#二叉树的递归遍历
// 前序遍历·递归·LC144_二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //也可以把result 作为全局变量,只需要一个函数即可。
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, result);
preorder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 中序遍历·递归·LC94_二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
inorder(root.right, list);
}
}
// 后序遍历·递归·LC145_二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
}
}
后面写二叉树的递归算法,****就是要注意1、采用什么递归遍历 2、对结点的处理逻辑
一般是中左右,对中结点进行处理。
如果需要用到左右结点的返回值的,使用后续遍历,左右中。
#二叉树的迭代遍历
前序和中序是完全两种代码风格,这是因为前序遍历中访问节点(遍历节点)和处理节点(将元素放进result数组中)可以同步处理****,但是中序就无法做到同步!
对于中序遍历可以用一个指针来访问节点,访问到最底层,每次将访问的节点放进栈,如果访问到了最底层,将访问的节点放进栈。
再来看后序遍历,先序遍历是中左右,后续遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了。
二叉树的非递归遍历要使用栈。
// 前序遍历顺序:中-左-右,入栈顺序:中-右-左
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result; //返回空链表
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 中序遍历顺序: 左-中-右 入栈顺序: 左-右
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if (cur != null){ // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
stack.push(cur); // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层 不等于空,入栈并指向左孩子
cur = cur.left;
}else{ //从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据)
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val); //中
cur = cur.right; //右
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null){ //先放左子树,再放右子树
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
二叉树的层序遍历
102、二叉树的层序遍历
一层一层的处理
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result= new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return result;
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) //控制层数
{
List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>(); //每次都新建一个ArrayList 防止被修改
int len=queue.size(); //每层的个数
while(len>0) //遍历每层的结点,也可以使用for循环
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
result.add(tmp);
}
return result;
}
}
#107、二叉树的层序遍历二
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
示例 1:
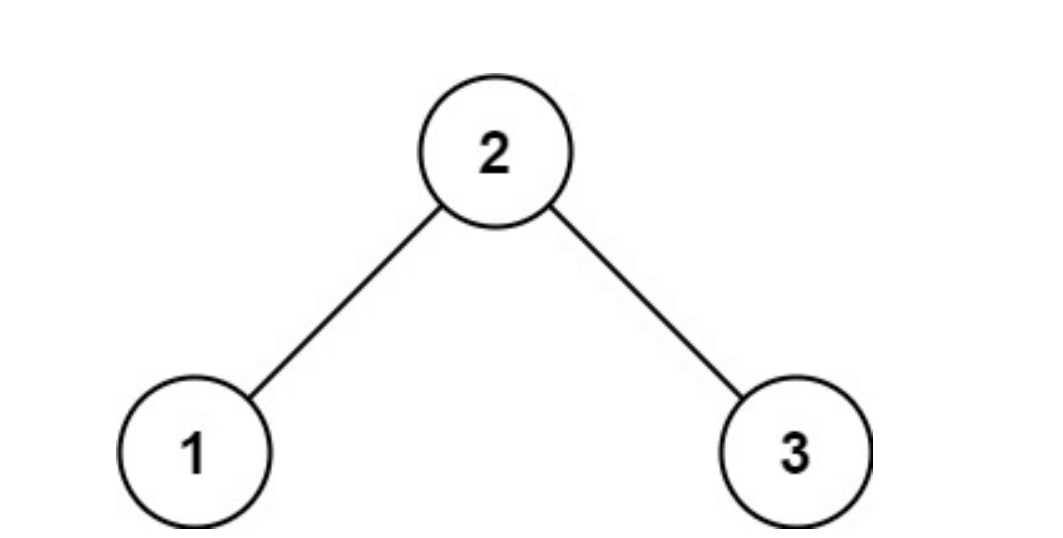
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
把每层的列表从头插入结果中就可以
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans= new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
List<Integer> tmp= new ArrayList<>();
int len=queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
ans.add(0,tmp); //每次都从头开始插入
}
return ans;
}
}
#199、二叉树的右视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:
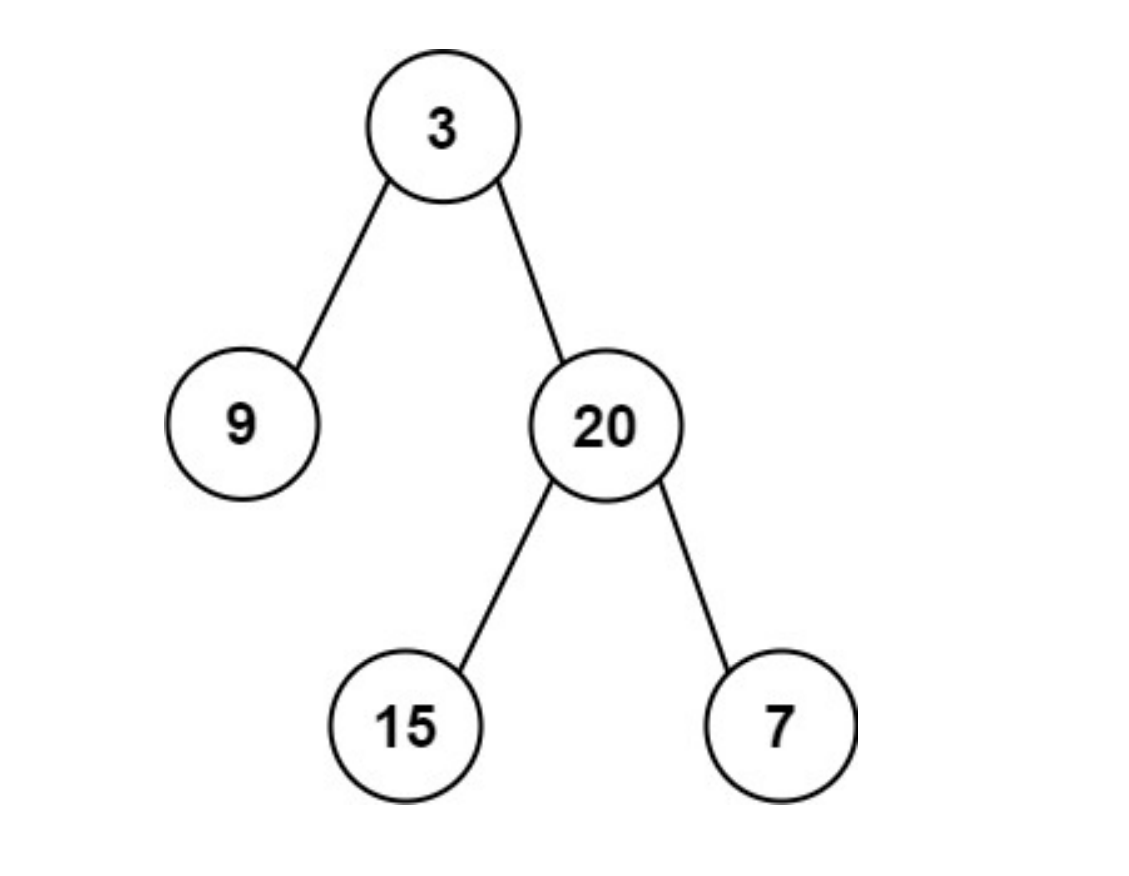
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
即利用队列的长度,把每一层的最后一个结点加入结果中
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
//即看到的都是每一层的最后一个结点
List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
if(root==null) return ans; //一定要判断为空的情况,否则会空指针异常
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
if(len==1)
ans.add(node.val); //把每一层的最后一个结点加入
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
637、二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树的根节点 root , 以数组的形式返回每一层节点的平均值。与实际答案相差 10-5 以内的答案可以被接受。
示例 1:
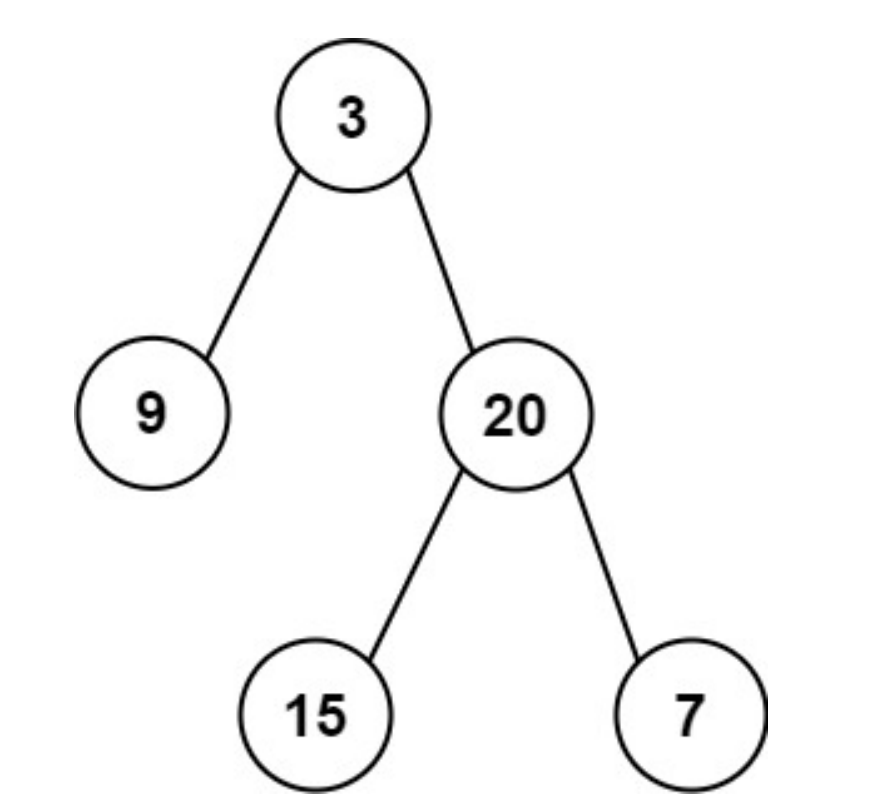
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
解释:第 0 层的平均值为 3,第 1 层的平均值为 14.5,第 2 层的平均值为 11 。
因此返回 [3, 14.5, 11] 。
使用一个sum来计算每层的和
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> ans =new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
int n=len;
double sum=0;
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
sum += node.val;
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
ans.add(sum/n);
}
return ans;
}
}
429、N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
示例 1:
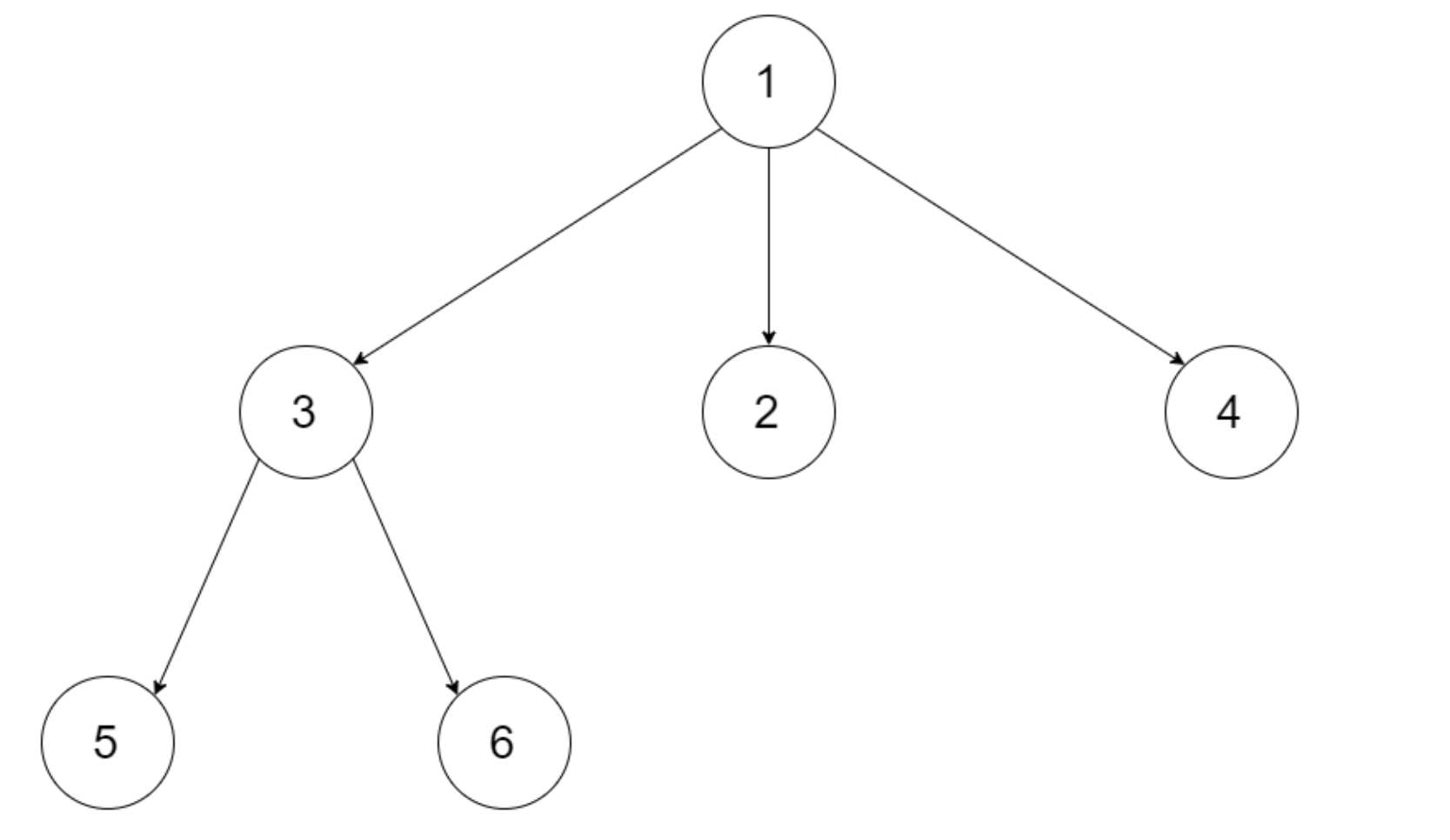
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans= new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root==null) return ans;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>();
while(len>0)
{
Node node =queue.poll();
tmp.add(node.val);
len--;
List<Node> childrens =node.children;
for(Node c:childrens)
{
if(c!=null)
queue.add(c);
}
}
ans.add(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
}
515、找出每层的最大值
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。
示例1:
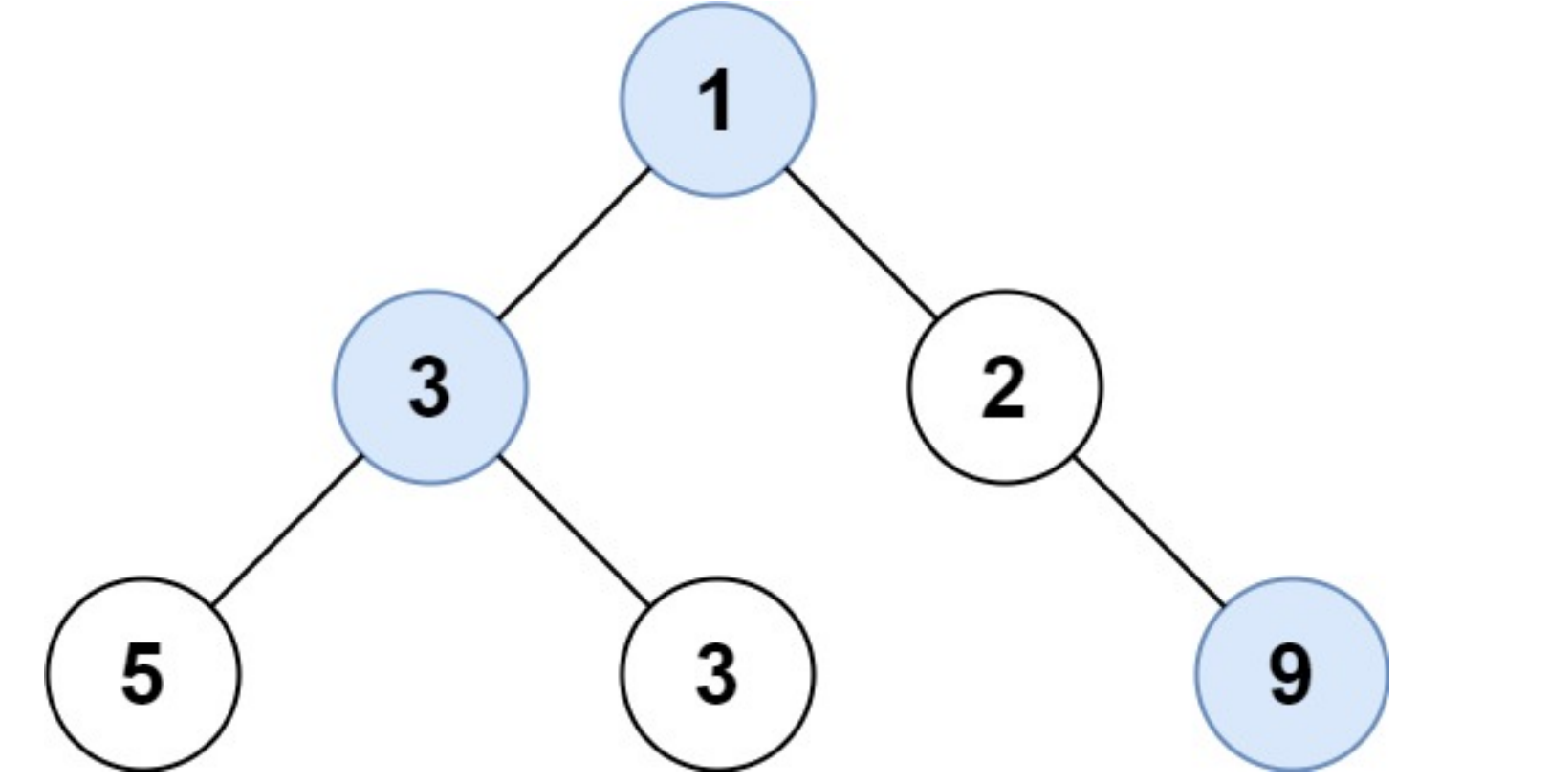
输入: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
输出: [1,3,9]
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans =new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE; //记录每一层的最大值
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.val>max)
max=node.val;
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
ans.add(max);
}
return ans;
}
}
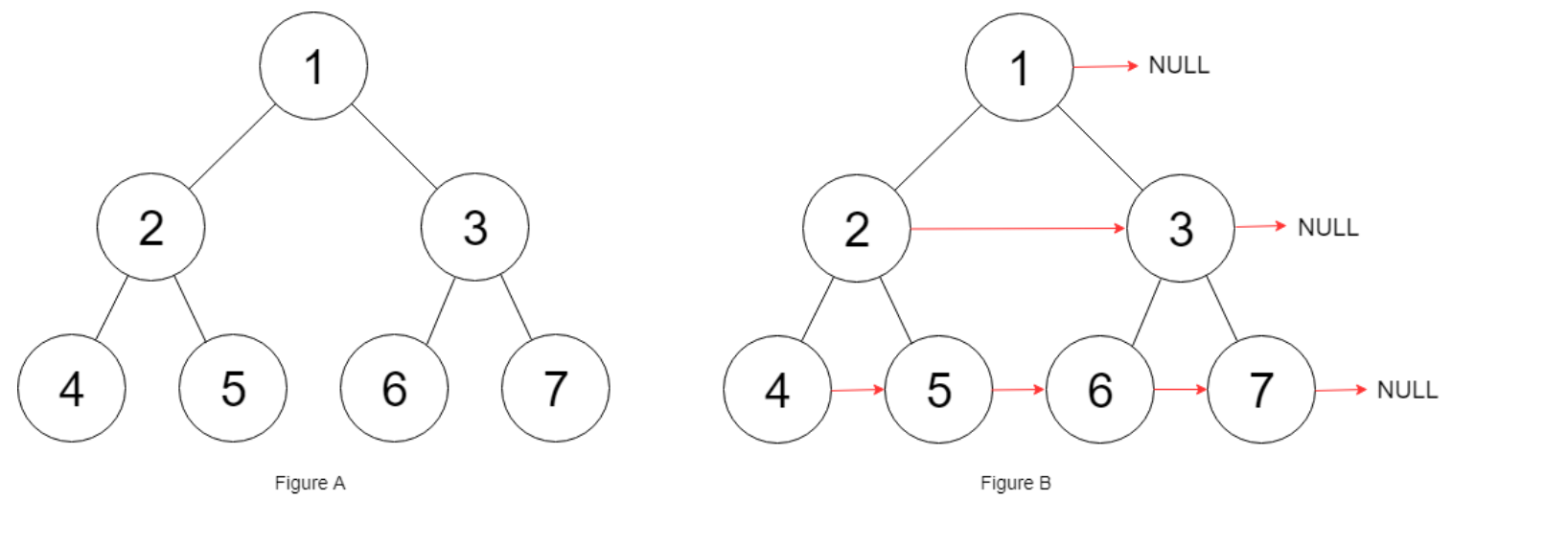
116、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例 1:
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue =new LinkedList<>();
if(root==null) return root;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
Node node = queue.poll(); //本质上还是找到每层的最后一个结点
if(len==1)
{
node.next=null;
}
else
{
Node nextNode =queue.peek();
node.next=nextNode;
}
len--;
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
#104、 二叉树的最大深度
使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序呢求的是高度
层序遍历:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int hight=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len=queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
hight++;
}
return hight;
}
}
后续遍历:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
int leftDepth =maxDepth(root.left); //左
int rightDepth =maxDepth(root.right); //右
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1; //中
}
}
前序遍历:
class Solution {
public:
int result;//使用result来记录最大深度
void getDepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
getDepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) { // 右
getDepth(node->right, depth + 1);
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getDepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
101、 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
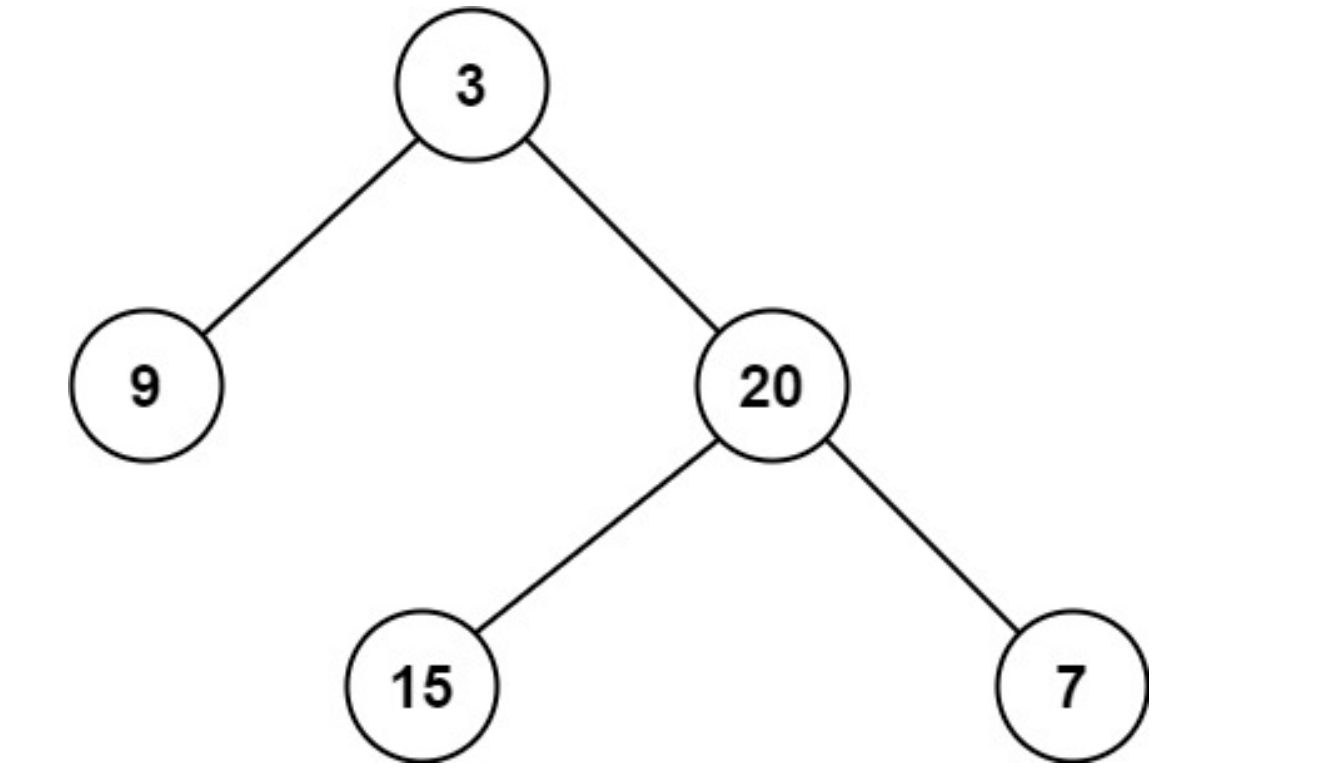
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
即当左右孩子都为空的时候就返回
层序遍历
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int depth=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len=queue.size();
depth++;
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
if(node.right==null && node.left==null)
return depth;
len--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
递归法
如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
class Solution {
//递归法
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left==null)
return rightDepth+1; //否则没有左孩子的分支会被当成最小值
if(root.right==null)
return leftDepth+1;
return Math.min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}
}
#226、翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
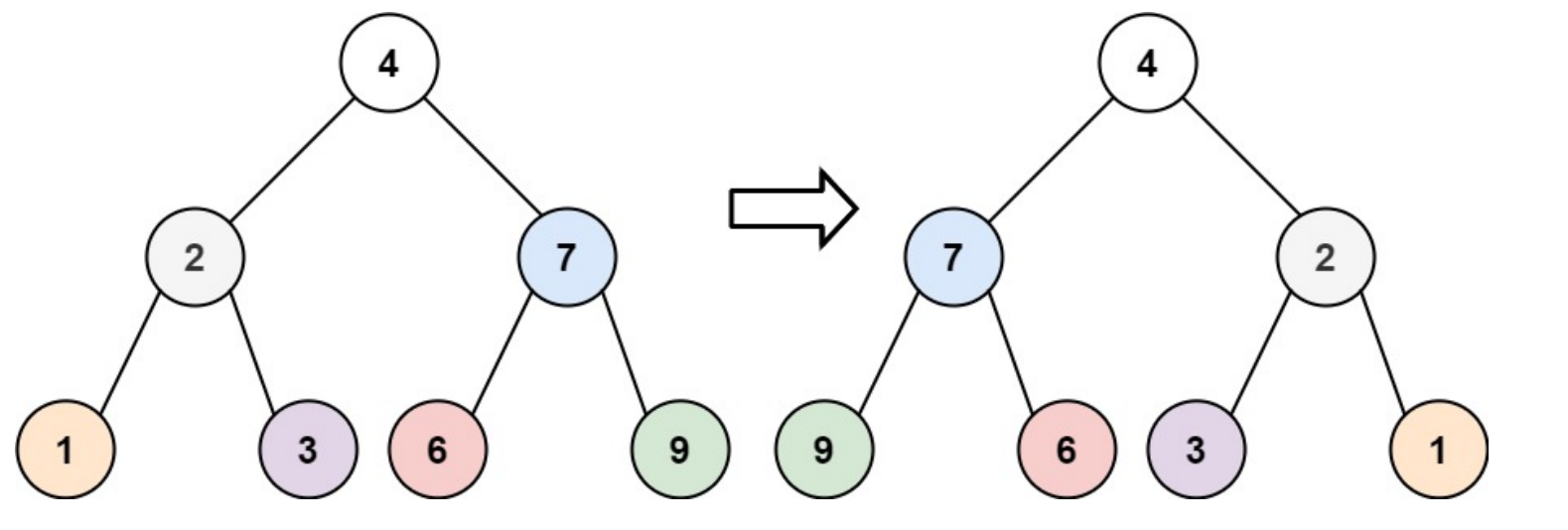
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
采用层序遍历,每取出一个结点就交换其左右孩子
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//采用层序遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
if(root==null)
return root;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len =queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
TreeNode tmp =node.right;
node.right=node.left;
node.left=tmp;
if(node.left!=null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null) queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
}
return root;
}
}
递归法:
对一个结点交换左右,然后进行左右递归
class Solution {
/**
* 前后序遍历都可以
* 中序不行,因为先左孩子交换孩子,再根交换孩子(做完后,右孩子已经变成了原来的左孩子),再右孩子交换孩子(此时其实是对原来的左孩子做交换)
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
swapChildren(root); //也可以中左右
return root;
}
private void swapChildren(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
}
#114、二叉树展开为链表
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
- 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
示例 1:
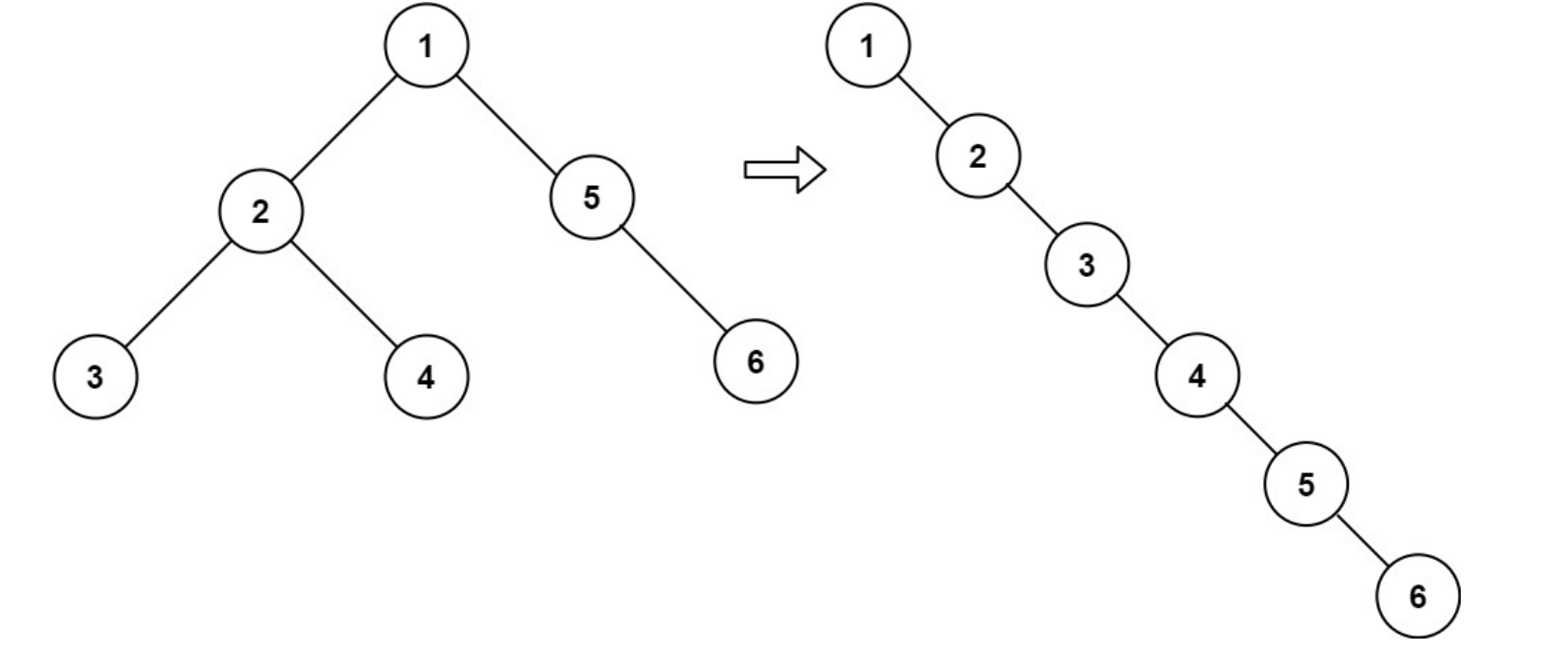
输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
class Solution {
//保存前序遍历的结果
List<TreeNode> list=new ArrayList<>();
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
preorder(root);
for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++)
{
TreeNode pre=list.get(i-1);
TreeNode cur=list.get(i);
pre.left=null;
pre.right=cur;
}
}
//构造树,然后值是结点
public void preorder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return;
list.add(root);
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
}
递归+回溯的思路,将前序遍历反过来遍历,那么第一次访问的就是前序遍历中最后一个节点。那么可以调整最后一个节点,再将最后一个节点保存到pre里,再调整倒数第二个节点,将它的右子树设置为pre,再调整倒数第三个节点,依次类推直到调整完毕。和反转链表的递归思路是一样的。
class Solution {
//反前序遍历
TreeNode pre;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
//先找到最后一个结点,然后记录
root.left=null;
root.right=pre;
pre=root;
}
}
#101、对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
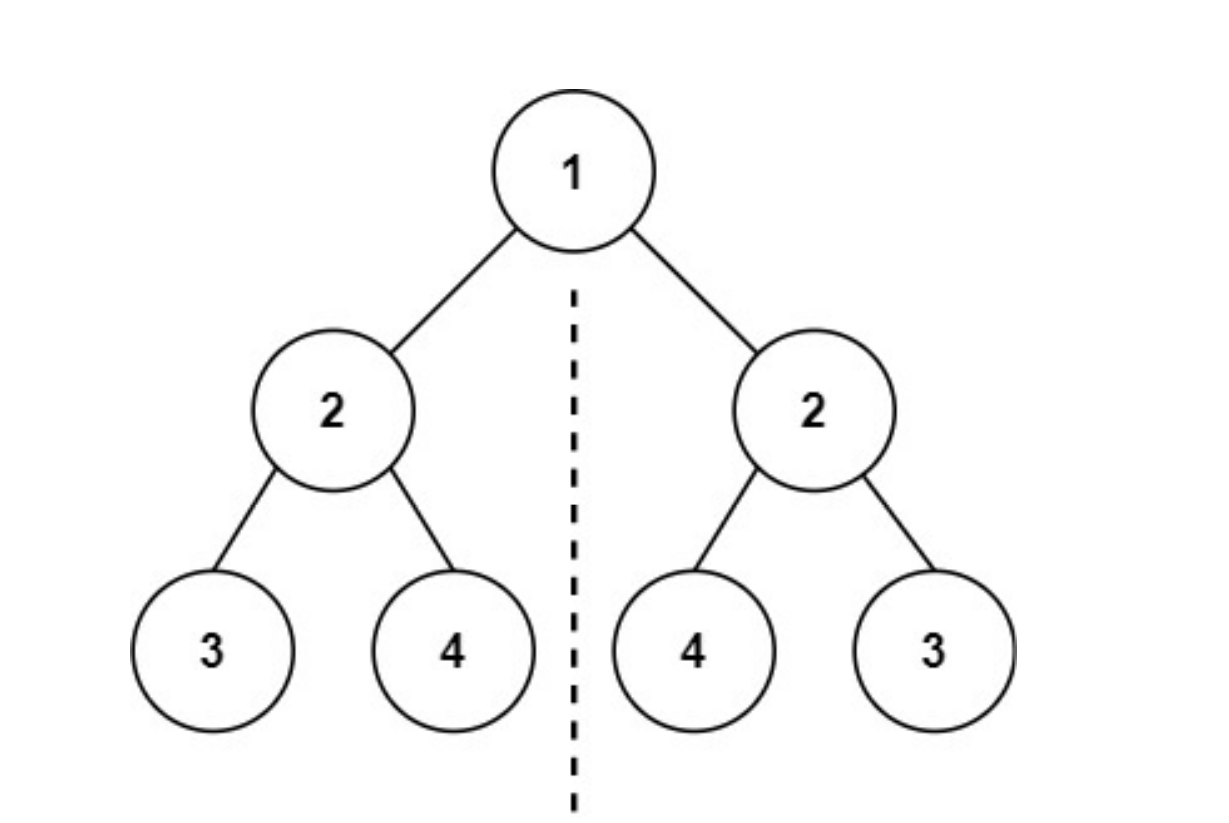
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
使用一个队列,类似于层序遍历的方式,只不过不用加len来判断层数,并且空结点也要入队。
而本题的迭代法中我们使用了队列,需要注意的是这不是层序遍历,而且仅仅通过一个容器来成对的存放我们要比较的元素,
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
//把空节点也看成结点
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root.left);
queue.add(root.right);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
//不符合就返回false
TreeNode leftnode =queue.poll(); //每次取出需要比较的两个结点
TreeNode rightnode =queue.poll(); //每次取出需要比较的两个结点
if(leftnode==null && rightnode ==null)
continue;
if(leftnode==null||rightnode==null||leftnode.val!=rightnode.val)
return false;
queue.add(leftnode.left);
queue.add(rightnode.right);
queue.add(leftnode.right);
queue.add(rightnode.left);
}
return true;
}
}
递归法:
class Solution {
private boolean copmare(TreeNode leftnode, TreeNode rightnode)
{
if(leftnode==null && rightnode!=null) return false;
else if(leftnode!=null && rightnode==null) return false;
else if(leftnode==null && rightnode==null) return true;
else if(leftnode.val!=rightnode.val) return false; //也可以合在一起判断
else //说明leftnode和rightnode相等
return copmare(leftnode.left,rightnode.right) && copmare(leftnode.right,rightnode.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return copmare(root.left,root.right);
}
}
100、相同的树
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
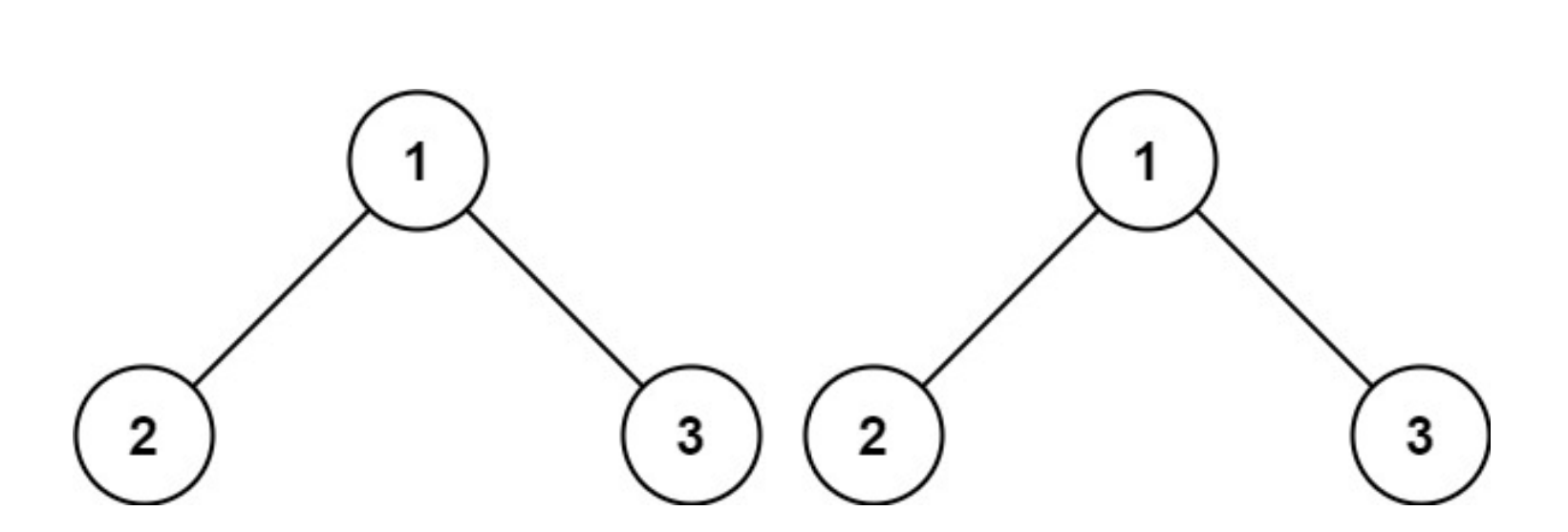
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
输出:true
和对称二叉树一样
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//使用同一个队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(p);
queue.add(q);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node1 =queue.poll();
TreeNode node2 =queue.poll();
if(node1==null && node2==null)
continue;
else if(node1==null &&node2!=null)
return false;
else if(node1!=null && node2==null)
return false;
else if(node1.val!=node2.val)
return false;
queue.add(node1.left);
queue.add(node2.left);
queue.add(node1.right);
queue.add(node2.right);
}
return true;
}
}
递归法
class Solution {
//递归法:求树是否相等
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&& q==null) return true;
else if(p==null &&q!=null) return false;
else if(p!=null &&q==null) return false;
else if(p.val!=q.val) return false;
else //即结点相同,判读左右结点
{
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
}
572、另一棵树的子树
给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
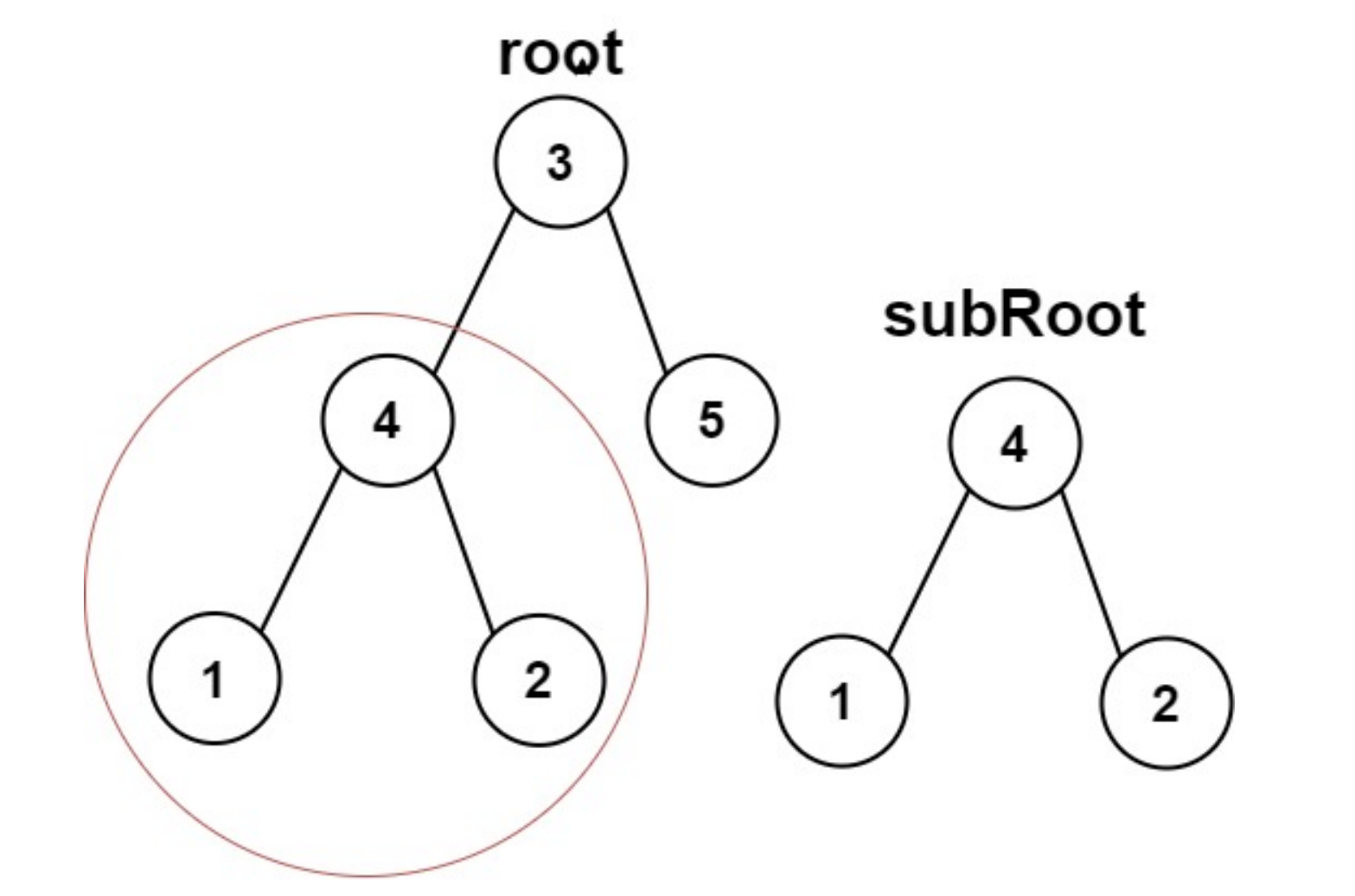
输入:root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2]
输出:true
采用遍历+判断树是否相等
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q)
{
if(p==null && q==null) return true;
else if(p==null||q==null||p.val!=q.val) return false; //直接合在一起写
else{ //说明结点值相同
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
if(isSameTree(node,subRoot))
return true;
if(node.left!=null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null) queue.add(node.right);
}
return false;
}
}
559、n叉树的最大深度
class Solution {
/*递归法,后序遍历求root节点的高度*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0; //递归出口
int depth = 0;
if (root.children != null){
for (Node child : root.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(child));
}
}
return depth + 1; //中节点
}
}
#110、平衡二叉树
在递归法求高度的基础上,每次递归要判断是否是平衡二叉树。
class Solution { //递归法求高度,因为是求高度,所以是后序遍历:左右中
private int getHight(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null) return 0;
int leftHight=getHight(root.left);
if(leftHight==-1)
return -1; //用-1代表不是平衡二叉树
int rightHight=getHight(root.right);
if(rightHight==-1)
return -1;
if(Math.abs(leftHight-rightHight)>1)
return -1;
return Math.max(leftHight,rightHight)+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(getHight(root)==-1) return false;
else
return true;
}
}
层序遍历
class Solution { //层次遍历求高度
private int getHigth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int hight=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len=queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
hight++;
}
return hight;
}
//层次遍历判断
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
int len=queue.size();
while(len>0)
{
TreeNode node =queue.poll();
int leftHight =getHigth(node.left);
int rightHight =getHigth(node.right);
if(Math.abs(leftHight-rightHight)>1)
return false;
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
len--;
}
}
return true;
}
}
#543、二叉树的直径
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
示例 1:
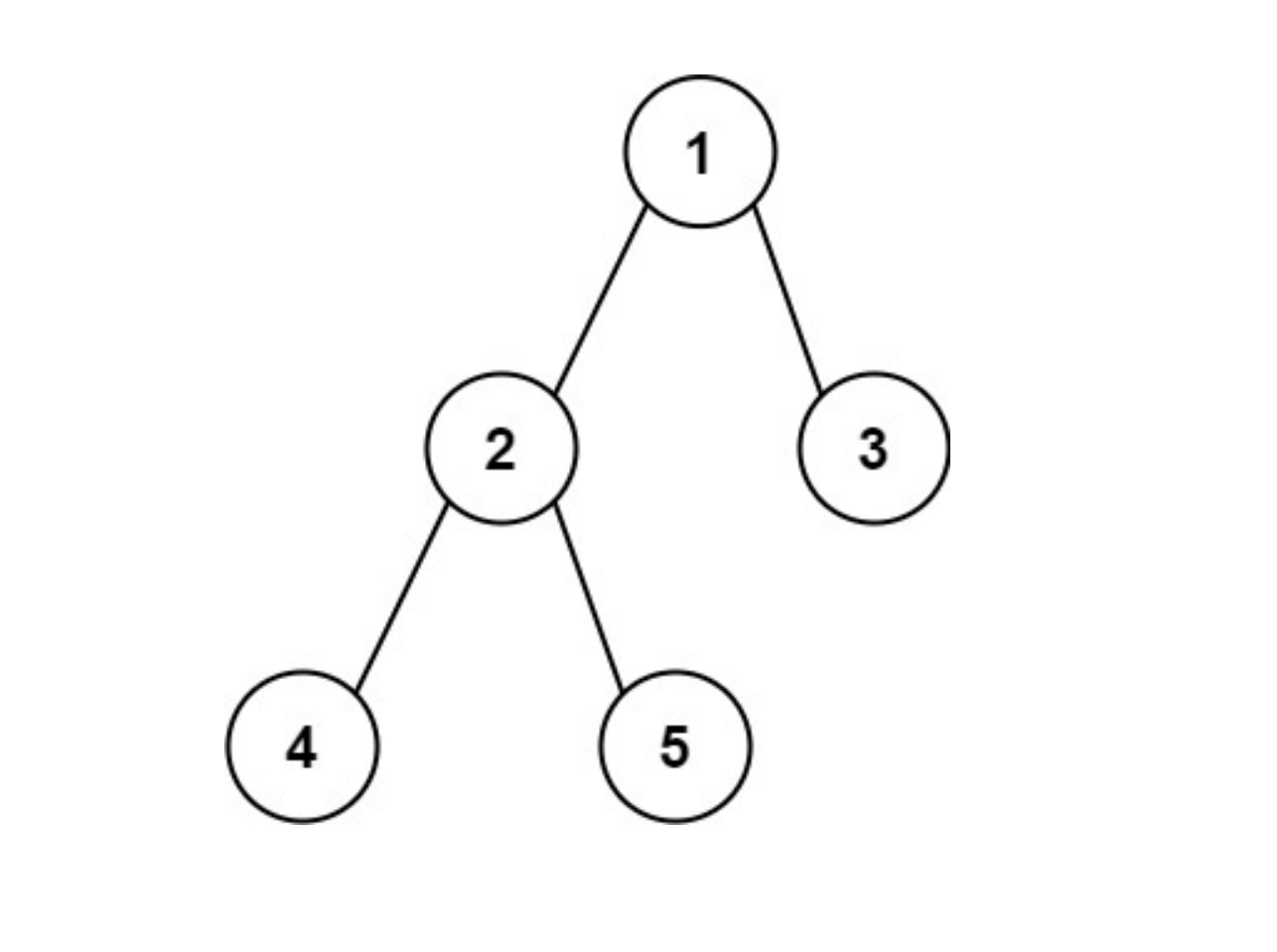
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:3
解释:3 ,取路径 [4,2,1,3] 或 [5,2,1,3] 的长度。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:1
一开始以为就是根节点的左右子树的深度之和,后来发现最长路径不一定经过根结点。
class Solution {
//直径,即树中找最长路径,最长路径不一定经过根结点
//对于经过的每一个结点来说,最长路径就是左右子树的深度 之和
int maxd=0; //记录最大直径
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
height(root);
return maxd;
}
//递归求深度
public int height(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return 0;
int left=height(root.left);
int right=height(root.right);
//在遍历的过程中找以每个结点为根的最大直径
maxd=Math.max(maxd,left+right); //将每个节点最大直径(左子树深度+右子树深度)当前最大值比较并取大者
return Math.max(left,right)+1; //返回结点深度
}
}














![[水墨:创作周年纪念] 特别篇!](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9b1710e567234c45b9f648d4e8f84c2e.jpeg)