目录
-
- 3 CornerNet(角点网络)
-
- 3.1 概述
- 3.2 检测角点
-
- 3.2.1 检测角点概述
- 3.2.2 训练中的惩罚调整
- 3.2.3 焦点损失变体计算
- 3.2.4 下采样与偏移量预测
- 3.3 角点分组
-
- 3.3.1 角点分组的需求与启发
- 3.3.2 关联嵌入在角点分组中的应用
- 3.3.3 “拉近”损失和“推开”损失计算
- 3.4 角点池化
-
- 3.4.1 角点池化的需求与原理
- 3.4.1 角点池化的计算过程
- 3.4.1 右下角角点池化层
- 3.4.1 预测模块中的角点池化
- 3.5 沙漏网络
-
- 3.5.1 沙漏网络概述
- 3.5.1 CornerNet 中的沙漏网络
- 4 Experiments(实验)
-
- 4.4 Comparison with State-of-the-art Detectors(与最先进检测器的比较)
- 4.4.1 Introduction
- 4.4.2 Comparison Results
- 4.4.3 Analysis of Performance
- 4.4.4 Limitations
- 4.4.5 Future Work
- 4.4.6 Conclusion
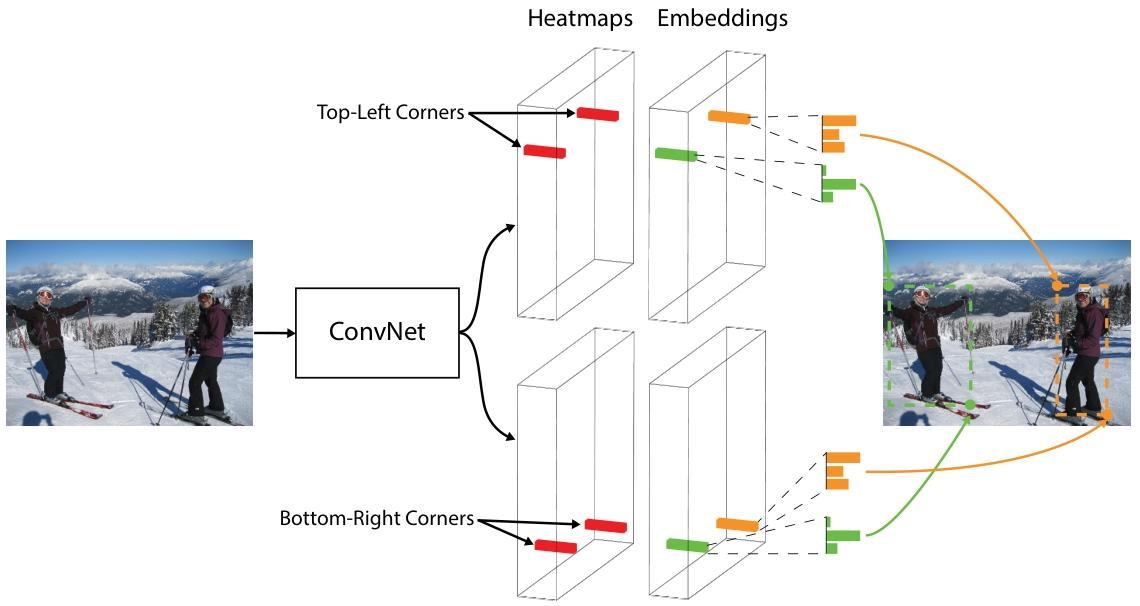
Fig. 1 We detect an object as a pair of bounding box corners grouped together. A convolutional network outputs a heatmap for all top-left corners, a heatmap for all bottom-right corners, and an embedding vector for each detected corner. The network is trained to predict similar embeddings for corners that belong to the same object.
图1展示了CornerNet的整体流程。
在CornerNet中,使用单个卷积神经网络来检测目标。具体来说,将目标检测视为检测目标边界框的左上角和右下角这一对关键点。
网络结构如下:
- 使用hourglass网络作为骨干网络,它后面接着两个预测模块,一个用于预测左上角的角点(top-left corners),另一个用于预测右下角的角点(bottom-right corners)。
- 每个预测模块都有自己的corner pooling模块ÿ



















