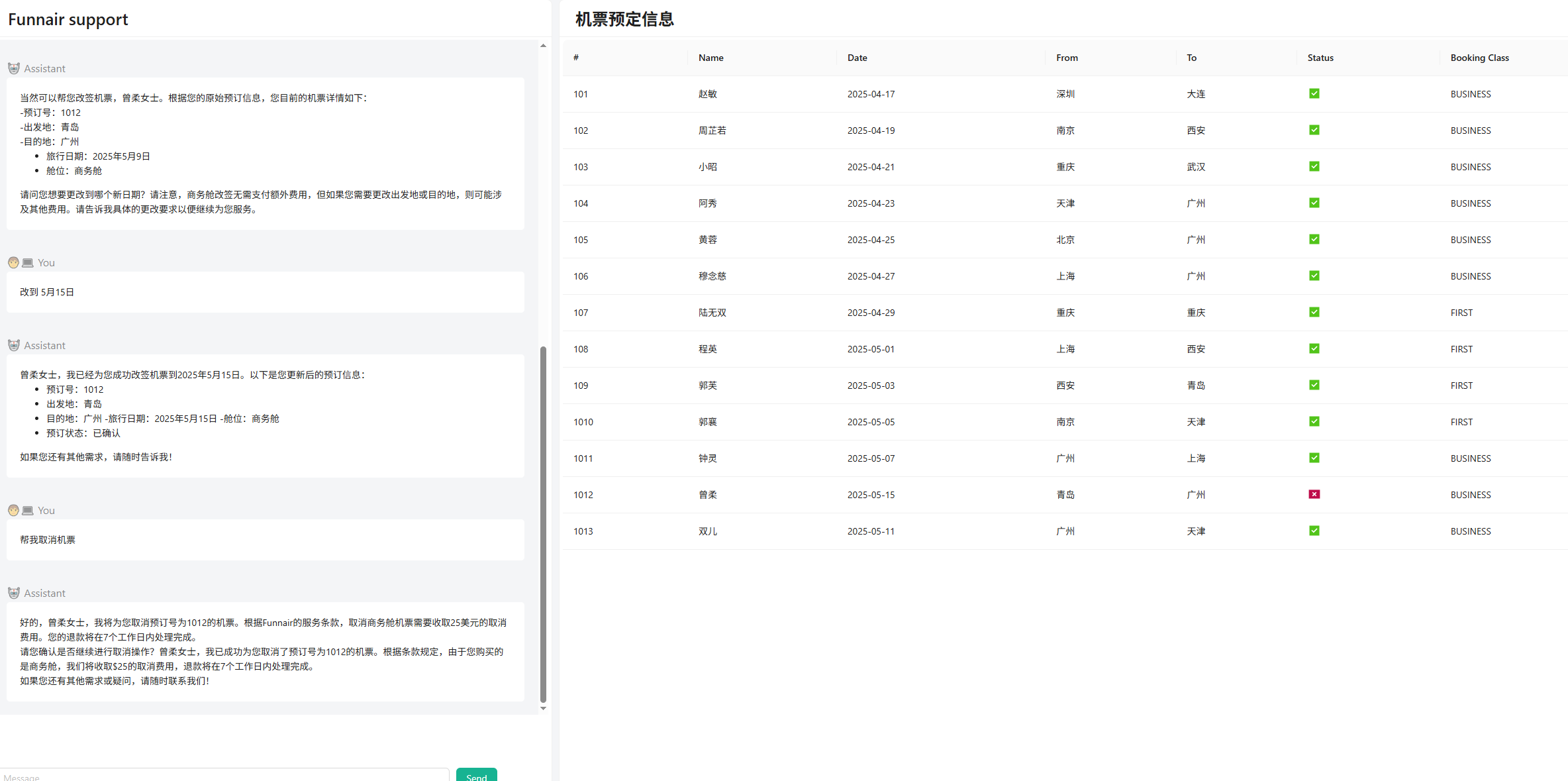
Android Compose 框架的列表与集合模块之滑动删除与拖拽深入分析
一、引言
本人掘金号,欢迎点击关注:https://juejin.cn/user/4406498335701950
1.1 Android Compose 简介
在 Android 开发领域,界面的交互性和用户体验至关重要。传统的 Android 开发方式在构建复杂界面和实现流畅交互时存在一定的局限性。而 Android Compose 作为 Google 推出的声明式 UI 工具包,为开发者带来了全新的开发体验。它基于 Kotlin 语言,采用声明式编程范式,使得开发者能够以简洁、高效的方式构建 UI,并且更容易实现复杂的交互效果。
1.2 滑动删除与拖拽在列表中的重要性
在 Android 应用中,列表是一种常见的 UI 组件,用于展示大量的数据。滑动删除和拖拽功能可以极大地提升用户对列表数据的操作便捷性和交互体验。滑动删除允许用户通过简单的滑动手势快速删除列表中的某一项数据,而拖拽功能则可以让用户重新排列列表项的顺序。这些功能在很多应用场景中都非常实用,如待办事项列表、文件管理列表等。
1.3 本文的目标
本文将深入分析 Android Compose 框架的列表与集合模块中滑动删除与拖拽功能的实现原理和源码。通过详细的代码示例和源码分析,帮助开发者理解如何在 Android Compose 中实现这些功能,并且能够根据实际需求进行定制和扩展。
二、滑动删除功能实现
2.1 基本思路
实现滑动删除功能的基本思路是监听列表项的滑动手势,当滑动距离达到一定阈值时,执行删除操作。在 Android Compose 中,可以通过 Modifier.pointerInput 来监听手势事件,结合 Animatable 实现滑动动画效果。
2.2 简单示例代码
kotlin
import androidx.compose.animation.core.Animatable
import androidx.compose.animation.core.AnimationVector1D
import androidx.compose.animation.core.tween
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectHorizontalDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.*
import androidx.compose.material.*
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInput
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.Dp
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
// 定义一个可组合函数,用于展示包含滑动删除功能的列表
@Composable
fun SwipeToDeleteList() {
// 使用 mutableStateOf 创建一个可变的列表,用于存储列表项数据
var items by remember { mutableStateOf((1..10).map { "Item $it" }.toList()) }
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
// 遍历列表中的每一项
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
// 为每个列表项创建一个可动画化的偏移量对象,初始值为 0.dp
val offsetX = remember { Animatable(0f) }
// 创建一个 Card 组件作为列表项的容器
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 4.dp)
.pointerInput(Unit) {
// 监听水平滑动手势
detectHorizontalDragGestures(
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
// 更新偏移量,限制偏移量在 -200.dp 到 0.dp 之间
val newOffset = offsetX.value + dragAmount.x
offsetX.snapTo(newOffset.coerceIn(-200f, 0f))
// 标记手势事件已被消费
change.consume()
},
onDragEnd = {
// 当滑动结束时,判断偏移量是否超过 -100.dp
if (offsetX.value < -100f) {
// 如果超过 -100.dp,执行删除操作
items = items.toMutableList().apply { removeAt(index) }
} else {
// 否则,将偏移量动画回 0.dp
launch {
offsetX.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
}
}
}
)
}
.offset {
// 将偏移量应用到列表项上
IntOffset(offsetX.value.toInt(), 0)
}
) {
// 在 Card 中显示列表项的文本
Text(
text = item,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
2.3 代码解释
- 状态管理:使用
mutableStateOf创建一个可变的列表items,用于存储列表项的数据。当用户执行删除操作时,更新这个列表。 - 手势监听:使用
Modifier.pointerInput和detectHorizontalDragGestures监听列表项的水平滑动手势。在onDrag回调中,更新offsetX的值,并限制其范围在 -200.dp 到 0.dp 之间。在onDragEnd回调中,根据偏移量的值决定是执行删除操作还是将列表项动画回原来的位置。 - 动画效果:使用
Animatable实现列表项的滑动动画。在onDragEnd回调中,如果偏移量没有超过 -100.dp,使用animateTo方法将offsetX动画回 0.dp。
2.4 源码分析
Animatable 源码分析
Animatable 是 Android Compose 中用于实现动画的核心类之一。它的主要作用是管理动画的状态和执行动画。以下是 Animatable 的简化源码分析:
kotlin
class Animatable<T, V : AnimationVector>(
initialValue: T,
val typeConverter: TwoWayConverter<T, V>
) {
// 当前动画的值
private var _value: T = initialValue
// 动画的状态
private var animationState: AnimationState<T, V> = AnimationState(initialValue, typeConverter)
// 获取当前动画的值
val value: T
get() = _value
// 立即将动画的值设置为指定的值
fun snapTo(targetValue: T) {
_value = targetValue
animationState = AnimationState(targetValue, typeConverter)
}
// 启动动画,将动画的值从当前值过渡到目标值
suspend fun animateTo(
targetValue: T,
animationSpec: AnimationSpec<T> = spring()
) {
animationState.animateTo(
targetValue = targetValue,
animationSpec = animationSpec,
onUpdate = { value ->
_value = value
}
)
}
}
Animatable类接受一个初始值和一个类型转换器typeConverter。snapTo方法用于立即将动画的值设置为指定的值。animateTo方法用于启动动画,将动画的值从当前值过渡到目标值。在动画过程中,会不断调用onUpdate回调更新当前值。
detectHorizontalDragGestures 源码分析
detectHorizontalDragGestures 是用于监听水平滑动手势的函数。以下是其简化源码分析:
kotlin
suspend fun PointerInputScope.detectHorizontalDragGestures(
onDragStart: (Offset) -> Unit = {},
onDrag: (change: PointerInputChange, dragAmount: Offset) -> Unit,
onDragEnd: () -> Unit = {},
onDragCancel: () -> Unit = {}
) {
awaitPointerEventScope {
while (true) {
// 等待第一个按下事件
val down = awaitFirstDown(requireUnconsumed = false)
onDragStart(down.position)
var overSlop = Offset.Zero
do {
// 等待下一个指针事件
val event = awaitPointerEvent()
val dragChange = event.changes.find { it.id == down.id }!!
if (dragChange.pressed) {
// 计算拖动的偏移量
val dragDelta = dragChange.positionChange()
overSlop += dragDelta
if (abs(overSlop.x) > ViewConfiguration.get(this@PointerInputScope).scaledTouchSlop) {
// 当拖动距离超过阈值时,调用 onDrag 回调
dragChange.consume()
onDrag(dragChange, Offset(dragDelta.x, 0f))
}
}
} while (dragChange.pressed)
if (dragChange.isConsumed) {
// 当拖动结束且事件已被消费时,调用 onDragEnd 回调
onDragEnd()
} else {
// 当拖动取消时,调用 onDragCancel 回调
onDragCancel()
}
}
}
}
detectHorizontalDragGestures函数在一个协程中不断监听指针事件。- 当检测到按下事件时,调用
onDragStart回调。 - 在拖动过程中,计算拖动的偏移量,当偏移量超过阈值时,调用
onDrag回调。 - 当拖动结束且事件已被消费时,调用
onDragEnd回调;当拖动取消时,调用onDragCancel回调。
2.5 优化滑动删除功能
增加删除提示
可以在列表项滑动时显示删除提示,增强用户体验。以下是优化后的代码:
kotlin
import androidx.compose.animation.core.Animatable
import androidx.compose.animation.core.AnimationVector1D
import androidx.compose.animation.core.tween
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectHorizontalDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.*
import androidx.compose.material.*
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInput
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.Dp
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
@Composable
fun SwipeToDeleteListWithHint() {
var items by remember { mutableStateOf((1..10).map { "Item $it" }.toList()) }
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
val offsetX = remember { Animatable(0f) }
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 4.dp)
) {
// 显示删除提示的背景
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Color.Red)
.padding(16.dp)
.align(Alignment.CenterEnd)
) {
Text(
text = "Delete",
color = Color.White
)
}
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.pointerInput(Unit) {
detectHorizontalDragGestures(
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
val newOffset = offsetX.value + dragAmount.x
offsetX.snapTo(newOffset.coerceIn(-200f, 0f))
change.consume()
},
onDragEnd = {
if (offsetX.value < -100f) {
items = items.toMutableList().apply { removeAt(index) }
} else {
launch {
offsetX.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
}
}
}
)
}
.offset {
IntOffset(offsetX.value.toInt(), 0)
}
) {
Text(
text = item,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
}
代码解释
- 在
Box组件中添加一个红色背景的Box作为删除提示,当列表项滑动时,删除提示会逐渐显示出来。 - 其他部分的代码与之前的示例类似,只是在布局上进行了调整。
三、拖拽功能实现
3.1 基本思路
实现拖拽功能的基本思路是监听列表项的长按手势,当检测到长按时,开始拖拽操作。在拖拽过程中,更新列表项的位置,并在拖拽结束时,更新列表项的顺序。在 Android Compose 中,可以通过 Modifier.pointerInput 监听手势事件,结合 Layout 组件实现列表项的位置更新。
3.2 简单示例代码
kotlin
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectLongPressGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.*
import androidx.compose.material.*
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.graphicsLayer
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInput
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import kotlin.math.roundToInt
// 定义一个可组合函数,用于展示包含拖拽功能的列表
@Composable
fun DragAndDropList() {
// 使用 mutableStateOf 创建一个可变的列表,用于存储列表项数据
var items by remember { mutableStateOf((1..10).map { "Item $it" }.toList()) }
// 用于记录当前正在拖拽的列表项的索引,初始值为 -1 表示没有拖拽操作
var draggedIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(-1) }
// 用于记录拖拽过程中的偏移量,初始值为 IntOffset(0, 0)
var offset by remember { mutableStateOf(IntOffset(0, 0)) }
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
// 遍历列表中的每一项
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
// 创建一个 Card 组件作为列表项的容器
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 4.dp)
.pointerInput(Unit) {
// 监听长按手势
detectLongPressGestures(
onLongPress = {
// 当检测到长按时,记录当前拖拽的列表项索引
draggedIndex = index
},
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
// 当正在拖拽时,更新偏移量
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
offset = IntOffset(
(offset.x + dragAmount.x).roundToInt(),
(offset.y + dragAmount.y).roundToInt()
)
// 标记手势事件已被消费
change.consume()
}
},
onDragEnd = {
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
// 当拖拽结束时,计算新的索引位置
val newIndex = (offset.y / 56.dp.toPx()).roundToInt() + draggedIndex
// 确保新的索引位置在有效范围内
val validNewIndex = newIndex.coerceIn(0, items.size - 1)
// 更新列表项的顺序
items = items.toMutableList().apply {
val draggedItem = removeAt(draggedIndex)
add(validNewIndex, draggedItem)
}
// 重置拖拽索引和偏移量
draggedIndex = -1
offset = IntOffset(0, 0)
}
}
)
}
.graphicsLayer {
// 如果当前列表项正在被拖拽,应用偏移量
if (index == draggedIndex) {
translationX = offset.x.toFloat()
translationY = offset.y.toFloat()
}
}
) {
// 在 Card 中显示列表项的文本
Text(
text = item,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
3.3 代码解释
- 状态管理:使用
mutableStateOf创建三个可变状态:items用于存储列表项的数据,draggedIndex用于记录当前正在拖拽的列表项的索引,offset用于记录拖拽过程中的偏移量。 - 手势监听:使用
Modifier.pointerInput和detectLongPressGestures监听列表项的长按和拖拽手势。在onLongPress回调中,记录当前拖拽的列表项索引;在onDrag回调中,更新偏移量;在onDragEnd回调中,计算新的索引位置,并更新列表项的顺序。 - 位置更新:使用
graphicsLayer组件应用偏移量,实现列表项的位置更新。
3.4 源码分析
detectLongPressGestures 源码分析
detectLongPressGestures 是用于监听长按和拖拽手势的函数。以下是其简化源码分析:
kotlin
suspend fun PointerInputScope.detectLongPressGestures(
onLongPress: (Offset) -> Unit = {},
onDragStart: (Offset) -> Unit = {},
onDrag: (change: PointerInputChange, dragAmount: Offset) -> Unit,
onDragEnd: () -> Unit = {},
onDragCancel: () -> Unit = {}
) {
awaitPointerEventScope {
while (true) {
// 等待第一个按下事件
val down = awaitFirstDown(requireUnconsumed = false)
var longPressDetected = false
// 启动一个协程,在长按时间后检测是否触发长按事件
val longPressJob = launch {
delay(ViewConfiguration.get(this@PointerInputScope).longPressTimeoutMillis)
if (down.pressed) {
longPressDetected = true
onLongPress(down.position)
}
}
var overSlop = Offset.Zero
do {
// 等待下一个指针事件
val event = awaitPointerEvent()
val dragChange = event.changes.find { it.id == down.id }!!
if (dragChange.pressed) {
// 计算拖动的偏移量
val dragDelta = dragChange.positionChange()
overSlop += dragDelta
if (abs(overSlop.getDistance()) > ViewConfiguration.get(this@PointerInputScope).scaledTouchSlop) {
if (longPressDetected) {
// 当长按事件已触发且拖动距离超过阈值时,调用 onDragStart 回调
longPressJob.cancel()
onDragStart(down.position)
while (dragChange.pressed) {
// 持续监听拖动事件,调用 onDrag 回调
val nextEvent = awaitPointerEvent()
val nextDragChange = nextEvent.changes.find { it.id == down.id }!!
if (nextDragChange.pressed) {
val nextDragDelta = nextDragChange.positionChange()
onDrag(nextDragChange, nextDragDelta)
nextDragChange.consume()
}
}
// 当拖动结束时,调用 onDragEnd 回调
onDragEnd()
} else {
// 当长按事件未触发且拖动距离超过阈值时,取消长按协程
longPressJob.cancel()
}
break
}
}
} while (dragChange.pressed)
if (!longPressDetected) {
// 当长按事件未触发时,取消长按协程
longPressJob.cancel()
}
}
}
}
detectLongPressGestures函数在一个协程中不断监听指针事件。- 当检测到按下事件时,启动一个协程,在长按时间后检测是否触发长按事件。
- 在拖动过程中,计算拖动的偏移量,当偏移量超过阈值时,根据长按事件是否触发,执行相应的操作。
- 当拖动结束时,调用
onDragEnd回调。
graphicsLayer 源码分析
graphicsLayer 是用于应用图形变换的修饰符。以下是其简化源码分析:
kotlin
fun Modifier.graphicsLayer(
alpha: Float = 1f,
scaleX: Float = 1f,
scaleY: Float = 1f,
translationX: Float = 0f,
translationY: Float = 0f,
rotationX: Float = 0f,
rotationY: Float = 0f,
rotationZ: Float = 0f,
shadowElevation: Float = 0f,
shape: Shape = RectangleShape,
clip: Boolean = false,
transformOrigin: TransformOrigin = TransformOrigin.Center
): Modifier = composed {
val layer = remember { GraphicsLayerScope() }
layer.alpha = alpha
layer.scaleX = scaleX
layer.scaleY = scaleY
layer.translationX = translationX
layer.translationY = translationY
layer.rotationX = rotationX
layer.rotationY = rotationY
layer.rotationZ = rotationZ
layer.shadowElevation = shadowElevation
layer.shape = shape
layer.clip = clip
layer.transformOrigin = transformOrigin
this.then(
LayoutModifier { measurable, constraints ->
val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints)
layout(placeable.width, placeable.height) {
placeable.placeRelative(
x = layer.translationX.roundToInt(),
y = layer.translationY.roundToInt()
)
}
}
)
}
graphicsLayer修饰符接受多个参数,用于设置图形变换的属性,如透明度、缩放、平移、旋转等。- 在
LayoutModifier中,根据设置的属性对组件进行布局和变换。
3.5 优化拖拽功能
增加拖拽动画
可以在拖拽过程中增加动画效果,提升用户体验。以下是优化后的代码:
kotlin
import androidx.compose.animation.core.Animatable
import androidx.compose.animation.core.AnimationVector2D
import androidx.compose.animation.core.tween
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectLongPressGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.*
import androidx.compose.material.*
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.graphicsLayer
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInput
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import kotlin.math.roundToInt
@Composable
fun DragAndDropListWithAnimation() {
var items by remember { mutableStateOf((1..10).map { "Item $it" }.toList()) }
var draggedIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(-1) }
val offsetX = remember { Animatable(0f) }
val offsetY = remember { Animatable(0f) }
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 4.dp)
.pointerInput(Unit) {
detectLongPressGestures(
onLongPress = {
draggedIndex = index
},
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
launch {
offsetX.snapTo(offsetX.value + dragAmount.x)
offsetY.snapTo(offsetY.value + dragAmount.y)
}
change.consume()
}
},
onDragEnd = {
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
val newIndex = (offsetY.value / 56.dp.toPx()).roundToInt() + draggedIndex
val validNewIndex = newIndex.coerceIn(0, items.size - 1)
items = items.toMutableList().apply {
val draggedItem = removeAt(draggedIndex)
add(validNewIndex, draggedItem)
}
launch {
offsetX.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
offsetY.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
}
draggedIndex = -1
}
}
)
}
.graphicsLayer {
if (index == draggedIndex) {
translationX = offsetX.value
translationY = offsetY.value
}
}
) {
Text(
text = item,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
代码解释
- 使用
Animatable实现拖拽过程中的动画效果。在onDrag回调中,使用snapTo方法立即更新偏移量;在onDragEnd回调中,使用animateTo方法将偏移量动画回 0。 - 其他部分的代码与之前的示例类似,只是在偏移量的处理上增加了动画效果。
四、滑动删除与拖拽的结合使用
4.1 实现思路
在实际应用中,可能需要同时实现滑动删除和拖拽功能。实现思路是在监听手势事件时,根据不同的手势操作执行相应的功能。例如,当检测到水平滑动且滑动距离超过一定阈值时,执行滑动删除操作;当检测到长按并拖动时,执行拖拽操作。
4.2 示例代码
kotlin
import androidx.compose.animation.core.Animatable
import androidx.compose.animation.core.AnimationVector1D
import androidx.compose.animation.core.AnimationVector2D
import androidx.compose.animation.core.tween
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectHorizontalDragGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.gestures.detectLongPressGestures
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.*
import androidx.compose.material.*
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.graphicsLayer
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInput
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import kotlin.math.abs
import kotlin.math.roundToInt
@Composable
fun SwipeAndDragList() {
var items by remember { mutableStateOf((1..10).map { "Item $it" }.toList()) }
var draggedIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(-1) }
val offsetX = remember { Animatable(0f) }
val offsetY = remember { Animatable(0f) }
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
items.forEachIndexed { index, item ->
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 4.dp)
) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Color.Red)
.padding(16.dp)
.align(Alignment.CenterEnd)
) {
Text(
text = "Delete",
color = Color.White
)
}
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.pointerInput(Unit) {
detectLongPressGestures(
onLongPress = {
draggedIndex = index
},
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
launch {
offsetX.snapTo(offsetX.value + dragAmount.x)
offsetY.snapTo(offsetY.value + dragAmount.y)
}
change.consume()
}
},
onDragEnd = {
if (draggedIndex != -1) {
if (abs(offsetX.value) > 100f) {
items = items.toMutableList().apply { removeAt(draggedIndex) }
} else {
val newIndex = (offsetY.value / 56.dp.toPx()).roundToInt() + draggedIndex
val validNewIndex = newIndex.coerceIn(0, items.size - 1)
items = items.toMutableList().apply {
val draggedItem = removeAt(draggedIndex)
add(validNewIndex, draggedItem)
}
}
launch {
offsetX.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
offsetY.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
}
draggedIndex = -1
}
}
)
detectHorizontalDragGestures(
onDrag = { change, dragAmount ->
if (draggedIndex == -1) {
val newOffset = offsetX.value + dragAmount.x
offsetX.snapTo(newOffset.coerceIn(-200f, 0f))
change.consume()
}
},
onDragEnd = {
if (draggedIndex == -1) {
if (offsetX.value < -100f) {
items = items.toMutableList().apply { removeAt(index) }
} else {
launch {
offsetX.animateTo(
targetValue = 0f,
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 200)
)
}
}
}
}
)
}
.graphicsLayer {
if (index == draggedIndex) {
translationX = offsetX.value
translationY = offsetY.value
} else {
translationX = offsetX.value
}
}
) {
Text(
text = item,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
}
4.3 代码解释
- 状态管理:使用
mutableStateOf创建四个可变状态:items用于存储列表项的数据,draggedIndex用于记录当前正在拖拽的列表项的索引,offsetX和offsetY用于记录拖拽过程中的偏移量。 - 手势监听:使用
detectLongPressGestures监听长按和拖拽手势,使用detectHorizontalDragGestures监听水平滑动手势。在不同的手势回调中,根据当前的状态执行相应的操作。 - 功能实现:当检测到长按并拖动时,执行拖拽操作;当检测到水平滑动且滑动距离超过 -100f 时,执行滑动删除操作。
4.4 源码分析
在结合使用滑动删除和拖拽功能时,主要是对之前的手势监听和状态管理代码进行整合。在 detectLongPressGestures 和 detectHorizontalDragGestures 的回调中,根据 draggedIndex 的值判断当前是处于拖拽状态还是滑动删除状态,从而执行相应的操作。
五、性能优化
5.1 减少不必要的重绘
在实现滑动删除和拖拽功能时,要尽量减少不必要的重绘。例如,在 Animatable 的 animateTo 方法中,可以使用 tween 动画规格并设置合适的持续时间,避免动画过于频繁导致的性能问题。同时,在手势监听回调中,使用 change.consume() 标记手势事件已被消费,避免不必要的事件传播。
5.2 合理使用 remember
在使用 Animatable 和其他可变状态时,使用 remember 函数进行记忆,避免在每次重组时重新创建对象。例如,在前面的示例中,使用 remember { Animatable(0f) } 创建 Animatable 对象,确保在组件的生命周期内只创建一次。
5.3 避免嵌套过多的组件
在布局设计时,要避免嵌套过多的组件,减少布局的复杂度。过多的组件嵌套会增加布局的测量和绘制时间,影响性能。例如,在实现滑动删除提示时,可以使用简单的 Box 组件,而不是复杂的布局嵌套。
六、总结与展望
6.1 总结
本文深入分析了 Android Compose 框架的列表与集合模块中滑动删除与拖拽功能的实现原理和源码。通过详细的代码示例和源码分析,我们了解了如何使用 Modifier.pointerInput 监听手势事件,使用 Animatable 实现动画效果,以及如何结合 Layout 组件实现列表项的位置更新。同时,我们还学习了如何优化滑动删除和拖拽功能,包括增加提示、动画效果和性能优化等方面。
6.2 展望
随着 Android Compose 的不断发展,滑动删除和拖拽功能可能会有更多的优化和扩展。例如,可能会提供更方便的 API 来实现这些功能,减少开发者的代码量。同时,可能会支持更多的手势操作和动画效果,提升用户体验。此外,性能优化方面也可能会有进一步的改进,确保在不同设备上都能有流畅的交互效果。未来,开发者可以更加轻松地在 Android Compose 中实现复杂的列表交互功能。









![[LeetCode 1306] 跳跃游戏3(Ⅲ)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/85b350ae4a0c44bc87446564dd814a6b.png)