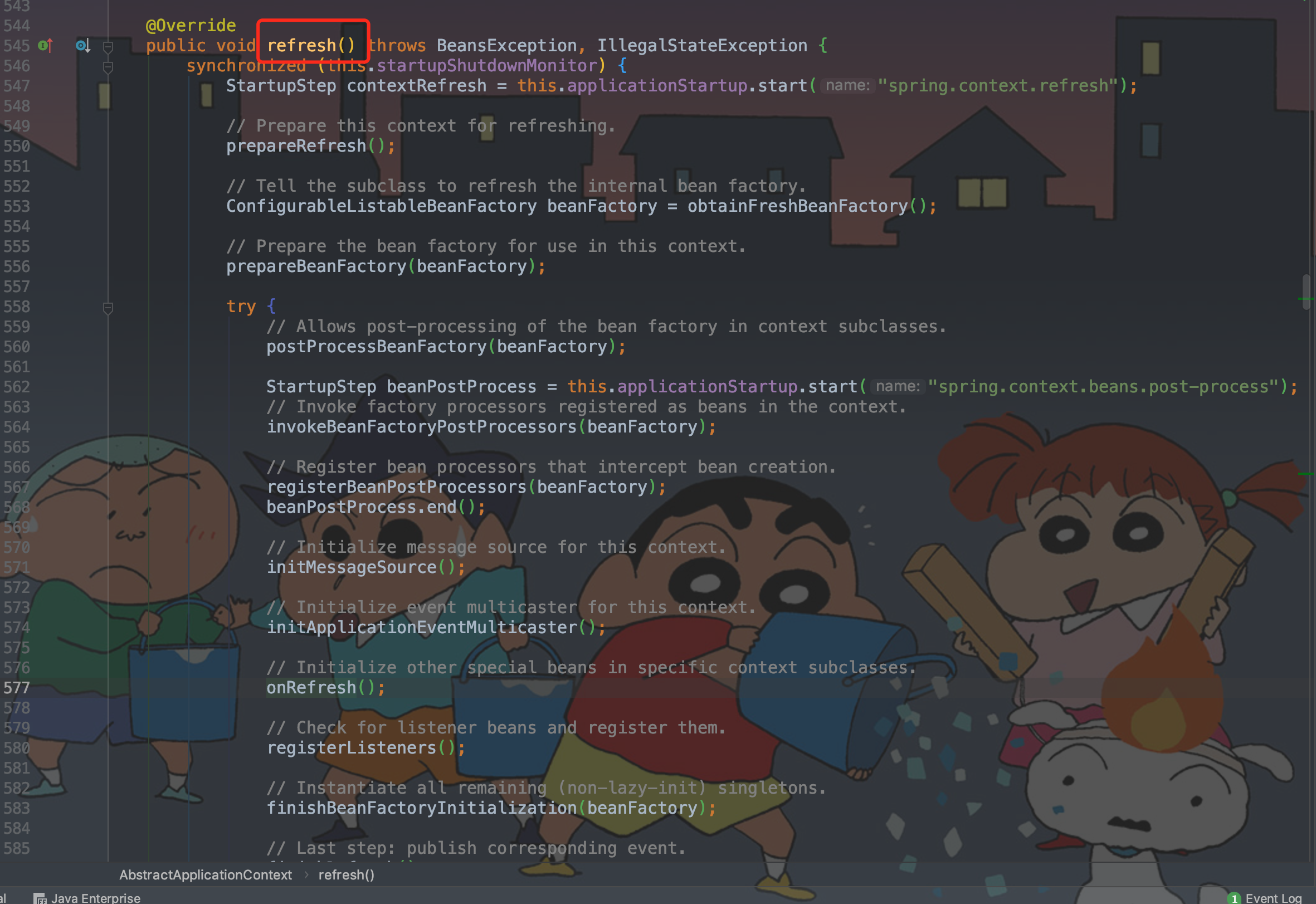
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
/**
* 刷新应用上下文
*
* @param context
*/
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
// 判断是否注册关闭的钩子,是则注册钩子
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}
/**
* Refresh the underlying {@link ApplicationContext}.
*
* @param applicationContext the application context to refresh
*/
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
/**
* 刷新IOC容器
*
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IllegalStateException
*/
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing. 准备刷新上下文
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 通知子类刷新内部工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 准备Bean工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后处理,这部分涉及Web服务器的启动,如servlet
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用在上下文中注册为 bean 的工厂处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 注册拦截 bean 创建的 bean 处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context. 初始化此上下文的消息源
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context. 为该上下文初始化事件多播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 初始化特定上下文子类中的其他特殊 bean
/**
* SpringBoot 一键启动web工程的关键方法
* 创建 WebServer启动Web服务
* SpringBoot启动内嵌的 Tomcat 首先要在pom文件配置内嵌容器为tomcat
* SpringBoot 嵌入式 Servlet 容器,默认支持的 webServe:Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow
* <exclusion>
* <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
* <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
* </exclusion>
*/
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them. 检查侦听器 bean 并注册
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event. 发布事件
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 销毁bean
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
2.7、onRefresh
onRefresh方法中创建WebServer、创建Tomcat对象,是SpringBoot一键启动web工程的关键。SpringBoot 嵌入式 Servlet 容器,默认支持的 webServe:Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow,但要在POM文件加入tomcat相关配置。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion> <!--必须要把内嵌的 Tomcat 容器-->
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
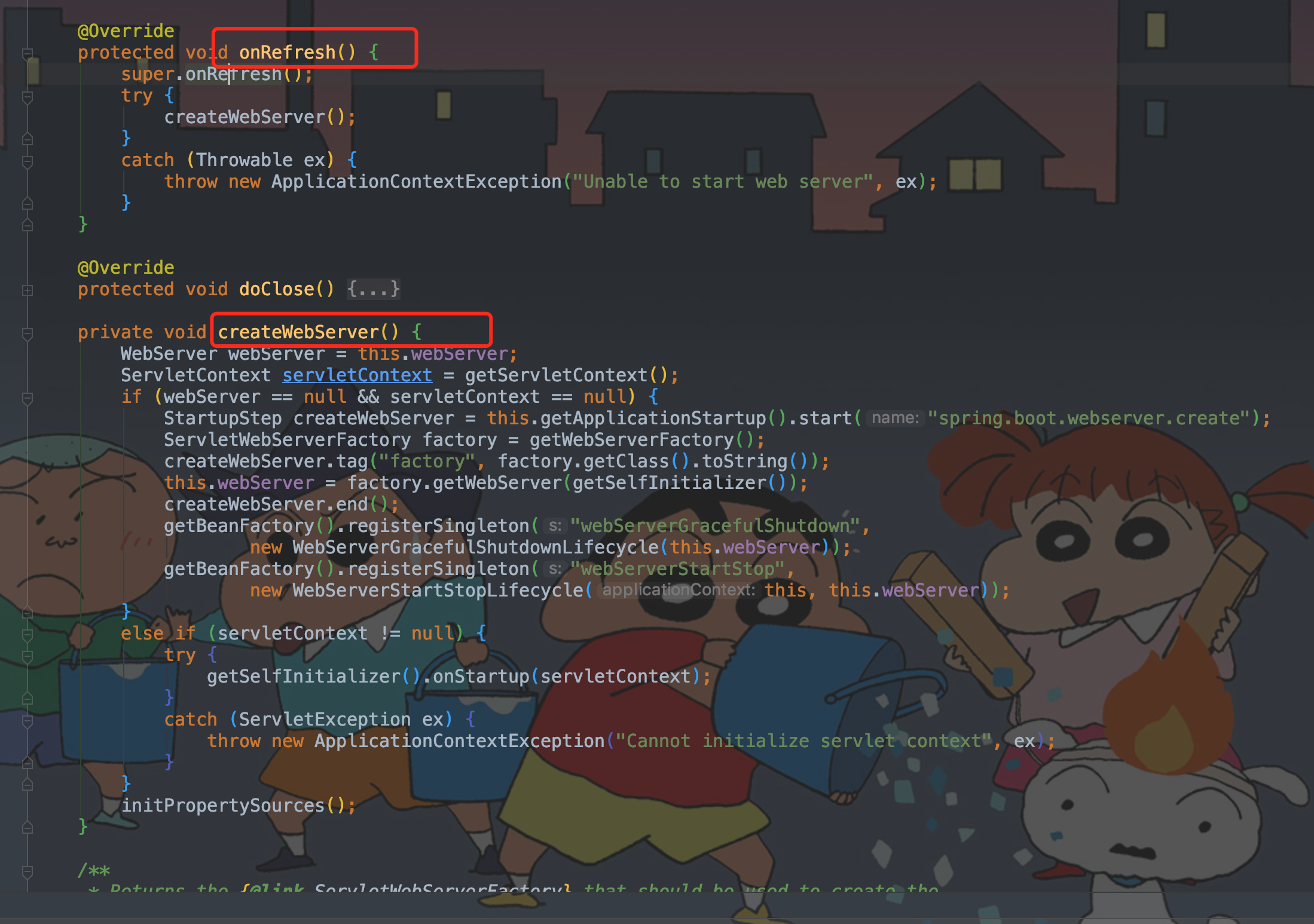
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException
/**
* 创建 WebServer启动Web服务
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
// 初始化给定应用程序上下文的主题资源
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 创建Web 服务
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
/**
* super.onRefresh();
* Initialize the theme capability.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
/**
* 初始化给定应用程序上下文的主题资源,自动检测一个名为“themeSource”的bean。
* 如果没有这样的,将使用默认的(空的)ThemeSource。
*/
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}
/**
* 创建Web 服务
*/
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
// 获取web server
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
// 获取创建容器的工厂
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
/**
* 获取 tomcat 、Jetty 或 Undertow 容器
* 从 getWebServer 方法点进去,找到 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 的实现方法,
* 与之对应的还有 Jetty 和 Undertow。这里配置了基本的连接器、引擎、虚拟站点等配置。
* 自动配置类 ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 导入了 ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration(配置类),
* 根据条件装配判断系统中到底导入了哪个 Web 服务器的包,创建出服务器并启动
* 默认是 web-starter 导入 tomcat 包,容器中就有 TomcatServletWebServerFactory,创建出 Tomcat 服务器并启动
*/
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
createWebServer.end();
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
// 启动web server
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
/**
* 获取tomcat 容器
* 配置了基本的连接器、引擎、虚拟站点等配置
* @param initializers
* @return
*/
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
/**
* 创建了Tomcat对象,并设置参数
*/
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
// 设置工作忙碌
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
// 初始化tomcat 连接,默认NIO
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
// 配置基本的连接器、引擎、虚拟站点
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
// 设置自动部署为false
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
// 准备上下文
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
// 返回TomcatWebServer服务
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link TomcatWebServer} instance.
* @param tomcat the underlying Tomcat server
* @param autoStart if the server should be started
* @param shutdown type of shutdown supported by the server
* @since 2.3.0
*/
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
// 初始化Tomcat
initialize();
}
/**
* 初始化Tomcat
* @throws WebServerException
*/
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
2.8、afterRefresh
afterReftesh() 刷新后处理,是个一空实现的扩展接口,留着后期扩展如用户自定义容器刷新后的处理逻辑。
2.9、停止计时并打印启动完毕相关日志
2.10、started
started 发布监听应用启动事件。
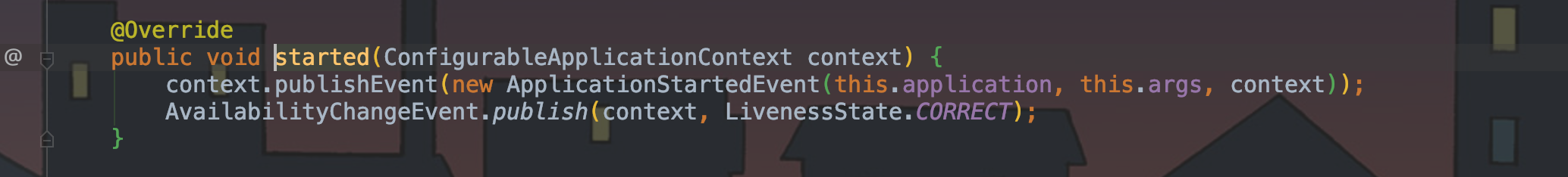
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
/**
* 发布应用监听启动事件
* @param context
*/
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// listener.started(context) 中交由context.publishEvent()方法处理
// 实际上是发送了一个ApplicationStartedEvent的事件
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.started", (listener) -> listener.started(context));
}
/**
* 发布应用启动事件ApplicationStartedEvent.
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, LivenessState.CORRECT);
}
2.11、callRunners
callRunners,执行runner主要是遍历所有的runner获取所有的ApplicationRuner 和CommandLineRunner 来初始化参数,其中callRuner(是一个回调函数)。
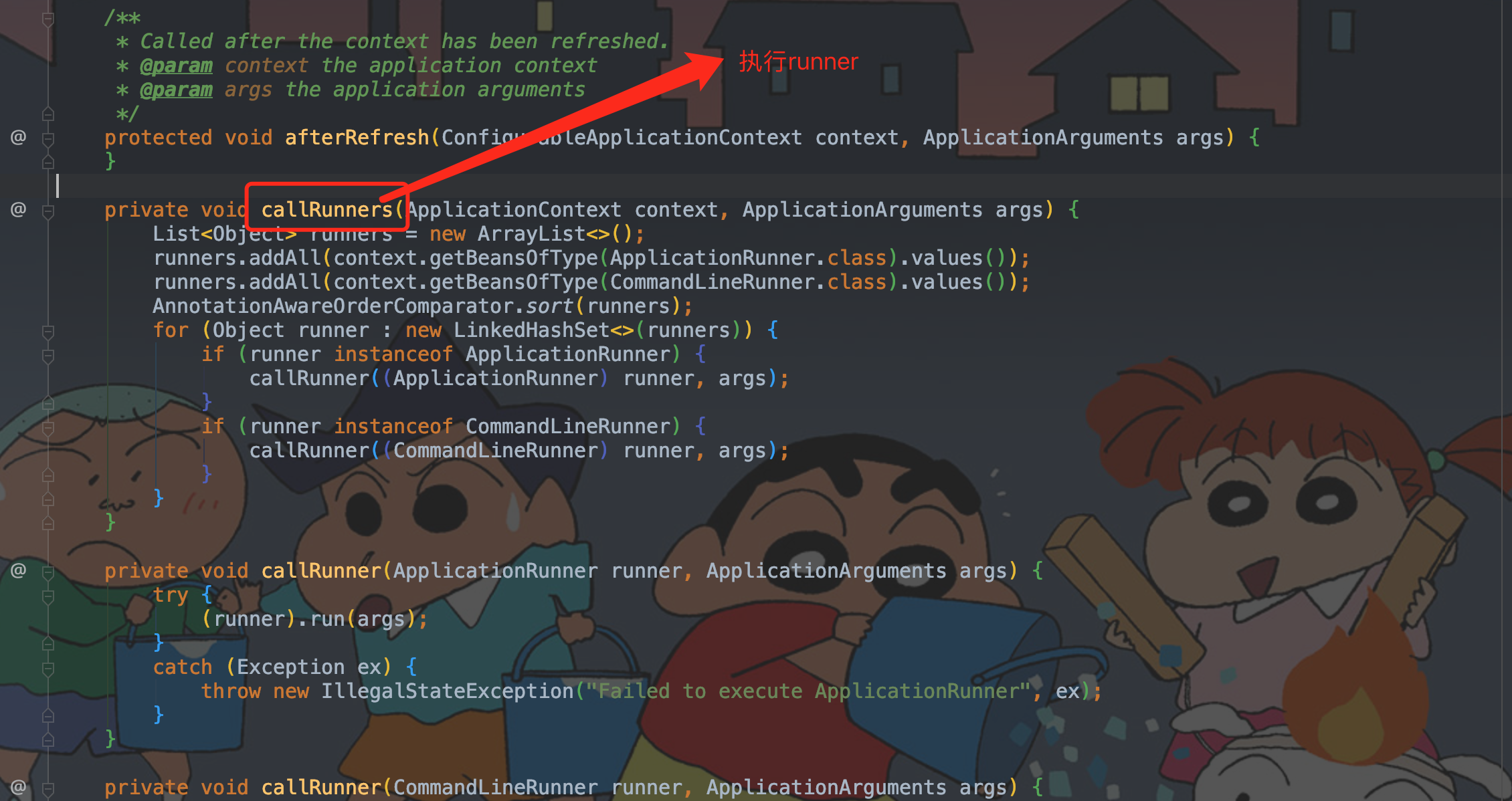
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args)
/**
* 执行runner 初始化参数
* @param context
* @param args
*/
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
// 遍历所有runner
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
/**
* 回调函数callRunner 处理 ApplicationRunner
*/
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
/**
* 回调函数callRunner 处理 CommandLineRunner
*/
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
2.12、running
running 发布上下文完成准备事件,listeners.running() 发布上下文完成准备事件同前面的listeners.started() 方法一样,都是发布了一个running事件,代码也相同。
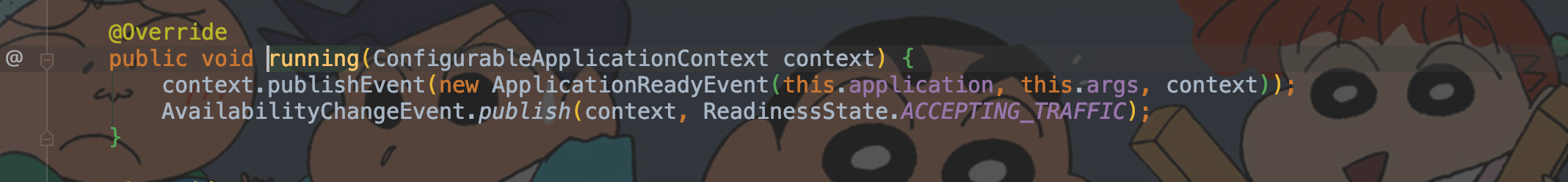
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context)
/**
* 发布上下文完成准备事件
* 与上面的 listeners.started() 方法一样
* @param context
*/
void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// listener.started(context) 中交由context.publishEvent()方法处理
// 实际上是发送了一个ApplicationStartedEvent的事件
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.running", (listener) -> listener.running(context));
}
/**
* 发布上下文完成准备事件
* Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has
* been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and
* {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called.
* @param context the application context.
* @since 2.0.0
*/
@Override
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC);
}
这也是SpringBoot启动流程两大过程中的第二阶段的启动方法run中最后一个方法了,该方法执行完成后,SpringApplication的run(String… args)方法执行结束,至此Spring Boot的ApplicationContext 启动结束。
四、总结
SpringBoot启动流程总结就是下面两张图片,一个创建SpringApplication实例,一个执行run方法,所有的猫腻都在其中。