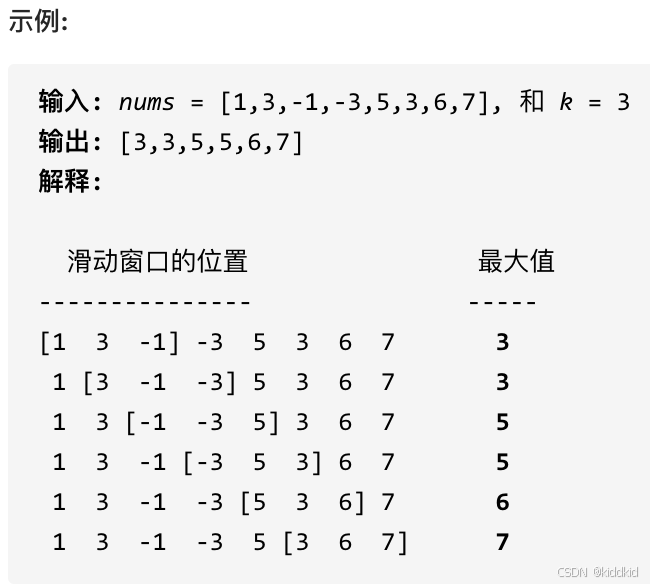
目录
面对对象C的程序设计(范例)
面对对象C的程序设计(应用)
进一步谈论我上面给出的代码——继承
实现一个面对对象的文本编辑器
所以,什么是继承
重申我们对菜单的抽象
抽象菜单项目
抽象菜单动画
实现菜单功能
初始化我们的菜单
关于我们的图标设置,显示和隐藏
菜单本体功能
关于切换focus的菜单和进入父子菜单的函数
完整的测试文件
终于,我们来到了这个令人激动的部分了,现在,我们终于把所有的基础工作做好了,就差我们的动态组件了。
面对对象C的程序设计(范例)
我想,你可能使用过C++这门语言,他派生于C,但是最终的惯用编程范式又远远不同于C。尽管如此,C仍然可以按照一个相对变扭的方式完成面对对象的程序设计。这是因为在C语言本质上是过程化语言,没有直接的类和对象概念,因此面向对象设计需要通过结构体、函数指针等手段模拟实现。
面对对象,首先讲究的就是把所有的目标看成对象。举个例子,现在我们来看看动态多级菜单这个东西,按照面对对象的设计思路。我们说面对对象它通过抽象和封装将数据与功能结合,形成具有特定属性和行为的对象。
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
void (*move)(struct Point*, int, int);
} Point;
void movePoint(Point* p, int dx, int dy) {
p->x += dx;
p->y += dy;
}
int main() {
Point p = {0, 0, movePoint};
p.move(&p, 5, 3);
return 0;
}这个就是一个将点看作对象的例子。
我们设计对象的时候,要思考对象能干什么,进一步的,才需要知道他需要有什么。这种方式可以辅助一个习惯于面对过程的朋友设计一个对象。
面对对象C的程序设计(应用)
我们现在把上面谈到的用一下。
-
他能显示多级的文字菜单
-
他能将目前选中的文本区域进行反色
-
他能再切换选中文本的时候演示一个阻塞的动画(提示,笔者的框架没有做异步,这需要牵扯到中断,笔者不打算现在做)
-
如果一个子项存在子菜单,他能显示出来这个子菜单,然后还能返回去(怎么样触发进入和返回不是我们关心的,他能!)
-
他可以显示和隐藏我们的icon,为此,我们还需要注册接口。
为了做到上面的事情,我们要想他要拥有什么。
-
一个简略的文本编辑器,他能展示文字,我们菜单的文本绘制基本上依赖于这个文本编辑器
-
一个负责动画演示的结构体(对象),他能完成我们对“他能再切换选中文本的时候演示一个阻塞的动画”这个任务
-
一个菜单子项结构体数组,他维护了当前这个菜单子项的文本显示,是否有子菜单,甚至,还需要有callback行为的结构体数组(这个是额外任务,笔者没有做callback)
typedef void* CCgraphicWidgetBase;
/* update requist functions */
typedef void(*Update)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Hide)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Show)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef struct{
Update update;
Hide hide;
Show show;
}CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation;
typedef struct
{
CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation common;
void (*switchToIndex)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t index);
void (*enabled_showAnimations)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t enabled);
void (*setIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*, CCGraphic_Image* image, uint8_t size);
void (*showIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
void (*hideIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
CCGraphic_Menu* (*enterSub)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
CCGraphic_Menu* (*backParent)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
}CCGraphic_MenuOperations;
typedef struct __CCGraphic_Menu{
// 菜单项数组
CCGraphic_MenuItem* menuItemArrays;
// 菜单项数组个数
uint8_t menuArraySize;
// 内部主控件
CCGraphicTextEdit* internelTextEdit;
// 动画负责的结构体
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animation_holder;
// 操作
CCGraphic_MenuOperations operations;
// 当前维护的其他信息
uint8_t current_offset;
uint8_t enabled_animations;
CCGraphic_Image* icons_sources;
uint8_t icon_size;
uint8_t icon_state;
}CCGraphic_Menu;任务:你可以改进这个抽象!你可以看到零碎一地的变量成员不太美观!
进一步谈论我上面给出的代码——继承
让我们进一步讨论更多的概念,上面的代码出现了一个很有意思的片段
typedef void* CCgraphicWidgetBase;
/* update requist functions */
typedef void(*Update)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Hide)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Show)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef struct{
Update update;
Hide hide;
Show show;
}CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation;
typedef struct
{
CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation common;
void (*switchToIndex)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t index);
void (*enabled_showAnimations)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t enabled);
void (*setIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*, CCGraphic_Image* image, uint8_t size);
void (*showIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
void (*hideIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
CCGraphic_Menu* (*enterSub)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
CCGraphic_Menu* (*backParent)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
}CCGraphic_MenuOperations;仔细研究一下,你会发现,我们似乎复用了一个结构体:CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation,也就是组件Widget的通用操作。为了理解这个特征,我们先不着急,实现一个完全面对对象的,一个简单的文本编辑器
实现一个面对对象的文本编辑器
#ifndef CCGraphic_TextEdit_H
#define CCGraphic_TextEdit_H
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_WidgetBase.h"
#include "Graphic/base/CCGraphic_Point/CCGraphic_Point.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_Size/CCGraphic_Size.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_WidgetBase.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextItem.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextConfig.h"
typedef struct __CCGraphicTextEdit CCGraphicTextEdit;
// 前向声明:定义一个名为 `CCGraphicTextEdit` 的结构体类型。
typedef struct {
CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation operation;
// 控件通用操作,提供基本控件功能。
void (*appendText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* appendee);
// 函数指针:向文本控件追加文本。
void (*setText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text);
// 函数指针:设置控件内的完整文本内容。
void (*newLineText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text);
// 函数指针:在控件中新起一行并写入文本。
void (*clear)(CCGraphicTextEdit*);
// 函数指针:清空控件中的文本。
void (*relocate)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size);
// 函数指针:重新定位控件位置并调整控件尺寸。
} CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations;
// 结构体 `CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations`:定义文本控件支持的操作集合。
typedef struct __CCGraphicTextEdit {
uint8_t acquired_stepped_update;
// 标记是否启用分步更新机制的标志变量。
CCDeviceHandler* borrowed_device;
// 设备处理器指针,用于管理外部设备资源。
CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations operations;
// 文本控件支持操作的集合。
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* handle;
// 控件中的具体文本项句柄,用于操作字符显示内容。
} CCGraphicTextEdit;
// 结构体 `CCGraphicTextEdit`:定义文本控件的属性与操作。
void CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit(
CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self,
CCDeviceHandler* handler,
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* inited
);
// 函数声明:初始化 `CCGraphicTextEdit` 控件,传入控件对象、设备处理器和已初始化的文本项。
#endif你可能会问,怎么看起来这么奇怪,我们应该如何调用功能呢?你看,这就是思维没有转变过来,笔者想要说的是,现在功能被集成进入了结构体,意味着,我们想要调用的不叫函数了,是一个结构体的方法。
static void __helper_on_set_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, char* sources, uint32_t shown_time)
{
edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);
HAL_Delay(shown_time * 1000);
edit->operations.clear(edit);
}看到了吗?当我们想要设置文本的时候,不是
CCGraphicTextEdit_setText(edit, sources);
而是
edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);
看起来好像没什么区别,我想说的是,你现在不知道,也没法去引用一个函数,叫“给一个是CCGraphicTextEdit的结构体设置文本”的函数,你找不到,我藏起来了(笑),而是,一个属于CCGraphicTextEdit这个类的对象可以被设置文本,文本是sources,这就是面对对象的设计思考范式。换而言之,一个CCGraphicTextEdit的对象可以设置文本,他能设置文本而且优先的投射到绘图设备上,而你完全不知道底下发生了什么,只知道这样做一定没有问题!
在源文件中,我们才将如何实现暴露出来
#include "Graphic/widgets/components/CCGraphic_TextEdit/CCGraphic_TextEdit.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextItem.h"
#include "Graphic/CCGraphic_device_adapter.h"
static void __pvt_update_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:更新控件所依赖的设备内容。
{
text_self->borrowed_device->operations.update_device_function(
text_self->borrowed_device
// 调用设备的更新函数,使文本控件的内容刷新显示。
);
}
static void __pvt_show(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:绘制并显示文本控件内容。
{
CCGraphicWidget_drawAsciiTextItem(
text_self->borrowed_device, text_self->handle
// 绘制文本控件的内容。
);
if(text_self->acquired_stepped_update)
// 如果启用了分步更新,则执行设备更新。
__pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_hide(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:隐藏控件,即清除其显示区域。
{
text_self->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function(
text_self->borrowed_device,
text_self->handle->tl_point.x,
text_self->handle->tl_point.y,
text_self->handle->TexthandleSize.width,
text_self->handle->TexthandleSize.height
// 清除控件所在区域的内容。
);
__pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_clear_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:清除控件中的文本内容。
{
CCGraphic_Point tl = text_self->handle->tl_point;
CCGraphic_Size size = text_self->handle->TexthandleSize;
// 获取控件左上角坐标和尺寸,用于清除操作。
text_self->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function(
text_self->borrowed_device, tl.x, tl.y, size.width, size.height
// 执行清除操作。
);
__pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_append_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:向控件追加文本。
{
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text);
// 设置追加的文本内容。
__pvt_show(text_self);
// 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_newLine_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:在控件中新建一行并写入文本。
{
CCGraphic_Point new_begin =
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_on_newLine_point(text_self->handle);
// 获取新行起始点坐标。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text);
// 设置文本内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setIndexedPoint(text_self->handle, &new_begin);
// 更新文本项的绘制位置。
__pvt_show(text_self);
// 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_setText(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:设置控件的完整文本内容。
{
__pvt_clear_text(text_self);
// 清除原有内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setIndexedPoint(
text_self->handle,
&(text_self->handle->tl_point)
// 重置文本绘制位置为控件起点。
);
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text);
// 设置新的文本内容。
__pvt_show(text_self);
// 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_relocate(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size)
// 静态函数:重新定位控件位置并调整尺寸。
{
__pvt_hide(edit);
// 隐藏控件内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_relocate(edit->handle, p, size);
// 重新设置控件位置和尺寸。
}
void CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit(
CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self,
CCDeviceHandler* handler,
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* inited
)
// 初始化函数:设置文本编辑控件的初始状态。
{
text_self->acquired_stepped_update = 0;
// 初始化为未启用分步更新。
text_self->borrowed_device = handler;
// 绑定设备处理器。
text_self->handle = inited;
// 设置文本项句柄。
text_self->operations.appendText = __pvt_append_text;
text_self->operations.clear = __pvt_clear_text;
text_self->operations.newLineText = __pvt_newLine_text;
text_self->operations.setText = __pvt_setText;
text_self->operations.relocate = __pvt_relocate;
// 绑定控件的各类操作函数。
text_self->operations.operation.hide = (Hide)__pvt_hide;
text_self->operations.operation.show = (Show)__pvt_show;
text_self->operations.operation.update = (Update)__pvt_update_text;
// 绑定通用控件操作。
}可以看到,代码被分成了一层一层的,关心哪一个方法,只需要进入对应的方法查看即可。
所以,什么是继承
继承允许一个类从另一个类中获取属性和方法,从而实现代码复用和逻辑扩展。也就是说,我们认为继承表达了“一个对象是另一个对象”的陈述。比如说。
typedef struct {
CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation operation;
// 控件通用操作,提供基本控件功能。
void (*appendText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* appendee);
// 函数指针:向文本控件追加文本。
void (*setText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text);
// 函数指针:设置控件内的完整文本内容。
void (*newLineText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text);
// 函数指针:在控件中新起一行并写入文本。
void (*clear)(CCGraphicTextEdit*);
// 函数指针:清空控件中的文本。
void (*relocate)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size);
// 函数指针:重新定位控件位置并调整控件尺寸。
} CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations; 表达了CCGraphicTextEdit的功能集合是CCGraphicWidget的一个超集,他不光拥有一个Widget该有的操作,而且,还有自己跟Widget独有的操作,这就是继承的力量——复用接口,甚至可以是实现!
重申我们对菜单的抽象
根据最之前的描述,菜单本身应该是一个树状的结构,你可以看到:
抽象菜单项目
#ifndef CCGraphic_MenuItem_H
#define CCGraphic_MenuItem_H
#include "Graphic/CCGraphic_common.h"
/* This version we use simple menu Item */
/* announced the menu type for the further usage */
// 预声明 `CCGraphic_Menu` 类型,用于菜单关联。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_Menu CCGraphic_Menu;
// 结构体 `CCGraphic_Menu` 的前向声明,以便在结构中使用指针引用该类型。
#define NO_SUB_MENU (NULL)
// 定义宏 `NO_SUB_MENU` 表示没有子菜单,为空指针。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuItem {
char* text;
// 菜单项显示的文本内容。
CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu;
// 指向子菜单的指针,若无子菜单则为 `NO_SUB_MENU`。
CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu;
// 指向父菜单的指针,用于返回或层级控制。
} CCGraphic_MenuItem;
// 定义菜单项结构体 `CCGraphic_MenuItem`,包含菜单文字、子菜单及父菜单指针。
void CCGraphic_MenuItem_register_menuItem(
CCGraphic_MenuItem* item,
// 菜单项指针,用于注册菜单项。
CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu,
// 父菜单指针,将菜单项附加到此菜单下。
char* text,
// 菜单项文本内容。
CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu
// 子菜单指针,可为 `NO_SUB_MENU`。
);
// 函数声明:将菜单项注册到指定父菜单下,同时设置菜单项文本和子菜单。
#endif提示:需要做callback?(用户明确选择了这个菜单项目)试一下在CCGraphic_MenuItem中添加抽象!完成你的代码!
抽象菜单动画
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuAnimations CCGraphic_MenuAnimations;
// 前向声明 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimations` 结构体,表示菜单动画的管理结构。
typedef void (*DoByStep)(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations*);
// 定义一个函数指针类型 `DoByStep`,指向以 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimations*` 为参数的函数,
// 该函数用于执行逐步动画操作。
typedef struct {
DoByStep doByStep;
// 操作结构体,包含逐步执行动画的函数指针。
} CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations;
// 定义 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations` 结构体,封装了逐步动画执行的操作。
/*
this struct shouldn't be registered by programmers
it shoule be registered by program, so no interface is
publiced!
*/
// 该结构体不应由程序员手动注册,而是由程序自动注册,因此没有提供公开接口。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuAnimations {
/* animating rectangle */
// 定义菜单动画的结构体。
CCDeviceHandler* handler;
// 设备处理器,用于控制设备的操作。
CCGraphic_Point tl_point;
// 动画的起始点(左上角坐标)。
CCGraphic_Size animationOffsetSize;
// 动画的偏移尺寸,用于表示动画区域的大小。
int16_t x_step;
// x轴每步移动的像素值,用于控制动画的水平位移。
int16_t y_step;
// y轴每步移动的像素值,用于控制动画的垂直位移。
CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations op;
// 操作对象,包含执行逐步动画的函数指针。
uint8_t is_doing;
// 标志位,表示动画是否正在进行中。
} CCGraphic_MenuAnimations;
// 定义菜单动画结构体,封装了动画的状态、操作及设备控制。
初始化一个动画的办法是:
static void __pvt_init_animations(
CCGraphic_Menu* menu,
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations
) {
/* no animations are registered */
// 如果没有提供动画对象,直接返回。
if (animations == NULL) {
return;
}
// 获取菜单中的文本编辑项句柄,进行后续动画初始化。
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* internelTextEdit = menu->internelTextEdit->handle;
/* calculate the animations holding size */
// 计算动画的大小,首先设置动画起始点为文本编辑项的起始点。
animations->tl_point = internelTextEdit->tl_point;
// 设置动画的高度为字体的大小(通过 `__fetch_font_size` 获取字体的高度)。
animations->animationOffsetSize.height = __fetch_font_size(internelTextEdit->font_size).height;
// 设置动画的宽度为文本处理器的宽度。
animations->animationOffsetSize.width = internelTextEdit->TexthandleSize.width;
// 设置设备处理器,使用菜单中的文本编辑项借用的设备。
animations->handler = menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device;
// 设置每步的水平和垂直步长(默认值)。
animations->x_step = _DEFAULT_X_STEP;
animations->y_step = _DEFAULT_Y_STEP;
// 设置执行逐步动画操作的函数指针,指向 `__pvt_doByStep` 函数。
animations->op.doByStep = __pvt_doByStep;
/* set state */
// 设置动画状态为未开始。
animations->is_doing = 0;
} 对于逐步开始动画的办法是
/* do by steps */
static void __pvt_doByStep(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations)
{
// 如果动画尚未开始(is_doing 为 0),则直接返回,避免不必要的操作。
if (!animations->is_doing) return;
// 使用设备的操作对象反转(擦除)动画区域,传入当前动画的起始位置(tl_point)和尺寸。
animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(
animations->handler,
animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,
animations->animationOffsetSize.width,
animations->animationOffsetSize.height
);
// 更新动画的起始点(左上角坐标),按水平步长(x_step)和垂直步长(y_step)更新。
animations->tl_point.x += animations->x_step;
animations->tl_point.y += animations->y_step;
// 再次调用反转(擦除)区域,传入更新后的动画位置和尺寸。
animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(
animations->handler,
animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,
animations->animationOffsetSize.width,
animations->animationOffsetSize.height
);
// 调用更新设备函数,刷新屏幕以显示动画效果。
animations->handler->operations.update_device_function(
animations->handler
);
} 看到了吗,非必要不调用刷新设备的操作就在这里体现了。当然,当我们配置不需要动画的时候
static void __pvt_do_as_immediate(
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations,
CCGraphic_Point* end_tpl)
{
if(!animations->is_doing) return;
animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(
animations->handler,
animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,
animations->animationOffsetSize.width,
animations->animationOffsetSize.height
);
animations->tl_point = *end_tpl;
animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(
animations->handler,
animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,
animations->animationOffsetSize.width,
animations->animationOffsetSize.height
);
animations->handler->operations.update_device_function(
animations->handler);
}直接拉到最后就好了。
实现菜单功能
到了真正实现的时候,一切反而水到渠成。
初始化我们的菜单
void CCGraphic_init_Menu(
CCGraphic_Menu* blank_menu,
CCGraphic_MenuItem* menuItemArrays,
uint8_t menuArraySize,
CCGraphicTextEdit* configured_menu,
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* blank_animations,
uint8_t enabled_animations
)
{
blank_menu->internelTextEdit = configured_menu;
blank_menu->menuItemArrays = menuItemArrays;
blank_menu->menuArraySize = menuArraySize;
blank_menu->animation_holder = blank_animations;
blank_menu->current_offset = 0;
blank_menu->icon_state = 0;
blank_menu->enabled_animations = enabled_animations;
// map the functions
blank_menu->operations.common.hide = (Hide)__pvt_hide_CCGraphic_Menu;
blank_menu->operations.common.show = (Show)__pvt_show_CCGraphic_Menu;
blank_menu->operations.common.update = (Update)__pvt_update;
blank_menu->operations.switchToIndex = __pvt_switchIndex;
blank_menu->operations.enabled_showAnimations =
__pvt_setAnimationShowState_wrapper;
// icons
blank_menu->operations.setIcon = __pvt_setIcon;
blank_menu->operations.hideIcon = __pvt_hideIcon;
blank_menu->operations.showIcon = __pvt_showIcon;
blank_menu->operations.enterSub = __pvt_enterSub;
blank_menu->operations.backParent = __pvt_backParent;
__pvt_init_animations(blank_menu, blank_animations);
}关于我们的图标设置,显示和隐藏
static void __pvt_setIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu, CCGraphic_Image* sources, uint8_t size)
{
// 设置菜单的图标源和图标数量
menu->icons_sources = sources;
menu->icon_size = size;
// 初始化每个图标的尺寸和位置
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < menu->icon_size; i++) {
// 设置图标的高度和宽度
sources[i].image_size.height = ICON_HEIGHT;
sources[i].image_size.width = ICON_WIDTH;
// 设置每个图标的位置,`y` 方向依次排列
sources[i].point.x = 0;
sources[i].point.y = i * ICON_HEIGHT;
}
// 显示图标
__pvt_showIcon(menu);
}
static void __pvt_showIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 如果没有图标源,则不执行任何操作
if (!menu->icons_sources) return;
// 设置图标的状态为显示(1)
menu->icon_state = 1;
CCGraphic_Point tlp;
CCGraphic_Size _size;
// 获取显示图标的位置和大小
__pvt_providePoint(menu, &tlp, 1);
__pvt_provideSize(menu, &_size, 1);
// 设置动画的显示状态为 0(关闭动画)
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0);
// 将菜单项的文本编辑区域重新定位到指定的位置和大小
menu->internelTextEdit->operations.relocate(menu->internelTextEdit, tlp, _size);
// 遍历图标源,逐一绘制每个图标
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < menu->icon_size; i++) {
CCGraphicWidget_draw_image(
menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device,
&menu->icons_sources[i]
);
}
// 设置动画的显示状态为 1(启用动画)
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 1);
// 仅显示文本编辑器
__pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
}
static void __pvt_hideIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 如果没有图标源,则不执行任何操作
if (!menu->icons_sources) return;
CCGraphic_Point tlp;
CCGraphic_Size _size;
// 设置图标的状态为隐藏(0)
menu->icon_state = 0;
// 获取隐藏图标的位置和大小
__pvt_providePoint(menu, &tlp, 0);
__pvt_provideSize(menu, &_size, 0);
// 设置动画的显示状态为 0(关闭动画)
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0);
// 将菜单项的文本编辑区域重新定位到指定的位置和大小
menu->internelTextEdit->operations.relocate(menu->internelTextEdit, tlp, _size);
// 清除图标区域
menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function(
menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device,
0, 0, ICON_WIDTH, ICON_HEIGHT * menu->icon_size
);
// 仅显示文本编辑器
__pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
} 图标的绘制就是让位子绘制,清除掉重新绘制这个思路。
菜单本体功能
static void __pvt_update(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 调用文本编辑器的更新操作,刷新菜单显示
menu->internelTextEdit->operations.operation.update(
menu->internelTextEdit
);
}
// 更新动画状态
static void __pvt_setAnimationShowState(
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations, uint8_t is_doing)
{
// 如果动画状态没有变化,直接返回
if(is_doing == animations->is_doing){
return;
}
// 如果动画正在进行,先逆向绘制区域,清除之前的显示
animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(
animations->handler,
animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,
animations->animationOffsetSize.width,
animations->animationOffsetSize.height
);
// 更新动画状态
animations->is_doing = is_doing;
// 更新设备,刷新显示
animations->handler->operations.update_device_function(
animations->handler);
}
/*
以下是显示/隐藏图标时,提供布局计算的函数
*/
static void __pvt_providePoint(
CCGraphic_Menu* menu,
CCGraphic_Point* p,
uint8_t icons_enabled)
{
// 根据是否启用图标,设置图标显示的起始位置
p->x = icons_enabled ? ICON_WIDTH : 0;
p->y = 0;
}
static void __pvt_provideSize(
CCGraphic_Menu* menu,
CCGraphic_Size* size,
uint8_t icons_enabled
){
// 根据是否启用图标,调整文本区域的宽度和高度
size->width = menu->internelTextEdit->handle->TexthandleSize.width -
(icons_enabled ? ICON_HEIGHT : 0);
size->height = menu->internelTextEdit->handle->TexthandleSize.height;
}
// 获取当前菜单项是否有子菜单
static inline CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_current_owns_subMenu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
return menu->menuItemArrays[
menu->current_offset].subMenu;
}
// 获取当前菜单项的父菜单
static inline CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_owns_parent_current(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
return menu->menuItemArrays[
menu->current_offset].parentMenu;
}
// 仅显示文本编辑器的内容,更新菜单显示
void __pvt_show_textEditOnly(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 如果菜单没有项,则直接返回
if(menu->menuArraySize == 0){
return;
}
// 设置动画状态为不显示
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0);
// 设置文本编辑器的内容,显示第一项菜单
CCGraphicTextEdit* edit = menu->internelTextEdit;
edit->operations.setText(edit, menu->menuItemArrays[0].text);
// 显示后续菜单项
for(uint8_t i = 1; i < menu->menuArraySize; i++)
{
edit->operations.newLineText(edit, menu->menuItemArrays[i].text);
}
// 设置动画状态为显示
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 1);
}
// 隐藏菜单和图标
void __pvt_hide_CCGraphic_Menu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 隐藏图标
__pvt_hideIcon(menu);
// 隐藏文本编辑器
menu->internelTextEdit->operations.operation.hide(menu->internelTextEdit);
// 获取动画控制器
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animation = menu->animation_holder;
// 如果没有动画控制器,则返回
if(!animation) return;
// 如果动画正在进行,则停止动画
if(animation->is_doing){
__pvt_setAnimationShowState(animation, 0);
}
}
/* 绘制菜单显示 */
void __pvt_show_CCGraphic_Menu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{
// 仅显示文本编辑器内容
__pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
}
// 执行动画,逐步更新菜单位置直到目标位置
void __pvt_do_stepped_animate(
CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations,
CCGraphic_Point* end_tl_p
)
{
// 如果动画步长为负,表示需要向下移动
if(animations->y_step < 0){
// 逐步向下执行动画,直到达到目标位置
while(animations->tl_point.y > end_tl_p->y){
__pvt_doByStep(animations); // 执行单步动画
#ifdef REQ_ANIMATION_DELAY
// 延时,模拟动画效果
__device_delay(ANIMATION_DELAY_MS);
#endif
}
}
// 如果动画步长为正,表示需要向上移动
else
{
// 逐步向上执行动画,直到达到目标位置
while(animations->tl_point.y < end_tl_p->y){
__pvt_doByStep(animations); // 执行单步动画
#ifdef REQ_ANIMATION_DELAY
// 延时,模拟动画效果
__device_delay(ANIMATION_DELAY_MS);
#endif
}
}
}关于切换focus的菜单和进入父子菜单的函数
// 切换菜单项索引并执行动画
static void __pvt_switchIndex(
CCGraphic_Menu* menu, uint8_t index)
{
// 如果索引没有变化,不做任何操作
if(index == menu->current_offset) return;
// 如果新索引大于当前索引,表示需要向下移动
if(index > menu->current_offset){
// 如果当前动画步长为负,改为正值
if(menu->animation_holder->y_step < 0){
menu->animation_holder->y_step =
-menu->animation_holder->y_step;
}
}
// 如果新索引小于当前索引,表示需要向上移动
else{
// 如果当前动画步长为正,改为负值
if(menu->animation_holder->y_step > 0){
menu->animation_holder->y_step =
-menu->animation_holder->y_step;
}
}
// 更新当前菜单项的索引
menu->current_offset = index;
// 计算目标位置
CCGraphic_Point end_tlp;
end_tlp = menu->animation_holder->tl_point;
end_tlp.y = index * menu->animation_holder->animationOffsetSize.height;
// 如果启用了动画,执行逐步动画
if(menu->enabled_animations)
__pvt_do_stepped_animate(menu->animation_holder, &end_tlp);
else
// 否则,立即执行动画
__pvt_do_as_immediate(menu->animation_holder, &end_tlp);
}
// 进入子菜单并显示子菜单的内容
static CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_enterSub(CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu)
{
// 缓存父菜单的图标状态
uint8_t cached_icon_state = parentMenu->icon_state;
// 获取父菜单的子菜单
CCGraphic_Menu* subone = __pvt_current_owns_subMenu(parentMenu);
// 如果没有子菜单,返回NULL
if(!subone) return NULL;
// 隐藏当前菜单
parentMenu->operations.common.hide(parentMenu);
// 恢复父菜单的图标状态
parentMenu->icon_state = cached_icon_state;
// 如果子菜单有图标,显示图标,否则显示子菜单
if(subone->icon_state){
subone->operations.showIcon(subone);
}else{
subone->operations.common.show(subone);
}
// 返回子菜单
return subone;
}
// 返回父菜单并显示父菜单的内容
static CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_backParent(CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu)
{
// 缓存子菜单的图标状态
uint8_t cached_icon_state = subMenu->icon_state;
// 获取子菜单的父菜单
CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu = __pvt_owns_parent_current(subMenu);
// 如果没有父菜单,返回NULL
if(!parentMenu) return NULL;
// 隐藏当前子菜单
subMenu->operations.common.hide(subMenu);
// 恢复子菜单的图标状态
subMenu->icon_state = cached_icon_state;
// 如果父菜单有图标,显示图标,否则显示父菜单
if(parentMenu->icon_state){
parentMenu->operations.showIcon(parentMenu);
}else{
parentMenu->operations.common.show(parentMenu);
}
// 返回父菜单
return parentMenu;
}完整的测试文件
现在来看看完整的测试文件!
#include "Test/OLED_TEST/oled_test.h"
#include "Test/GraphicTest/graphic_test.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/components/CCGraphic_TextEdit/CCGraphic_TextEdit.h"
void test_oled_iic_functionalities()
{
OLED_Handle handle;
user_init_hard_iic_oled_handle(&handle);
test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 1, 2);
HAL_Delay(1000);
test_clear(&handle);
test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 2, 1);
HAL_Delay(1000);
test_clear(&handle);
}
void test_oled_spi_functionalities()
{
OLED_Handle handle;
user_init_hard_spi_oled_handle(&handle);
test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 1, 2);
HAL_Delay(1000);
test_clear(&handle);
test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 2, 1);
HAL_Delay(1000);
test_clear(&handle);
}
static void __helper_on_set_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, char* sources, uint32_t shown_time)
{
edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);
HAL_Delay(shown_time * 1000);
edit->operations.clear(edit);
}
#define SET_TEXT_CONV(SRC, SECS) do{ sources = SRC;\
__helper_on_set_text(&edit, sources, SECS);}while(0)
static void __test_common(CCDeviceHandler* handler)
{
CCGraphicTextEdit edit;
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem item;
CCGraphic_Point p;
p.x = 0;
p.y = 0;
CCGraphic_Size acceptablesize =
CCGraphicWidget_MaxAcceptable_Size(handler);
CCGraphicWidget_init_AsciiTextItem(
&item, p, acceptablesize, ASCII_6x8
);
CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit(
&edit, handler, &item
);
edit.acquired_stepped_update = 1;
char* sources;
SET_TEXT_CONV("Hello! Welcome CCGraphic SimpleTest!", 5);
SET_TEXT_CONV("If you see this sentences, "
"it means that you have passed the GraphicTest"
"and congratulations!", 7);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On Base begin", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Points", 4);
on_test_draw_points(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Lines", 4);
on_test_draw_line(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Circles", 4);
on_test_draw_circle(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Rectangle", 4);
on_test_draw_rectangle(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Triangle", 4);
on_test_draw_triangle(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Ellipse", 4);
on_test_draw_ellipse(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Arc", 4);
on_test_draw_arc(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On Base end", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On widget begin", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Image Drawing", 4);
/* widget test */
on_test_draw_image(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Ascii Draw", 4);
on_test_draw_ascii(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On widget end", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On component begin", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test TextEdit", 4);
/* components test */
on_test_component_textEdit_test(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Frame", 4);
on_test_component_frame_test(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Menu", 4);
on_test_component_menu(handler);
HAL_Delay(1000);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On component end", 4);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Finish Testing, enjoy!", 4);
}
void test_graphic_hardiic_functionalities()
{
CCDeviceHandler handler;
on_test_init_hardiic_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}
void test_graphic_soft_spi_functionalities()
{
CCDeviceHandler handler;
on_test_init_softspi_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}
void test_graphic_hard_spi_functionalities()
{
CCDeviceHandler handler;
on_test_init_hardspi_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}效果就是这个完整的测试视频:
完整测试视频
目录导览
总览
协议层封装
OLED设备封装
绘图设备抽象
基础图形库封装
基础组件实现
动态菜单组件实现