目录
- 认识搜索引擎
- 搜索的核心思路
- 倒排索引介绍
- 项目简介
- 模块管理
- 构建索引模块
- 数据库设计
- 正排索引
- 倒排索引
- 程序入口类Indexer类
- 扫描文档子模块
- FileScanner类
- 构建文档子模块
- 构建标题
- parseTitle方法
- 构建url
- parseUrl方法
- 构建内容
- parseContent方法
- 构建正排索引子模块
- 正排索引实体类
- mapper接口
- xml
- AppConfig类
- 构建索引方法(两种)
- saveForwardIndexes方法(构建正排索引,单线程版本)
- saveForwardIndexesConcurrentf方法(构建 + 保存正排索引 多线程版本)
- 构建倒排索引子模块
- 引入Ansj分词库
- 倒排索引实体类
- mapper接口
- xml文件
- 构建索引方法(两种)
- saveInvertedIndexes方法(构建倒排索引,单线程版本)
- saveForwardIndexesConcurrent方法(构建倒排索引,多线程版本)
- 统计正派倒排索引的构建时间
- 搜索模块
- 查询关键字文章子模块
- 查询语句
- 获取拆分关键字子模块
- 关键字建立综合权重子模块
- 前端展示子模块
- 对搜索出的内容中关键字高亮展示
- 项目开发重难点
- 索引构建模块
- 倒排索引与正排索引构建
- 正则表达式
- 批量插入 + 多线程
- 搜索模块
- 联表查询优化
- 多词查询时的权重聚合
- 项目总结
认识搜索引擎
像百度搜索这样,输入要搜索的内容,点击搜索,就会出现若干条结果,每条结果包含标题,内容描述,展示url,图片,图标等相关的内容。如下图输入"恰似故人归"点击百度一下,就会出现如下的页面。

搜索引擎的本质就是输入一个查询词,得到若干个搜索结果,其中包含了标题,描述,展示url和点击url。
搜索的核心思路
我们把每一个网页称为一个文档,每一次的搜索就是在所有文档中查找查询词,检查文档中是否包含要查询的词或字符串。但是细想这种方法直接暴力且开销巨大,随着文档的增多,搜索的时间也随之延长,而搜索引擎往往对效率要求非常高,试想如果你的每一次搜索都需要1分钟时间才会有相应的搜素结果你还会用这个搜索引擎吗?
因此我们想到倒排索引,这是一种专门针对搜素引擎场景而设计的数据结构。
倒排索引介绍
文档:被检索的html页面
正排索引:一个文档中包含了那些词,描述一个文档的基本信息,将文档中的词进行分词处理并存储。
倒排索引:一个词被那些文档所引用,描述一个词的基本信息,存储了这个词都存在在那些文档中,这个词在文档中的重要程度。
项目简介
如今,大大小小的网站以及软件都可能会涉及到搜索这一功能,因此,计划写出一个基于web的搜索相关文档的搜索引擎项目。以锻炼自己的能力,加强对技术的应用,能够更好的掌握相关的技术,了解互联网的发展。众所周知,搜索本身看起来貌似很简单,很多方法其实都可以做出来,比如简简单单的sql语句的模糊匹配也就可以实现这一功能,为什么非要做一个项目来实现搜索引擎呢?最主要的原因还是相关的性能问题,试想一下,若在平时生活中搜索一个词的时间长达几分钟甚至更长,这是人们所接受不了的,因此,设计一个搜索引擎就显现的非常的重要,能够加快搜索的性能,能够实现很快出结果,在性能上能够进行日常的应用
下面我们对Java API文档实现一个搜索引擎。
首先我们需要在官方页面下载Java API文档到本地,此处附上下载地址:java api文档下载地址
模块管理
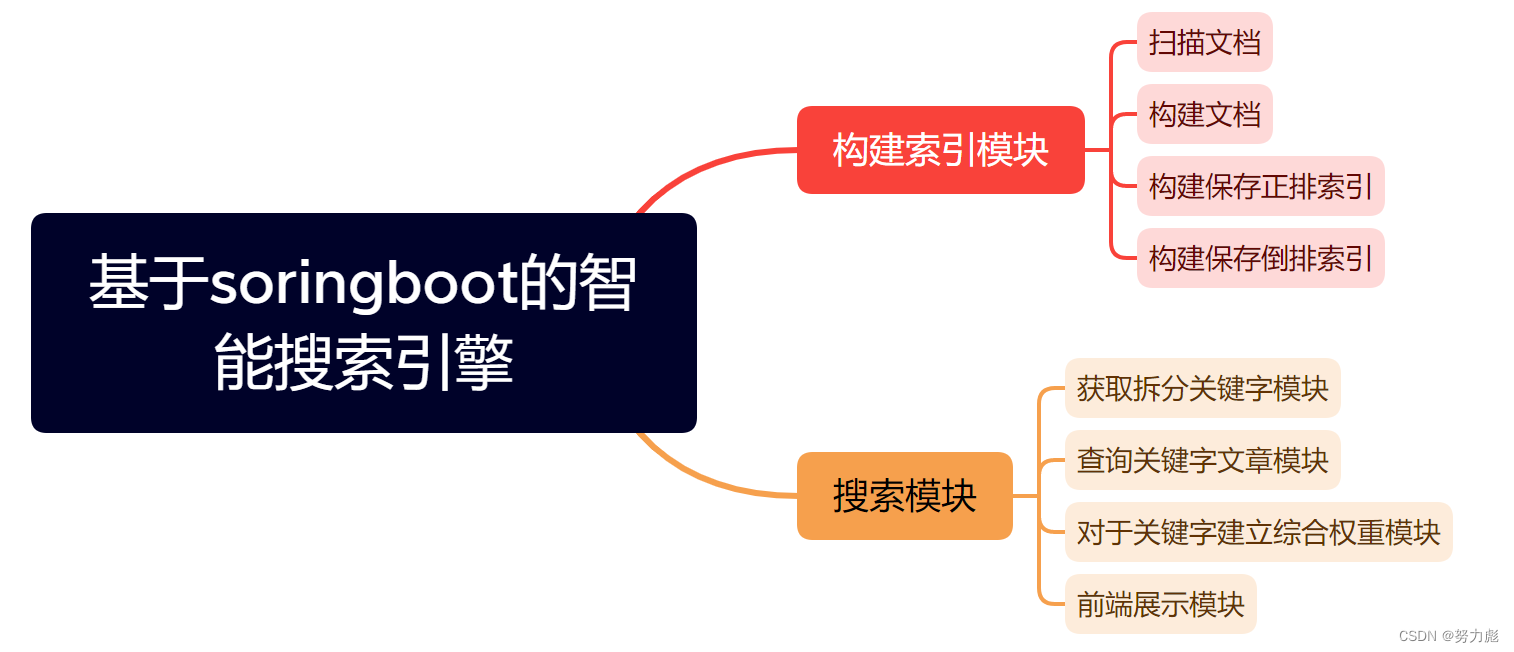
构建索引模块
数据库设计
该设计的数据库主要作用是进行正排索引和倒排索引的保存。
建立searcher_refactor数据库
CREATE SCHEMA `searcher_refactor` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 ;
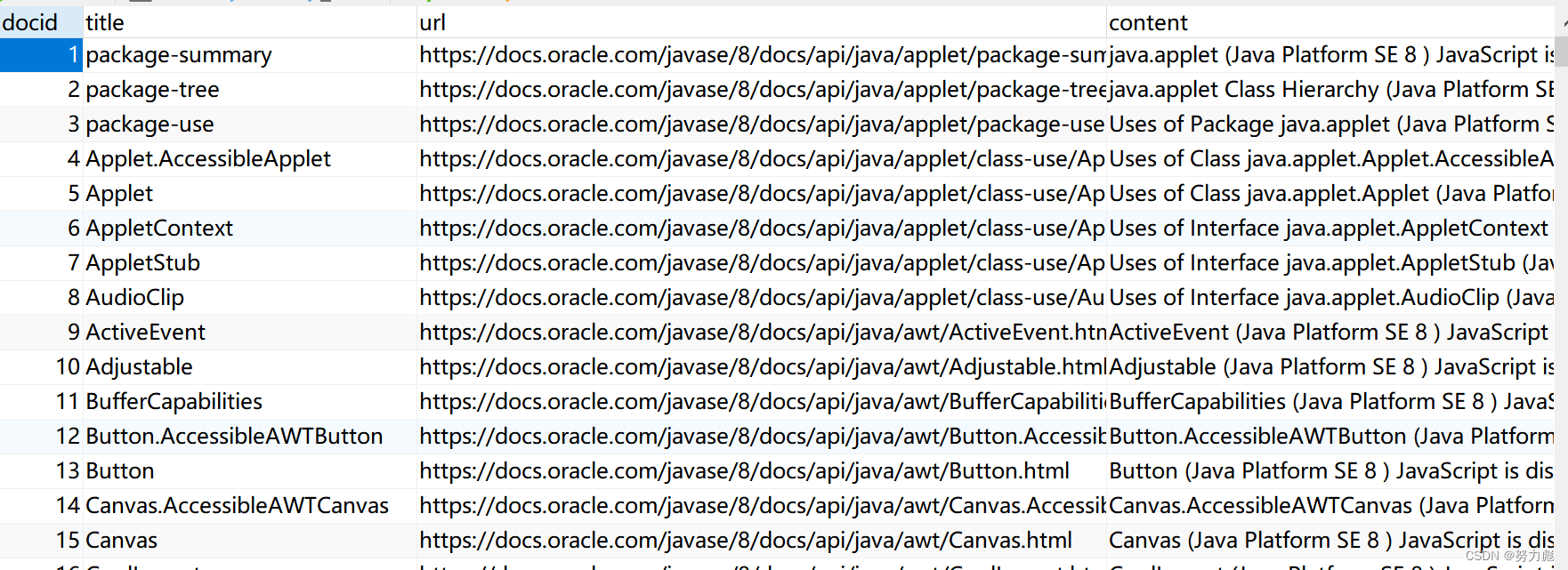
正排索引
正排索引的字段主要有:
docId --文章的id
title --文章的标题
url --文章对应的url
content --文章的正文
表的结构如图所示。
建表语句如下:
CREATE TABLE `searcher_refactor`.`forward_indexes` (
`docid` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`url` VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
`content` LONGTEXT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`docid`))
COMMENT = '存放正排索引\ndocid -> 文档的完整信息';
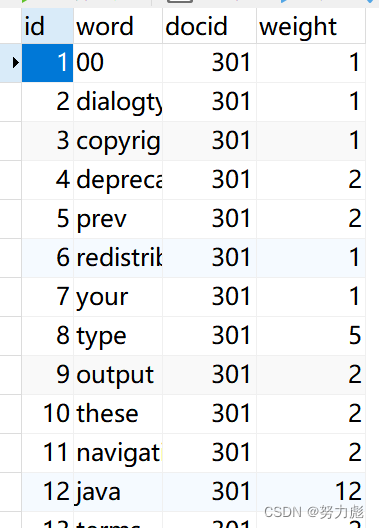
倒排索引
id --对应单词的id
word --对应的单词
docid --对应的文章id
weight --该单词在该文章对应的权重
表的结构如下图所示。
建表语句如下:
CREATE TABLE `searcher_refactor`.`inverted_indexes` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`word` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`docid` INT NOT NULL,
`weight` INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`))
COMMENT = '倒排索引\n通过 word -> [ { docid + weight }, { docid + weight }, ... ]';
程序入口类Indexer类
存储构建索引模块代码的整体逻辑:
-
扫描出来所有的 html 文件,并把他们放到一个list集合里面
-
针对每个 html 文件,得到其 标题、URL、正文信息,把这些信息封装成一个对象(文档 Document)
-
进行正排索引的保存
-
进行倒排索引的生成保存
-
关闭线程池
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.command;
import com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.core.IndexManager;
import com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.model.Document;
import com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.util.FileScanner;
import com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.properties.IndexerProperties;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.ansj.splitWord.analysis.ToAnalysis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 构建索引的模块,是整个程序的逻辑入口
*/
@Slf4j // 添加 Spring 日志的使用
@Component // 注册成 Spring 的 bean
//@Profile("run") // 让跑测试的时候不加载这个 bean(run != test)
public class Indexer implements CommandLineRunner {
// 需要依赖 FileScanner 对象
private final FileScanner fileScanner;
private final IndexerProperties properties;
private final IndexManager indexManager;
private final ExecutorService executorService;
@Autowired // 构造方法注入的方式,让 Spring 容器,注入 FileScanner 对象进来 —— DI
public Indexer(FileScanner fileScanner, IndexerProperties properties, IndexManager indexManager, ExecutorService executorService) {
this.fileScanner = fileScanner;
this.properties = properties;
this.indexManager = indexManager;
this.executorService = executorService;
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
ToAnalysis.parse("随便分个什么,进行预热,避免优化的时候计算第一次特别慢的时间");
log.info("这里的整个程序的逻辑入口");
// 1. 扫描出来所有的 html 文件,并把他们放到一个list集合里面
log.debug("开始扫描目录,找出所有的 html 文件。{}", properties.getDocRootPath());
List<File> htmlFileList = fileScanner.scanFile(properties.getDocRootPath(), file -> {
//定义我们索要搜寻的文件名的后缀为.html
return file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".html");
});
log.debug("扫描目录结束,一共得到 {} 个文件。", htmlFileList.size());
// 2. 针对每个 html 文件,得到其 标题、URL、正文信息,把这些信息封装成一个对象(文档 Document)
File rootFile = new File(properties.getDocRootPath());
List<Document> documentList = htmlFileList.stream()
.parallel() // 【注意】由于我们使用了 Stream 用法,所以,可以通过添加 .parallel(),使得整个操作变成并行,利用多核增加运行速度
.map(file -> new Document(file, properties.getUrlPrefix(), rootFile))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
log.debug("构建文档完毕,一共 {} 篇文档", documentList.size());
// 3. 进行正排索引的保存
indexManager.saveForwardIndexesConcurrent(documentList);
log.debug("正排索引保存成功。");
// 4. 进行倒排索引的生成保存
indexManager.saveInvertedIndexesConcurrent(documentList);
log.debug("倒排索引保存成功。");
// 5. 关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
扫描文档子模块
FileScanner类
- 以 rootPath 作为根目录,开始进行文件的扫描,把所有符合条件的 File 对象,作为结果,以 List 形式返回
- rootPath 根目录的路径,调用者需要确保这个目录存在 && 一定是一个目录
- filter 通过针对每个文件调用 filter.accept(file) 就知道,文件是否满足条件
- 返回满足条件的所有文件
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.util;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j // 添加日志
@Service // 注册成 Spring bean
public class FileScanner {
/**
* 以 rootPath 作为根目录,开始进行文件的扫描,把所有符合条件的 File 对象,作为结果,以 List 形式返回
* @param rootPath 根目录的路径,调用者需要确保这个目录存在 && 一定是一个目录
* @param filter 通过针对每个文件调用 filter.accept(file) 就知道,文件是否满足条件
* @return 满足条件的所有文件
*/
public List<File> scanFile(String rootPath, FileFilter filter) {
List<File> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
File rootFile = new File(rootPath);
// 针对目录树进行遍历,深度优先 or 广度优先即可,确保每个文件都没遍历到即可
// 我们这里采用深度优先遍历,使用递归完成
traversal(rootFile, filter, resultList);
return resultList;
}
private void traversal(File directoryFile, FileFilter filter, List<File> resultList) {
// 1. 先通过目录,得到该目录下的孩子文件有哪些
File[] files = directoryFile.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
// 说明有问题,我们不管(一般是权限等的问题),通常咱们遇不到这个错误
return;
}
// 2. 遍历每个文件,检查是否符合条件
for (File file : files) {
// 通过 filter.accept(file) 的返回值,判断是否符合条件
if (filter.accept(file)) {
// 说明符合条件,需要把该文件加入到结果 List 中
resultList.add(file);
}
}
// 3. 遍历每个文件,针对是目录的情况,继续深度优先遍历(递归)
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
traversal(file, filter, resultList);
}
}
}
}
构建文档子模块
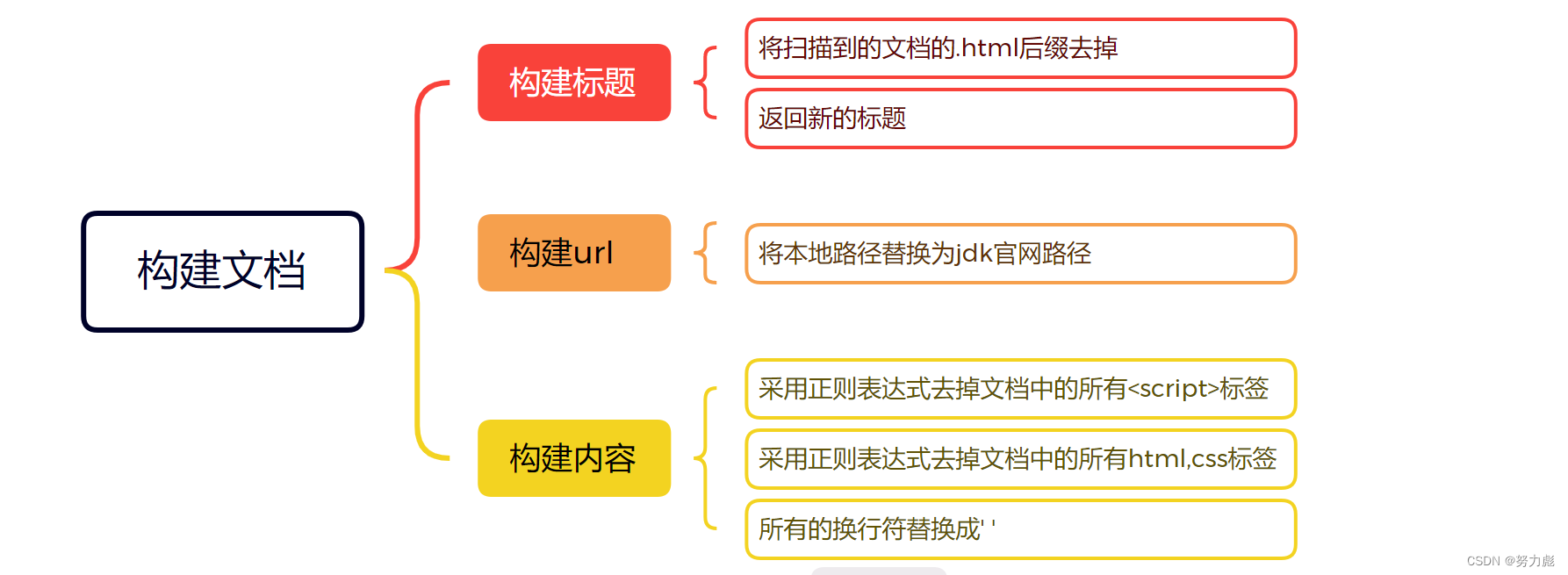
构建标题
parseTitle方法
private String parseTitle(File file) {
// 从文件名中,将 .html 后缀去掉,剩余的看作标题
String name = file.getName();
String suffix = ".html";
return name.substring(0, name.length() - suffix.length());
}
构建url
parseUrl方法
@SneakyThrows
private String parseUrl(File file, String urlPrefix, File rootFile) {
// 需要得到一个相对路径,file 相对于 rootFile 的相对路径
// 比如:rootFile 是 D:\课程\2022-08-02-Java19-22班-项目-2\docs\api
// file 是 D:\课程\2022-08-02-Java19-22班-项目-2\docs\api\javax\sql\DataSource.html
// 则相对路径就是:javax\sql\DataSource.html
// 把所有反斜杠(\) 变成正斜杠(/)
// 最终得到 java/sql/DataSource.html
String rootPath = rootFile.getCanonicalPath();
//如果本地目录中存在/,就把他变为\
rootPath = rootPath.replace("/", "\\");
if (!rootPath.endsWith("\\")) {
rootPath = rootPath + "\\";
}
String filePath = file.getCanonicalPath();
String relativePath = filePath.substring(rootPath.length());
relativePath = relativePath.replace("\\", "/");
return urlPrefix + relativePath;
}
构建内容
parseContent方法
@SneakyThrows
private String parseContent(File file) {
StringBuilder contentBuilder = new StringBuilder();
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file)) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "ISO-8859-1")) {
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
contentBuilder.append(line).append(" ");
}
return contentBuilder.toString()
.replaceAll("<script.*?>.*?</script>", " ")
.replaceAll("<.*?>", " ")
.replaceAll("\\s+", " ")
.trim();
}
}
}
构建正排索引子模块
构建正排索引的过程其实就是向数据库中插入正排索引的过程
正排索引实体类
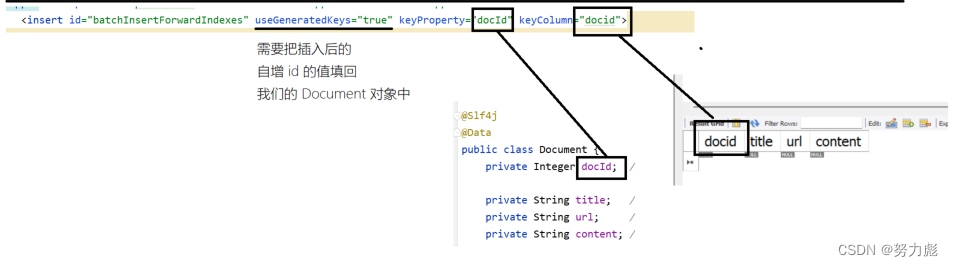
public class Document {
private Integer docId; // docId 会在正排索引插入后才会赋值
private String title; // 从文件名中解析出来
// 注意这里的url是两个信息(1. 官网的https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/ 2. 相对路径的相对位置)
private String url;
private String content; // 从文件中读取出来,并且做一定的处理
// 专门给测试用例用的构造方法
public Document(String title, String url, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.url = url;
this.content = content;
}
public Document(File file, String urlPrefix, File rootFile) {
this.title = parseTitle(file);
this.url = parseUrl(file, urlPrefix, rootFile);
this.content = parseContent(file);
}
mapper接口
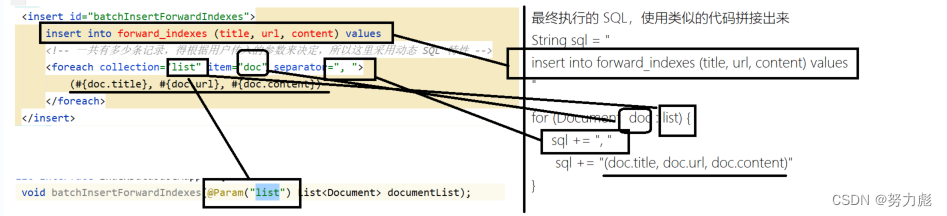
void batchInsertForwardIndexes(@Param("list") List<Document> documentList);
xml
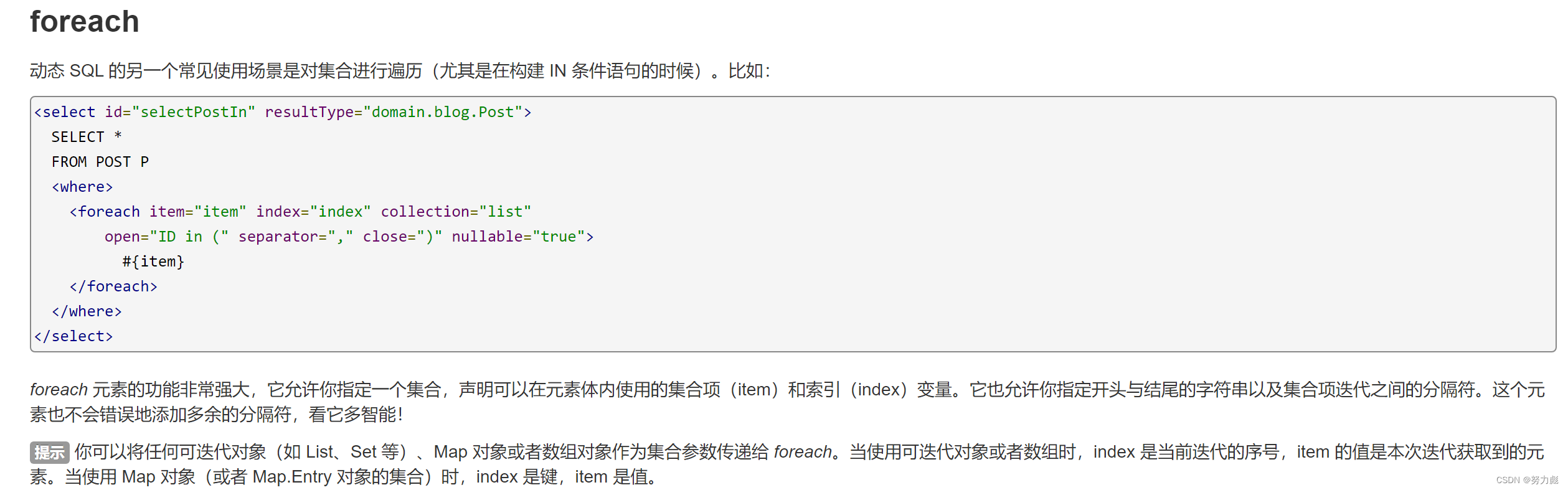
<insert id="batchInsertForwardIndexes" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="docId" keyColumn="docid">
insert into forward_indexes (title, url, content) values
<!-- 一共有多少条记录,得根据用户传入的参数来决定,所以这里采用动态 SQL 特性 -->
<foreach collection="list" item="doc" separator=", ">
(#{doc.title}, #{doc.url}, #{doc.content})
</foreach>
</insert>
注意这里我们使用了动态sql的特性,为了提高构建正排索引的效率,我们在插入正排索引的时候使用了批量插入(待会我们会在构建正排索引中介绍)的方式,那么在mybatis实现的过程中,我们就需要使用动态sql中对集合的遍历
application.yml配置文件:
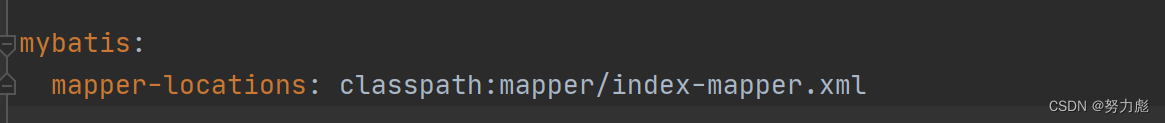
在Spring的配置文件中,指定mybatis查找mapper xml文件的路径
classpath:就代表从src/main/resources下进行查找【这个实际上是错误的理解,但现在这么理解关系不大】完整路径: src/main/resources/mapper/index-mapper.xml
AppConfig类
这个类是给后序创建索引中的多线程版本提供服务的
这个类负责创建一个线程池,把线程池交给bean去管理,
为什么要把线程池交给bean去管理呢?
每次使用appconfig去配置这个线程池的代码的时候就还是相当于是一个
单例模式,其实我可以将创建线程池的方法放到idexManager类当中去,但是每次都要new实例,如果放到一个配置类里交给spring去管理就意味着每次我只需要在需要的地方注入我这个bean对象即可,相当于我ThreadPoolExecutor这个类从始至终都只new了一个实例,这就是单例模式,也就是说只要被spring管理的,没有经过特殊处理的,都是单例模式
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public ExecutorService executorService() {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
8, 20, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable task) {
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
thread.setName("批量插入线程");
return thread;
}
},
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
return executor;
}
}
构建索引方法(两种)
saveForwardIndexes方法(构建正排索引,单线程版本)
// 先批量生成、保存正排索引(单线程版本)
public void saveForwardIndexes(List<Document> documentList) {
// 1. 批量插入时,每次插入多少条记录(由于每条记录比较大,所以这里使用 10 条就够了)
int batchSize = 10;
// 2. 一共需要执行多少次 SQL? 向上取整(documentList.size() / batchSize)
int listSize = documentList.size();
int times = (int) Math.ceil(1.0 * listSize / batchSize); // ceil(天花板): 向上取整
log.debug("一共需要 {} 批任务。", times);
// 3. 开始分批次插入
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += batchSize) {
// 从 documentList 中截取这批要插入的 文档列表(使用 List.subList(int from, int to)
int from = i;
int to = Integer.min(from + batchSize, listSize);
List<Document> subList = documentList.subList(from, to);
// 针对这个 subList 做批量插入
mapper.batchInsertForwardIndexes(subList);
}
}

下面我们可以对上述的单线程的插入方法进行一个改动,加入多线程
saveForwardIndexesConcurrentf方法(构建 + 保存正排索引 多线程版本)

@Timing("构建 + 保存正排索引 —— 多线程版本")
@SneakyThrows
public void saveForwardIndexesConcurrent(List<Document> documentList) {
// 1. 批量插入时,每次插入多少条记录(由于每条记录比较大,所以这里使用 10 条就够了)
int batchSize = 10;
// 2. 一共需要执行多少次 SQL? 向上取整(documentList.size() / batchSize)
int listSize = documentList.size();
int times = (int) Math.ceil(1.0 * listSize / batchSize); // ceil(天花板): 向上取整
log.debug("一共需要 {} 批任务。", times);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(times); // 统计每个线程的完全情况,初始值是 times(一共多少批)
// 3. 开始分批次插入
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += batchSize) {
// 从 documentList 中截取这批要插入的 文档列表(使用 List.subList(int from, int to)
int from = i;
int to = Integer.min(from + batchSize, listSize);
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() { // 内部类 / lambda 表达式里如果用到了外部变量,外部变量必须的 final(或者隐式 final 的变量)
List<Document> subList = documentList.subList(from, to);
// 针对这个 subList 做批量插入
mapper.batchInsertForwardIndexes(subList);
latch.countDown(); // 每次任务完成之后,countDown(),让 latch 的个数减一
}
};
executorService.submit(task); // 主线程只负责把一批批的任务提交到线程池,具体的插入工作,由线程池中的线程完成
}
// 4. 循环结束,只意味着主线程把任务提交完成了,但任务有没有做完是不知道的
// 主线程等在 latch 上,直到 latch 的个数变成 0,也就是所有任务都已经执行完了
latch.await();
}
构建倒排索引子模块
引入Ansj分词库
我们在将单词存入倒排索引表中的时候,其实是将正排索引表中存储的标题还有内容进行分词,统计权重后才存入表中的,而分词的操作中,我们需要引入分词库ansj
<!-- Java 版本的一个分词库,本身是支持中文分词的,只是咱的文档中没有中文。但英文分词它也支持 -->
<!-- https://github.com/NLPchina/ansj_seg -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ansj</groupId>
<artifactId>ansj_seg</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
倒排索引实体类
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.model;
import lombok.Data;
// 这个对象映射 inverted_indexes 表中的一条记录(我们不关心表中的 id,就不写 id 了)
@Data
public class InvertedRecord {
private String word;
private int docId;
private int weight;
public InvertedRecord(String word, int docId, int weight) {
this.word = word;
this.docId = docId;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
mapper接口
void batchInsertInvertedIndexes(@Param("list") List<InvertedRecord> recordList);
xml文件
<!-- 不关心自增 id -->
<insert id="batchInsertInvertedIndexes">
insert into inverted_indexes (word, docid, weight) values
<foreach collection="list" item="record" separator=", ">
(#{record.word}, #{record.docId}, #{record.weight})
</foreach>
</insert>
构建索引方法(两种)
saveInvertedIndexes方法(构建倒排索引,单线程版本)
首先在Document类中构建我们文档的分词以及计算权重方法:
private final static HashSet<String> ignoredWordSet = new HashSet<>();
static {
ignoredWordSet.add(" ");
ignoredWordSet.add("\t");
ignoredWordSet.add("。");
ignoredWordSet.add(".");
ignoredWordSet.add(",");
ignoredWordSet.add("(");
ignoredWordSet.add(")");
ignoredWordSet.add("/");
ignoredWordSet.add("-");
ignoredWordSet.add(";");
}
// 针对文档进行分词,并且分别计算每个词的权重
public Map<String, Integer> segWordAndCalcWeight() {
// 统计标题中的每个词出现次数 | 分词:标题有哪些词
List<String> wordInTitle = ToAnalysis.parse(title)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(Term::getName)
.filter(s -> !ignoredWordSet.contains(s))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 统计标题中,每个词的出现次数 | 统计次数
Map<String, Integer> titleWordCount = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : wordInTitle) {
int count = titleWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
titleWordCount.put(word, count + 1);
}
// 统计内容中的词,以及词的出现次数
List<String> wordInContent = ToAnalysis.parse(content)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(Term::getName)
.filter(s -> !ignoredWordSet.contains(s))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<String, Integer> contentWordCount = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : wordInContent) {
int count = contentWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
contentWordCount.put(word, count + 1);
}
// 计算权重值
Map<String, Integer> wordToWeight = new HashMap<>();
// 先计算出有哪些词,不重复
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordInTitle);
wordSet.addAll(wordInContent);
for (String word : wordSet) {
int titleCount = titleWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
int contentCount = contentWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
int weight = titleCount * 10 + contentCount;
wordToWeight.put(word, weight);
}
return wordToWeight;
}
然后写saveInvertedIndexes方法:
//保存倒排索引,单线程版本
@SneakyThrows
public void saveInvertedIndexes(List<Document> documentList) {
int batchSize = 10000; /* 批量插入时,最多 10000 条 */
List<InvertedRecord> recordList = new ArrayList<>(); // 放这批要插入的数据
for (Document document : documentList) {
Map<String, Integer> wordToWeight = document.segWordAndCalcWeight();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wordToWeight.entrySet()) {
String word = entry.getKey();
//这个docid是我们构建正排索引的时候数据库的自增id
int docId = document.getDocId();
int weight = entry.getValue();
InvertedRecord record = new InvertedRecord(word, docId, weight);
recordList.add(record);
// 如果 recordList.size() == batchSize,说明够一次插入了
if (recordList.size() == batchSize) {
// 每次批量插入1000条数据
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList);
// 批量插入后清空 list,视为让 recordList.size() = 0
recordList.clear();
}
}
}
// recordList 还剩一些,之前放进来,但还不够 batchSize 个的,所以最后再批量插入一次
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList); // 批量插入
recordList.clear();
}
saveForwardIndexesConcurrent方法(构建倒排索引,多线程版本)
static class InvertedInsertTask implements Runnable {
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private final int batchSize;
private final List<Document> documentList;
private final IndexDatabaseMapper mapper;
InvertedInsertTask(CountDownLatch latch, int batchSize, List<Document> documentList, IndexDatabaseMapper mapper) {
this.latch = latch;
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.documentList = documentList;
this.mapper = mapper;
}
@Override
public void run() {
List<InvertedRecord> recordList = new ArrayList<>(); // 放这批要插入的数据
for (Document document : documentList) {
Map<String, Integer> wordToWeight = document.segWordAndCalcWeight();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wordToWeight.entrySet()) {
String word = entry.getKey();
//这个id是前面插入正排索引的时候赋给Document实体类的id
int docId = document.getDocId();
int weight = entry.getValue();
InvertedRecord record = new InvertedRecord(word, docId, weight);
recordList.add(record);
// 如果 recordList.size() == batchSize,说明够一次插入了
if (recordList.size() == batchSize) {
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList); // 批量插入
recordList.clear(); // 清空 list,视为让 list.size() = 0
}
}
}
// recordList 还剩一些,之前放进来,但还不够 batchSize 个的,所以最后再批量插入一次
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList); // 批量插入
recordList.clear();
latch.countDown();
}
}
@Timing("构建 + 保存倒排索引 —— 多线程版本")
@SneakyThrows
public void saveInvertedIndexesConcurrent(List<Document> documentList) {
int batchSize = 10000; // 批量插入时,最多 10000 条
//每个线程每次处理50篇文档
int groupSize = 50;
int listSize = documentList.size();
int times = (int) Math.ceil(listSize * 1.0 / groupSize);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(times);
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += groupSize) {
int from = i;
int to = Integer.min(from + groupSize, listSize);
//每次只截取50个
List<Document> subList = documentList.subList(from, to);
Runnable task = new InvertedInsertTask(latch, batchSize, subList, mapper);
executorService.submit(task);
}
latch.await();
}
统计正派倒排索引的构建时间
我们使用aop进行记时操作
定义接口
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.aop;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
// 用来统计时间的
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Timing {
String value();
}
定义切面类
package com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimingAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.peixinchen.searcher.indexer.aop.Timing)")
public void timingPointcut() {}
@Around("timingPointcut()")
public Object timing(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
Timing annotation = method.getAnnotation(Timing.class);
String value = annotation.value();
long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
double ms = e * 1.0 - b;
double s = ms / 1000;
log.info("{} 耗时 {} 秒。", value, s);
}
}
}
插入正排索引的时间1.005秒为:

插入倒排索引的时间为123.339秒:

搜索模块
查询关键字文章子模块
查询语句
上述我们所做的工作都是将文档进行分词后保存到我们数据库的过程,下面我们将实现搜索功能
我们先来看最基本的一个搜索逻辑:
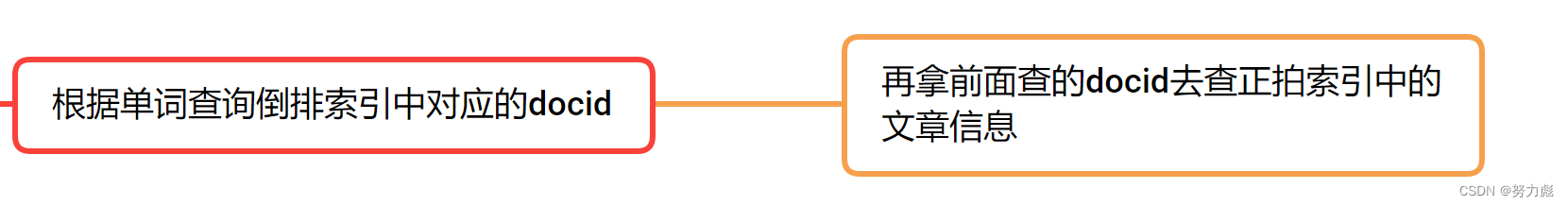
我们在前端输入一个词,然后根据词去倒排+正排索引中去搜索,然后就可以获得文档列表(并针对这个文档可以做分页)
假设此时我们搜索list这个词:使用单表查询:就需要写两条语句,而且还不能保证搜索出来的文档一定是按照权重降序排列的,如下:
select docid, weight from inverted_indexes where word = 'list' order by weight desc;
select * from forward_indexes where docid in (...);//无序
所以此时我门就需要使用联表查询进行处理来保证我们最终查询的结果是有序的:
这里的join代表的是内连接(inner join),也可以只写JOIN。只有进行连接的两个表中,都存在与连接标准相匹配的数据才会被保留下来,相当于两个表的交集。如果前后连接同一张表,也叫自连接。
select ii.docid, title, url, content from inverted_indexes ii join forward_indexes fi on ii.docid = fi.docid where word = 'list' order by weight desc; //有序
获取拆分关键字子模块
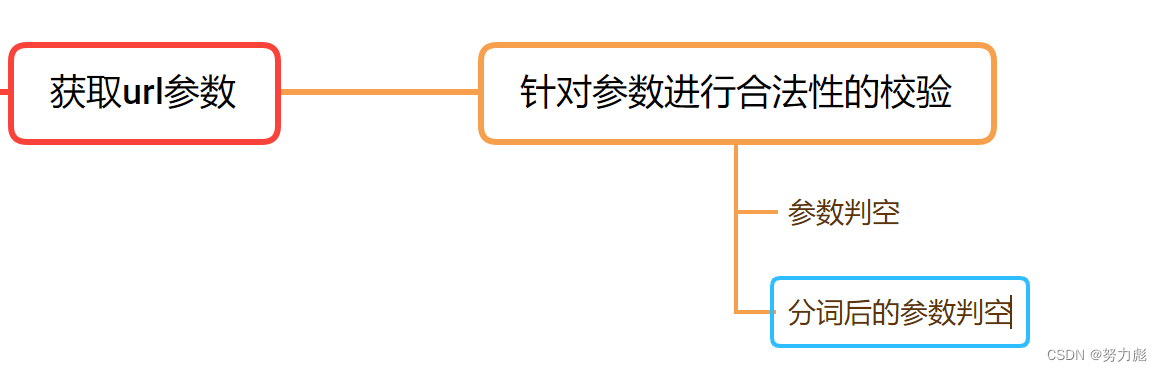
这里主要就是对前端输入的查询条件进行分词操作,同样会使用到Ansj分词库进行分词
核心代码如下:
// 参数的合法性检查 + 处理
if (query == null) {
log.debug("query 为 null,重定向到首页");
return "redirect:/";
}
query = query.trim().toLowerCase();
if (query.isEmpty()) {
log.debug("query 为空字符串,重定向到首页");
return "redirect:/";
}
// 分词
List<String> queryList = ToAnalysis.parse(query)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.map(Term::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (queryList.isEmpty()) {
log.debug("query 分词后一个词都没有,重定向到首页");
return "redirect:/";
}
关键字建立综合权重子模块
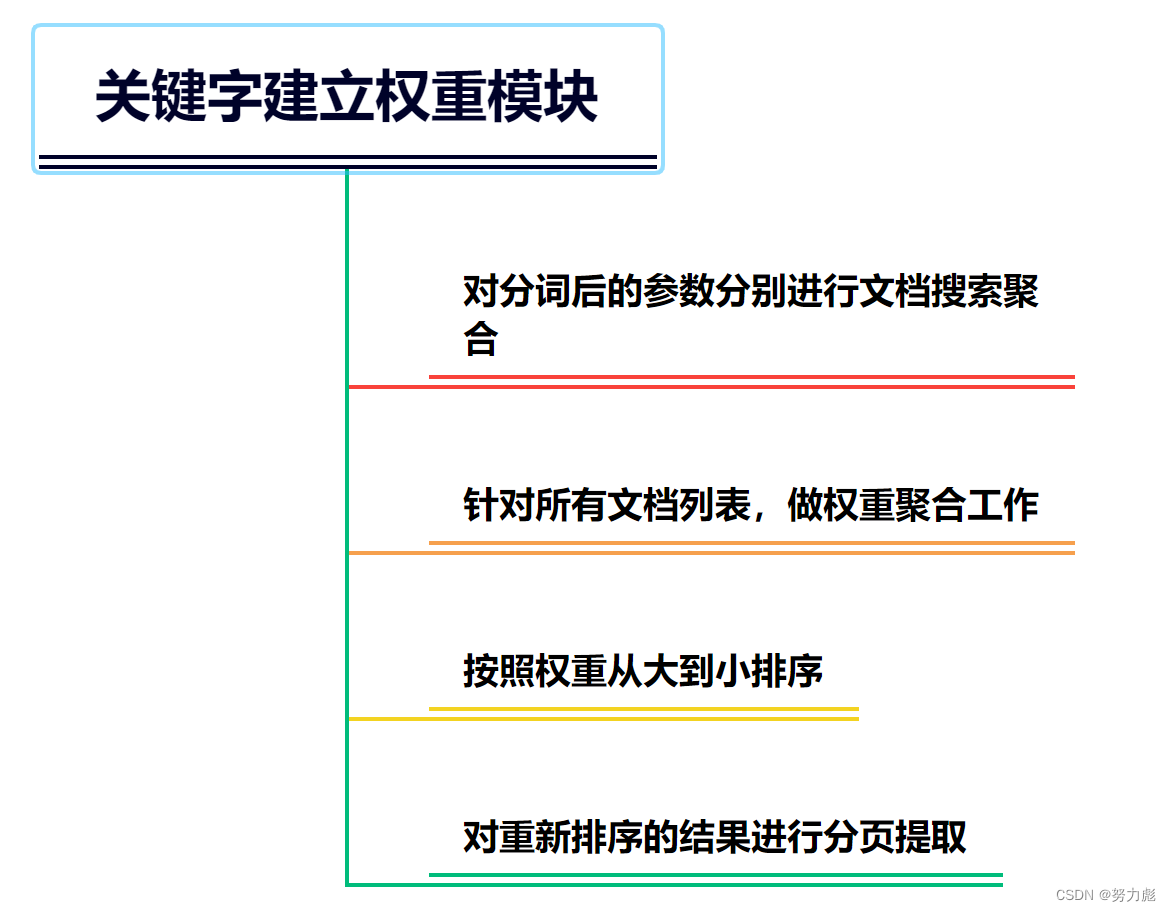
核心代码:
int limit = 20;
int offset = 0;
int page = 1;
if (pageString != null) {
pageString = pageString.trim();
try {
page = Integer.parseInt(pageString);
if (page <= 0) {
page = 1;
}
limit = page * 20;
} catch (NumberFormatException ignored) {}
}
log.debug("limit = {}, offset = {}, page = {}", limit, offset, page);
// 分别搜索 -> 聚合 -> 排序 -> 区间
List<DocumentWightWeight> totalList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : queryList) {
List<DocumentWightWeight> documentList = mapper.queryWithWeight(s, limit, offset);
totalList.addAll(documentList);
}
// 针对所有文档列表,做权重聚合工作
// 维护:
// docId -> document 的 map
Map<Integer, DocumentWightWeight> documentMap = new HashMap<>();
for (DocumentWightWeight documentWightWeight : totalList) {
int docId = documentWightWeight.getDocId();
if (documentMap.containsKey(docId)) {
DocumentWightWeight item = documentMap.get(docId);
item.weight += documentWightWeight.weight;
continue;
}
DocumentWightWeight item = new DocumentWightWeight(documentWightWeight);
documentMap.put(docId, item);
}
Collection<DocumentWightWeight> values = documentMap.values();
// Collection 没有排序这个概念(只有线性结构才有排序的概念),所以我们需要一个 List
List<DocumentWightWeight> list = new ArrayList<>(values);
// 按照 weight 的从大到小排序了
Collections.sort(list, (item1, item2) -> {
return item2.weight - item1.weight;
});
int from = (page - 1) * 20;
int to = Integer.min(from + 20, list.size());
// 从 list 中把分页区间取出来
List<DocumentWightWeight> subList = list.subList(from, to);
List<Document> documentList = subList.stream()
.map(DocumentWightWeight::toDocument)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
前端展示子模块
前端采用相关的thymeleaf模版技术来进行的渲染操作。
model.addAttribute("query", query);
model.addAttribute("docList", documentList);
model.addAttribute("page", page);
return "search";
因为使用到了thymeleaf模板,所以我们要在templates目录下撰写我们的搜索页面searth.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-hans" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title th:text="${query} + ' - 智能搜索'"></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/query.css">
</head>
<body>
<!-- th:xxx 是 thymeleaf 的语法 -->
<!-- <div th:text="'你好 ' + ${name} + ' 世界'"></div>-->
<div class="header">
<div class="brand"><a href="/">智能搜索</a></div>
<form class="input-shell" method="get" action="/web">
<input type="text" name="query" th:value="${query}">
<button>智能搜索</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="result">
<!-- th:utext 和 th:text 的区别:要不要进行 HTML 转义 -->
<!-- <div th:text="'<span>你好 th:text</span>'"></div>-->
<!-- <div th:utext="'<span>你好 th:utext</span>'"></div>-->
<div class="result-item" th:each="doc : ${docList}">
<a th:href="${doc.url}" th:text="${doc.title}"></a>
<div class="desc" th:utext="${doc.desc}"></div>
<div class="url" th:text="${doc.url}"></div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 一直上一页可能走到 page <= 0 的情况 -->
<!-- 一直下一页可能走到 page > 上限的情况 -->
<div class="pagination">
<a th:href="'/web?query=' + ${query} + '&page=' + ${page - 1}">上一页</a>
<a th:href="'/web?query=' + ${query} + '&page=' + ${page + 1}">下一页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
对搜索出的内容中关键字高亮展示
这里的高亮展示只针对我们query参数分词后的第一个词,当然后期的高亮展示也可根据业务需求进行调整
package com.peixinchen.searcher.web;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DescBuilder {
public Document build(List<String> queryList, Document doc) {
// 找到 content 中包含关键字的位置
// query = "list"
// content = "..... hello list go come do ...."
// desc = "hello <i>list</i> go com..."
String content = doc.getContent().toLowerCase();
String word = "";
int i = -1;
for (String query : queryList) {
i = content.indexOf(query);
if (i != -1) {
word = query;
break;
}
}
if (i == -1) {
// 这里中情况如果出现了,说明咱的倒排索引建立的有问题
log.error("docId = {} 中不包含 {}", doc.getDocId(), queryList);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
// 前面截 120 个字,后边截 120 个字
int from = i - 120;
if (from < 0) {
// 说明前面不够 120 个字了
from = 0;
}
int to = i + 120;
if (to > content.length()) {
// 说明后面不够 120 个字了
to = content.length();
}
String desc = content.substring(from, to);
desc = desc.replace(word, "<i>" + word + "</i>");
doc.setDesc(desc);
return doc;
}
}
controller层的代码:
// lambda 中无法使用非 final 变量
List<String> wordList = queryList;
documentList = documentList.stream()
.map(doc -> descBuilder.build(wordList, doc))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
项目开发重难点
索引构建模块
倒排索引与正排索引构建
正则表达式
在正排索引构建的过程中,我们使用了正则表达式,这里当时也是查询了一下如何使用的

批量插入 + 多线程
如果一条一条的执行索引插入数据库的操作,其实是非常耗时的,也是非常低效的
所以我们将保存索引数据插入表的操作改成批量插入操作
那么什么是批量插入?

如果要实现批量插入的话:我们就要使用到mybatis中的动态sql的特性了:因为前面我们保存文档对象使用的是list集合,所以最终我们使用foreach来对list集合进行遍历
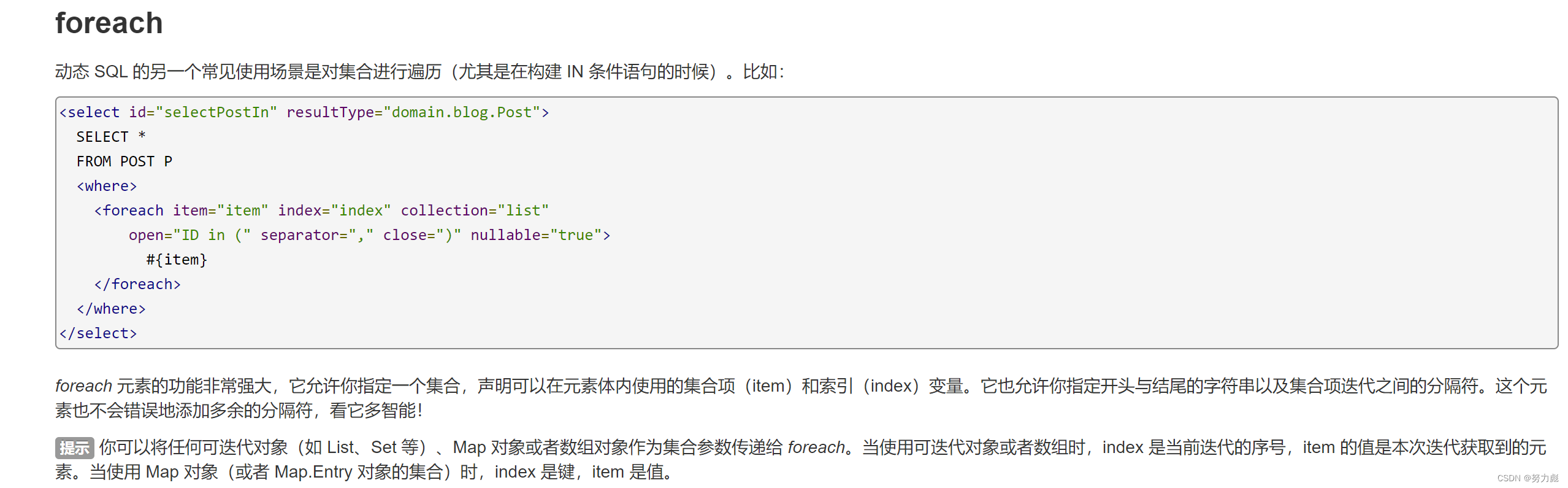
同时我们可以将批量插入的操纵并行化,所以引入了线程池,将我们的插批量插入操作并行化
搜索模块
联表查询优化
搜索模块的查询语句为:
select ii.docid, title, url, content from inverted_indexes ii join forward_indexes fi on ii.docid = fi.docid where word = 'list' order by weight desc; //有序
但是这条语句时有缺陷的:
例如我们搜索单条语句的时候:
select docid, weight from inverted_indexes where word = 'list' order by weight desc;
这样的一条查询语句所需要的时间为1.8秒左右,在之前我们了解到inverted_indexes中的数据大概有200多w条,可想而知最后的查询会非常慢
查询很慢,应该怎么办?
答:向表中新建索引(针对 word列去建索引)
建索引的过程,就是把 word 列作为key,docid 作为value,新建一棵搜索树(B+树)
从key查找value,则时间复杂度变成O(log(n)),如果是200w条只需要执行21次,远远小于O(n)的时间复杂度执行的次数,这个时间复杂度相当于要执行200w次
建索引的速度很慢,而且会导致数据插入很慢,所以,表中的数据已经插入完成的情况下,添加索引
(1)未使用索引:

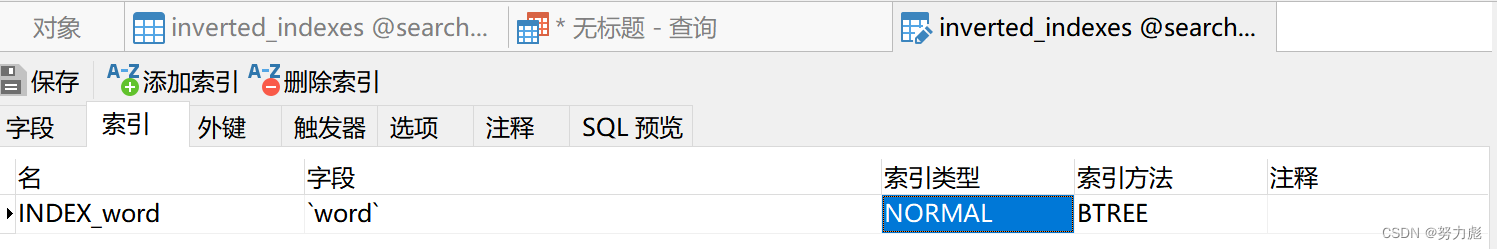
(2)给word字段添加一个普通查询索引,名字叫做INDEX_word
选中数据表,单击右键

找到索引
名字可以随便取
字段我选择的是word,类型我选的是NORMAL,方法用的是BTREE
执行以下sql语句:
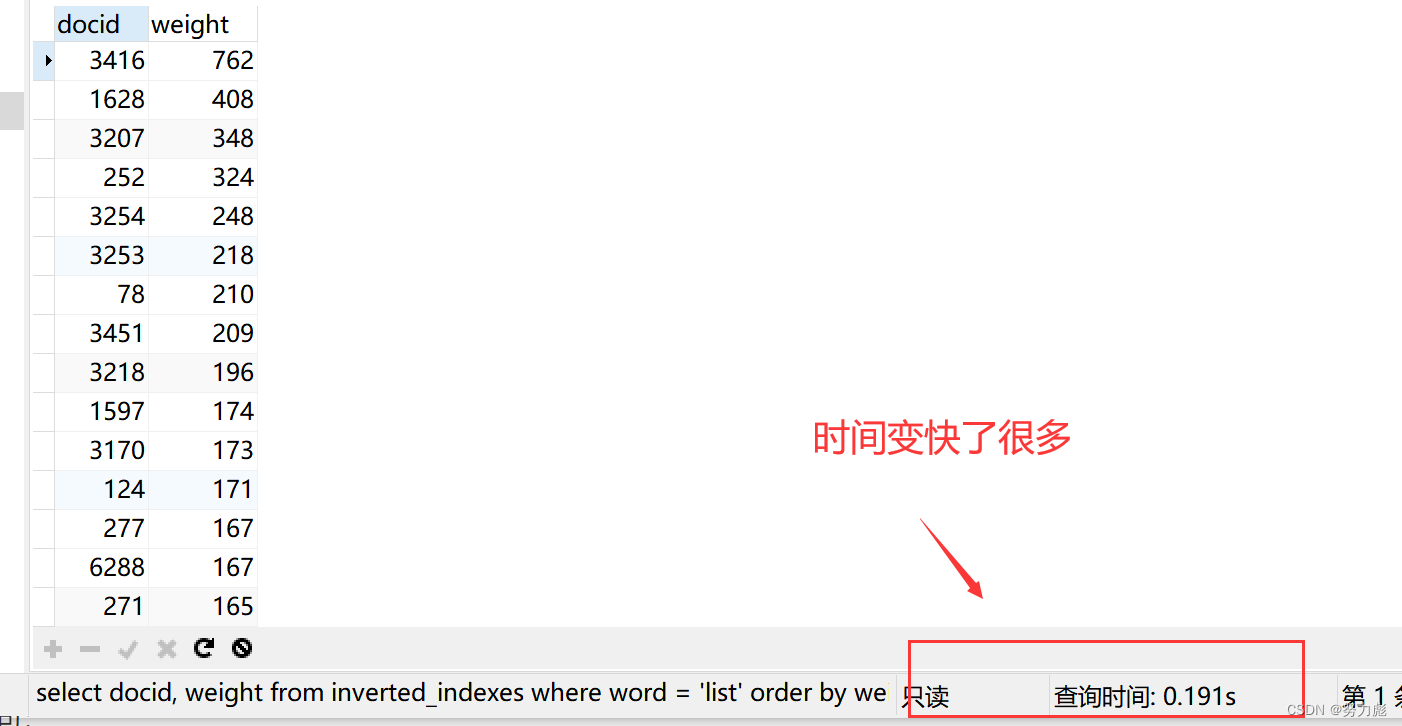
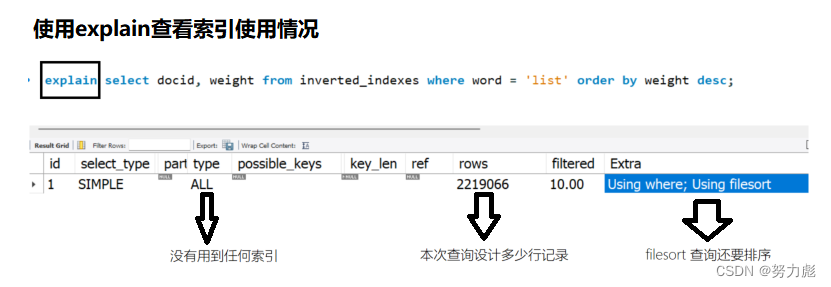
使用explain查看索引的建立情况:
explain select docid, weight from inverted_indexes where word = 'list' order by weight desc;
建立索引情况:
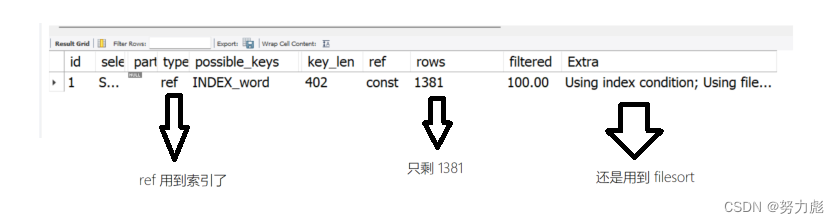
当然除了可以给word列建立索引的方式以外,我们还可以给word和weight按照先后顺序来建议索引,给word加索引是为了保证检索的时候提升检索速度,而我们给weight添加索引的时候是为了增加排序速度,因为索引本质上是搜索树,搜索数有序,所以它直接可以用索引排序了,所以速度就提升非常明显啊
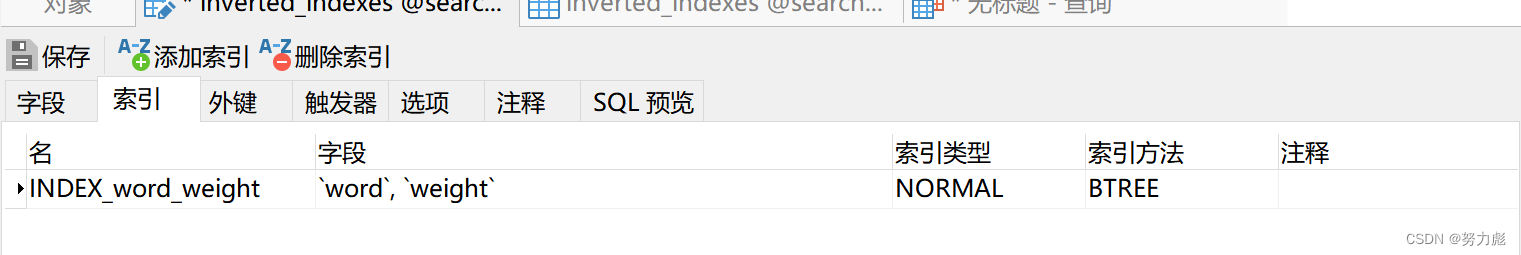
可以看到查询的速率上来了:没有用到filesort
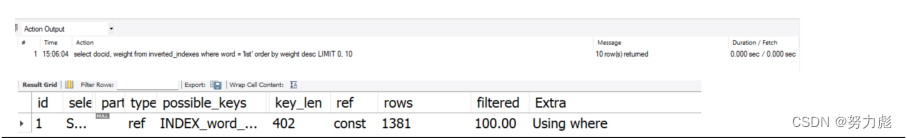
所以最终我们在查询的时候,要为我门表中的字段增添索引
多词查询时的权重聚合
(1)首先思考一个问题,假设我现在搜索的词语为list map string,,那么我要取搜索到的结果的第三页的结果,请问我该怎么找到?先给出一个想法:

答案:不正确
那么该怎么取呢?

所以我们每次取某一页的结果,都要对结果从第一条开始到这一页的最后一条语句进行聚合权重,然后重新排序,虽然这样时间复杂度高,但是一般来说啊,就是用户不会选,特别后面的,实际中呢,就是基本上是针对前几页做热点数据优化,后面的就是不会太管他,或者是说慢一点就慢一点,现实中也是这样的,就是针对用户经常访问的商品,你放的离用户近一点,如果用户很少用就慢就慢一点嘛,他愿意访问这点东西,他是愿意等的,其实是。
(2)假设此时搜索的关键词为list string map三个关键字的时候,会出现很多个文档,那么让这些文档如何排序进行展示

思路
先将分词后的结果保存到一个list数组里面去:
List<DocumentWightWeight> totalList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : queryList) {
List<DocumentWightWeight> documentList = mapper.queryWithWeight(s, limit, offset);
totalList.addAll(documentList);
}
接下来做权重的重新聚合工作
// 针对所有文档列表,做权重聚合工作
// 维护:
// docId -> document 的 map
Map<Integer, DocumentWightWeight> documentMap = new HashMap<>();
for (DocumentWightWeight documentWightWeight : totalList) {
int docId = documentWightWeight.getDocId();
if (documentMap.containsKey(docId)) {
DocumentWightWeight item = documentMap.get(docId);
item.weight += documentWightWeight.weight;
continue;
}
DocumentWightWeight item = new DocumentWightWeight(documentWightWeight);
documentMap.put(docId, item);
}
假设
list这个词出现再了docid为1的文档里,权重为13,同时list这个词出现再了docid为2的文档里,权重为22
String出现在了docid为1的文档里、权重为7,
map出现在了docid为1的文档里、权重为1,
那么同时搜索list String map的时候,它会将docid和DocumentWightWeight存成一个map集合,然后不同的词相同的docid号中的weight进行累加
在重新聚合的结果中根据weight进行由大到小的排序
Collection<DocumentWightWeight> values = documentMap.values();
// Collection 没有排序这个概念(只有线性结构才有排序的概念),所以我们需要一个 List
List<DocumentWightWeight> list = new ArrayList<>(values);
// 按照 weight 的从大到小排序了
Collections.sort(list, (item1, item2) -> {
return item2.weight - item1.weight;
});
对排序后的结果进行分页展示(截取区间):
int from = (page - 1) * 20;
int to = Integer.min(from + 20, list.size());
// 从 list 中把分页区间取出来
List<DocumentWightWeight> subList = list.subList(from, to);
List<Document> documentList = subList.stream()
.map(DocumentWightWeight::toDocument)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
项目总结
1.为什么要做这个项目?
同时由于搜索引擎的应用非常的广泛,为了了解这个搜索引擎背后的原理以及对于spring的熟悉程度,做了一个基于springboot的搜索引擎项目来锻炼自己。同时,也是为了在以后的生活以及工作中能够应用到这个项目中的一些知识点等。
2.本项目的难点是什么?
本项目的难点在于正排索引以及倒排索引的设计,首先需要记录每一篇文章的标题以及各个文章之间的分词,文章利用正则表达式进行单词的挑选,在设计正则表达式时是挺不容易的,最后通过查询搞清了正则表达式的一些相关用法,其次就是后来的调优阶段,在首先插入的时候需要半个小时之久,插入两百多万条数据确实不是一个小的数目,最后通过批量的插入以及相关的线程池的多线程解决了此问题
同时在搜索模块中使用索引加快查询的速度,并对多词查询的结果的展示进行了权重的聚合排序展示
3.本次项目对你最大的提升是什么?
通过本次项目,最大的提升莫过于技术方面的提升,使得自己对于springboot框架更加清楚基本流程是什么,以及对于每一个数据他背后所存在的意义是什么,每个注解的意义是什么,该怎么使用,以及对于spring框架的熟悉,在中间碰到了许许多多的错误,通过一点点的摸索,解决相关的问题,同时,对于自己处理能力的方法以及手段有了进一步的提升。