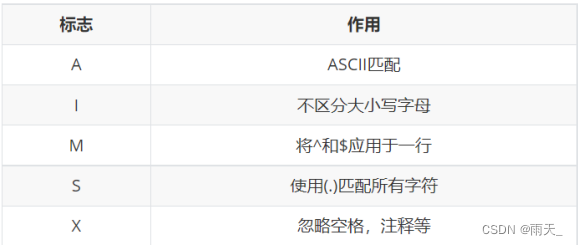
平时在Vue项目中经常用到路由,但是也仅仅处于会用的层面,很多基础知识并不是真正的理解。于是就趁着十一”小长假“查阅了很多资料,总结下路由相关的知识,查缺不漏,加深自己对路由的理解。
路由
在 Web 开发过程中,经常遇到路由的概念。那么到底什么是路由呢?简单来说,路由就是 URL 到函数的映射。
路由这个概念本来是由后端提出来的,在以前用模板引擎开发页面的时候,是使用路由返回不同的页面,大致流程是这样的:
1、浏览器发出请求;
2、服务器监听到 80 或者 443 端口有请求过来,并解析 UR L路径;
3、服务端根据路由设置,查询相应的资源,可能是 html 文件,也可能是图片资源…,然后将这些资源处理并返回给浏览器;
4、浏览器接收到数据,通过content-type决定如何解析数据
简单来说,路由就是用来跟后端服务器交互的一种方式,通过不同的路径来请求不同的资源,请求HTML页面只是路由的其中一项功能。
服务端路由
当服务端接收到客户端发来的 HTTP 请求时,会根据请求的 URL,找到相应的映射函数,然后执行该函数,并将函数的返回值发送给客户端。
对于最简单的静态资源服务器,可以认为,所有 URL 的映射函数就是一个文件读取操作。对于动态资源,映射函数可能是一个数据库读取操作,也可能进行一些数据处理,等等。
客户端路由
服务端路由会造成服务器压力比较大,而且用户访问速度也比较慢。在这种情况下,出现了单页应用。
单页应用,就是只有一个页面,用户访问网址,服务器返回的页面始终只有一个,不管用户改变了浏览器地址栏的内容或者在页面发生了跳转,服务器不会重新返回新的页面,而是通过相应的js操作来实现页面的更改。
前端路由其实就是:通过地址栏内容的改变,显示不同的页面。
前端路由的优点:
前端路由可以让前端自己维护路由与页面展示的逻辑,每次页面改动不需要通知服务端。
更好的交互体验:不用每次从服务端拉取资源。
前端路由的缺点: 使用浏览器的前进、后退键时会重新发送请求,来获取数据,没有合理利用缓存。
前端路由实现原理: 本质就是监测 URL 的变化,通过拦截 URL 然后解析匹配路由规则。
前端路由的实现方式
1、hash模式(location.hash + hashchange 事件)
hash 模式的实现方式就是通过监听 URL 中的 hash 部分的变化,触发haschange事件,页面做出不同的响应。但是 hash 模式下,URL 中会带有 #,不太美观。
2、history模式
history 路由模式的实现,基于 HTML5 提供的 History 全局对象,它的方法有:
history.go():在会话历史中向前或者向后移动指定页数
history.forward():在会话历史中向前移动一页,跟浏览器的前进按钮功能相同
history.back():在会话历史记录中向后移动一页,跟浏览器的后腿按钮功能相同
history.pushState():向当前浏览器会话的历史堆栈中添加一个状态,会改变当前页面url,但是不会伴随这刷新
history.replaceState():将当前的会话页面的url替换成指定的数据,replaceState 会改变当前页面的url,但也不会刷新页面
window.onpopstate:当前活动历史记录条目更改时,将触发popstate事件
history路由的实现,主要是依靠pushState、replaceState和window.onpopstate实现的。但是有几点要注意:
当活动历史记录条目更改时,将触发 popstate 事件;
调用history.pushState()或history.replaceState()不会触发 popstate 事件
popstate 事件只会在浏览器某些行为下触发,比如:点击后退、前进按钮(或者在 JavaScript 中调用history.back()、history.forward()、history.go()方法)
a 标签的锚点也会触发该事件
对 pushState 和 replaceState 行为的监听
如果想监听 pushState 和 replaceState 行为,可以通过在方法里面主动去触发 popstate 事件,另一种是重写history.pushState,通过创建自己的eventedPushState自定义事件,并手动派发,实际使用过程中就可以监听了。具体做法如下:
function eventedPushState(state, title, url) {
var pushChangeEvent = new CustomEvent("onpushstate", {
detail: {
state,
title,
url
}
});
document.dispatchEvent(pushChangeEvent);
return history.pushState(state, title, url);
}
document.addEventListener(
"onpushstate",
function(event) {
console.log(event.detail);
},
false
);
eventedPushState({}, "", "new-slug");
router 和 route 的区别
route 就是一条路由,它将一个 URL 路径和一个函数进行映射。而 router 可以理解为一个容器,或者说一种机制,它管理了一组 route。
概括为:route 只是进行了 URL 和函数的映射,在当接收到一个 URL 后,需要去路由映射表中查找相应的函数,这个过程是由 router 来处理的。
动态路由和静态路由
静态路由
静态路由只支持基于地址的全匹配。
动态路由
动态路由除了可以兼容全匹配外还支持多种”高级匹配模式“,它的路径地址中含有路径参数,使得它可以按照给定的匹配模式将符合条件的一个或多个地址映射到同一个组件上。
动态路由一般结合角色权限控制使用。
动态路由的存储有两种方式:
将路由存储到前端
将路由存储到数据库
动态路由的好处:
灵活,无需手动维护
存储到数据库,增加安全性
实现一个路由
一个简单的Router应该具备哪些功能
以 Vue为例,需要有 链接、容器、component组件和path路由路径:
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>
<!-- 使用 router-link 组件进行导航 -->
<!-- 通过传递 to 来指定链接 -->
<!-- <router-link> 将呈现一个带有正确 href属性的<a>标签 -->
<router-link to="/">Go to Home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">Go to About</router-link>
</p>
<!-- 路由出口 -->
<!-- 路由匹配到的组件将渲染在这里 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
const routes = [{
path: '/',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
}]
以React为例,需要有容器、路由、组件和链接:
<BrowserRouter>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<App />}>
<Route index element={<Home />} />
<Route path="teams" element={<Teams />}>
<Route path=":teamId" element={<Team />} />
<Route path="new" element={<NewTeamForm />} />
<Route index element={<LeagueStandings />} />
</Route>
</Route>
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
<div>
<h1>Home</h1>
<nav>
<Link to="/">Home</Link> | {""}
<Link to="about">About</Link>
</nav>
</div>
综上,一个简单的 Router 应该具备以下功能:
1、容器(组件)
2、路由
3、业务组件 & 链接组件
不借助第三方工具库,如何实现路由
不借助第三方工具库实现路由,我们需要思考以下几个问题:
如何实现自定义标签,如vue的,React的
如何实现业务组件
如何动态切换路由
准备工作
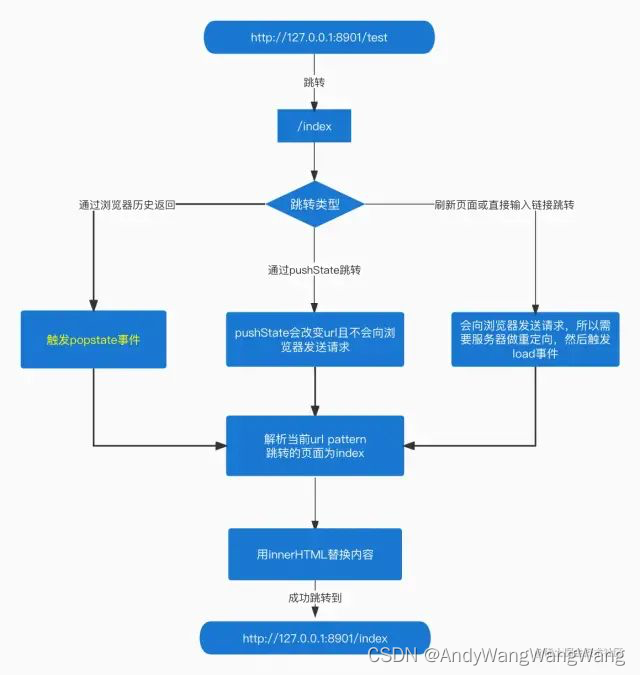
1、根据对前端路由 history 模式的理解,将大致过程用如下流程图表示:
2、如果不借助第三方库,我们选择使用 Web components 。Web Components由三项主要技术组成,它们可以一起使用来创建封装功能的定制元素。
Custom elements(自定义元素) :一组JavaScript API,允许我们定义 custom elements及其行为,然后可以在界面按照需要使用它们。
Shadow DOM(影子DOM) :一组JavaScript API,用于将封装的“影子”DOM树附加到元素(与主文档分开呈现)并控制关联的功能。通过这种方式,可以保持元素的功能私有。
HTML template(HTML模版) :和可以编写不在页面显示的标记模板,然后它们可以作为自定义元素结构的基础被多次重用。
另外还需要注意 Web Components 的生命周期:
connectedCallback:当 custom element 首次被插入文档DOM时,被调用
disconnectedCallback:当 custom element 从文档DOM中删除时,被调用
adoptedCallback:当custom element 被移动到新的文档时,被调用
attributeChangedCallback:当 custom element 增加、删除、修改自身属性时,被调用
3、Shadow DOM
3.1 Shadow DOM 特有的术语:
- Shadow host:一个常规DOM节点,Shadow DOM 会被附加到这个节点上
- Shadow tree:Shadow DOM 内部的 DOM 树
- Shadow boundary:Shadow DOM 结束的地方,也是常规DOM开始的地方
- Shadow root:Shadow tree 的根节点
3.2 Shadow DOM的重要参数mode:
- open:shadow root 元素可以从 js 外部访问根节点
- close :拒绝从 js 外部访问关闭的 shadow root 节点
- 语法:`const shadow = this.attachShadow({mode:closed});`
4、 通过自定义标签创建容器组件、路由、业务组件和链接组件标签,使用
**CustomElementRegistry.define()**注册自定义元素。其中,Custom elements 的简单写法举例:
<my-text></my-text>
<script>
class MyText extends HTMLElement{
constructor(){
super();
this.append(“我的文本”);
}
}
window.customElements.define("my-text",MyText);
</script>
5、组件的实现可以使用 Web Components,但是这样有缺点,我们没有打包引擎处理 Web Components组件,将其全部加载过来。
为了解决以上问题,我们选择动态加载,远程去加载一个 html 文件。html文件里面的结构如下:支持模版(template),脚本(template),脚本(script),样式(style),非常地像vue。组件开发模版如下:
<template>
<div>商品详情</div>
<div id="detail">
商品ID:<span id="product-id" class="product-id" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
this.querySelector("#product-id").textContent = history.state.id;
</script>
<style>
.product-id{
color:red;
}
</style>
6、监听路由的变化:
popstate可以监听大部分路由变化的场景,除了pushState 和 replaceState。
pushState 和 replaceState可以改变路由,改变历史记录,但是不能触发popstate事件,需要自定义事件并手动触发自定义事件,做出响应。
7、整体架构图如下:
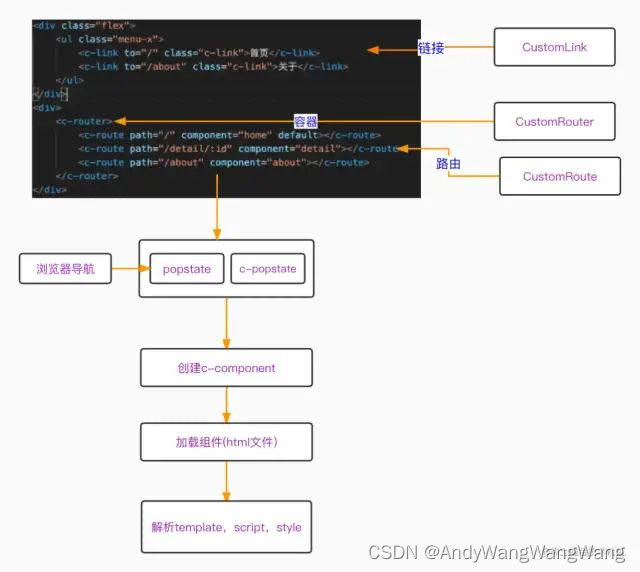
- 组件功能拆解分析如下:
链接组件 — CustomLink(c-link)
当用户点击标签后,通过event.preventDefault();阻止页面默认跳转。根据当前标签的to属性获取路由,通过history.pushState(“”,“”,to)进行路由切换。
// <c-link to="/" class="c-link">首页</c-link>
class CustomLink extends HTMLElement {
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("click", ev => {
ev.preventDefault();
const to = this.getAttribute("to");
// 更新浏览器历史记录
history.pushState("", "", to)
})
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-link", CustomLink);
容器组件 — CustomRouter(c-router)
主要是收集路由信息,监听路由信息的变化,然后加载对应的组件
路由 — CustomRoute(c-route)
主要是提供配置信息,对外提供getData 的方法
// 优先于c-router注册
// <c-route path="/" component="home" default />
class CustomRoute extends HTMLElement {
#data = null;
getData() {
return {
default: this.hasAttribute("default"),
path: this.getAttribute("path"),
component: this.getAttribute("component")
}
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-route", CustomRoute);
业务组件 — CustomComponent(c-component)
实现组件,动态加载远程的html,并解析
完整代码实现
index.html:
<div class="product-item">测试的产品</div>
<div class="flex">
<ul class="menu-x">
<c-link to="/" class="c-link">首页</c-link>
<c-link to="/about" class="c-link">关于</c-link>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<c-router>
<c-route path="/" component="home" default />
<c-route path="/detail/:id" component="detail" />
<c-route path="/about" component="about" />
</c-router>
</div>
<script src="./router.js"></script>
home.html:
<template>
<div>商品清单</div>
<div id="product-list">
<div>
<a data-id="10" class="product-item c-link">香蕉</a>
</div>
<div>
<a data-id="11" class="product-item c-link">苹果</a>
</div>
<div>
<a data-id="12" class="product-item c-link">葡萄</a>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
let container = this.querySelector("#product-list");
// 触发历史更新
// 事件代理
container.addEventListener("click", function (ev) {
console.log("item clicked");
if (ev.target.classList.contains("product-item")) {
const id = +ev.target.dataset.id;
history.pushState({
id
}, "", `/detail/${id}`)
}
})
</script>
<style>
.product-item {
cursor: pointer;
color: blue;
}
</style>
detail.html:
<template>
<div>商品详情</div>
<div id="detail">
商品ID:<span id="product-id" class="product-id" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
this.querySelector("#product-id").textContent=history.state.id;
</script>
<style>
.product-id{
color:red;
}
</style>
about.html:
<template>
About Me!
</template>
route.js:
const oriPushState = history.pushState;
// 重写pushState
history.pushState = function (state, title, url) {
// 触发原事件
oriPushState.apply(history, [state, title, url]);
// 自定义事件
var event = new CustomEvent("c-popstate", {
detail: {
state,
title,
url
}
});
window.dispatchEvent(event);
}
// <c-link to="/" class="c-link">首页</c-link>
class CustomLink extends HTMLElement {
connectedCallback() {
this.addEventListener("click", ev => {
ev.preventDefault();
const to = this.getAttribute("to");
// 更新浏览历史记录
history.pushState("", "", to);
})
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-link", CustomLink);
// 优先于c-router注册
// <c-toute path="/" component="home" default />
class CustomRoute extends HTMLElement {
#data = null;
getData() {
return {
default: this.hasAttribute("default"),
path: this.getAttribute("path"),
component: this.getAttribute("component")
}
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-route", CustomRoute);
// 容器组件
class CustomComponent extends HTMLElement {
async connectedCallback() {
console.log("c-component connected");
// 获取组件的path,即html的路径
const strPath = this.getAttribute("path");
// 加载html
const cInfos = await loadComponent(strPath);
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: "closed" });
// 添加html对应的内容
this.#addElement(shadow, cInfos);
}
#addElement(shadow, info) {
// 添加模板内容
if (info.template) {
shadow.appendChild(info.template.content.cloneNode(true));
}
// 添加脚本
if (info.script) {
// 防止全局污染,并获得根节点
var fun = new Function(`${info.script.textContent}`);
// 绑定脚本的this为当前的影子根节点
fun.bind(shadow)();
}
// 添加样式
if (info.style) {
shadow.appendChild(info.style);
}
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-component", CustomComponent);
// <c-router></c-router>
class CustomRouter extends HTMLElement {
#routes
connectedCallback() {
const routeNodes = this.querySelectorAll("c-route");
console.log("routes:", routeNodes);
// 获取子节点的路由信息
this.#routes = Array.from(routeNodes).map(node => node.getData());
// 查找默认的路由
const defaultRoute = this.#routes.find(r => r.default) || this.#routes[0];
// 渲染对应的路由
this.#onRenderRoute(defaultRoute);
// 监听路由变化
this.#listenerHistory();
}
// 渲染路由对应的内容
#onRenderRoute(route) {
var el = document.createElement("c-component");
el.setAttribute("path", `/${route.component}.html`);
el.id = "_route_";
this.append(el);
}
// 卸载路由清理工作
#onUploadRoute(route) {
this.removeChild(this.querySelector("#_route_"));
}
// 监听路由变化
#listenerHistory() {
// 导航的路由切换
window.addEventListener("popstate", ev => {
console.log("onpopstate:", ev);
const url = location.pathname.endsWith(".html") ? "/" : location.pathname;
const route = this.#getRoute(this.#routes, url);
this.#onUploadRoute();
this.#onRenderRoute(route);
});
// pushStat或replaceSate
window.addEventListener("c-popstate", ev => {
console.log("c-popstate:", ev);
const detail = ev.detail;
const route = this.#getRoute(this.#routes, detail.url);
this.#onUploadRoute();
this.#onRenderRoute(route);
})
}
// 路由查找
#getRoute(routes, url) {
return routes.find(function (r) {
const path = r.path;
const strPaths = path.split('/');
const strUrlPaths = url.split("/");
let match = true;
for (let i = 0; i < strPaths.length; i++) {
if (strPaths[i].startsWith(":")) {
continue;
}
match = strPaths[i] === strUrlPaths[i];
if (!match) {
break;
}
}
return match;
})
}
}
window.customElements.define("c-router", CustomRouter);
// 动态加载组件并解析
async function loadComponent(path, name) {
this.caches = this.caches || {};
// 缓存存在,直接返回
if (!!this.caches[path]) {
return this.caches[path];
}
const res = await fetch(path).then(res => res.text());
// 利用DOMParser校验
const parser = new DOMParser();
const doc = parser.parseFromString(res, "text/html");
// 解析模板,脚本,样式
const template = doc.querySelector("template");
const script = doc.querySelector("script");
const style = doc.querySelector("style");
// 缓存内容
this.caches[path] = {
template,
script,
style
}
return this.caches[path];
}