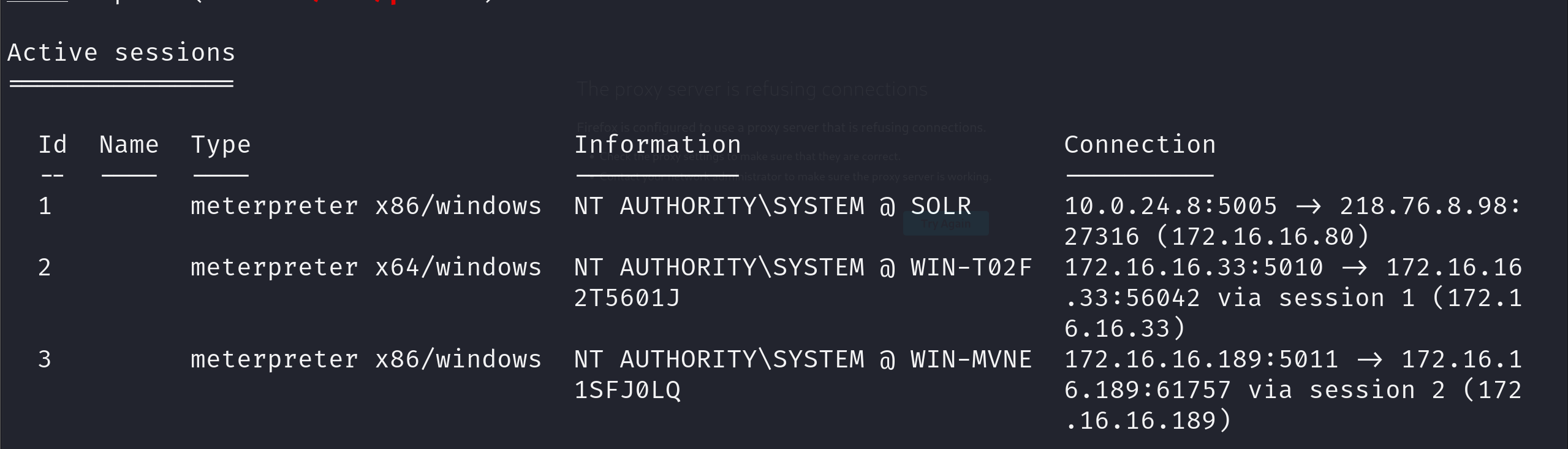
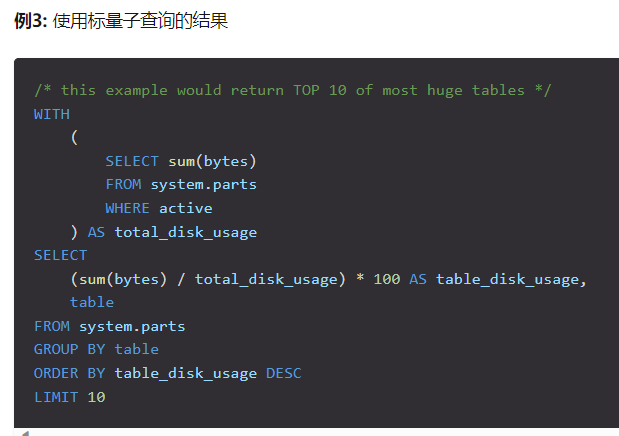
机器学习文章回顾
生信机器学习入门1 - 数据预处理与线性回归(Linear regression)预测
生信机器学习入门2 - 机器学习基本概念
生信机器学习入门3 - Scikit-Learn训练机器学习分类感知器
生信机器学习入门4 - scikit-learn训练逻辑回归(LR)模型和支持向量机(SVM)模型
1. 决策树(Decision Tree)
决策树,是一种以树形数据结构来展示决策规则和分类结果的模型,属于归纳学习算法,其重点是将看似无序、杂乱的已知数据转化成可以预测未知数据的树状模型,每一条从根结点(对最终分类结果贡献最大的属性)到叶子结点(最终分类结果)的路径都代表一条决策的规则。
决策树工作流:

1.1 概率与熵之间的关系图
# 定义了一个函数 entropy 来计算给定概率 p 的熵,并使用这个函数来绘制概率与熵之间的关系图
def entropy(p):
# 熵的计算公式为 −plog2(p)−(1−p)log2(1−p)
return - p * np.log2(p) - (1 - p) * np.log2((1 - p))
# 生成步长为0.1的数组
x = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.01)
# 使用列表推导式计算每个概率值 p 的熵
# 如果 p 为 0,则熵值为 None,因为 log2(0)log2(0) 是未定义的,会导致数学错误
ent = [entropy(p) if p != 0 else None for p in x]
plt.ylabel('Entropy')
plt.xlabel('Class-membership probability p(i=1)')
plt.plot(x, ent)
plt.show()

1.2 构建决策树(Decision Tree)分类器
使用 scikit-learn 库中的 DecisionTreeClassifier 来训练一个决策树模型。
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from distutils.version import LooseVersion
# 参数说明
# criterion='gini':设置决策树在每个节点上进行分割时使用基尼不纯度(Gini impurity)作为衡量标准,
# 基尼不纯度是一种衡量一个节点内样本类别分布不均匀性的指标。
# max_depth=4:设置决策树的最大深度为 4。限制树的深度可以防止过拟合,
# 即模型在训练数据上表现很好,但在未见过的数据上表现不佳。
# random_state=1:设置随机数生成器的种子,确保结果的可复现性。
tree_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini',
max_depth=4,
random_state=1)
tree_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 使用 np.vstack 函数将训练数据集 X_train 和测试数据集 X_test 垂直堆叠起来,形成一个更大的特征矩阵 X_combined
X_combined = np.vstack((X_train, X_test))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
# 绘图图形和颜色生成
markers = ('o', 's', '^', 'v', '<')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# 绘图
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
lab = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
lab = lab.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, lab, alpha=0.3, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
# 图加上分类样本
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0],
y=X[y == cl, 1],
alpha=0.8,
c=colors[idx],
marker=markers[idx],
label=f'Class {cl}',
edgecolor='black')
# 高亮显示测试数据集样本
if test_idx:
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0],
X_test[:, 1],
c='none',
edgecolor='black',
alpha=1.0,
linewidth=1,
marker='o',
s=100,
label='Test set')
plot_decision_regions(X_combined, y_combined,
classifier=tree_model,
test_idx=range(105, 150))
plt.xlabel('Petal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('Petal width [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

1.3 决策树模型可视化
from sklearn import tree
feature_names = ['Sepal length', 'Sepal width',
'Petal length', 'Petal width']
# 使用 scikit-learn 库中的 tree 模块来绘制训练好的决策树模型 tree_model 的可视化图形
tree.plot_tree(tree_model,
feature_names=feature_names,
filled=True)
plt.savefig('tree_model.png')
plt.show()

2.2 构建随机森林(Random Forest)分类器
随机森林由众多独立的决策树组成(数量从几十至几百不等), 它通过汇总所有决策树的预测结果来形成最终预测,即通过对所有树的预测进行投票或加权平均计算而获得。
使用 scikit-learn 库中的 RandomForestClassifier 类来训练一个随机森林模型。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
"""
参数:
n_estimators=25:设置随机森林中决策树的数量为 25,
n_estimators 参数控制随机森林的“森林”中有多少棵树;更多的树通常会提高模型的性能,但同时也会增加计算成本。
random_state=1:设置随机数生成器的种子,确保结果的可复现性。
n_jobs=2:设置并行运行的作业数,这个参数控制可以并行运行多少棵树的构建过程。
"""
forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=25,
random_state=1,
n_jobs=2)
forest.fit(X_train, y_train)
plot_decision_regions(X_combined, y_combined,
classifier=forest, test_idx=range(105, 150))
plt.xlabel('Petal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('Petal width [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()