
直方图均衡化是一种在图像处理技术,通过调整图像的直方图来增强图像的对比度。
本博客不利用opencv库,仅利用numpy、matplotlib来实现直方图均衡、自适应直方图均衡、对比度受限自适应直方图均衡
直方图均衡
包括四个流程
- 计算图像RGB三通道的归一化直方图
- 计算变换函数,
k
k
k为输入像素值,输出像素值为
s
=
T
(
k
)
s=T(k)
s=T(k)
s = T ( k ) = ( L − 1 ) ∑ j = 0 k p r ( r j ) = ( L − 1 ) ∑ j = 0 k n j M N = L − 1 M N ∑ j = 0 k n j s=T(k)=(L-1)\sum_{j=0}^kp_r(r_j)=(L-1)\sum_{j=0}^k\frac{n_j}{MN}=\frac{L-1}{MN}\sum_{j=0}^kn_j s=T(k)=(L−1)∑j=0kpr(rj)=(L−1)∑j=0kMNnj=MNL−1∑j=0knj
其中L=256,表示256个像素值, p r ( r j ) p_r(r_j) pr(rj)表示像素值为 j j j的像素点概率,MN表示像素点个数, n j n_j nj表示像素值为j的像素点个数, k ∈ [ 0 , L − 1 ] k\in[0, L-1] k∈[0,L−1] - 对于每个通道的每个像素点,通过变换函数实现变换
- 三个通道的所有像素点变换后,合并起来,组合成新的RGB图像
直方图均衡利用全图的直方图统计信息,提升全图的对比度,对局部图的对比度提升较小,所以需要自适应直方图均衡。
自适应直方图均衡(Adaptive Histogram Equalization, AHE)
包括4个步骤
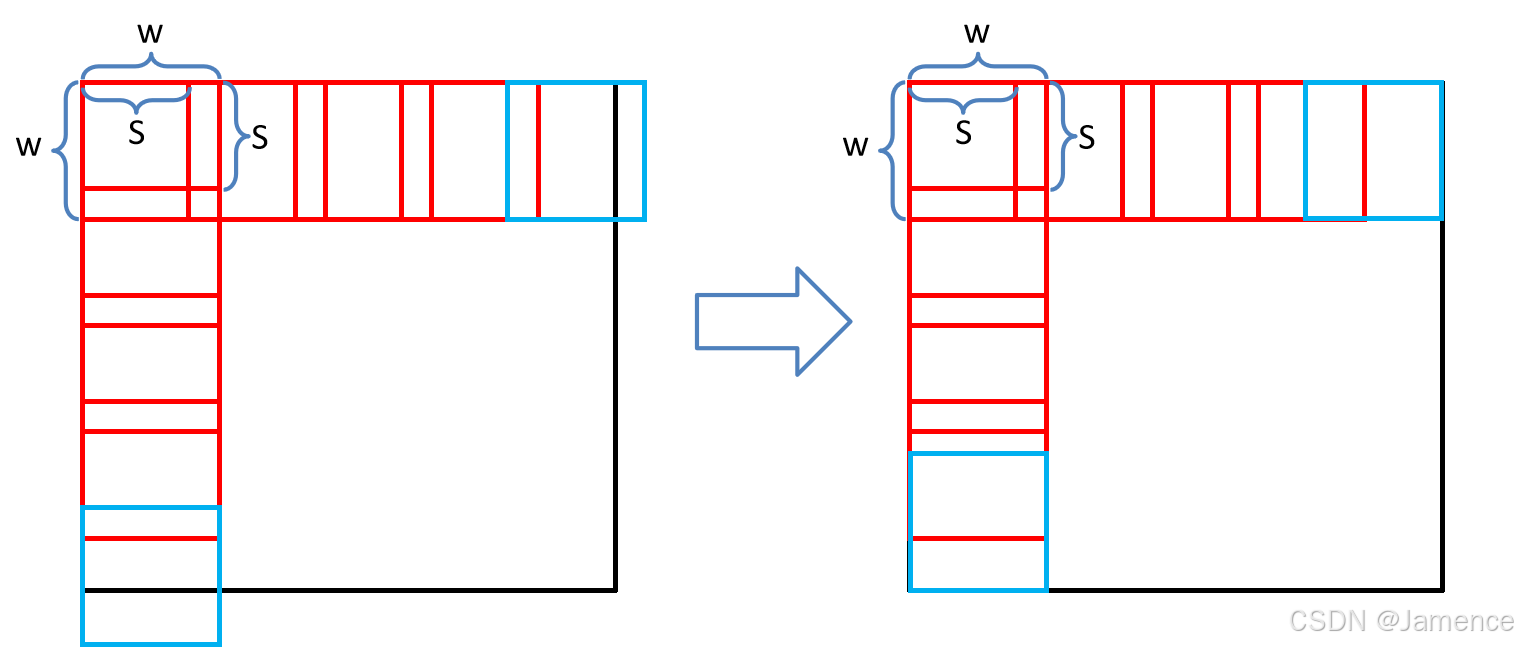
- 设置滑动窗口大小
W (window size)以及步长S (stride),需要保证W>=S - 滑动窗口从图像左上角开始,向右、向下滑动。滑动过程中,窗口可能会滑出图像区域。为了避免该情况,如果窗口超出图像区域,把图像拉回来,贴到最近的边缘。如下图,蓝色窗口滑出图像区域,将其拉回。
](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/35a44c0d48104898a96962dbcbc235fc.png)
- 对滑动窗口内的像素值统计直方图,进行变换。包括:
- 在窗口
W*W区域内,统计直方图 - 在窗口
W*W区域内,计算变换函数 - 如果窗口位于图像边缘(窗口在图像四个角、四条边上),变换函数作用于窗口内所有像素点
- 如果窗口位于图像内,变换函数仅作用于窗口中心的
S*S区域,可以理解为利用窗口的统计信息优化窗口内局部区域的对比度
- 在窗口
- 三个通道的所有像素点变换后,合并起来,组合成新的RGB图像
自适应直方图均衡对滑动窗口内的图像进行对比度增强,提升图像局部的对比度。一方面,局部对比度提升过大,容易失真;另一方面,不同局部区域的直方图统计信息差距明显,导致增强后的图像有明显的块状结构。
对比度受限自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histogram equalization, CLAHE)
具备6个步骤
- 设置滑动窗口
W,直方图阈值T。 - 滑动窗口从图像左上角开始,向右、向下滑动。滑动过程中,窗口可能会滑出图像区域。为了避免该情况,采用和直方图均衡不同的策略,对原图做边缘的零填充。

- 对滑动窗口内的像素值进行变换。变换逻辑为:
- 在窗口
W*W区域内,统计直方图 - 通过对直方图裁剪,限制对比度。将直方图中超过直方图阈值
T的部分均分到直方图的每个块中。
- 计算每个窗口的变换函数
- 通过对目标窗口的像素值进行插值,缓解自适应直方图均衡带来的分块问题

- 目标窗口D内,目标像素点位于4个子窗口,a、b、c、d
- 每个子窗口有4个上、下、左、右的领域窗口。例如子窗口a的领域窗口是A、B、C、D,子窗口b的领域窗口是B、M、D、E。
- 需要讨论一些边界情况:如果窗口D在图像的左上角,那么子窗口a的领域窗口只有D;如果窗口D在紧挨图像上边缘,那么子窗口b的领域窗口只有D和E…
- 通过目标像素点和领域窗口的插值,实现变换。例如,对于在子窗口a的像素点,先计算在A、B、C、D四个窗口变换函数下的变换值,通过距离插值,得到最终变换值。
- 三个通道的所有像素点变换后,合并起来,组合成新的RGB图像
- 在窗口
实验对比结果
对于自适应直方图均衡,参数设置为:W=64, S=20
对于对比度受限自适应直方图均衡,参数设置为:W=40, T=10
ori:原图
1:直方图均衡
2:自适应直方图均衡
3:对比度受限自适应直方图均衡
样例1

RGB三通道直方图比较:

样例2

RGB三通道直方图比较:

三种算法比较
| 直方图均衡 | 自适应直方图均衡 | 对比度受限自适应直方图均衡 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 增强效果 | 对比度较原图增强;图像较连续;局部区域增强不明显,部分局部区域比较暗 | 对比度较原图增强;图像不连续,有块状效应;局部区域增强较明显 | 对比度较原图增强;图像连续,无块状效应;局部区域对比度也有提升 |
| 直方图比较 | 直方图变得均衡,但首或尾可能值特别大 | 直方图变得均衡,但首或尾值依旧比其他位置大 | 直方图均衡化程度没有前两者高 |
| 运行时间 | 快 | 慢 | 中等 |
整体代码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import PIL
import numpy as np
from pylab import subplots_adjust
depth = 3
def show_histogram(img):
"""
展示三个通道直方图
:param img: 图像(numpy)
:return: void,但是显示图像
"""
plot.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plot.hist(img[:, :, 0].flatten(), 256)
plot.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plot.hist(img[:, :, 1].flatten(), 256)
plot.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plot.hist(img[:, :, 2].flatten(), 256)
plot.show()
def get_histogram(img, normed = True) :
"""
计算img的直方图
由于img有三个通道,需要在三个通道上做直方图,根据norm参数设置为0~1的概率值还是整数值
:param img: 三维矩阵,长*宽*通道数
:param normd: 是否做归一化
:return: 在rgb通道上的直方图
"""
his = np.zeros((3, 256))
total_num = img.shape[0] * img.shape[1]
for dep in range(depth) :
for hei in range(img.shape[0]) :
for wid in range(img.shape[1]) :
his[dep][img[hei][wid][dep]] += 1
if normed == True :
his /= total_num
return his
def histogramEqualization(img, save_pth='no') :
"""
计算直方图均衡化之后的图像
计算+保存 直方图均衡化之后的图像
:param img: 输入图像(numpy)
:param save_pth: 保存路径
:return: 直方图均衡之后的图像(numpy)
"""
### 计算直方图
his = get_histogram(img, normed = True)
### 计算累加和
his_culsum = np.zeros((3, 256))
for dep in range(depth) :
sum_tmp = 0.0
for index in range(256) :
sum_tmp += his[dep][index]
his_culsum[dep][index] = sum_tmp
his_cdf = 255.0 * his_culsum
### Q1 整数化处理(测试三种取整方式)?
# his_cdf = np.around(his_cdf, 0)
his_cdf = np.floor(his_cdf)
# img_hisequa = np.zeros(img.shape)
### Q2 保存图片前后的直方图不同意?
### Q3 numpy类型图片颜色显示不正确?
### 设置映射
new_photo = PIL.Image.new('RGB', (img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
img_hisequa = np.array(new_photo)
for hei in range(img.shape[0]) :
for wid in range(img.shape[1]) :
r = img[hei][wid][0]
g = img[hei][wid][1]
b = img[hei][wid][2]
img_hisequa[hei][wid][0] ,img_hisequa[hei][wid][1], img_hisequa[hei][wid][2] = int(his_cdf[0][r]), int(his_cdf[1][g]), int(his_cdf[2][b])
if save_pth != 'no' :
img = PIL.Image.fromarray(img_hisequa.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
img.save(save_pth, quality= 95)
return img_hisequa
def AHE(img, W, S, save_pth = 'no') :
"""
对图像做自适应直方图均衡化
对图像做自适应直方图均衡化,保存到save_pth(当save_pth=no时不处理)
:param img: 输入numpy图像
:param W: 窗口边长参数W
:param S: 影响区域大小边长/stride
:param save_pth: 保存图像路径
:return:
"""
assert W >= S
### 按照S得到在水平方向和竖直方向滑动的次数,如果不能取整,加一
img_height = img.shape[0]
img_width = img.shape[1]
hei_num = img_height / S
if hei_num > int(hei_num) :
hei_num = int(hei_num) + 1
else:
hei_num = int(hei_num)
wid_num = img_width / S
if wid_num > int(wid_num) :
wid_num = int(wid_num) + 1
else :
wid_num = int(wid_num)
print(hei_num, wid_num)
# 处理边缘(采用窗口为W,影响区域为W处理,最后一个区域采用同样的W大小,可以忽视重叠部分)
new_photo = PIL.Image.new('RGB', (img_width, img_height))
img_hisequa = np.array(new_photo)
for hei_i in range(1, hei_num + 1) :
sta_hei = S * (hei_i - 1)
end_hei = S * (hei_i)
if end_hei > img_height :
sta_hei = img_height - W
end_hei = img_height
img_hisequa[sta_hei:end_hei, 0: W, :] = histogramEqualization(img[sta_hei:end_hei, 0: W, :])
img_hisequa[sta_hei:end_hei, img_width - W: img_width, :] = histogramEqualization(img[sta_hei:end_hei, img_width - W: img_width, :])
for wid_i in range(1, wid_num + 1) :
sta_wid = S * (wid_i - 1)
end_wid = S * (wid_i)
if end_wid > img_width :
sta_wid = img_width - W
end_wid = img_width
img_hisequa[0: W, sta_wid: end_wid, :] = histogramEqualization(img[0: W, sta_wid: end_wid, :])
img_hisequa[img_height - W: img_height, sta_wid: end_wid, :] = histogramEqualization(img[img_height - W: img_height, sta_wid: end_wid, :])
#其次处理内部
### 类似的,计算内部区域滑动次数,有小数,加一
pad_num = int((W - S) / 2)
assert (W - S) % 2 == 0
img_height_inside = img_height - 2 * W
img_width_inside = img_width - 2 * W
hei_num_inside = img_height_inside / S
if hei_num_inside > int(hei_num_inside) :
hei_num_inside = int(hei_num_inside) + 1
else :
hei_num_inside = int(hei_num_inside)
wid_num_inside = img_width_inside / S
if wid_num_inside > int(wid_num_inside) :
wid_num_inside = int(wid_num_inside) + 1
else :
wid_num_inside = int(wid_num_inside)
### 将窗口W按照S滑动,最后一个区域也采用W窗口,影响区域为S,尽管会重叠,但是效果相同
base_left = W
base_right = img_width - W
base_up = W
base_down = img_height - W
for hei_i in range(1, hei_num_inside + 1) :
for wid_i in range(1, wid_num_inside + 1) :
up = base_up + S * (hei_i - 1)
down = base_up + S * hei_i
if down > base_down :
up = base_down - S
down = base_down
left = base_left + S * (wid_i - 1)
right = base_left + S * wid_i
if right > base_right :
left = base_right - S
right = base_right
img_tmp = histogramEqualization(img[up - pad_num: down + pad_num, left - pad_num: right + pad_num, :])
img_hisequa[up: down, left: right, :] = img_tmp[pad_num: img_tmp.shape[0] - pad_num, pad_num: img_tmp.shape[1] - pad_num,:]
if save_pth != 'no' :
img_save = PIL.Image.fromarray(img_hisequa.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
img_save.save(save_pth, quality = 95)
return img_hisequa
def clip(his, threshold = 1.0) :
"""
裁剪直方图,阈值threshold = threshold_value * len(his) / total_num
:param his: 直方图numpy(一维)
:param threshold: 阈值 threshold_value * len(his) / total_num,
threshold_value表示数量
:return:裁剪之后的直方图
"""
total_num = np.sum(his)
# print(total_num)
threshold_value = total_num / len(his) * threshold
value_average = 0
for i in range(len(his)) :
if his[i] >= threshold_value :
value_average += his[i] - threshold_value
value_average /= len(his)
his_clip = np.zeros(his.shape)
for i in range(len(his)) :
if his[i] >= threshold_value :
his_clip[i] = threshold_value + value_average
else :
his_clip[i] = his[i] + value_average
return his_clip
def get_his_clip_histogramEqualization(img, threshold = 1.0) :
"""
对裁剪后的直方图做均衡,在单通道上实现,其中调用了clip函数。
:param img: 输入图片(单通道图片numpy)
:param threshold:阈值threshold = threshold_value * len(his) / total_num
:return:返回直方图的累计分布函数(即映射函数)
"""
his = np.zeros(256)
total_num = img.shape[0] * img.shape[1]
for hei in range(img.shape[0]):
for wid in range(img.shape[1]):
his[img[hei][wid]] += 1
his /= total_num
his_clip = clip(his, threshold= threshold)
his_culsum = np.zeros(256)
sum_tmp = 0
for index in range(256):
sum_tmp += his_clip[index]
his_culsum[index] = sum_tmp
his_cdf = 255.0 * his_culsum
his_cdf = np.floor(his_cdf)
return his_cdf
def CLAHE_single_channel(img, W, T):
"""
对单通道图像做CLAHE处理,即直方图裁剪+插值,其中调用了get_his_clip_histogramEqualization来
得到裁剪后的直方图
:param img: input image
:param W: window size W*W
:param T: histogram threshold = threshold_value * len(his) / sum(hist)
:return: 对单通道图像做了CLAHE处理之后的单通道图像(numpy)
"""
### clip
img_height = img.shape[0]
img_width = img.shape[1]
W_hei_num = (img_height // W)
W_wid_num = (img_width // W)
img = np.pad(img, ((0,W - (img_height - W_hei_num * W)),(0,W - (img_width - W_wid_num * W))),'constant',constant_values= (0,0))
W_hei_num = img.shape[0] // W
W_wid_num = img.shape[1] // W
res_img = np.zeros(img.shape)
### 对单通道做直方图均衡
#### 对整除的部分做处理
his_map = {}
for w_hei_i in range(W_hei_num):
for w_wid_i in range(W_wid_num):
up = w_hei_i * W
down = (w_hei_i + 1) * W
left = w_wid_i * W
right = (w_wid_i + 1) * W
his_tmp = get_his_clip_histogramEqualization(img[up: down, left: right], T)
his_map[(w_hei_i, w_wid_i)] = his_tmp
### 插值
for i_h in range(W_hei_num * W):
for i_w in range(W_wid_num * W):
### 计算左上角的块在W_hei_num,W_wid_num块中的横纵坐标
## 从0开始,向下取整
left_up_h = int((i_h - W / 2) / W)
left_up_w = int((i_w - W / 2) / W)
### 计算距离
dis_x = i_h - left_up_h * W - W / 2
dis_x /= W
dis_y = i_w - left_up_w * W - W / 2
dis_y /= W
### 左上角
if left_up_h < 0 and left_up_w < 0:
res_img[i_h][i_w] = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
### 右上角
elif left_up_h < 0 and left_up_w >= W_hei_num - 1:
res_img[i_h][i_w] = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, left_up_w)][img[i_h, i_w]]
### 右下角
elif left_up_h >= W_hei_num - 1 and left_up_w >= W_hei_num - 1:
res_img[i_h][i_w] = his_map[(left_up_h, left_up_w)][img[i_h, i_w]]
### 左下角
elif left_up_h >= W_hei_num - 1 and left_up_w < 0:
res_img[i_h][i_w] = his_map[(left_up_h, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
### 四个边界
## 上边
elif left_up_h < 0 :
left = his_map[(0, left_up_w)][img[i_h, i_w]]
right = his_map[(0, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
res_img[i_h][i_w] = (1 - dis_y) * left + dis_y * right
## 下边
elif left_up_h >= W_hei_num - 1 :
left = his_map[(W_hei_num - 1, left_up_w)][img[i_h, i_w]]
right = his_map[(W_hei_num - 1, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
res_img[i_h][i_w] = (1 - dis_y) * left + dis_y * right
## 左边
elif left_up_w < 0 :
up = his_map[(left_up_h, 0)][img[i_h, i_w]]
down = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, 0)][img[i_h, i_w]]
res_img[i_h][i_w] = (1 - dis_x) * up + dis_x * down
## 右边
elif left_up_w >= W_wid_num - 1 :
up = his_map[(left_up_h, W_wid_num - 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
down = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, W_wid_num - 1)][img[i_h, i_w]]
res_img[i_h][i_w] = (1 - dis_x) * up + dis_x * down
else :
left_up = his_map[(left_up_h, left_up_w)][img[i_h][i_w]]
left_down = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, left_up_w)][img[i_h][i_w]]
right_up = his_map[(left_up_h, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h][i_w]]
right_down = his_map[(left_up_h + 1, left_up_w + 1)][img[i_h][i_w]]
res_img[i_h][i_w] = (1 - dis_y) * ((1 - dis_x) * left_up + dis_x * left_down) + dis_y * ((1 - dis_x) * right_up + dis_x * right_down)
return res_img[:img_height, :img_width]
### 处理右边+下边的边界部分
def CLAHE(img, W, T, save_pth = 'no') :
"""
:param img: input image
:param W: window size W*W
:param T: histogram threshold = threshold_value * len(his) / sum(hist)
:return:
"""
# save_pth = 'astro_result3.jpg'
res_img = img.copy()
res_img[: ,:, 0] = CLAHE_single_channel(img[:,:,0],W, T)
res_img[:, :, 1] = CLAHE_single_channel(img[:,:,1],W, T)
res_img[:, :, 2] = CLAHE_single_channel(img[:,:,2],W, T)
if save_pth != 'no' :
img_save = PIL.Image.fromarray(res_img.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
img_save.save(save_pth, quality=95)
return res_img
### 以下三个函数为测试直方图均衡化,自适应直方图均衡化,限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化,简单调用
def callhistogramEqualization() :
img1_path = './rock.jpg'
img1 = PIL.Image.open(img1_path, 'r')
img1_numpy = np.array(img1)
histogramEqualization(img1_numpy, 'rock_result1.jpg')
show_histogram(img1_numpy)
img1res_path = 'rock_result1.jpg'
img1res = PIL.Image.open(img1res_path, 'r')
img1res_numpy = np.array(img1res)
show_histogram(img1res_numpy)
def callAHE() :
img1_path = './rock.jpg'
img1 = PIL.Image.open(img1_path, 'r')
img1_numpy = np.array(img1)
AHE(img1_numpy, W=48, S=16, save_pth='rock_result2.jpg')
show_histogram(img1_numpy)
img1res_path = 'rock_result2.jpg'
img1res = PIL.Image.open(img1res_path, 'r')
img1res_numpy = np.array(img1res)
show_histogram(img1res_numpy)
def callCLAHE() :
img1_path = './rock.jpg'
img1 = PIL.Image.open(img1_path, 'r')
img1_numpy = np.array(img1)
CLAHE(img1_numpy, W=40, T = 10, save_pth='rock_result3.jpg')
# CLAHE(img1_numpy, W=40, A=0, T=10, save_pth='astro_result3.jpg')
show_histogram(img1_numpy)
img1res_path = 'rock_result3.jpg'
img1res = PIL.Image.open(img1res_path, 'r')
img1res_numpy = np.array(img1res)
show_histogram(img1res_numpy)
def getResult() :
img1Pth = './astronaut.jpg'
img1 = PIL.Image.open(img1Pth, 'r')
img1_numpy = np.array(img1)
img1_numpy_he = histogramEqualization(img1_numpy)
img1_numpy_ahe = AHE(img1_numpy, W=64, S=20)
img1_numpy_clahe = CLAHE(img1_numpy, W=40, T = 10)
fg = plot.figure()
# plot.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0)
ax1 = plot.subplot(221)
ax1.set_title('origin')
ax1.axis('off')
ax1.imshow(img1_numpy)
ax2 = plot.subplot(222)
ax2.set_title(1)
ax2.axis('off')
ax2.imshow(img1_numpy_he)
ax3 = plot.subplot(223)
ax3.set_title(2)
ax3.axis('off')
ax3.imshow(img1_numpy_ahe)
ax4 = plot.subplot(224)
ax4.set_title(3)
ax4.axis('off')
ax4.imshow(img1_numpy_clahe)
plot.tight_layout()
plot.savefig('./result_1.jpg')
plot.show()
img2Pth = './rock.jpg'
img2 = PIL.Image.open(img2Pth, 'r')
img2_numpy = np.array(img2)
img2_numpy_he = histogramEqualization(img2_numpy)
img2_numpy_ahe = AHE(img2_numpy, W=64, S=20)
img2_numpy_clahe = CLAHE(img2_numpy, W=40, T = 10)
plot.figure()
ax1 = plot.subplot(221)
ax1.set_title('origin')
ax1.axis('off')
ax1.imshow(img2_numpy)
ax2 = plot.subplot(222)
ax2.set_title(1)
ax2.axis('off')
ax2.imshow(img2_numpy_he)
ax3 = plot.subplot(223)
ax3.set_title(2)
ax3.axis('off')
ax3.imshow(img2_numpy_ahe)
ax4 = plot.subplot(224)
ax4.set_title(3)
ax4.axis('off')
ax4.imshow(img2_numpy_clahe)
plot.tight_layout()
plot.savefig('./result_2.jpg')
plot.show()
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# callhistogramEqualization()
# callAHE()
# callCLAHE()
# img1res_path = 'astor_official_result2.jpg'
# img1res = PIL.Image.open(img1res_path, 'r')
# img1res_numpy = np.array(img1res)
# show_histogram(img1res_numpy)
getResult()



















