这一章节就来讲讲ReactDOM.render()方法的内部实现与流程吧。
因为初始化的源码文件部分所涵盖的内容很多,包括创建渲染、更新渲染、Fiber树的创建与diff,element的创建与插入,还包括一些优化算法,所以我就整个的React执行流程画了一个简单的示意图。
React源码执行流程图
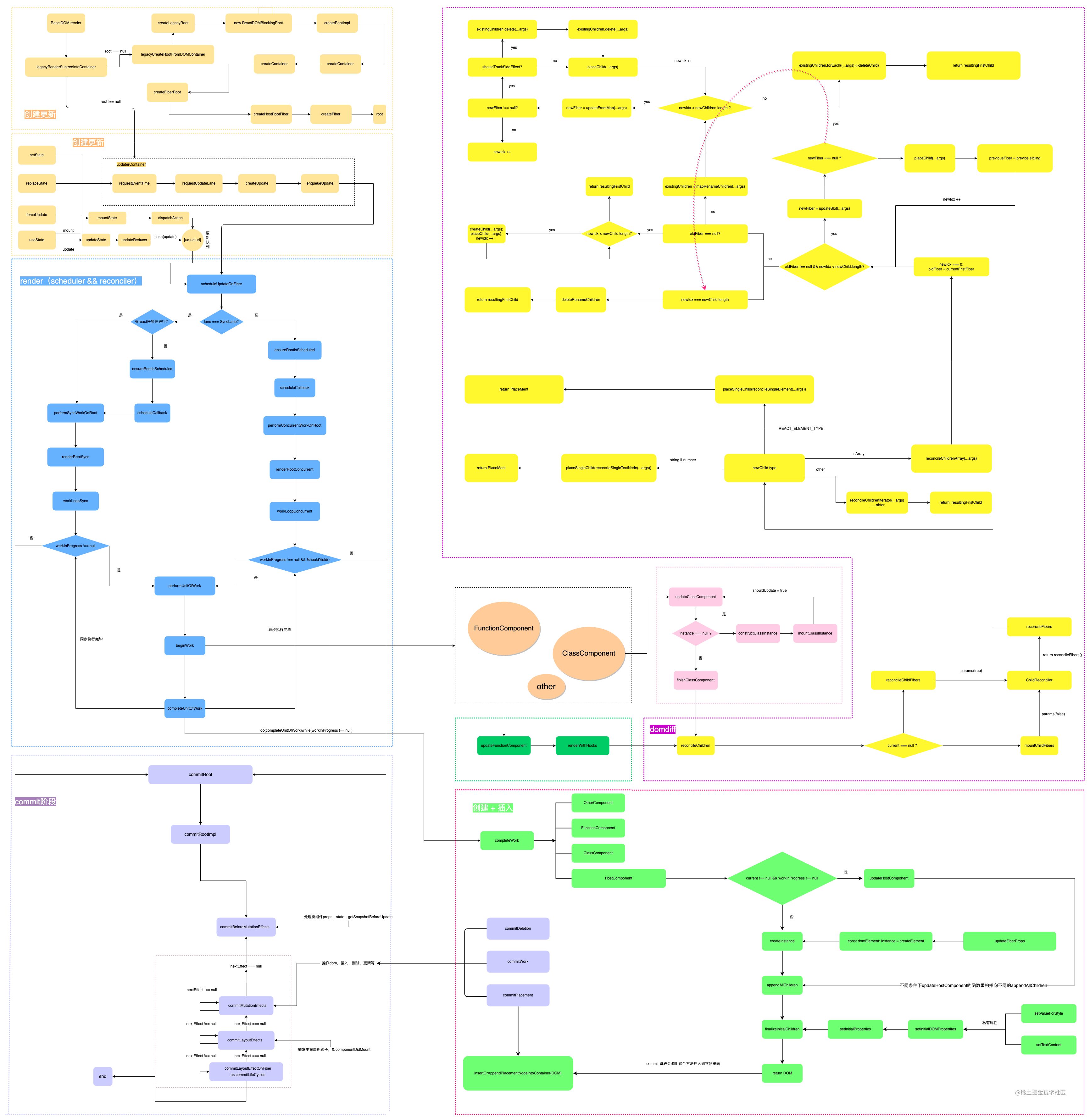
从图中我们很清晰的看到ReactDOM.render()之后我们的组件具体干了什么事情,那么我们进入源码文件一探究竟吧。
// packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMLegacy.js
export function render(
element: React$Element<any>, // 经过babel解析后的element
container: Container, // 根组件节点: document.getElementById('root')..
callback: ?Function,// 回调
) {
// 做合法容器的验证(根组件)
invariant(
isValidContainer(container),
'Target container is not a DOM element.',
);
// 开发模式下
if (__DEV__) {
const isModernRoot =
isContainerMarkedAsRoot(container) &&
container._reactRootContainer === undefined;
if (isModernRoot) {
console.error(
'You are calling ReactDOM.render() on a container that was previously ' +
'passed to ReactDOM.createRoot(). This is not supported. ' +
'Did you mean to call root.render(element)?',
);
}
}
// 返回 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
false,
callback,
);
}
所以当前render函数仅仅只是做了部分逻辑,阅读React源码,给你一个直观的感受就是他拆分的颗粒度非常的细,很多重复命名的函数,可能是见名知意的变量名只有那么几个常见的组合吧,这也是React作者的用心良苦吧。
追根究底我们还是得看一看legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer究竟干了些不为人知的事情呢
legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, // 父级组件
children: ReactNodeList, // 当前元素
container: Container, // 容器 eg:getElementById('root')
forceHydrate: boolean, callback: ?Function,
) {
if (__DEV__) {
topLevelUpdateWarnings(container);
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback === undefined ? null : callback, 'render');
}
// TODO: Without `any` type, Flow says "Property cannot be accessed on any
// member of intersection type." Whyyyyyy.
let root: RootType = (container._reactRootContainer: any);
let fiberRoot;
// 如果有根组件,表示不是初始化渲染,则走下面的批量更新
// 没有根组件,那么就要去创建根组件了
if (!root) {
// 初始化挂载
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// 不必要的批量更新
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
});
} else {
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// 批量更新
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
}
return getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
}
- 有根节点的情况下,我们判定为非首次渲染状态,执行
updateContainer - 没有根节点的情况下,我们判定为首次渲染,接着去创建根节点,执行
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer,拿到了root之后,我们会去触发执行updateContainer
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer
function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container: Container, // 容器
forceHydrate: boolean, // value:false
): RootType {
const shouldHydrate =
forceHydrate || shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container);
// First clear any existing content.
if (!shouldHydrate) {
let warned = false;
let rootSibling;
while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) {
if (__DEV__) {
if (
!warned &&
rootSibling.nodeType === ELEMENT_NODE &&
(rootSibling: any).hasAttribute(ROOT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME)
) {
warned = true;
console.error(
'render(): Target node has markup rendered by React, but there ' +
'are unrelated nodes as well. This is most commonly caused by ' +
'white-space inserted around server-rendered markup.',
);
}
}
container.removeChild(rootSibling);
}
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (shouldHydrate && !forceHydrate && !warnedAboutHydrateAPI) {
warnedAboutHydrateAPI = true;
console.warn(
'render(): Calling ReactDOM.render() to hydrate server-rendered markup ' +
'will stop working in React v18. Replace the ReactDOM.render() call ' +
'with ReactDOM.hydrate() if you want React to attach to the server HTML.',
);
}
}
// 关注createLegacyRoot
return createLegacyRoot(
container,
shouldHydrate
? {
hydrate: true,
}
: undefined,
);
}
createLegacyRoot
export function createLegacyRoot(
container: Container, // 容器
options?: RootOptions,
): RootType {
//关注ReactDOMBlockingRoot
return new ReactDOMBlockingRoot(container, LegacyRoot, options);
}
相关参考视频讲解:进入学习
ReactDOMBlockingRoot
function ReactDOMBlockingRoot(
container: Container, // 容器
tag: RootTag, // LegacyRoot = 0;BlockingRoot = 1;ConcurrentRoot = 2;
options: void | RootOptions,
) {
this._internalRoot = createRootImpl(container, tag, options);
}
- 我们在这里看到
this._internalRoot出来了,因为在先前这个值会给到fiberRoot,所以我们再去看一看这个_internalRoot是怎么创建出来的
createRootImpl
function createRootImpl(
container: Container, tag: RootTag, options: void | RootOptions,
) {
// Tag is either LegacyRoot or Concurrent Root
const hydrate = options != null && options.hydrate === true;
const hydrationCallbacks =
(options != null && options.hydrationOptions) || null;
const mutableSources =
(options != null &&
options.hydrationOptions != null &&
options.hydrationOptions.mutableSources) ||
null;
// 关注createContainer
const root = createContainer(container, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks);
markContainerAsRoot(root.current, container);
const containerNodeType = container.nodeType;
if (enableEagerRootListeners) {
const rootContainerElement =
container.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE ? container.parentNode : container;
listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement);
} else {
if (hydrate && tag !== LegacyRoot) {
const doc =
containerNodeType === DOCUMENT_NODE
? container
: container.ownerDocument;
// We need to cast this because Flow doesn't work
// with the hoisted containerNodeType. If we inline
// it, then Flow doesn't complain. We intentionally
// hoist it to reduce code-size.
eagerlyTrapReplayableEvents(container, ((doc: any): Document));
} else if (
containerNodeType !== DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE &&
containerNodeType !== DOCUMENT_NODE
) {
ensureListeningTo(container, 'onMouseEnter', null);
}
}
if (mutableSources) {
for (let i = 0; i < mutableSources.length; i++) {
const mutableSource = mutableSources[i];
registerMutableSourceForHydration(root, mutableSource);
}
}
// 关注root
return root;
}
- 见名知意
关注createContainer为创建容器,看其源码
createContainer
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.old.js
export function createContainer(
containerInfo: Container, // 容器
tag: RootTag, // LegacyRoot = 0;BlockingRoot = 1;ConcurrentRoot = 2;
hydrate: boolean, hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
): OpaqueRoot {
// 关注createFiberRoot
return createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks);
}
createFiberRoot
export function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any, tag: RootTag, hydrate: boolean, hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
): FiberRoot {
const root: FiberRoot = (new FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate): any);
if (enableSuspenseCallback) {
root.hydrationCallbacks = hydrationCallbacks;
}
// 关注createHostRootFiber
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(tag);
root.current = uninitializedFiber;
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
// 初始化更新队列
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber);
return root;
}
- 关注
root.current、uninitializedFiber.stateNode这两个玩意儿,后面有大作用,我们还是看看createHostRootFiber吧
createHostRootFiber
export function createHostRootFiber(tag: RootTag): Fiber {
let mode;
if (tag === ConcurrentRoot) {
mode = ConcurrentMode | BlockingMode | StrictMode;
} else if (tag === BlockingRoot) {
mode = BlockingMode | StrictMode;
} else {
mode = NoMode;
}
if (enableProfilerTimer && isDevToolsPresent) {
// Always collect profile timings when DevTools are present.
// This enables DevTools to start capturing timing at any point–
// Without some nodes in the tree having empty base times.
mode |= ProfileMode;
}
return createFiber(HostRoot, null, null, mode);
}
- 一眼望去这里便是对
tag的处理,到了后面便是去创建fiber节点
createFiber
const createFiber = function(
tag: WorkTag, pendingProps: mixed, key: null | string, mode: TypeOfMode,
): Fiber {
// $FlowFixMe: the shapes are exact here but Flow doesn't like constructors
return new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);
};
- 那么主角出来了,就是我们的
FiberNode,这里才走完初始化的创建流程,
所以大致的流程就是上面的图里画的那样子,创建流程我们就告一段落,那我们再去看看更新的流程是怎么玩的。
我们知道除了ReactDOM.render()会触发更新流程之外,我们还有setState、强制更新、hooks里面的setXxxx等等手段可以触发更新,所谓setState那么不正好是我们Component原型上挂的方法嘛。我们回顾一下Component,那些更新都是调用了updater触发器上的方法,那么我们去看一下这个东西。
const classComponentUpdater = {
isMounted,
// setState
enqueueSetState(inst, payload, callback) {
const fiber = getInstance(inst);
const eventTime = requestEventTime(); // 获取更新触发的时间
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber); // 获取任务优先级
//根据更新触发时间 + 更新优先级来创建更新任务对象
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane); // 创建更新任务对象
// const update: Update<*> = {
// eventTime, // 更新时间
// lane, // 优先级
// tag: UpdateState, // 更新类型:0更新,1替换。,2强制替换,3捕获型更新
// payload: null,// 需要更新的内容
// callback: null, // 更新完后的回调
// next: null, // 指向下一个更新
// };
// 把内容填上
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
// 开发环境下腰给个警告
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback, 'setState');
}
// 如果有回调,那么加上回调
update.callback = callback;
}
// const update: Update<*> = {
// eventTime, // 更新时间 you
// lane, // 优先级 you
// tag: UpdateState, // 更新类型:0更新,1替换。,2强制替换,3捕获型更新
// payload: null,// 需要更新的内容 you
// callback: null, // 更新完后的回调 you
// next: null, // 指向下一个更新
// };
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);// 推入更新队列
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);// 调度
if (__DEV__) {
if (enableDebugTracing) {
if (fiber.mode & DebugTracingMode) {
const name = getComponentName(fiber.type) || 'Unknown';
logStateUpdateScheduled(name, lane, payload);
}
}
}
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markStateUpdateScheduled(fiber, lane);
}
},
// replaceState
enqueueReplaceState(inst, payload, callback) {
const fiber = getInstance(inst);
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
update.tag = ReplaceState;
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback, 'replaceState');
}
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
if (__DEV__) {
if (enableDebugTracing) {
if (fiber.mode & DebugTracingMode) {
const name = getComponentName(fiber.type) || 'Unknown';
logStateUpdateScheduled(name, lane, payload);
}
}
}
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markStateUpdateScheduled(fiber, lane);
}
},
// forceUpdate
enqueueForceUpdate(inst, callback) {
const fiber = getInstance(inst);
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
update.tag = ForceUpdate;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback, 'forceUpdate');
}
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
if (__DEV__) {
if (enableDebugTracing) {
if (fiber.mode & DebugTracingMode) {
const name = getComponentName(fiber.type) || 'Unknown';
logForceUpdateScheduled(name, lane);
}
}
}
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markForceUpdateScheduled(fiber, lane);
}
},
};
updateContainer
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList, container: OpaqueRoot, parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, callback: ?Function,
): Lane {
if (__DEV__) {
onScheduleRoot(container, element);
}
const current = container.current;
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
if (__DEV__) {
// $FlowExpectedError - jest isn't a global, and isn't recognized outside of tests
if ('undefined' !== typeof jest) {
warnIfUnmockedScheduler(current);
warnIfNotScopedWithMatchingAct(current);
}
}
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current);
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markRenderScheduled(lane);
}
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent);
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (
ReactCurrentFiberIsRendering &&
ReactCurrentFiberCurrent !== null &&
!didWarnAboutNestedUpdates
) {
didWarnAboutNestedUpdates = true;
console.error(
'Render methods should be a pure function of props and state; ' +
'triggering nested component updates from render is not allowed. ' +
'If necessary, trigger nested updates in componentDidUpdate.\n\n' +
'Check the render method of %s.',
getComponentName(ReactCurrentFiberCurrent.type) || 'Unknown',
);
}
}
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);// 创建更新任务
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {element};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
console.error(
'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' +
'function. Instead received: %s.',
callback,
);
}
}
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(current, update); // 推入更新队列
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current, lane, eventTime); // 进行调度
return lane;
}
- 我们看到了
enqueueSetState、enqueueReplaceState、enqueueForceUpdate还是初始化时候走的updateContainer都是走了几乎一样的逻辑:requestEventTime=>requestUpdateLane=>createUpdate=>enqueueUpdate=>scheduleUpdateOnFiber
总结
本章从ReactDOM.render()开始讲解了,初始化的时候,根节点的创建与更新流程,以及在类组件原型上挂载的一些更新的方法,但是为什么这一章不直接把他更新流程讲完呢?因为下一章要讲一下fiberNode这个东西,简而言之他只是一个架构概念,并不是React独有的,但是现在很有必要一起来看一看这个,那么下一章我们来一起揭开FiberNode的神秘面纱吧