目录
1.概念:
2.信号的存储位置:
3.常见的信号的值以及对应的功能说明:
4.信号的值在系统源码中的定义:
5.响应方式:
6.改变信号的相应方式:
(1)设置信号的响应方式:
(2)默认:SIG_DFL;忽略:SIG_IGN;
(3)默认响应方式:
(4).自定义响应方式:
(5)忽略:
7.练习题目:
8.15号信号和9号信号
9.SIGCHLD信号
(1)验证信号
(2)处理僵死进程(wait结合信号)
1.概念:
信号是系统响应某个条件而产生的事件
,
进程接收到信号会执行相应的操作
;
与信号有关的系统调用在
<signal.h>
头文件中
:
2.信号的存储位置:
vim /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/signum.h
3.常见的信号的值以及对应的功能说明:

4.信号的值在系统源码中的定义:
信号名称 信号代号
#define SIGHUP 1
#define SIGINT 2
#define SIGQUIT 3
#define SIGILL 4
#define SIGTRAP 5
#define SIGABRT 6
#define SIGIOT 6
#define SIGBUS 7
#define SIGFPE 8
#define SIGKILL 9
#define SIGUSR1 10
#define SIGSEGV 11
#define SIGUSR2 12
#define SIGPIPE 13
#define SIGALRM 14
#define SIGTERM 15
#define SIGSTKFLT 16
#define SIGCHLD 17
#define SIGCONT 18
#define SIGSTOP 19
#define SIGTSTP 20
#define SIGTTIN 21
#define SIGTTOU 22
#define SIGURG 23#define SIGINT 2 // 键盘按下 Ctrl+c 时,会产生终端中断信号#define SIGQUIT 3 // 键盘按下 Ctrl+\ 时,会产生终端退出信号#define SIGKILL 9 // 该信号的响应方式不允许改变#define SIGPIPE 13 // 读端关闭的描述符,写端写入时产生,该信号会终止程序 ( 向无读进程的管道写数据 )#define SIGTERM 15 // 系统 kill 命令默认发送的信号#define SIGCHLD 17 // 子进程结束后,会默认给父进程发送该信号
5.响应方式:
三种响应方式
:
默认
,
忽略
,
自定义
;
6.改变信号的相应方式:
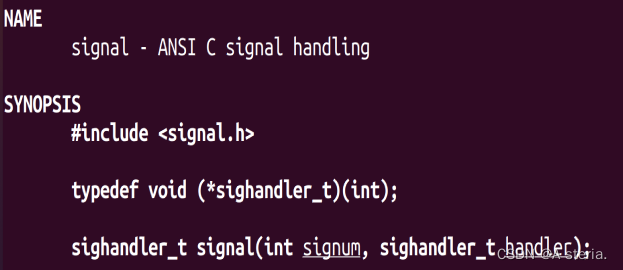
(1)设置信号的响应方式:
通过函数
signal();
man signal:
(2)默认:SIG_DFL;忽略:SIG_IGN;
自定义:void fun_sig(int sig);
(3)默认响应方式:
正常是默认
,
代码如下
:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
{
while(1)
{
printf("main run\n");
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
} 
ctr+c结束程序;
(4).自定义响应方式:
通过
signal
系统调用更改信号的响应方式
:

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<signal.h>
void sig_fun(int sig)
{
printf("sig=%d\n",sig);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGINT,sig_fun);
while(1);
{
printf("main run\n");
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
ps -ef|grep "程序名字"
kill -9 PID
或者ctrl+\结束程序;
(5)忽略:
将上面12行的代码修改成:
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<signal.h>
void sig_fun(int sig)
{
printf("sig=%d\n",sig);
siganl(sig,SIGDFL);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);
while(1);
{
printf("main run\n");
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
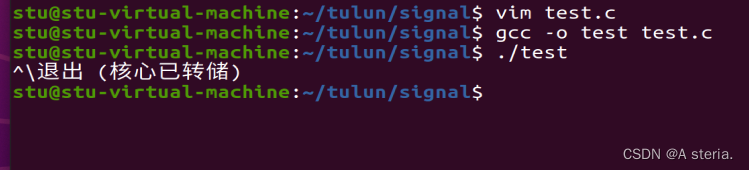
7.练习题目:
第一次打印信号的代号,第二次按照默认形式把进程结束;

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <signal.h>
void sig_fun(int sig)
{
printf("sig=%d\n",sig);
signal(sig,SIG_DFL);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGINT,sig_fun);
//signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN);
while(1)
{
printf("main run\n");
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
8.15号信号和9号信号
15: kill
默认发送的信号
9 :
强制结束的信号
,
不允许改变
9.SIGCHLD信号
子进程结束
,
父进程会收到内核发送的
SIGCHLD
信号
;
(1)验证信号
改变
SIGCHLD
信号的响应方式
(2)处理僵死进程(wait结合信号)


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
void fun(int sig)
{
printf("sig=%d\n",sig);
//int val=0;
//int id=wait(&val);
wait(NULL);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD,fun);
char *s=NULL;
int n=0;//控制父子进程执行的次数
pid_t id=fork();
assert(id!=-1);
if(id==0)//子进程
{
s="child";
n=3;
}
else//父进程
{
s="parent";
n=7;
// int val;
// wait(&val);
//printf("val=%d\n",val);
}
//父子进程一起执行
int i=0;
for(;i<n;i++)
{
printf("s=%s,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",s,getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}